Connective Tissue Disease, SLE, Scleroderma, Fibromyalgia
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
autoimmune, genetic, and cancer-related
Connective tissue disorders (those affecting the skin, joints, muscles, and vessels) are caused by
Lupus, RA, Scleroderma
Examples of Connective Tissue Disorders
Autoimmune response to chronic inflammations that leads to damage to collagen and elastin resulting in systemic organ damage
Pathophys for Connective Tissue Disorders
genetic mutations, FHx, infections, UV exposures, smoking, hormonal influences (especially in autoimmune)
Etiology of connective tissue disorders
Joint pain/stiffness, skin rashes/sensitivity, fatigue, muscle weakness, organ involvement
Common Symptoms of Connective tissue Disorders
Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease (UCTD)
The catch all for connective tissue disorders in which symptoms (joint pain, Reynauds, fatigue) are suggestive but criteria are not meant
Mild immune activity without severe damage (remains stable or improves over time)
Patho for UCTD - diagnosis based on presentation and labs
Mixed connective tissue disease
The term for features of MULTIPLE connective tissue diseases that tends to be progressive and be anti-U1 RNP positive
Immune system attacks multiple connective tissues leading to swollen fingers, joint pain, muscle weakness, and lung involvement
Patho for MCTD
NSAIDs, Corticosteroids, immunosuppressants (hydroxychloroquine for protection of organs), regular exercise, avoiding triggers (UV, cold), regular monitoring, anti-inflammatory foods, adequate hydration, PT, psych support
Treatment plan for Connective Tissue Diseases (general)
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
The most common type of lupus that is caused by genetics, environment, hormones, or viruses and affects the skin, joints, kidneys, and brain in sporadic flares
All ages (15-45 most common), female dominant, african american
Epi Stats for SLE
UV light (wear sunscreen), Sulfa based medications (Bactrim, Septra, Sulfalazine), Estrogen, Alcohol, Garlic, Processed foods and sugar, nightshade veggies (tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants, bell peppers), Dairy products, omega-6 rich oils (corn, sunflower, soybean)
What can worsen the symptoms of SLE?
Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus that is limited to the skin
Discoid Lupus erythematosus, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus, Acute cutaneous lupus
Types of CLE
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE)
What form of CLE is characterized by chronic skin RAISED, disc shaped erythematous plaque with adherent keratotic scales on the face, neck, and scalp that lead to scarring, skin atrophy (permanent alopecia and disfigurement)
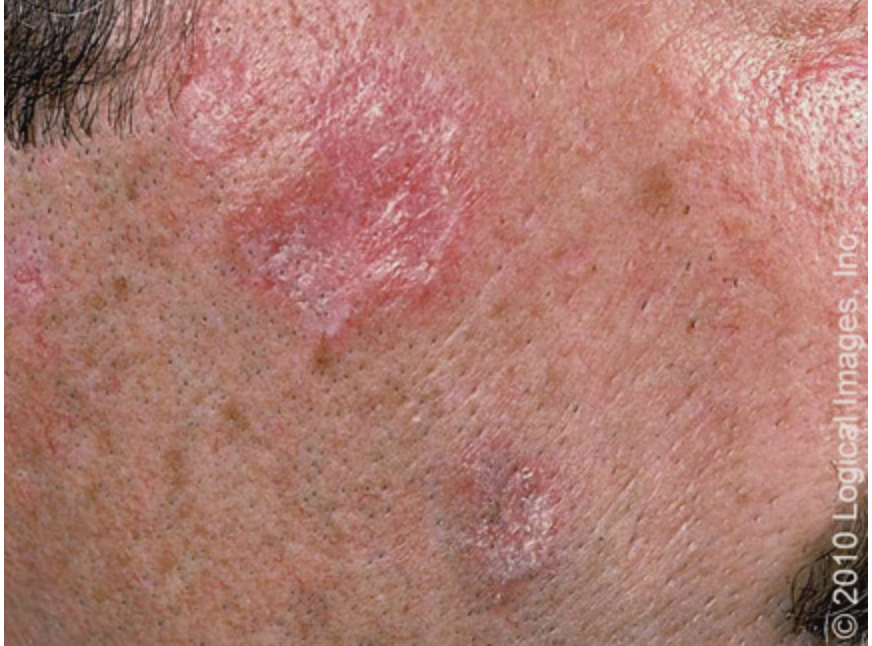
Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (SCLE)
What form of CLE is characterized by skin lesions triggered by sun exposure?
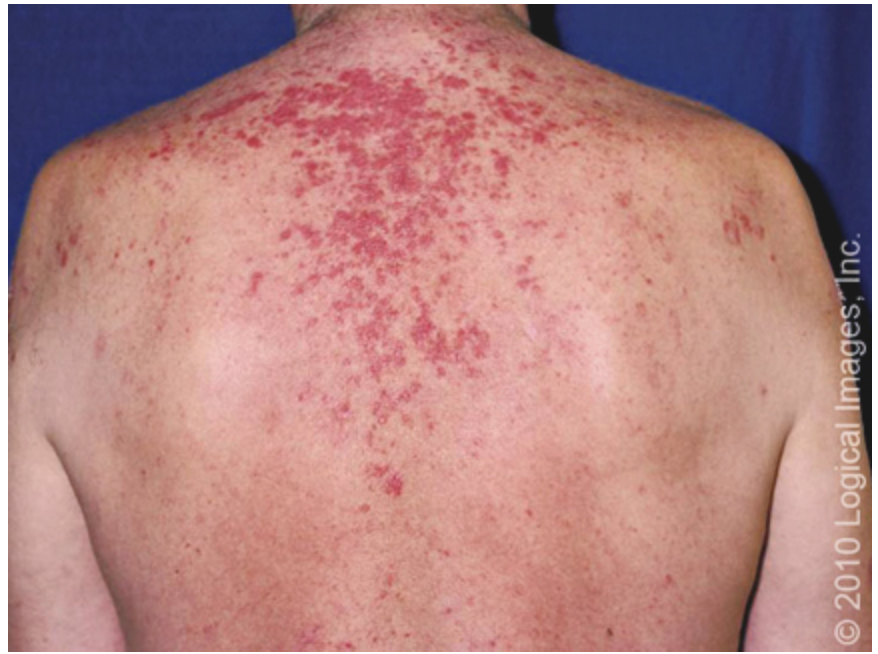
Acute Cutaneous Lupus
What form of CLE is characterized by by a butterfly shaped rash across the cheeks and nose
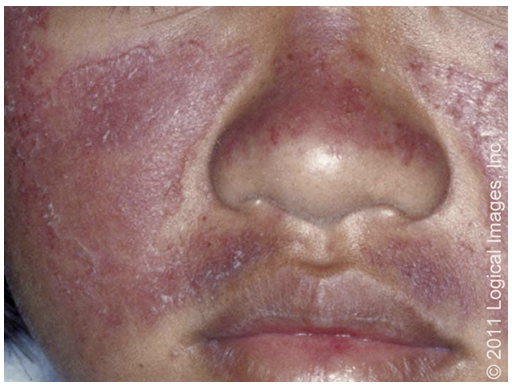
Drug Induced Lupus Erythematosus
What type of lupus occurs as a drug reaction (usually isoniazid, hydralazine, procainamide, methyldopa) but resolves when the meds are stopped?
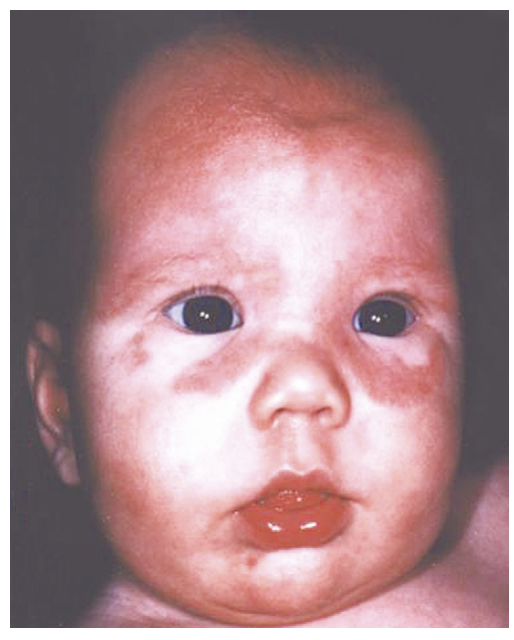
Neonatal lupus
A rare condition that affects the infants of women with lupus leading to skin rashes, liver problems, and heart issues (AV block, valvular lesions)
Fever, fatigue, weight changes, lymphadenopathy
Constitutional Features of Lupus
Malar (AKA butterfly rash sharply demarcated with induration/scaling), photosensitivity, oral/nasal ulcers, alopecia
Cutaneous Features of lupus

Arthralgia, arthritis (occurs in 95% of patients)
MSK Features of lupus
Pericarditis, endocarditis, valvular heart disease, Raynaud’s
Cardiac Features of lupus
Pleuritis (most common), pleural effusions, pneumonitis
Pulmonary Features of lupus
Anemia of Chronic disease, leukopenia (impaired immune system), lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia
Hematologic Features of lupus
Proteinuria, nephritis on biopsy (immune complex glomerulonephritis - type III)
Renal Features of lupus
Abd pain (40% of patients), peptic ulcers, N/V
GI Features of lupus
HA, seizures, anxiety, mood disorder, psychosis, cognitive decline, Gullian-Barre, polyneuropathy, other neuropathies
Neuropsych Features of lupus
Serositis (pleuritis, pericarditis), oral ulcers, arthritis, photosensitivity (90%), Blood disorders, proteinuria (500+ per day), ANA+, Anti-DNA or Anti-Sm or Antiphospholipid antibodies, Seizures or psychosis, malar rash, discoid rash
ACR criteria for Lupus - requires 4/11
unusually reaction to sunlight that may occur more than 1 week after sun exposure and exacerbate systemic symptoms
Photosensitivity is defined by the ACR as a result of an
Gradual, typically painless (unless it’s discoid lupus lesions those hurt) lesions of the palate, buccal, tongue or nose that are unilateral/asymmetric
Describe the Ulcers in Lupus
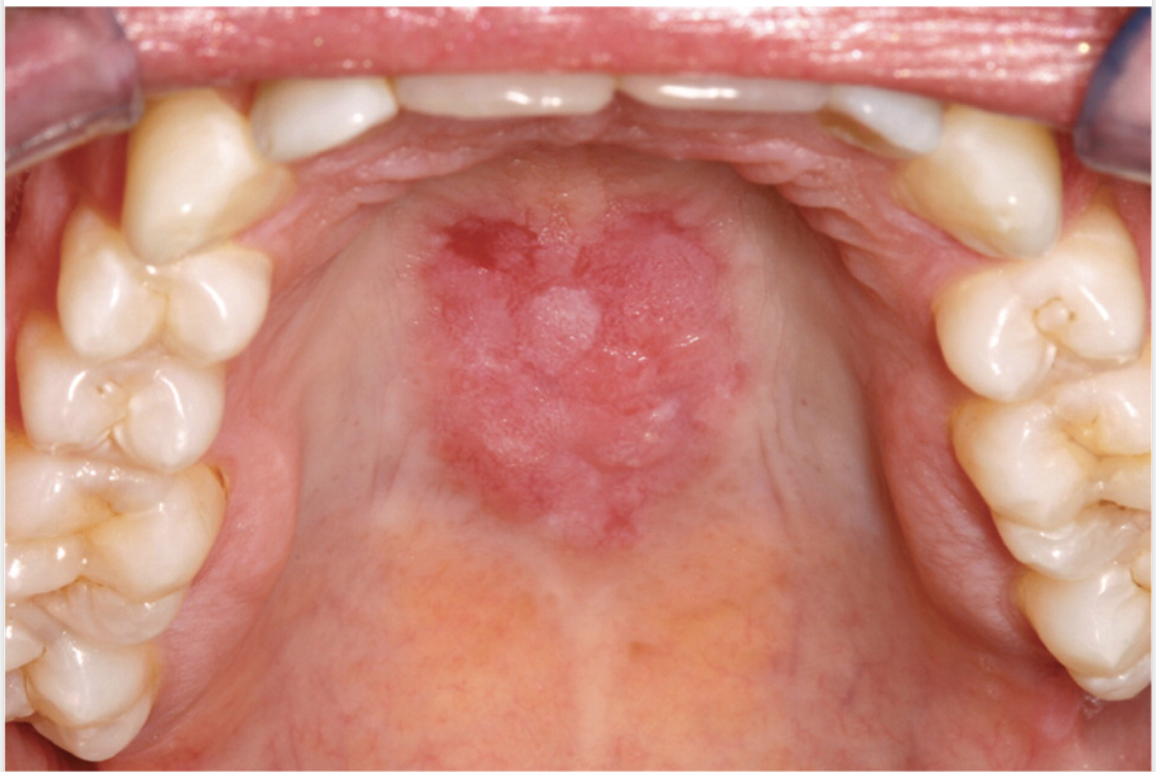
CBC, CMP (renal, lfts), ESR (correlates with disease activity but not specific), CRP, ANA (sensitivity 95%), Anti-smith (20% of patients (specific)), Anti-dsDNA (70% of patients specific), Decreased C3/4, UA
Lab test for Lupus
Anti-histone antibody
Labs for Drug induced lupus
Anti-Ro/SSA, AntiLa/SBB (if the other is neg)
Labs for Neonatal Lupus
CXR, echo, MRI, Renal U/S, Arthrocentesis, lumbar puncture
Other diagnostics for Lupus
NSAIDs (prn for arthralgias), Corticosteroids (acute exacerbations, renal), Cytotoxic agents (active glomerulonephritis - cyclophosphomide), Hydroxychloroquine (EVERY PATIENT ALL THE TIME - alternatives methotrexate, leflunomide), Mycophenolate, azathioprine, Biologics (belimumab, afrolumab)
Treatment plan for Lupus
With early diagnosis, close follow-up, and appropriate treatment 80-90% can live a normal lifespan
Prognosis of Lupus
Fibromyalgia
A chronic disorder characterized by widespread MSK pain and tenderness that usually is diagnosed in the middle of adult life (female dominant)
CNS amplifies or enhances pain processes (demonstrated by EMG, CSF, PET - so NOT an autoimmune, inflammation, joint, or muscle disorder)
What does research suggest the cause of Fibromyalgia?
Widespread pain throughout the body (arms, legs, chest, abd, back, butt), pain is often described as aching, burning, or throbbing, fatigue (overwhelming), trouble sleeping
Most common symptoms of Fibromyalgia
Muscle/joint tenderness (pelvis, TMJ), tenderness to touch, numbness/tingling of extremities, problems with thinking (fibro fog), heightened sensitivity to light, noise, odors, and temp, Digestive issues (bloating, constipations, IBS), irritable bladder, depression, anxiety
Other symptoms of Fibromyalgia
Widespread Pain Index (WPI)
What metric notes the number of areas in which the patient has had pain over the last week (score will be between 0-19)
Symptoms Severity Score (SSS)
What metric notes the sum of severity of the 3 symptoms + the extent of somatic symptoms (score between 0-12)
Fatigue, waking unrefreshed, cognitive symptoms, somatic symptoms in general (0 is nothing, 3 is severe)
Parts of the SSS
WPI 7+ and SSS 5+ (or WPI 4-6 and SSS 9+), generalized pain in 4/5 regions, symptoms present for 3 months
ACR 2016 Fibromyalgia Diagnostic Criteria
Exercise (most effective), CBT, acupuncture, massage therapy, sleep dysfunction management, diet/obesity management, address triggers of sleep disorders
Non-pharm treatment plan for Fibromyalgia
Antidepressants (duloxetine, milnacipran, amitriptyline (SNRIs, SSRIs)), Pregabalin, Gabapentin, NO OPIOIDS
Pharm treatment plan for Fibromyalgia
Self-care is important, stress reduction, regular sleep patterns, avoid stimulants, regular exercise
Tips for treating long term managing fibromyalgia
Scleroderma
A systemic autoimmune disease characterized by varying degrees of skin fibrosis, vascular damage, and a wide array of internal organ dysfunction (more common in 30-50 y/o African American/Native Women (4x))
Raynaud’s phenomenon, ANA+, skin thickening
Early Red Flags for Scleroderma
Cardiac involvement (30%) is most common cause of death followed by lung disease (25%)
Prognosis of Scleroderma
Patch, generalized, linear, En coup de sabre (Parry-Romberg Syndrome), Pansclerotic morphea
Types of localized (skin only) scleroderma (Morphea)
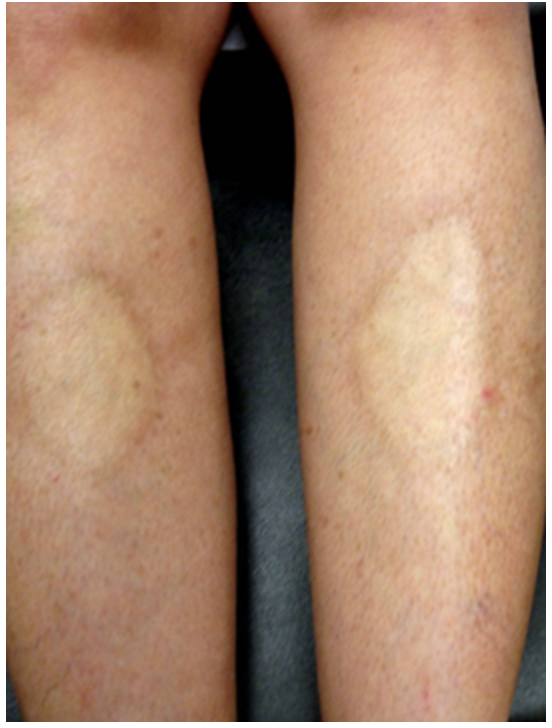
Scleroderma sine scleroderma
Systemic scleroderma that is rare (5%) without obvious skin thickening
Diffuse (30%)
Systemic scleroderma in which skin thickening extends to the proximal portion of the extremities and/or the trunk
Limited (65%)
Systemic scleroderma in which skin thickening is confined to the face and extremities, distal to the elbows and knees - does not progress to diffuse
Calcinosis (skin and digits), Raynaud’s, Esophageal motility dysfunction, Sclerodactyly of the fingers, telangiectasia on the skin of the fingers, nails, face, and mouths
CREST Syndrome is characterized by
Excessive collagen excess (severe thickening may lead to flexion contractures)
Skin changes in Scleroderma are due to
thinning of the lips, decreased in oral aperture, narrow nose bridge
Changes in the Skin of the Face in Scleroderma
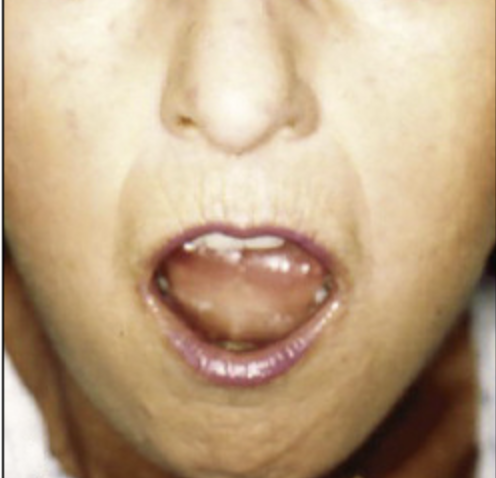
Early inflammatory, Fibrotic phase, late phase
Phases of the skin changes in Scleroderma
Calcinosis
Subcutaneous Ca2+ deposits that can be found on the fingertips and extensor surfaces (forearms, patellas) - no effective treatment
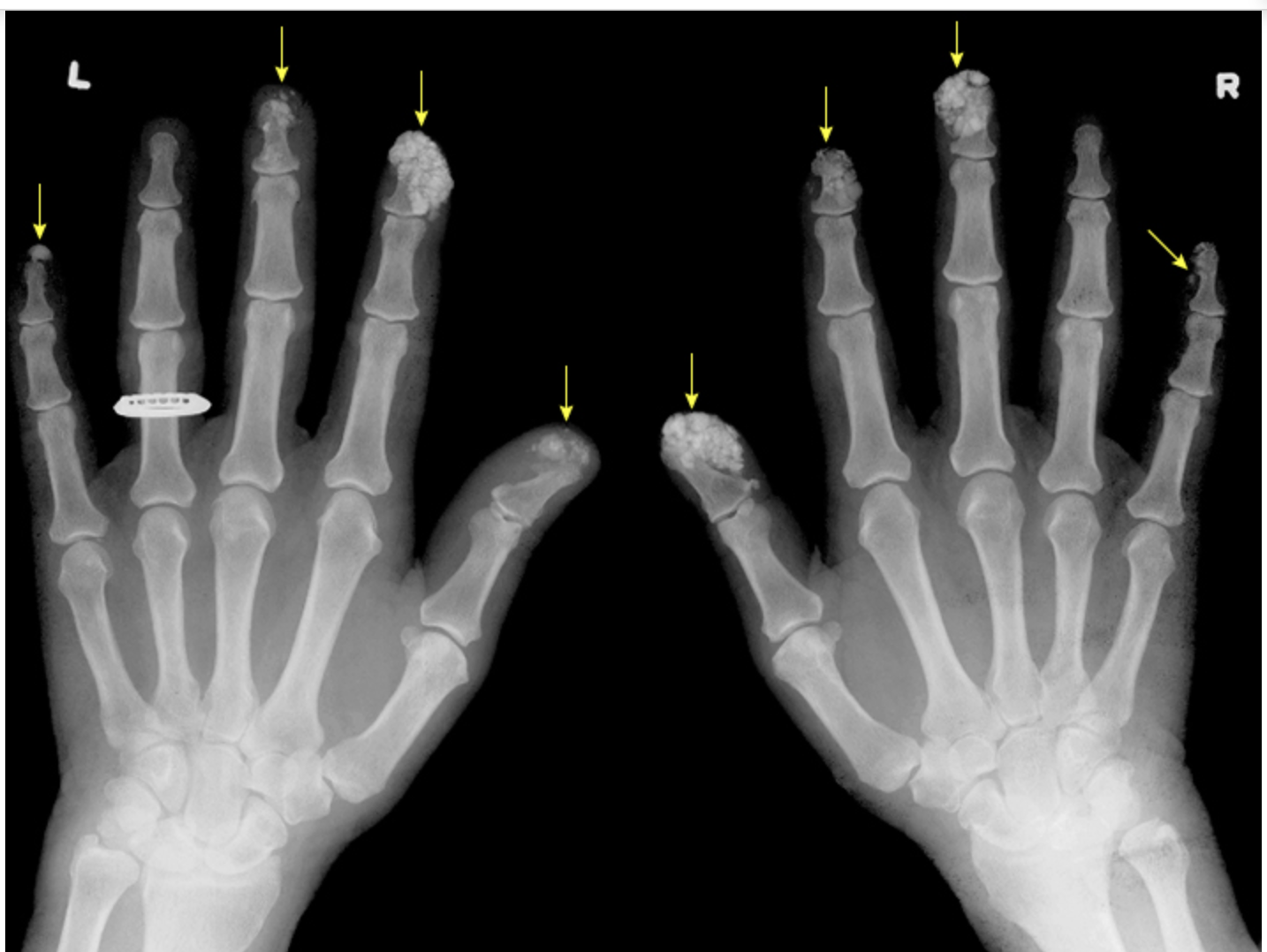
Sclerodactyly
Tightening and thickening of fingers and toes
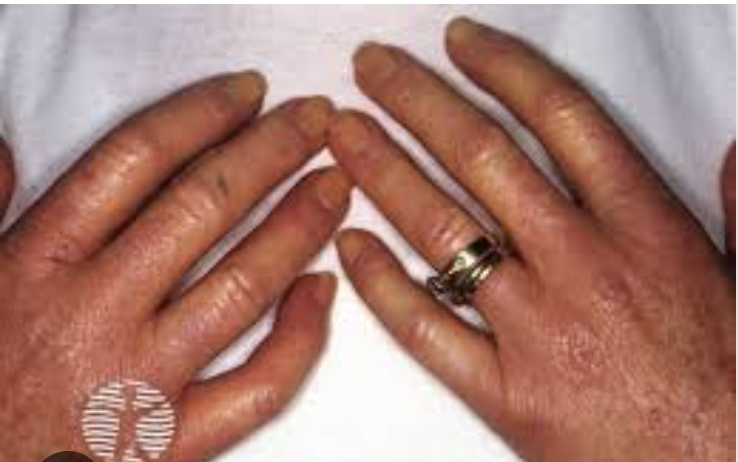
Rodnan Scores (0-3)
Skin thickening is scored with
Raynaud’s Phenomenon
Characterized by episodes of vasoconstriction of the digital arterial circulation in response to cold temperatures or emotional stressors and is typically the first manifestation of scleroderma (More common in females 4x)
autoimmune disease, medications, thoracic outlet syndrome
Secondary Raynaud Phenomenon is associated with
Later age of onset (20+ y/o), Male, asymmetry, can lead to ischemic ulceration, ANA+, nailfold capillary abnormalities
Secondary Raynaud’s Phenomenon is characterized by
painful fingertip ulcers or progression to digital gangrene and finger loss
Recurrent attacks of Raynaud’s can be associated with the development of ischemic complications like…
Cold avoidance, stress management, smoking cessation, protective clothing (gloves), avoid vasoconstrictive agents
Prevention Strategies for Raynaud Phenomenon
CCBs 🥇, phosphodiesterase inhibitors (viagra), topical vasodilators, prostaglandin Surgical interventions (refractory or complications of acute ischemic attacks)
Treatment plan for Raynaud’s
Interstitial Lung Disease
The most common lung manifestation in scleroderma (one of the most determinants of morbidity and mortality) that normal develops within the first 5 years (60% diffuse, 20% limited)
Scl-70, Anti-U3-RNP, Anti-Th/To
What antibodies are associated with interstitial lung disease?
Fine inspiratory crackles at lung bases, Restrictive pattern on PFTs (do these with DLCO annually), High-resolution CT (evidence of fibrosis - ground glass and reticular), nonspecific interstitial pneumonia on histology
Most common findings in Interstitial lung disease
Pulmonary arterial hypertension
A potentially life-threatening manifestation of Scleroderma that manifests as dyspnea and exertion on fatigue early and hypotension and lower edema later in disease
Screen scleroderma peeps annually with Transthoracic echo, Right heart cath greater than 25 mmhg (definitive)
How is Pulmonary arterial hypertension diagnosed?
GERD (75-95% of patients), delayed gastric emptying, constipation, diarrhea, esophageal constrictures
GI involvement occurs in both diffuse and limited scleroderma - what can this look like?
No late night meals, H2 blockers, PPIs, esophageal manometry, barium swallow, endoscopy
Game plan for GI involvement of Scleroderma
Scleroderma Renal crisis
A medical emergency characterized by rapid malignant HTN (150/90+) characterized by HA, visual disturbances, nosebleeds, CHF, pericardial effusion, and flash pulmonary edema (Rare but occurs in Diffuse)
Renal biopsy (confirms diagnosis), ACEI, NO HIGH DOSE STEROIDS
Gameplan for Scleroderma Renal crisis
Contractures, Resorption of distal finger tufts and deposition of calcium in joints, muscle weakness
MSK changes in Scleroderma - common and nonspecific
NSAIDs, low dose steroids, OT
Gameplan for MSK changes in Scleroderma
renal failure, malignant hypertension, severe wound infections secondary to infarcts, symptomatic chronic severe interstitial lung disease, heart failure
When to hospitalize Scleroderma patients