Chemistry Paper 2 RATES
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What is the rate of a reaction?
The speed at which a chemical reaction takes place.
What are the equations for rate of reaction?
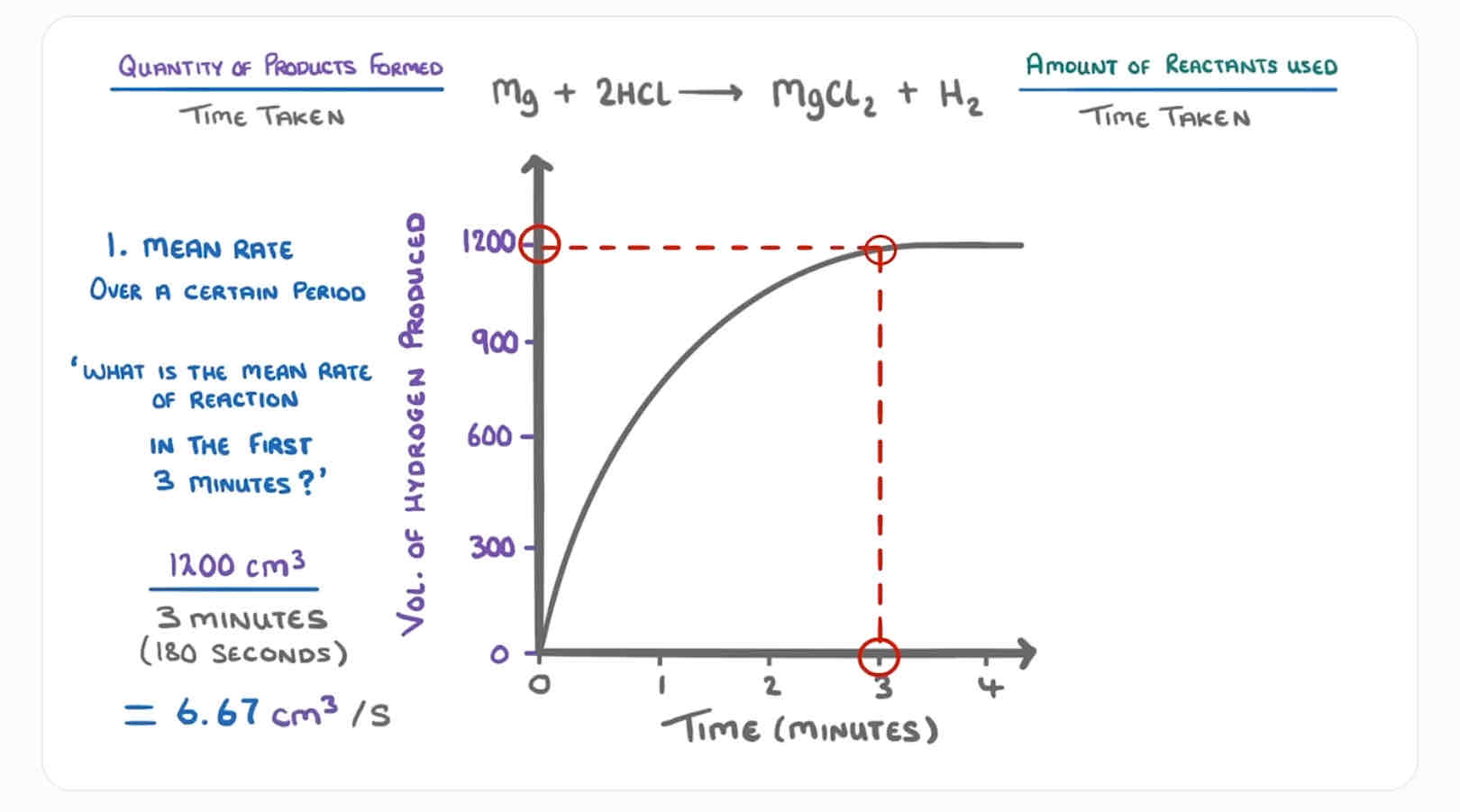
Quantity of product formed OR used / the time taken
What are factors the affect the rate of a reaction?
Catalyst, surface area, temperature, concentration and pressure.
What is collision theory?
In order for particles to react, they have to collide with each other with sufficient energy (activation energy)
If particles have more energy…
the more energy they can transfer during a collision
If particles collide more often (have a higher frequency)
The more successful collisions there will be
How does temperature effect the rate of reaction?
Particles gain more kinetic energy
So they move faster
And collide more frequently exceeding their activation energy
Meaning more successful collisions.
Concentration and pressure refer to what?
How many particles there are per unit of volume
What has the highest surface area; a solid block, small chunks, or powder?
Powder
Why does surface area increase rate of reaction?
More particles are exposed, meaning there is a greater chance of particles colliding, leading to more successful collisions.
What is activation energy?
The minimum amount of energy needed for a chemical reaction to take place.
What does a catalyst do?
Speed up the rate of a reaction without being used up and without being chemically changed
How does a catalyst work?
It provides an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy
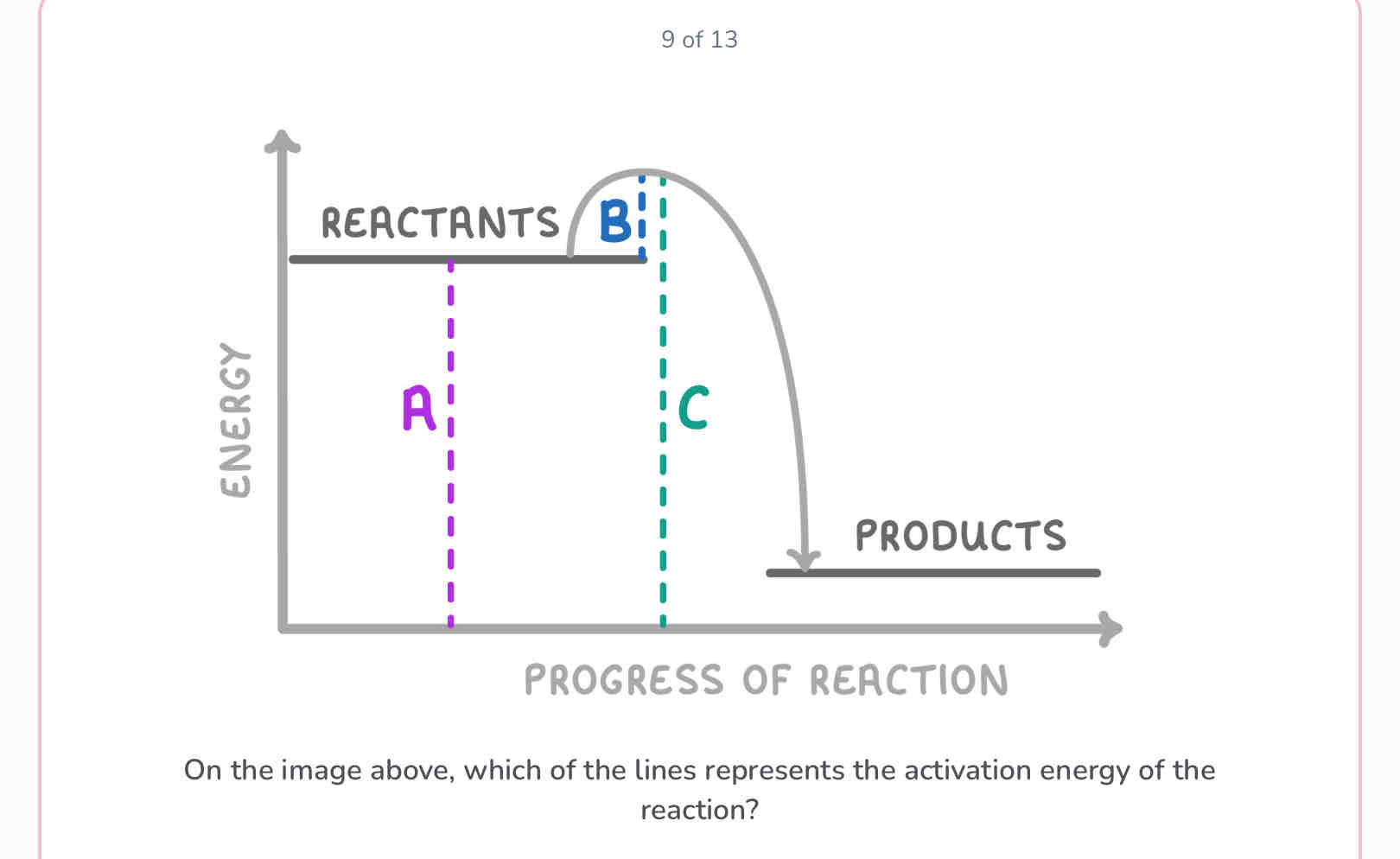
B
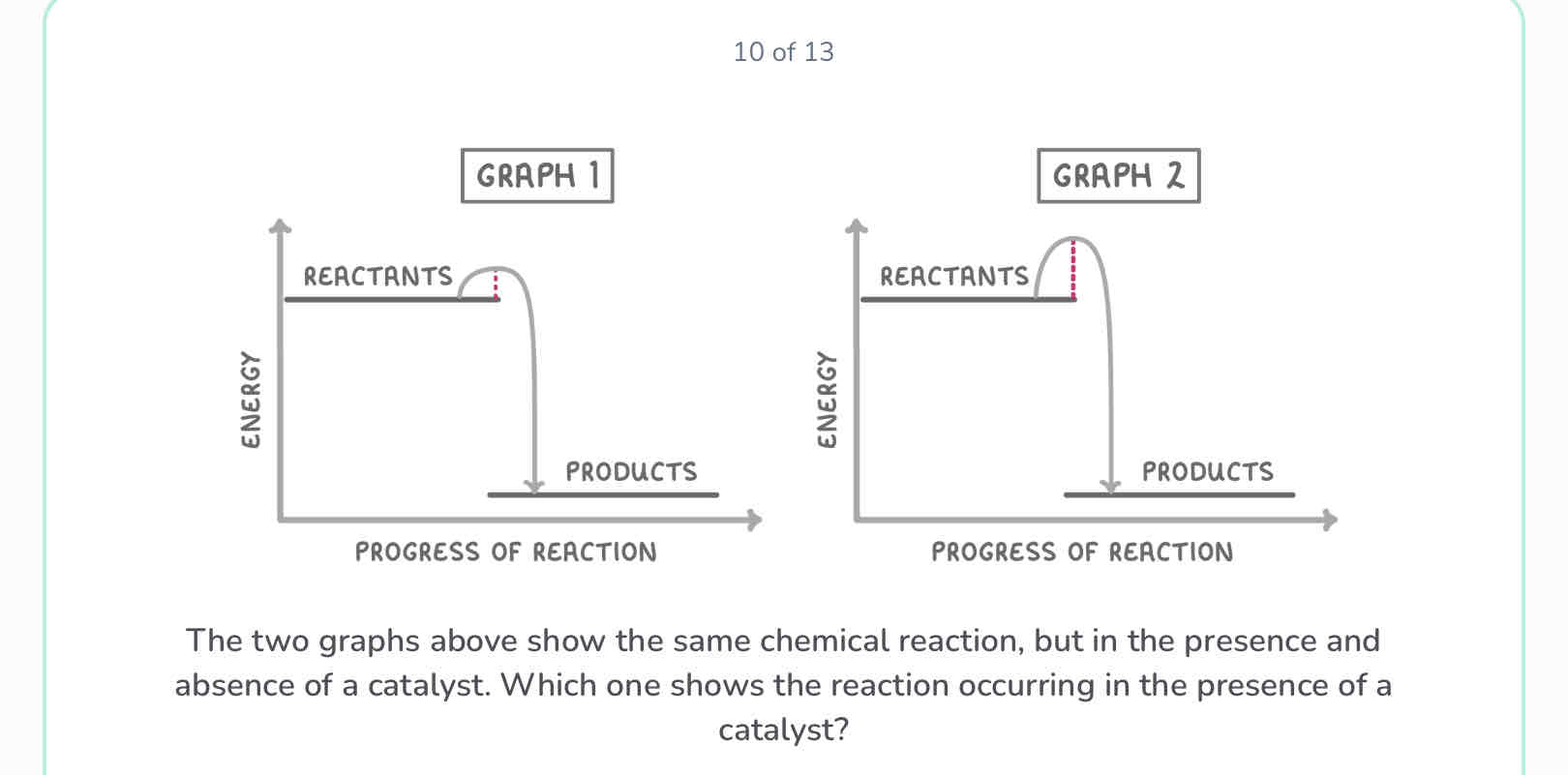
Graph 1
Do transition metals make good catalysts?
Yes
How do find mean rate of reaction? (Image)
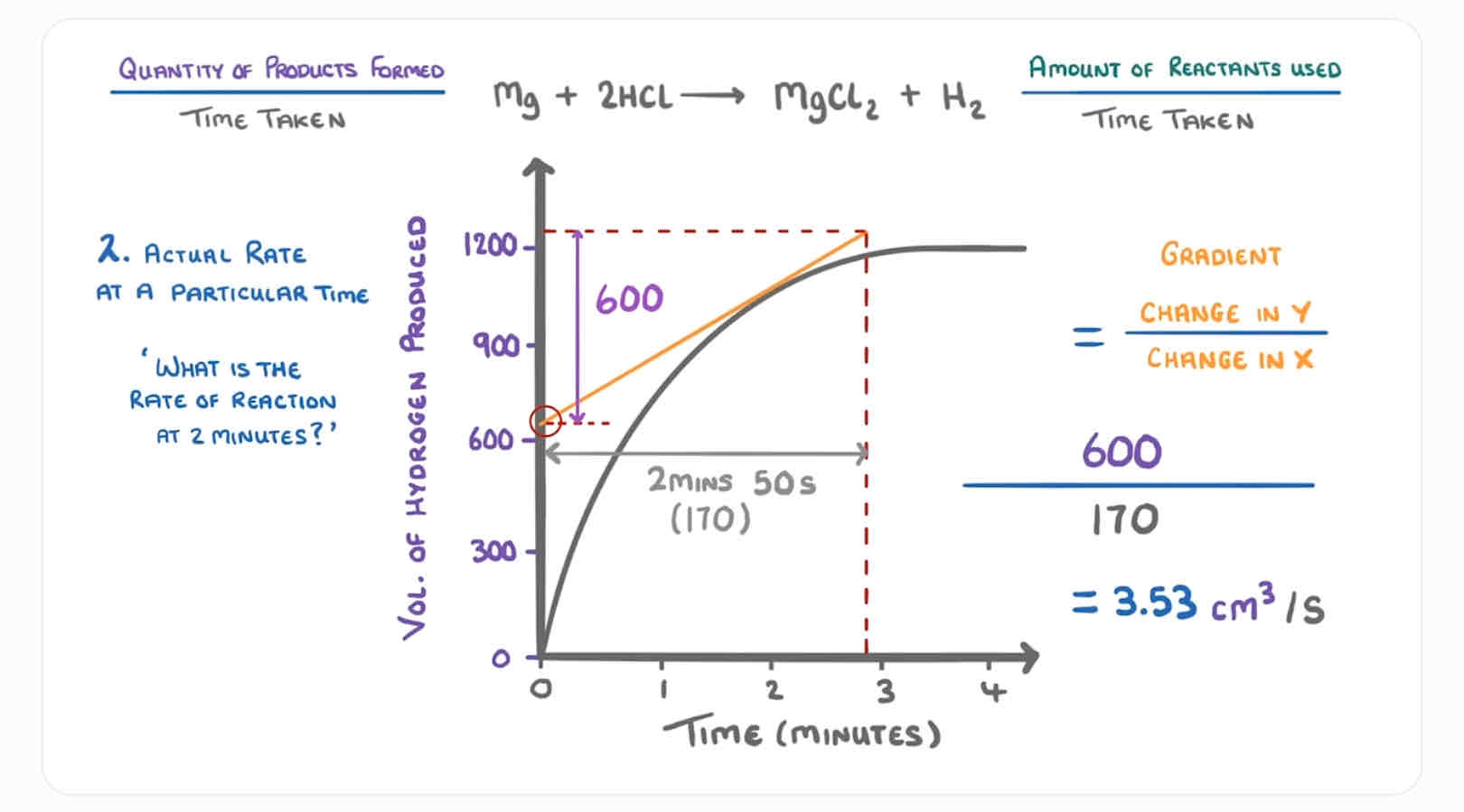
How do you find the rate of reaction at a specific time? (Image)
How do you find the rate of reaction at a specific time with an amount of the reactant on the y-axis? (Image)
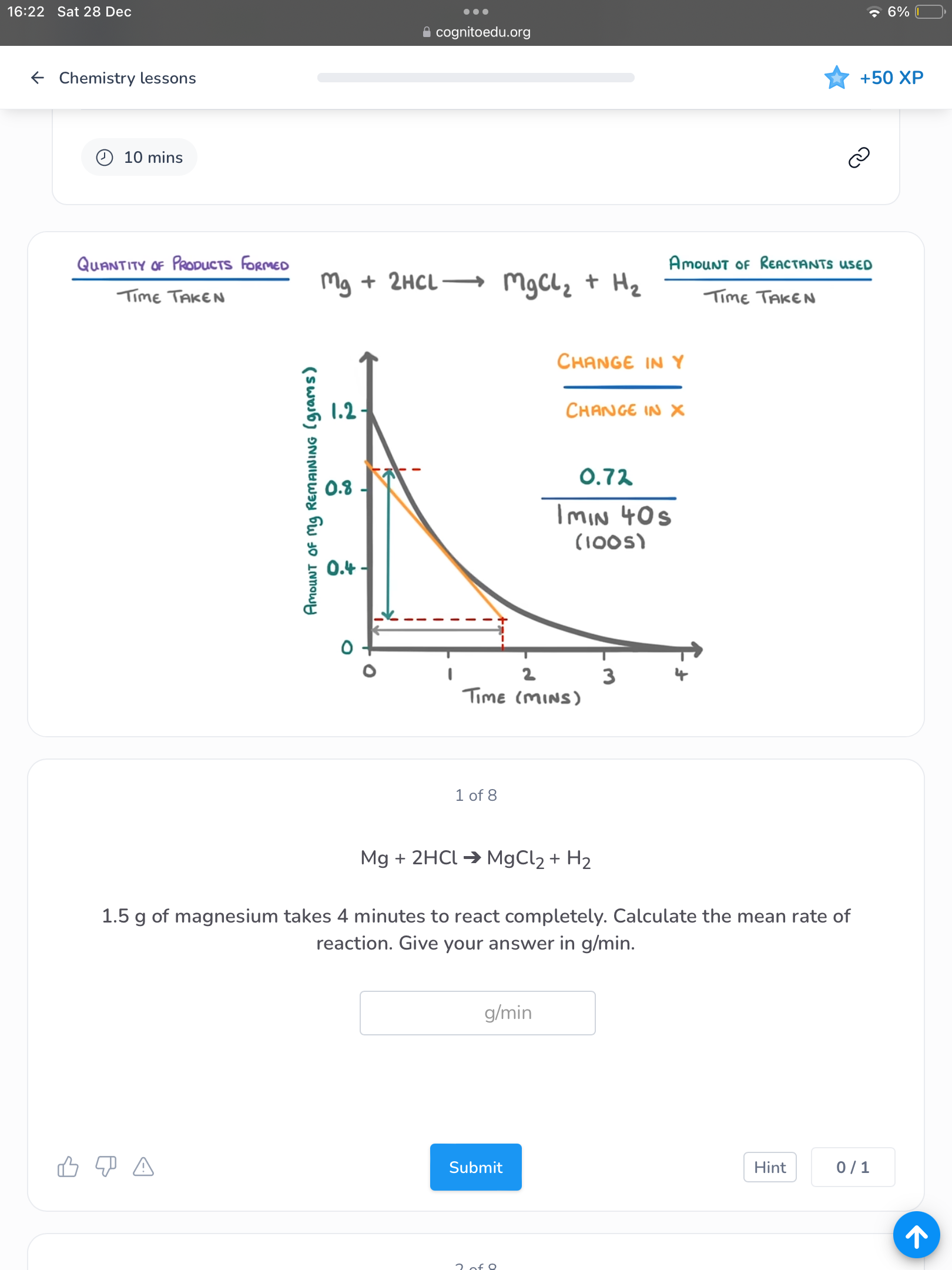
What is the equation to find the gradient?
Change in y OVER the change in x
In equilibrium, can the forward and backward reaction to at different rates?
Yes
What happens to the concentration in equilibrium? Why?
The concentration of reactants and products will not change BUT this does not mean their concentrations are the same as each other ; the molecules break down and reform at the same rate
what does it mean if equilibrium shifts to the right?
The products are favoured, meaning more products are formed, this is caused by an increase in temperature, reactant concentration, pressure or a decrease in the product concentration.
What does it mean when equilibrium shifts to the left? What causes this?
The reactants are favoured, resulting in more reactants present. This can be caused by an increase in product concentration, decrease in temperature, decrease in pressure, or a decrease in reactant doncentration.
If it says equilibrium ‘lies’ on one side what does this mean?
The side it ‘lies’ on is the side with more molecules.
Exo? Endo?
Equilibrium is always exothermic in one direction and endothermic in another.
What does a closed system mean?
Reactants and products can’t escape
In a reversible reaction, if the forward reaction is endothermic and you increase the temperature what would happen?
Equilibrium would shift to the right
In a reversible reaction, if the forward reaction is endothermic and you decrease the temperature, what would happen to the yield of products?
The yield of products would increase
What is Le Chatelier’s principle?
If there is a change in condition, equilibrium will shift to counteract the change.
If the forward reaction is exothermic and you decrease the temperature what will happen?
Decreasing the temperature is what happens in an exothermic reaction, the forward reaction goes from left to right, so equilibrium will shift to the right.
If the backward reaction is endothermic, what will happen to equilibrium if you increase the temperature?
Endothermic is taking in heat energy, and the backward reaction is going from right to left, so if you decrease the temperature (endo) then equilibrium will shift to the left.
If the pressure OR concentration increases on one side of a reaction, what happens to equilibrium?
Equilibrium will shift to whichever side has the lower pressure OR concentration (the side with the lesser amount of molecules)
What is pressure?
How many particles there are per unit of volume