Life Science - Chapter 4
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:40 PM on 8/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
1
New cards
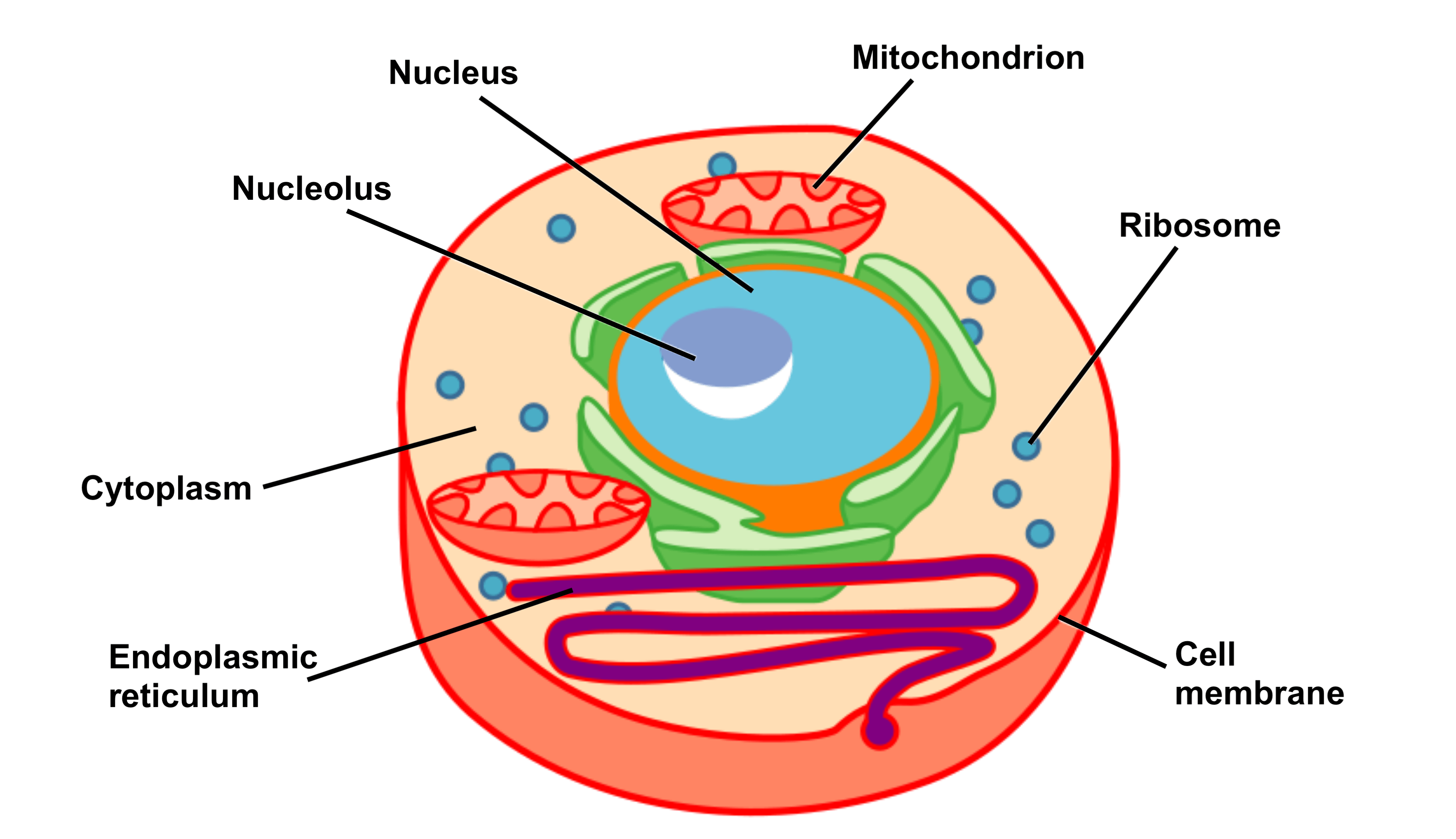
The covering that forms the outer boundary of the cell is called the ___.
cell membrane
2
New cards
The fluid mosaic model says that the cell membrane is made of a lipid bilayer and what other kind of molecule?
protein molecules
3
New cards
Diffusion and osmosis are example of ___ transport.
passive
4
New cards
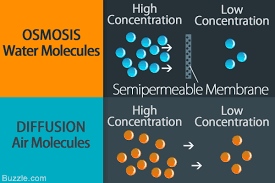
Diffusion is a type of osmosis.
False. (Kind of.) In both the phenomena, there is movement of particles from region of higher concentration to that of lower concentration. However, in the case of osmosis the movement of solvent is through a semi permeable membrane which is permeable only to water molecules. Hence osmosis is a special kind of diffusion.
5
New cards
Who was recognized as an honorary member of the Royal society of London because of his outstanding work in making and using lenses to see tiny organisms?
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
6
New cards
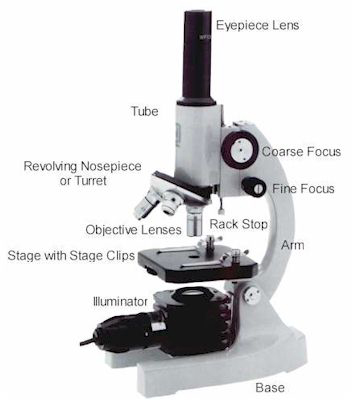
The first set of lenses that light waves pass through in a light microscope is called the ___.
objective
7
New cards
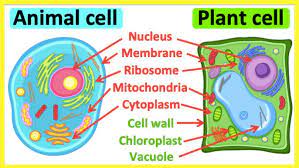
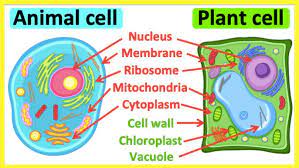
Plant cells are different from animals cells because their boundary includes a structure called the ___.
cell wall
8
New cards
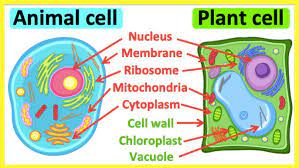
What are the powerhouses of the cell called?
mitochondria
9
New cards
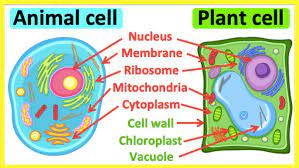
The organelles that function as storage containers in the cytoplasm are called ___.
vacuoles
10
New cards
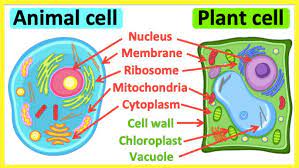
Which of these is NOT used to help cells move - a chloroplast, cilium, or flagellum?
a chloroplast
11
New cards
cell membrane
a thin covering that forms the outer boundary of the cell
12
New cards
selectively permeable
Allows only certain molecules to pass through
13
New cards
passive transport
the movement of substances through a membrane without the use of the cell’s own energy
14
New cards
2 main forms of passive transport
diffusion and osmosis
15
New cards
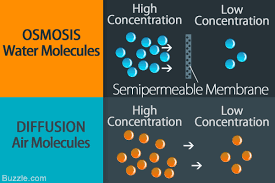
diffusion
The movement of molecules from a place where there are many of them (a high concentration) to a place where are few of them (a low concentration).
16
New cards
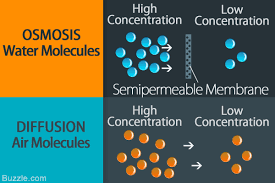
osmosis
The difference of water through a selectively permeable membrane.
17
New cards
active transport
The passage of particles through a membrane, requiring the use of cellular energy.
18
New cards
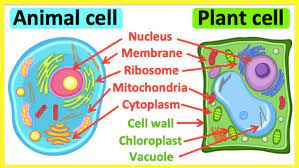
The thin covering that all cells have is the ___.
cell membrane
19
New cards
Select the membrane model considered to be the most accurate.
the fluid mosaic model
20
New cards
What did Leeuwenhoek call the organisms he viewed with his microscopes?
animalcules (or beasties)
21
New cards
What does osmosis not require a cell to do?
expend its own energy
22
New cards
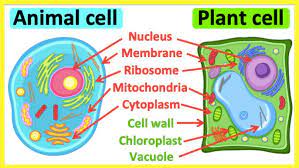
cell walls
A rigid structure manufactured by certain organisms and secreted to the exterior of the cell membrane; plants, fungi, and bacteria have cell walls.
23
New cards
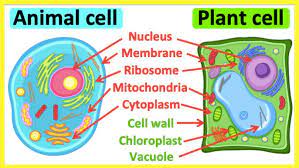
organelles
the parts of a cell that perform many of the functions needed to keep the cell alive.
24
New cards
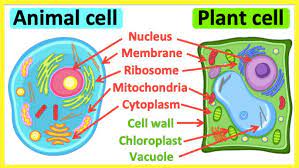
mitochondria
the cell’s powerhouse
25
New cards
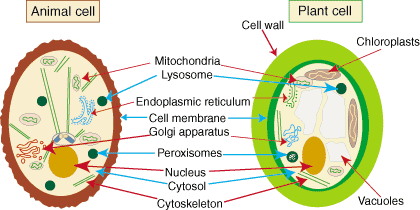
endoplasmic reticulum (ER for short)
A maze of pathways formed by a folded membrane passing throughout the cytoplasm.
26
New cards
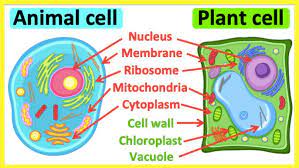
ribosomes
The tiny organelles that direct the assembling of proteins. They receive coded instructions from the nucleus to form proteins.
27
New cards
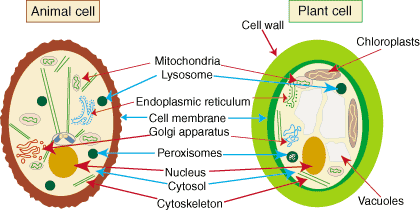
Golgi apparatus
A cellular organelle that collects chemicals from the cytoplasm, processes them, and secretes them.
28
New cards
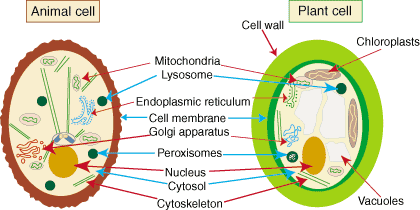
vacuoles
A membrane-bound sac that contains various substances, including water and wastes, within a cell.
29
New cards
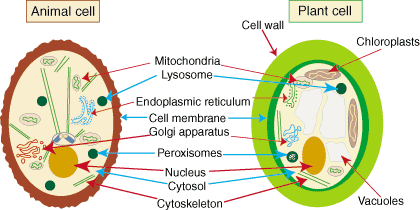
lysosomes
An organelle that contains digestive enzymes.
30
New cards
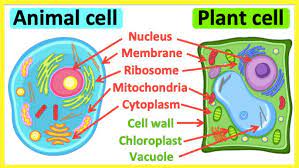
chloroplasts
A cellular organelle that contains chlorophyll and other pigments; the organelle in which photosynthesis occurs.
31
New cards
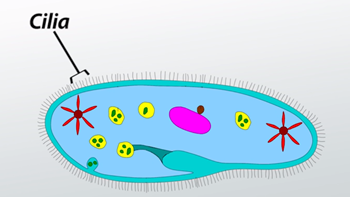
cilia
Short hairlike extensions from a cell membrane; aid in movement
32
New cards
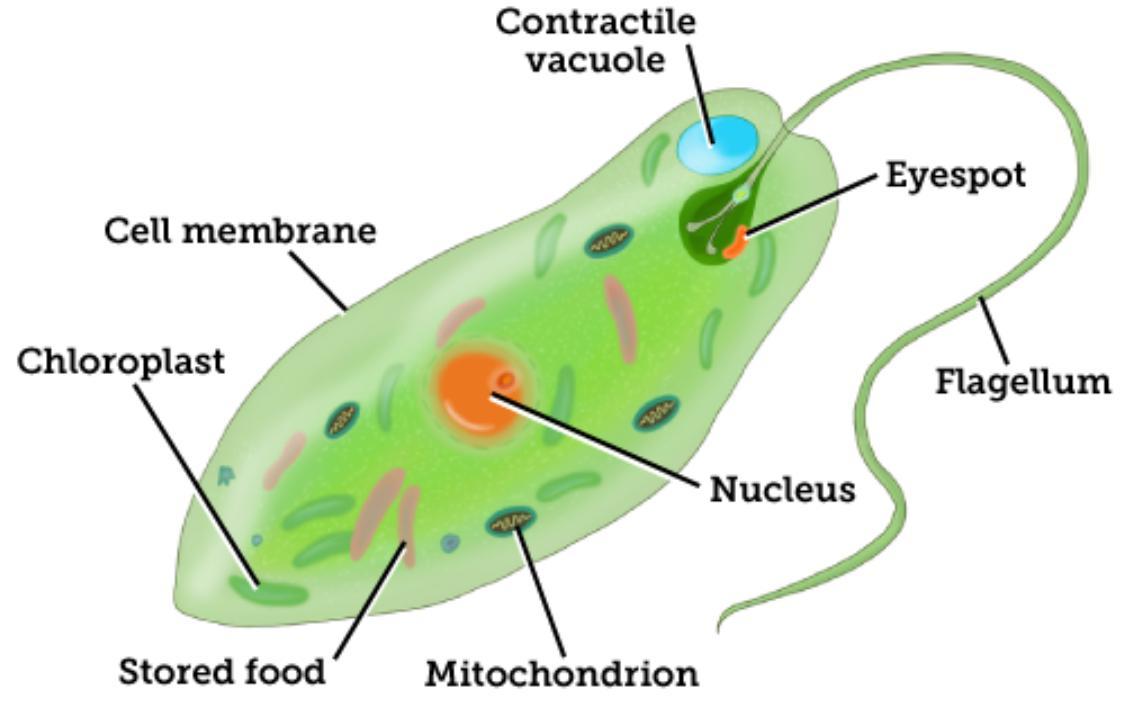
flagella (flagellum)
Long hairlike extensions from a cell membrane; aid in movement
33
New cards
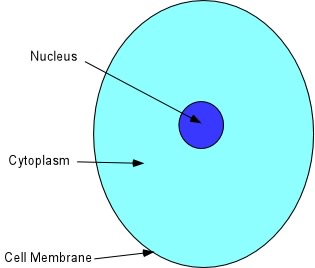
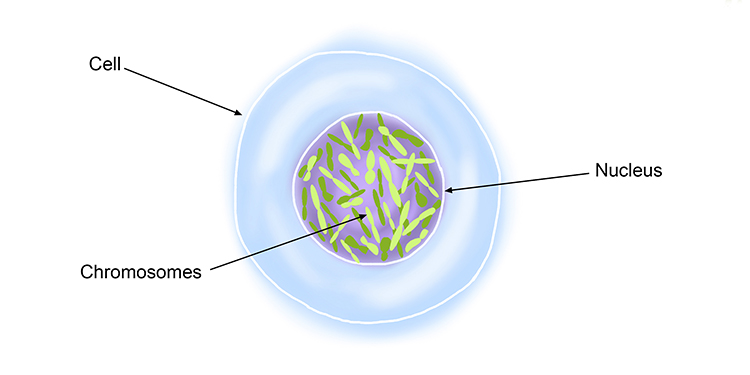
nucleus
The cellular organelle that contains the chromosomes; control center of the cell.
34
New cards
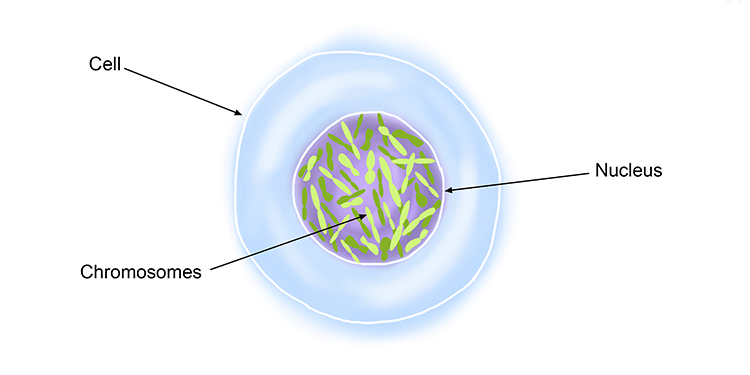
chromosomes
A strand of DNA with associated proteins; usually found in the nucleus of a cell; the basis of heredity.
35
New cards
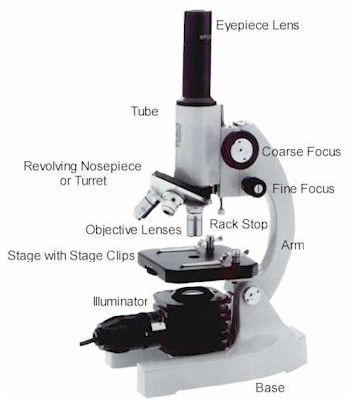
How do you find the total magnification of a compound light microscope?
Multiply the magnification powers of the eyepiece and objective lens in use.
36
New cards
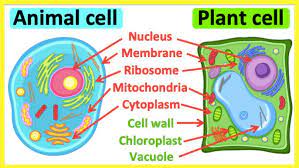
What organelles are referred to “powerhouses” of the cell?
mitochondria
37
New cards
What is the function of ribosomes?
They help maufacture proteins.
38
New cards
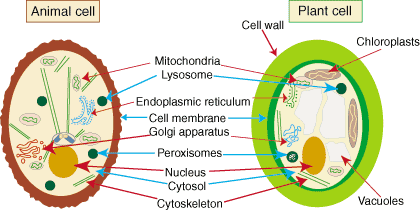
Which organelle collects and processes complex chemicals for the cell?
the Golgi apparatus
39
New cards
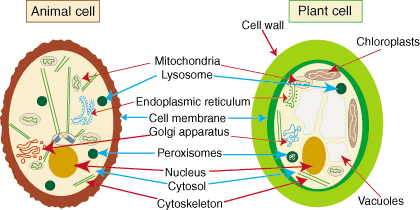
What structure contains a cell’s genetic information?
the nucleus
40
New cards
True or false. In the fluid model, the basic membrane structure is a double layer of proteins embedded with lipid molecules.
False, it’s the opposite. The basic structure is a double layer of LIPIDS with PROTEINS embedded.
41
New cards
Which process did you learn about that requires the cell to expend energy?
active transport
42
New cards
The spread of ammonia odor throughout a room is an example of ___.
diffusion
43
New cards
True or False. All cells are surrounded by a structure called the cell wall.
False. Only plant cells have a cell wall.
44
New cards
Calculate the total magnification of a microscope whose objective is 30x and whose eyepiece is 15x.
450x.
45
New cards
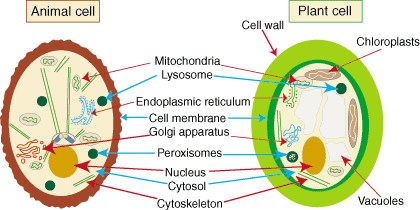
Which organelle processes chemicals in the cytoplasm
Golgi apparatus
46
New cards
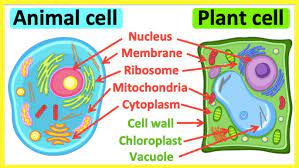
Which organelle processes energy from food?
mitochondria
47
New cards
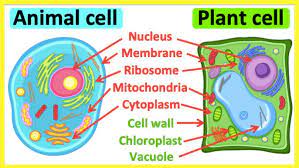
Which organelle serves as containers for different substances?
vacuole
48
New cards
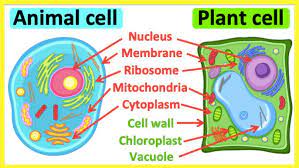
Which organelle assembles proteins?
ribosome
49
New cards
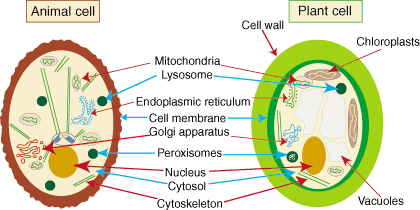
Which organelle contains enzymes?
lysosome
50
New cards
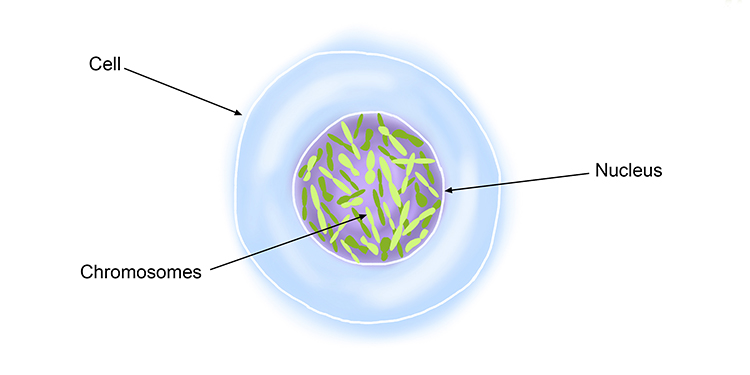
Which organelle contains the DNA?
nucleus
51
New cards
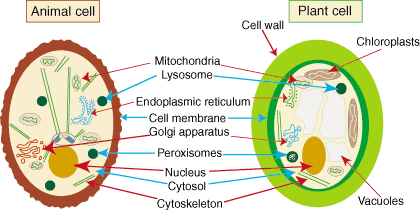
Which organelle serves as passageways throughout the cytoplasm?
endoplasmic reticulum
52
New cards
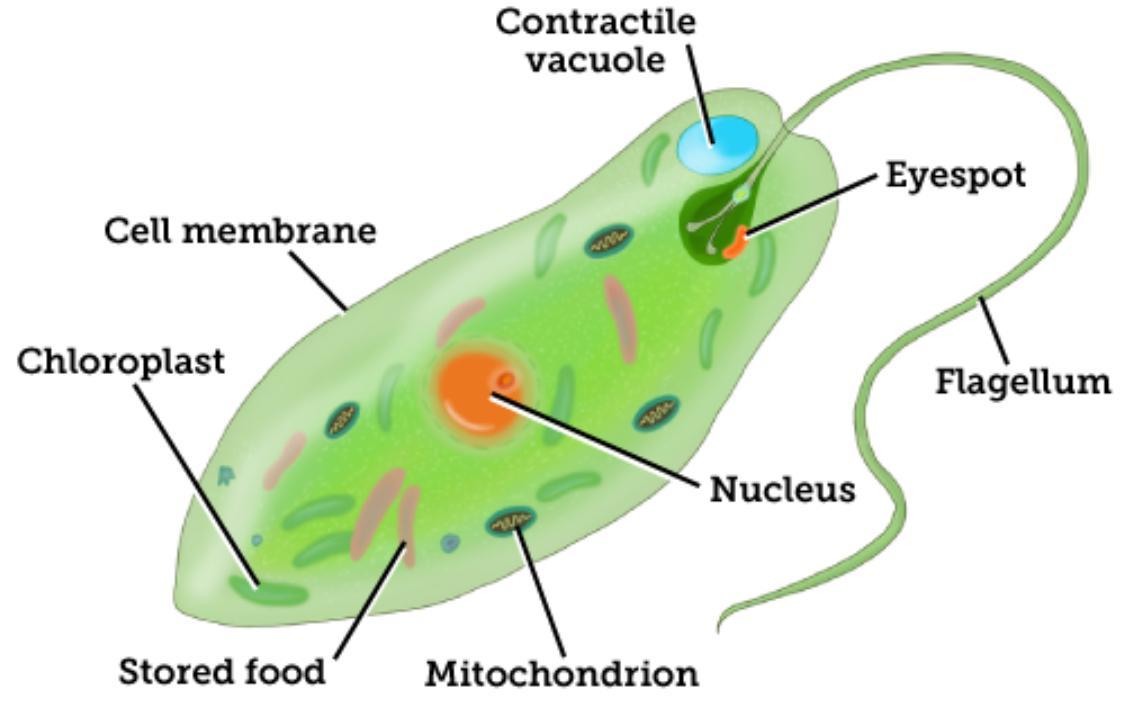
Which organelle is the control cener of the cell?
nucleus