Chemistry Final Semester 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/52
Last updated 5:28 AM on 12/20/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
1
New cards
matter
anything with mass and volume
2
New cards
physical properties
properties that can be measured or observed without changing the identity of the substance
3
New cards
chemical properties
properties that indicate how a substance reacts with other substances chemically
4
New cards
physical change
a change in the physical appearance of a substance without changing it chemically
5
New cards
chemical change
(reacting) when substances react to form new substances
6
New cards
homogenous mixture
a mixture with no uniform composition in which parts cannot be picked out
7
New cards
heterogenous mixture
a mixture with a uniform composition in which parts can be piked out
8
New cards
pure substances
substances with a uniform and definite composition, either as an element or compound
9
New cards
Kinetic Theory of Matter
matter is made of tiny particles that are constantly and randomly moving
10
New cards
examples of physical properties
color, texture, odor, taste, density, mass, freezing/melting point, etc.
11
New cards
how to determine if a physical change has been made
if the state of matter is different
12
New cards
examples of chemical properties
flammability, combustibility, burn ability, etc. often associated with “reacts with”
13
New cards
how to determine if a chemical change has been made
if there is a change in the properties such as rusting, corrosion, and decay
14
New cards
describe solids
definite volume, definite shape, non-compressible, high density
15
New cards
describe liquids
definite volume, in-definite shape, non-compressible, less dense than solids but more dense than gases
16
New cards
describe gases
in-definite volume, in-definite shape, compressible, low density
17
New cards
four rules of sig figs
(1)non-zero numbers are sig figs (2) no leading zeros (3) tailing zeros only after a decimal (4) captive zeros are sig figs
18
New cards
equation for percent error
% error= | (expected-experimental) | / expected x 100
19
New cards
how do you multiply/divide with sig figs
the answer is rounded to the same # of sig figs as the number with the least sig figs
20
New cards
how do you add/subtract with sig figs
the answer is rounded to the same # of decimal places as the number with the least in the calculation
21
New cards
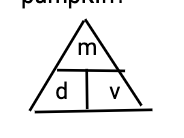
memorize the triangle ok
ok
22
New cards
who was Democritus
greek philosopher / first to think of the existence of atoms, believed tat matter was made of very small particles
23
New cards
what were the points to Daltons theory
A) All elements are made of indivisible particles (X) B) Atoms of the same element are the same in composition and mass (X) C) Atoms can combine only in whole number ratios (Y) D) Chemical reactions occur when elements join, separate, or rearrange (Y)
24
New cards
what did Thomson do
discover electrons
25
New cards
what did rutherford do
discover the nucleus
26
New cards
what did bohr do
study hydrogen, discover the bohr model
27
New cards
what is the equation to determine the average atomic mass of an atom and its isotopes
(% abundance 1)(atomic mass 1) + (% abundance 2)(atomic mass 2) +...../100
28
New cards
heisenburn principle of uncertainty
you cannot know both the position and speed of a particle
29
New cards
pauli excursion principle
it is not possible to have all identical quantum numbers
30
New cards
aufbau principle
electrons fill the lowest sublevel available then fill larger sublevels
31
New cards
hunds rule
each orbital in a sub-shell is filled once before more electrons are added
32
New cards
orbital diagram
a type of notation that illustrates an atom's electron distribution and electron spin within orbitals O OOO O
33
New cards
s sublevel
1 orbital, 2 electrons, spherical orbitals
34
New cards
p sublevel
3 orbital, 6 electrons, dumbell orbitals
35
New cards
d sublevel
5 orbital, 10 electrons, clover orbitals
36
New cards
f sublevel
7 orbital, 14 electrons, double clover orbitals
37
New cards
relationship between frequency and wavelength
higher frequency = smaller wavelength
38
New cards
relationship between energy and frequency
higher frequency = higher energy
39
New cards
equation for finding the energy of a photon
E = h (c/λ)
40
New cards
equation for finding the energy in an energy level
E = -(Rhc) / n^2
41
New cards
highest frequency of the electromagnetic radiation spectrum
gamma rays
42
New cards
lowest frequency of the electromagnetic radiation spectrum
radiowaves
43
New cards
electronegativity
tendency of an atom to take electrons
44
New cards
ionization energy
tendency of an atom to lose electrons
45
New cards
atomic radius
distance between the nuclei of two touching atoms / 2
46
New cards
shielding effect
a reduction of nuclear charge due to a difference in attraction force on the atom’s electrons
47
New cards
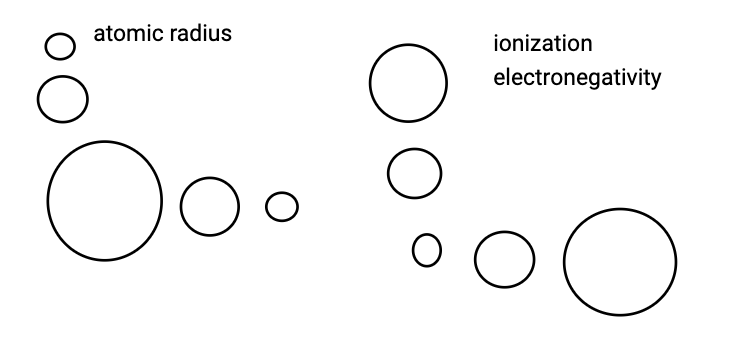
look here
k
48
New cards
ionic bonding
bonding between metals and nonmetals where they trade electrons, they form crystalline structures
49
New cards
covalent bonding
bonding between nonmetals where they share electrons
50
New cards
formula unit
the chemical formula of an ionic compound that lists the ions in the lowest ratio that equals a neutral electrical charge
51
New cards
empirical formula
simplest whole number ratio of atoms present in a compound
52
New cards
molecular formula
true whole number ration (multiple of the empirical)
53
New cards
types of chemical reactions
combination, decomposition, single-replacement, double-replacement, and combustion