APES Unit 8
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Last updated 12:32 AM on 4/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
1
New cards
point pollution
Pollutants discharged from a single identifiable location (e.g., pipes, ditches, channels, sewers, tunnels, containers of various types).
2
New cards
non-point pollution
pollution that comes from many sources, not easily to identify where the exact sources come from (EX: water, air)
3
New cards
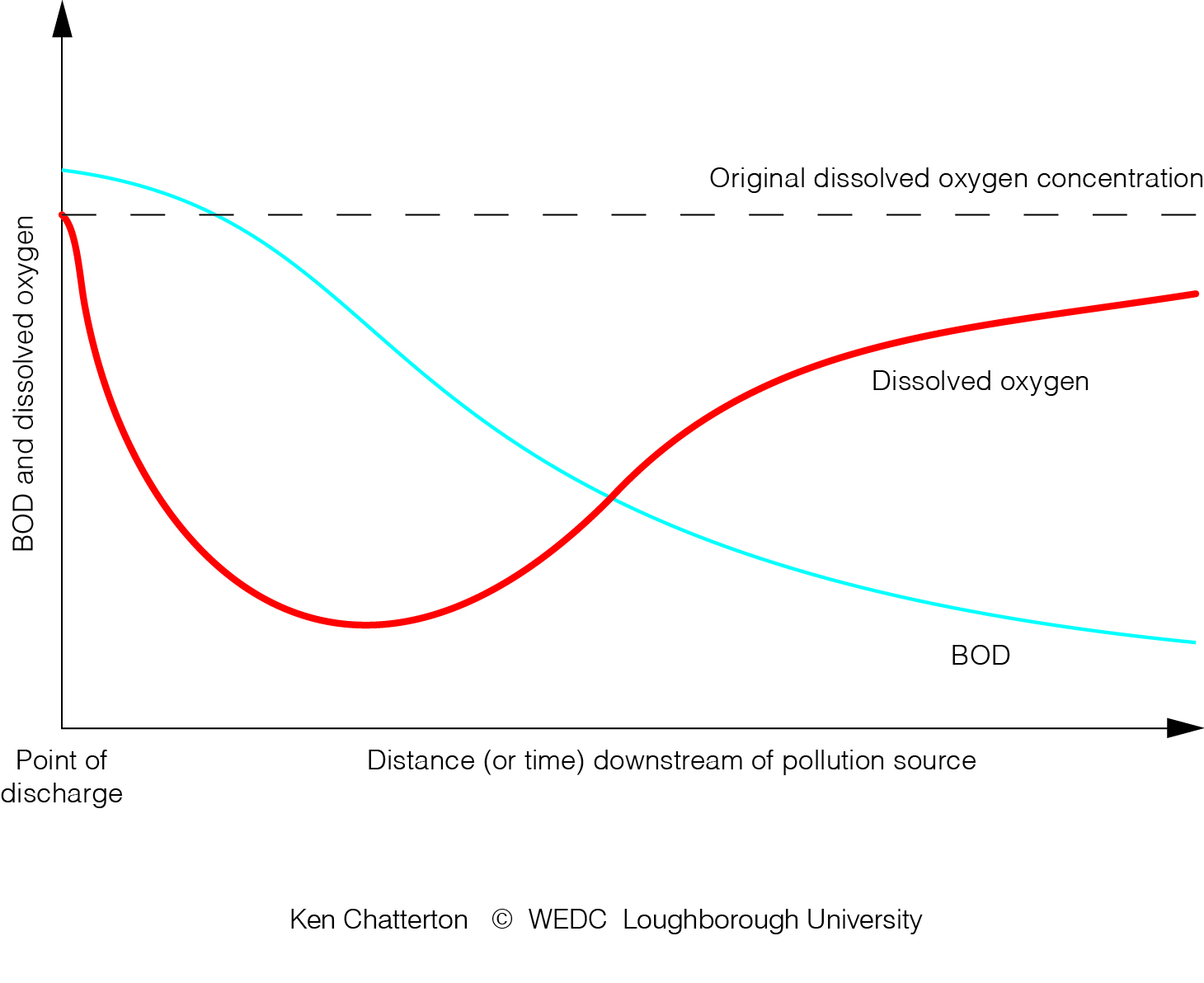
oxygen sag curve
Oxygen depletion from pollution in rivers and lakes (Less DO, less animals can survive)*
4
New cards
range of tolerance
the limits to the abiotic conditions that a species can tolerate (Amount of DO, food, space, etc)
5
New cards
What can nutrient pollution lead to?
Eutrophication and then dead zones
6
New cards
Dead zones
In a body of water, an area with extremely low oxygen concentration and very little life. Often caused by eutrophication
7
New cards
How does warm temperatures effect dissolved oxygen (DO)?
Lessens the amount of DO
8
New cards
Sediment Pollution
It reduces light infiltration, lower the amount of photosynthesis that can occur under water.
9
New cards
Endocrine disruptors
Chemicals that disrupt normal hormone functions. Can cause birth defects, developmental disorders, etc)
10
New cards
Endocrine system
Glands secrete hormones that regulate processes such as growth, reproduction, and nutrient use (metabolism) by body cells. Can be disrupted by pollution.
11
New cards
What is an example of an endocrine disruptor?
DDT
12
New cards
Ecological services of wetlands
water purification, flood protection, water filtration, and habitat
13
New cards
Wetland threats
commercial development, dam construction, overfishing, and pollutants from agriculture and industrial waste
14
New cards
Oligotrophic lakes
Lake with high DO, low BOD, low nutrients, low algae content, Usually high in the mountains.
15
New cards
Eutrophic lakes
Lakes with low DO, high BOD, high nutrients, high algae content
16
New cards
Biological demand of oxygen (BOD)
How much oxygen a species needs to survive
17
New cards
process of eutrophication
Nutrients added to water -\> algae bloom -\> algae die -\> algae decompose (consumes O2, BOD increases) -\> DO decreases -\> dead zone
18
New cards
Thermal pollution
a temperature increase in a body of water that is caused by human activity and that has a harmful effect on water quality and on the ability of that body of water to support life
19
New cards
Solutions to thermal pollution
Cooling towers (cools water being put in) and closed systems (keeps water out of watershed)
20
New cards
Thermal pollution graph
As the water temperature increases, the DO concentration decreases.

21
New cards
persistant organic pollutants (POPs)
compound with carbon in it that resists photochemical, biological and chemical degradation
22
New cards
Carcinogen
A cancer-causing substance, often found in POPs (EX: asbestos)
23
New cards
What do POPs cause?
Carcinogens, endocrine disruptors, nervous/immune system damage, Wildlife decline and reproductive impairment
24
New cards
How can POPs travel long distance?
Through wind, water, and bioaccumulation
25
New cards
Biomagnification
An increased concentration of substances per unit of body tissue. Gets worse the higher up the food chain
26
New cards
Bioaccumulation
The absorption of elements/compound by cells. Do not go away and can be passed on to next organism if current one is eaten.
27
New cards
Biomagnification/Bioaccumulation impacts of humans
Reproductive issues, nervous system issues, cardiovascular impacts
28
New cards
Biomagnification/Bioaccumulation impacts of top carnivores
egg shell thinning, developmental issue, reproductive problems
29
New cards
sanitary landfill
A place to deposit solid waste, where a layer of earth is dug up, lined with plastics or clay, storm water collection leachate collection and methane collection implanted, filled with waste, covered over by land

30
New cards
Landfill
Most common type of solid waste disposal, decomposition depends on trash and conditions, can contaminate groundwater and release harmful gases
31
New cards
Incinerators
Trash is burned, gets rid of trash volume, releases air pollutants
32
New cards
Illegal dumping
Happens if waste collection is too expensive, leads to environmental problems
33
New cards
ocean dumping
leads to trash islands, marine life killed by entangling or ingesting waste
34
New cards
3 Rs
reduce, reuse, recycle
35
New cards
Landfill mitigation
lowers the amount of landfills, done by incineration and habitat restoration
36
New cards
waste-to-energy
A system in which heat generated by incineration is used as an energy source rather than released into the atmosphere
37
New cards
Three stages of sewage treatment
Primary (physical, Secondary (biological), and tertiary (chemical)
38
New cards
Primary (physical) sewage treatment
screen or grate removes large objects from waste
39
New cards
Secondary (biological) sewage treatment
Solid waste settles to the bottom, waste water aerated to allow good bacteria to break down bad bacteria
40
New cards
Tertiary (chemical) sewage treatment
Water treated with CL, O3, or UV light to kill remaining bacteria
41
New cards
LD50
lethal dose (of a toxin) for 50% of the test population. Smaller the dose, the more toxic the substance is.
42
New cards
Pathogens
Microbes that cause disease
43
New cards
How do pathogens spread
Areas lack sanitary waste disposal/ have contaminated water supply -\> spread of infectious disease (tropical ones heading more north/south with climate change)
44
New cards
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA)
controls hazardous waste with a cradle to grave system
45
New cards
Neurotoxins
toxic substances, such as lead or mercury, that specifically poison nerve cells
46
New cards
Teratogens
agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm
47
New cards
How do you find the safe human dose of LD50?
The divide the dose by 1000