Year 11 Apres Mock Paper 1 Content
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Combination of Mentrual Cycle, Repodrocution in Humans and Plants and Preganancy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
the menstrual cycle is a
series of changes that occur in a women’s body around every 28 days
the changes in a women’s body is controlled by
sex hormones
menstruation is commonly known as
a period
ovulation is the
release of an egg
the released egg during ovulation travels
down the oviduct to the uterus
why does menstration occur?
fertilisation of an egg doesn’t occur
menstruation/a period is the
breakdown of the thickened uterus lining
ovulation occurs on day
14
menstruation lasts
5-7 days and signals the beginning of the next cycle
after menstruation what happens to the lining of the uterus?
begins to thicken again in prep for a possible implantation in the next cycle
before day 14 (ovulation) which hormone peaks?
oestrogen
oestrogen does what?
causes the uterus to build up and thicken
progesterone does what?
causes the uterus lining to thicken further
progesterone is high after
ovulation
when progesterone levels decrease,
the uterus lining breaks down, causing menstruation to occur
once the ova (egg) develops in the follicle, it produces what?
oestrogen
once ovulation occurs, the follicle becomes
corpus luteum and starts producing progesterone
corpus luteum is the
remains of the follicle in the ovary
the corpus luteum role is to
produce hormones for a potential pregnancy
progesterone maintains the uterus lining, however if the ova is not fertilised…
the corpus luteum and uterus lining break down and progesterone levels decrease
OR if egg is fertilised and pregnancy has occurred
the corpus luteum continues producing progesterone to prevent the uterus lining from breaking down and aborting the pregnancy
what does a foetus need from its mother’s blood?
amino acids, glucose, fatty acids, mineral ions, vitamins, water and oxygen
in the placenta, the mothers blood comes in very close proximity with the foetus, but never what?
mixes her blood with it
foetus’ blood connects to the placenta via the
umbilical cord
the mothers blood absorbs
wast p
a zygote is a
fertilised egg
an embryo is
initial stages of development of a multicellular organism
a foetus is an
unborn human
secondary sexual characteristics occur during
puberty
secondary sexual characteristics are controlled by
oestrogen and testosterone
female secondary sexual characteristics include:
breasts develop, body hair, menstrual cycle begins, hips widen
male secondary sexual characteristics include:
growth in p and testes, facial and body hair, voice breaks, testes begin to produce sperm
flowers are the
reproductive organs of plants
male parts of the flower
stamen = anther and filament
female parts of the flower
carpel = stigma, style and ovary
plants produce
pollen
pollen contains
a nucleus - which is the male gamete
pollen is produced in the
anther
pollination is the
transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma
2 types of pollination are called
wind and insect
insects are
pollinating agents
insects collect
nectar from flowers
when an insect enters the flower
it brushes against the anther, which deposits its sticky pollen onto
when an insect visits another flower,
it brushes against the stigma, depositing the pollen from the first flower, resulting in pollination
inside the ovary are the
ovules, containing the ova = female gamete
petals:
large and bright to attract insect
scent and nectar:
entice the insect to push parts of the stamen, to get to the sweetness
anther:
inside the flower and contains the pollen grains, stiff and firm to brush against insects
stigma:
inside the flower, where pollen grains stick to it when an insect brushes past
stamen:
enclosed within a flower so that insect must make contact with it
pollination in wind pollinated plants
the anther opens and sheds its pollen into open air. the pollen is blown by the wind and lands on the stigma
wind petals:
small and dull
wind scent and nectar:
absent
wind anthers:
swing loosely so that pollen grains fall easily
wind stigma:
outside the flower, large and feathery in order to catch pollen grains
wind stamen:
exposed so that wind can easily blow away pollen
cross vs self pollination:
pollen grains are transferred from a plants anther to another plants stigma vs pollen grains are transferred from the same flower’s
what do organisms use to respond to changes in their environment
communication systems - endocrine and hormonal
homeostasis is the
maintenance of a constant internal environment
examples of homeostasis?
the maintaining of body temperature and water content
what does a coordinated response require?
a receptor, stimuli and an effector
plants do what in order to grow
respond to stimuli
a tropism is a
directional response made by plants based on light and gravity
the response to light is called
phototropism
the response to gravity is called
geotropism
shoots grow
towards the light, away from gravity
roots grow
towards gravity, away from light
shoots are
positively phototropic and negatively geotropic
roots are
positively geotropic and negatively phototropic
auxin is a
plant growth hormone which controls the directional growth response of plants
where is auxin produced
at the tip of the shoots, which diffuses below the tips
in the shoots, auxin promotes
cell elongation in order to grow towards the light
in the roots, auxin inhibits
cell elongation in order to bend away from the light
the nervous system
works by nerves impulses, transmitted through nerve cells in a fast, short lived, response. it has a localised effect on the body.
the endocrine system…
works by hormones, transmitted through the blood stream in a slow, long lived, response. it has a widespread effect on the body.
CNS consists of
the brain and spinal cord and is linked to sense organs by nerves
stimulation of receptors in the sense organs causes
them to send electrical impulses along nerves in and out of the CNS, resulting in rapid responses.
synapses are
gaps between 2 neurons
role of neurotransmitters
they diffuse across the synapse, allowing for a new electrical signal in the next neuron
neurotransmitters are
chemical messengers that pass info from one neuron to the next
stages of the reflex arc
stimuli - receptors in sense organs detect stimulus - receptors send electrical impulses along sensory neurons to the CNS - which is where the relay neuron transfers the info to a motor neuron - to the effector to act accordingly
reflex arc: touching something hot
touching a hot object causes a stimulus
the receptors in your hand detected the stimulus and send electrical impulses via sensory organs to the CNS
the relay neuron then transfers the info to a motor neuron
the motor neuron travels to the effector (the muscle) which contracts and moves your hand away from the object
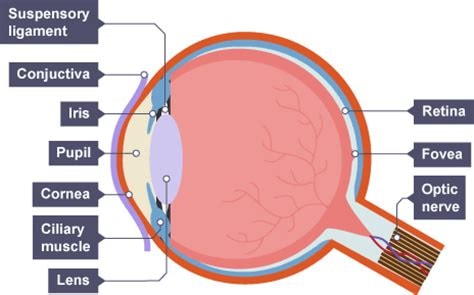
what is the function of the sclera
tough outer layer that protects the eye
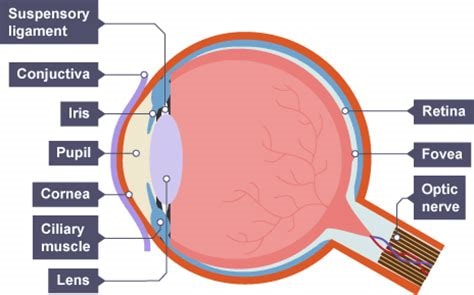
what is the function of the cornea
transparent lens that refracts light as it enters the eye
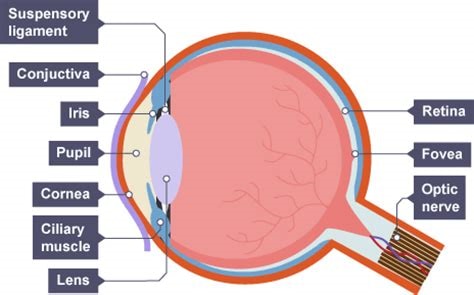
what is the function of the pupil
hole that allows light in
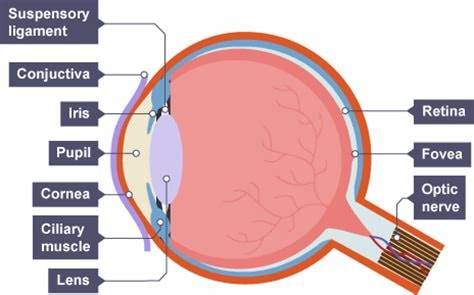
what is the function of the iris
controls the diameter of the pupil, therefore controlling how much light enters the pupil
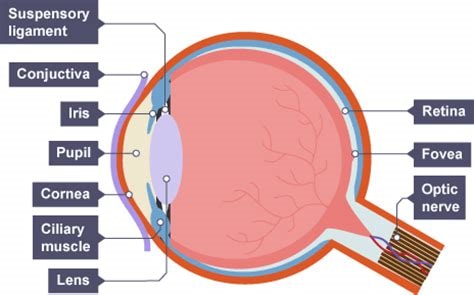
what is the function of the retina
a transparent disc that focuses light onto the retina (cones detect colour and rods detect light intensity)
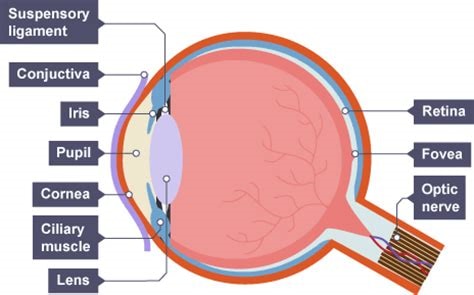
what is the function of the optic nerve
contains sensory neurons which carry out nerve impulses to the brain
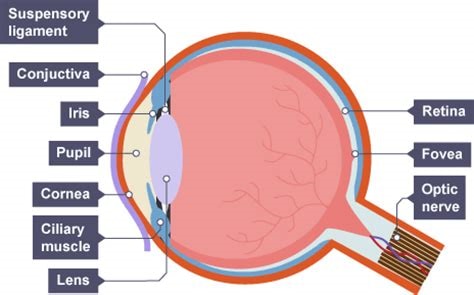
what is the function of the fovea
a region in the retina with the highest denisty of cones
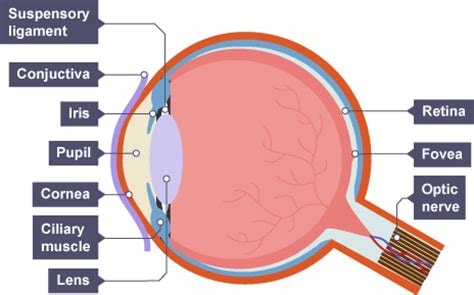
the blind spot of an eye is
the point at which the optic nerves leaves the eye and there are no receptor cells
when the eye sees a near object…
ciliary muscles contract, suspensory muscles relax and the lens becomes more convex - rounder
when the eye sees a far away object…
ciliary muscles relax, suspensory ligaments contract and the lens become less convex - flatter
in the iris there are the
circular and radial muscles
when the eye sees in dim light…
circular muscles relax, radical muscles contract and pupil dilates so that more light enters the eye
when the eye sees in bright light…
circular muscles contract, radical muscles relax and pupil constricts so that less light enters the eye
if the body is too warm what does the skin do?
starts to sweat, so that when it evaporates from the skin surface, it has a cooling effect. this is because heat energy is needed to change from liquid to gas and that energy is then taken away from the body by vapour