Module 2
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
200 Terms
C
Who is the word pharmacognosy for the first time ever his book Lehrbuch de materia medica?
a. Dioscorides
b. Seydler
c. Schmidt
d. Fluckiger
D
German pharmacist who obtained an impure alkaloid from Atropa belladonna fam Solanaceae
a. P. Robiquet
b. Seturner
c. Fluckiger
d. R. Brandes
e. J. Canventou
B
Known as deliberate addition of spurious material to a genuine portion with intent to defraud
a. admixture
b. sophistication
c. substitution
d. deterioration
A
Substitution occurs when an entirely different article is used or sold in place of of the one required. Admixture is the intentional or deliberate addition of a substance to the article
a. only statement 1 is correct
b. only statement 2 is correct
c. both statement is correct
d. both statement is incorrect
D
Natural growth inhibitor are present in the plants and effect bud opening, seed germination and development of dormancy
a. auxin
b. gibberelin
c. cytokinin
d. abscisic acid
e. ethylene
B
Synthesized in the leaves and they accumulate in large quantities in the immature seeds and fruits of the plants. The growth effects of these hormone arises by cell elongation in the subapical meristem region were young internodes are developing.
a. auxin
b. gibberelin
c. cytokinin
d. abscisic acid
e. ethylene
A
Typical defects are cell elongation giving an increase in a apical dominance inhibition of root growth adventitious root production and fruit set setting in the absence of pollination.
a. auxin
b. gibberelin
c. cytokinin
d. abscisic acid
e. ethylene
C
Which of the following statements is incorrect about photosynthesis
a. light-dependent phase of the photosynthesis occurs in the thylakoid membrane
b. it transforms light energy to chemical energy
c. chlorophyll b is the principal pigment in green plants
d. light reaction result in the production of NADPH, O2 and ATP
e. chlorophyll is extracted using acetone or alcohol
D
Evaluate the following statements
I. Photorespiration is a wasteful pathway that occurs when enzyme rubisco of the Calvin cycle on oxygen other than carbon dioxide
II. C3 plants are normal plants composing ~85% of plant species which do not have photosynthetic adaptation to reduce photorespiration
III. Light-dependent phase of photosynthesis occurs in membrane the of thylakoid membrane
IV. Light-independent phase photosynthesis also known as Calvin cycle can only occur environment with minimal to no light
a. One of the statement is true
b. Two of the statement is true
c. Three of the statement is true
d. All of the statement is true
B
the following statements are true about shikimic acid pathway except
a. shikimic acid pathway produce phenylpropanoids
b. it is known as the terpenoid pathway
c. this pathway is not found in both humans and animals
d. the pathway produces aromatic amino acid, phe, tyr, and trp
B
Identify substrate P in the figure below
a. DHAP
b. dehydroquinic acid
c. shikimic acid
d. chorismic acid
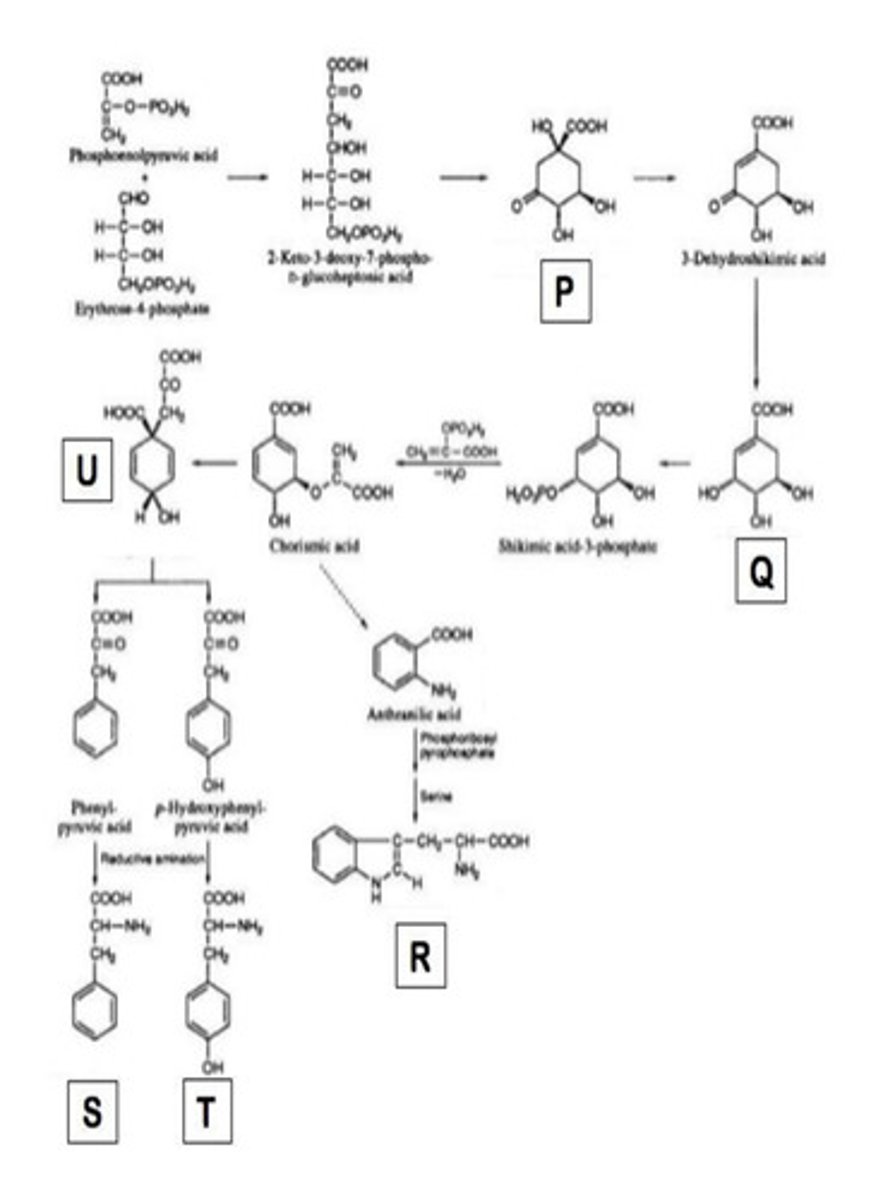
B
The following statements are true about methyl erythritol phosphate pathway except
a. also known as nonmevalonic pathway or DOXP pathway
b. the rate-limiting enzyme is DOXP synthase which catalyze the first step (pyruvate + glyceraldehyde)
c. this pathway is absent in archaea bacteria fungi and animals
d. plant use both in MVA and MEP pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis
D
In plants, the mevalonic acid pathway occurs in the plastid. On the other hand methyl erythritol pathway occurs in the cytosol
a. the first statement is correct while the second statement is incorrect
b. the first statement is incorrect while the second statement is correct
c. both statement re correct
d. both statement is incorrect
B
Precursor of retinol and phytol
a. geranyl pyrophosphate
b. geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate
c. squalene
d. farnesyl pyrophosphate
D
Which of the following are exclusively ketogenic amino acid
a. lysine
b. isoleucine
c. leucine
d. a and c
e. AOTA
A
Which of the following amino acid contains contains an isobutyl group?
a. leucine
b. isoleucine
c. valine
d. threonine
e. lysine
D
Find a branched-chain amino acids
a. thr, ser
b. val, lys, ile
c. asn, gln
d. val, leu, ile
B
Which of the following is considered the 21st amino acid
a. ornithine
b. selenocysteine
c. DOPA
d. pyrrolysine
C
Which of the following essential amino acid is only coded by a single codon?
a. R
b. T
c. W
d. V
e. F
D
Determine the intermediate precursor of phenylalanine
a. Anthranilic acid
b. Chorismic acid
c. Para-hydroxyphenulpyruvic acid
d. Phenylpyruvic acid
D
Glutamate has three ionizable group with pKa values of 2.19 4.35 and 9.67. Calculate the of glutamate
a. 6.51
b. 6.96
c. 5.37
d. 3.22
C
Analyze and select the underlying principle in the millon's test for protein
a. Based on the reaction of cupric ion of the reagent with the N of the peptide bond, purple or violet colored complex
b. Based on the nitration of protein which leads to the formation of yellow precipitate that turns to orange on the treatment with an ally alkali
c. Based on the reaction between phenolic group of protein with mercuric sulfate in the presence of sodium nitrate and so sulfuric acid resulting in the formation of red colored solution
d. Based on the reaction between the reagent and the amino a group of the free amino group of the test sample which leads to the oxidation of compound and its deamination and resulting in the deep formation of deep blue colored solution
D
In this level of organization hydrophobic interaction and oxidation of thiols to form disulfide bonds
a. primary structure
b. secondary structure
c. supersecondary structure
d. tertiary structure
e. quaternary structure
C
Which of the following is not true for secondary protein structure?
a. glycine is a helix breaker because it is too small
b. proline is a helix breaker because it lacks hydrogen bond parallel
c. parallel beta are more stable than antiparallel ones
d. every full rotation in alpha helix is described as pitch, while each measure distance between residue is called rise
C
Insoluble in water, neutral solvents, salts and alcohol but soluble in diluted acid or base
a. prolamine
b. albumin
c. glutelin
d. globulin
D
Which of the following reagent would be able to cleave a peptide with guanine residues in it?
a. 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene
b. cyanogen bromide
c. chymotrypsin
d. trypsin
C
Usage of Edman reagent and amino peptidase on the peptide CHEMISTRY, what consequences will give a positive result to the sample?
a. pauly diazo test
b. xanthroproteic test
c. nitroprusside test
d. hopkin's cole test
e. millon's test
C
End product of protein metabolism
a. bilirubin
b. uric acid
c. blood urea nitrogen
d. creatinine
B
In terms of nitrogen metabolism, humans are
a. uricotelic
b. ureotelic
c. homeostatic
d. ammoniotelic
C
Enzyme N
a. arginase
b. argininosuccinase
c. argininosuccinic synthethase
d. carbamoyl phosphate synthetase
e. ornithine transcarbamoylase
D
Both AST and ALT are hepatic biomarkers that previously known as SGPT and SGOT respectively they require thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) as a cofactor
a. the first statement is correct while the second statement is incorrect
b. the first statement is incorrect while the second statement is correct
c. both statement re correct
d. both statement is incorrect
C
Which of the following statements are true?
I. Alkaptonuria also known as black urine disease is manifested as crippling arthritis later in life and is the first discovered aminoacidopathy
II. Phenylketonuric children may not cyclamate us sweetener
III. The most common cause of albinism is an interruption in the functioning of the tyrosinase enzyme which synthesize melanin from tyr.
IV. MSUD is characterized by build up of amino acid, V, I. and L which block the brain transporter for other amino acid and thus lead to mental retardation
a. I, II, III
b. I, II, IV
c. I, III, IV
d. II, III, IV
C
Alkaloid that contains a ring nitrogen but do not come from amino acid
a. true alkaloid
b. protoalkaloid
c. pseudoalkaloid
d. flavonoid
A
Precursor of imidazole alkaloids
a. histidine
b. ornithine
c. tyrosine
d. tryptophan
B
Precursor of indole and isoquinoline alkaloid is tyrosine. The precursor of imidazole alkaloids is histidine
a. the first statement is correct while the second statement is incorrect
b. the first statement is incorrect while the second statement is correct
c. both statement are correct
d. both statement is incorrect
B
which of the following precursor of alkaloid is in correctly match lysine
a. lysine - piperidine alkaloid
b. phenylalanine - indole alkaloid
c. tryptophan - quinoline alkaloid
d. histidine - imidazole alkaloid
e. ornithine - tropane
B
Use the figure from the item 11 select the precursor of ergot alkaloid
a. Q
b. R
c. S
d. T
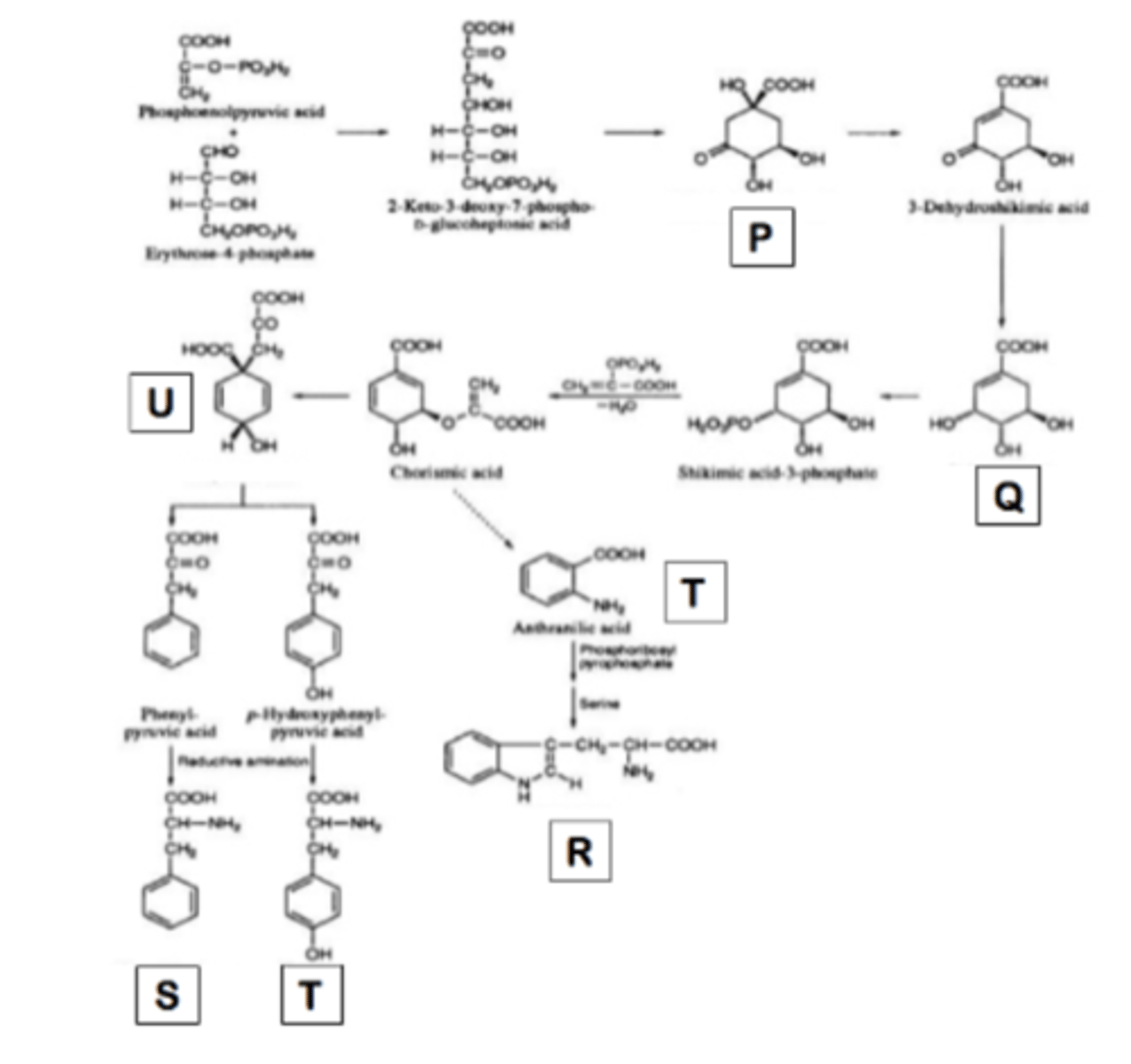
A
What is the classification of nicotine, sparteine, arecoline and coniine?
a. pyridine-piperidine
b. tropane
c. alkaloidal amine
d. purine
C
Pilocarpine
a. isoquinoline
b. quinoline
c. imidazole
d. indole
e. pyridine-piperidine
C
Select the statement that best describe Solanaceae alkaloid
I. The belladonna alkaloid are the most abundant in the plants after the fruit have ripened
II. The principal solanaceous alkaloids are hyoscyamine atropine and scopolamine
III. Atropine and scopolamine are competitive with acetylcholine at postganglionic synapse of parasympathetic nervous system producing antispasmodic effect
IV. Scopolamine is also known as hyoscyamine and atropine is also known as hyoscine.
a. I, II
b. III, IV
c. I, II, III
d. II, III, IV
D
Morphine and cocaine use as analgesic internally terminally ill cancer patient
a. paregoric
b. laudanum
c. dover's powder
d. brompton's cocktail
e. apomorphine
D
This is a cholinergic agonist of indole origin and can be used for glaucoma
a. reserpine
b. pilocarpine
c. atropine
d. eserine
e. strychnine
A
Classify goldenseal
a. isoquinoline
b. quinoline
c. indole
d. xanthine
e. pyridine-piperidine
E
Which has alkaloidal amine?
a. withania
b. green hellebore
c. dita
d. monkshood
e. abyssinian tea
C
a. theophylline
b. caffeine
c. theobroma
d. guanine
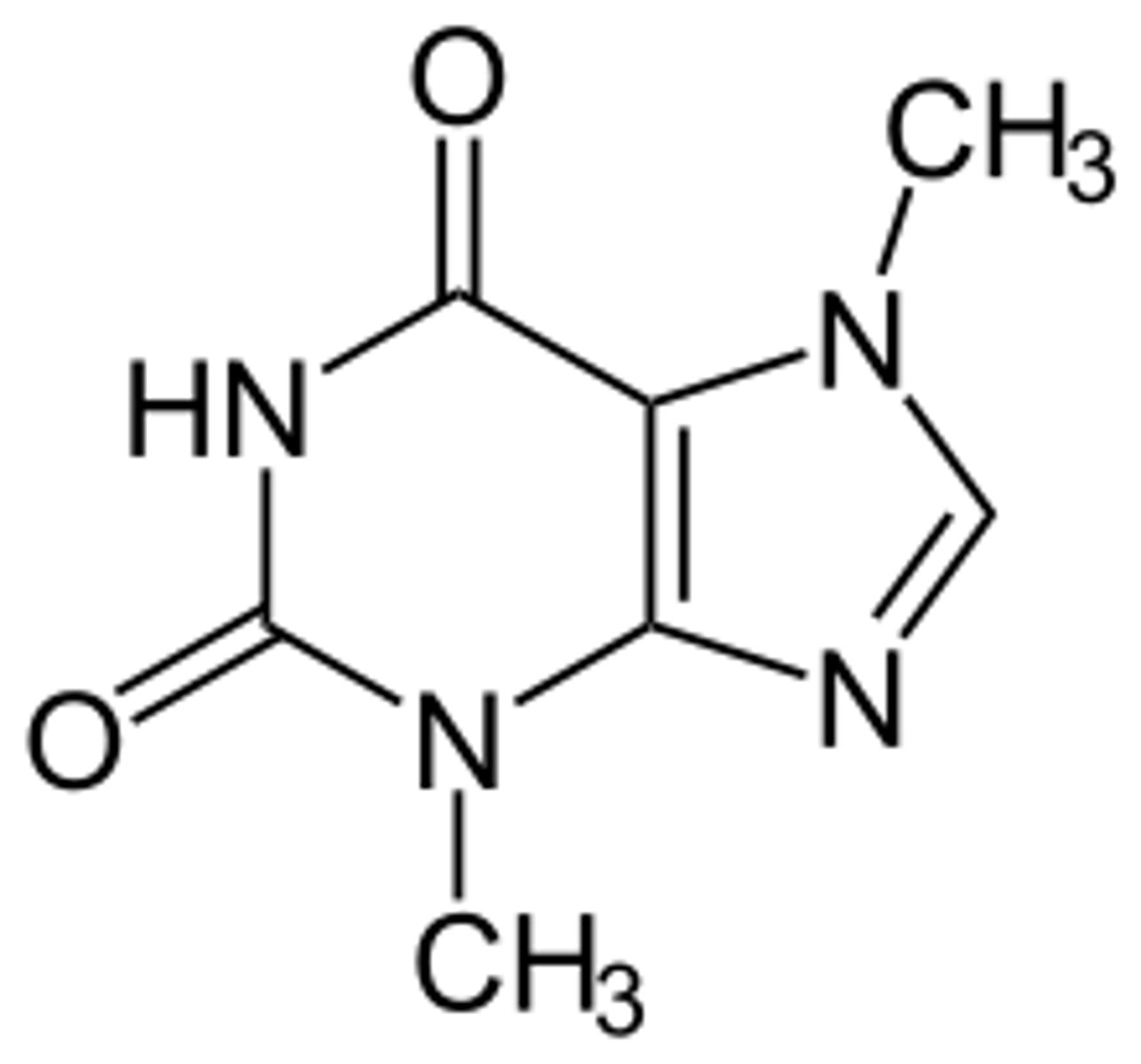
A
identify the test reagent for the presence of alkaloids which is a solution of potassium bismuth iodide and gives an orange colored precipitate
a. dragendroff's
b. mayer's
c. wagner's
d. hager's
B
Alkaloidal reagent in potassium iodide
a. wagner's reagent
b. marme's reagent
c. hager's reagent
d. murexide reagent
B
proposes that an enzyme's active site is flexible and undergo conformational changes to accommodate a substrate
a. lock and key theory
b. induced fit theory
c. michaelis menten theory
d. NOTA
D
Classify fumarase
a. hydrolase
b. ligase
c. transferase
d. lyase
D
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
A
Identify the zymogen that is activated by enzyme thrombin
a. fibrinogen
b. pepsinogen
c. prothrombin
d. procarbooxypeptidase
B
Vitamin k2
a. phytonadione
b. menaquinone
c. menadione
d. menadiol
C
Vitamin H
a. vitamin B5
b. vitamin B6
c. vitamin B7
d. vitamin B9
B
Vitamin d2
a. cholecalciferol
b. ergocalciferol
c. retinal
d. retinol
D
Which of the following is not true about cholecalciferol?
a. it is a vitamin d
b. it is initially and active and is further activated by both the liver and kidney
c. it maintains bone integrity
d. it is a water soluble vitamin
A
Which of the following forms of vitamin d3 is released by the liver?
a. calcifediol
b. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D
c. calcitriol
d. a and b
e. b and c
B
Its derivative, pyridoxal phosphate is required for transamination, decarboxylation, and deamination reactions.
a. Vitamin B2
b. Vitamin B6
c. Vitamin B9
d. Vitamin B12
A
Select the coenzyme that is required by CYP enzymes
a. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
b. Pyridoxal phosphate
c. Thiamine pyrophosphate
d. Ascorbic acid
D
Analyze the mechanism or catalytic strategy employed by pepsinogen
a. Utilization of the free energy IV. associated with the hydrolysis of ATP
b. Achievement of a high absolute rate of reaction that is suitable for integration with other physiological processes
c. Attainment of a high degree of specificity
d. Promotion of a reaction that is immeasurably slow at neutral pH
A
Analyze the mechanism involved in the regulation of DNA replication and synthesis of mRNA
a. Compartmentalization
b. Enzyme activation
c. Hormonal control
d. Concentration
C
analyze the mechanism involved in the regulation of phosphorylation and glycosylation
a. Enzyme activation
b. Hormonal control
c. Concentration
d. Compartmentalization
C
Noncompetitive enzyme inhibitors have which of the following effects on the Michaelis-Menten equation parameters: Vmax and Km?
a. Decrease both Vmax and Km derived
b. Decrease Km but no effect on Vmax
c. Decrease Vmax but no change on Km
d. Increase Km but no change in Vmax
d. Increase Vmax but no change in Km
E
What type of inhibition is presented by compound C?
a. Competitive
b. Noncompetitive
c. Irreversible
d. Competitive and irreversible
e. Noncompetitive and irreversible
B
Which of the following is not a pentose?
a. Arabinose
b Erythrose
c. Ribose
d. Lyxose
e. Xylose
A
Monosaccharides can be represented through Fischer projection and Haworth projection. Identify which of the following statements are true:
I. On a Fischer projection, the penultimate carbon determines whether a molecule is a D- or L- molecule.
II. L-sugars are depicted with their hydrogen molecule on the penultimate carbon on the left.
III. Haworth projections are used to depict cyclic monosaccharides.
IV. Alpha anomers of D-sugars have their anomeric OH drawn upward.
a. I, III
b. II, IV
c. I, II, III
d. II, III, IV
e. I, II, III, IV
B
Reaction of mannose with concentrated nitric acid will yield
a. mannuronic acid
b. mannaric acid
c. mannonic acid
d. mannitol
B
Select the category to which D-glucose and D-mannose belong
a. Enantiomers
b. Epimers
c. Aldose-ketose
d. Diastereomers
A
In the processing of cow's milk, the liquid separated from the coagulum is called:
a. Whey
b. Cheese
c. Buttermilk
d. Skim
e. Rennin
A
Liquor derived from the viscous leftover from extracting sugars from Beta vulgaris or Saccharum officinarum
a. Rum
b. Gin
c. Tequila
d. Whisky
e. Brandy
A
Find the homoglycans
a. Cellulose, starch, inulin
b. Heparin, agarose
c. Cellobiose, hyaluronic acid
d. Glycogen, agar
C
Choose the characteristics of amylopectin
I. Homopolymer of glucose
II. More branched than glycogen
III. Storage form of carbohydrate in plants
IV. Colors iodine violet
a. I, II
b. I, II, III
c. I, III, IV
d. I, II, III, IV
B
Which of the following converts starch to maltose?
a. Invertase
b. Diastase
c. Maltase
d. Pectase
B
Which of the following is not an official source of starch?
a. Oryza sativa
b. Manihot esculenta
c. Triticum aestivum
d. Solanum tuberosum
A
A polymer of glucose synthesized by the action of Leuconostoc mesenteroides in a sucrose medium and is used as a plasma expander at 10% is
a. Dextran
b. Hetastarch
c. Dextrin
d. Xanthan
D
This is derived from the inner part of the rind of Citrus aurantium
a. Bitter orange oil
b. Bergamot oil
c. Neroli oil
d. Pectin
A
This is sugar homopolymer fructofuranose, which was used by plants as a substitute for starch as a food source.
a. Inulin
b. Cellulose
c. Glycogen
d. Chitin
D
Chitin is a heteropolysaccharide that provides exoskeletons rigidity structural to and of wall cell fungi. Arthropods Peptidoglycan is a homopolysaccharide which is a component of the bacterial cell wall.
a. The first statement is correct while the second statement is incorrect.
b. The first statement is incorrect while the second statement is correct.
c. Both statements are correct.
d. Both statements are incorrect
C
Which of the following is FALSE ?
a. Pyroxylin is formed by the action of nitric and sulfuric acid
b. Pyroxylin is mixed with 3:1 ether- ethanol to make collodion
c. 3% camphor and 2% castor oil are added to collodion to impart waterproofing and flexibility, respectively
d. NOTA
B
Which of the following is needed the most in order to create cheese?
a. Zymase
b. Rennin
c. Coagulase
d. Two of the choices
e. None of the choices
A
Mucilages are physiologic substances produced naturally by organisms. Xanthan is an example of a plant mucilage.
a. The first statement is correct while the second statement is incorrect.
b. The first statement is incorrect while the second statement is correct.
c. Both statements are correct.
d. Both statements are incorrect
D
Acacia is normally used as a suspension agent in concentrations of around
a. 6%
b. 10%
c. 25%
d. 36%
e. 85%
B
Carrageenan comes from a
a. Plant exudate
b. Red alga
c. Bacterium
d. Brown alga
e. Plant seed
A
Determine a suitable chemical test for all monosaccharides
a. Benedict's test
b. Keller-Killani test
c. Biuret test
d. Sellwanoff's test
C
Which among the following sugars will produce a characteristic cotton-like crystals when heated with phenyl hydrazine?
a. Glucose
b. Mannose
c. Lactose
d. Maltose
C
Which of the following disaccharides will not produce a brick-red precipitate from the Benedict's test?
a. Gic-a1,4-Glc
b. Gal-ẞ1,4-Glc
c. Glc-al,a1-Glc
d. Two of the choices
e. All of the choices
B
Which will yield the following results:
(+) Molisch test
(+) Barfoed's test
(+) Benedict's test
(-) Seliwanoff's test
(-) Bial's test
(+) Mucic acid test
a. Glucose
b. Galactose
c. Fructose
d. Xylose
e. None of the above
A
Which sugar when tested for its identity will give the profile below:
Fehling's: brick red ppt
Mucic Acid Test: crystals that dissolve immediately after
Bial's: green solution
Seliwanoff's: cherry red solution
a. Ribulose
b. Ribose
c. Fructose
d. Galactose
e. Trehalose
B
Which among the following steps occur later than the rest?
a. Fructose-6-phosphate to fructose bisphosphate
b. 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolypyruvate
c. DHAP to G3P
d. 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to a phosphoglycerate
A
Which among the following steps occurs earlier than the rest?
a. Fructose-6-phosphate to fructose bisphosphate
b. 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolypyruvate
c. DHAP to G3P
d. 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to a phosphoglycerate
A
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the first substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis?
a. Phosphoglycerate kinase
b. GAP dehydrogenase
c. G3P dehydrogenase
d. Pyruvate kinase
e. Phosphofructokinase
E
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the second irreversible step of glycolysis?
a. Phosphoglycerate kinase
b. GAP dehydrogenase
c. G3P dehydrogenase
d. Pyruvate kinase
e. Phosphofructokinase
B
Pyruvate, upon the action of pyruvate decarboxylase yields
a. ethanol
b. lactate
c. acetyl-CoA
b. acetaldehyde
C
Identify complex IV of the electron transport chain
a. Succinate-CoQ reductase
b. Cytochrome c oxidase
c. CoQ-Cytochrome C reductase
d. NADH-COQ reductase
D
Step in TCA cycle which does not involve production of energy
a. Isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate
b. Succinate to fumarate
c. Alpha-ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA
d. Citrate to isocitrate
C
Which complex of the electron transport chain does antimycin A inhibit?
a. Succinate-CoQ reductase
b. Cytochrome c oxidase
c. CoQ-Cytochrome C reductase
d. NADH-COQ reductase
C
What is the rate-limiting enzyme of the TCA cycle?
a. Carnitine acyltransferase
b. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase
c. Isocitrate dehydrogenase
d. Succinate dehydrogenase
e. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
B
Which of the following is false about the mitochondrial shuttle systems?
a. Malate-aspartate shuttles generate more energy than glycerol-3- phosphate shuttles because they result to NADH in the mitochondrion instead of FADH2
b. Both shuttle systems allow the utilization of NAD+ from glycolysis to generate energy
c. Dihydroxyacetone phosphate is reduced to glycerol-3-phosphate in the cytosol through the G3P shuttle
d. Oxaloacetate is reduced to aspartate in the cytosol through the MA shuttle
B
Cytochrome c oxidase The principal tissues affected by this GSD are the liver, spleen, and primarily the muscles
a. GSD VI
b. GSD V
c. GSD III
d. GSD VII
C
The enzyme responsible for step number 4 is deficient in _______________ and leads to _________________
a. von Gierke's disease; hyperglycemia
b. glycogen synthase; hyperglycemia
c. von Gierke's disease; hypoglycemia
d. glycoygen synthase; hypoglycema
D
In process 8, what enzyme is responsible?
a. pyruvate carboxylase
b. pyruvate hydrogenase
c. pyruvate decarboxylase
d. pyruvate dehydrogenase
e. pyruvate transaminase