Fundamentals of Diagnostic Imaging
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
vindicate
what is the mnemonic that is used for universal differential diagnosis?
yes
can PTs order x-rays?
PCP
PTs must communicate the x-ray order to the patients _____ or health care provider about significant findings
plain film radiographs
-accuracy to less than a mm
- cheapest with exception of diagnostic US
- point source distortion
- 3D info --> 2D media
- BEST FOR BONE
less; more
things that are black on a radiograph are:
______ radiodense and ______ radiolucent (air)
more; more
things that are white on a radiograph are:
_____ radiodense and _____ radiopaque (bone)
true
T/F: cortical bone is more dense than trabecular bone
less
on a radiograph structures that are closest to the beam source are enlarged and have _____ resolution on film
higher
on a radiograph structures that are farther away are less enlarged and show _____ resolution
contrast
_____ can improve visualization of areas with minimal amounts
myelography
a radiographic study of the spinal cord after the injection of a contrast medium through a lumbar puncture
- abnormal results include: ruptured disc, spinal stenosis, nerve root injury, intervertebral tumor
arthrography
taking x-ray images after injection of contrast material into a joint
arthrogram
contrast media study of a joint and its soft tissue structures
- shows abnormalities of synovium, articular cartilage, capsule, and soft tissue
- limitations: not multiplanar and invasive
fluoroscopy
Real-time imaging technique using open-shutter X-rays
many uses include:
- angiography
- catheter placement
- arthrography
- myelography
- facet joint injection
alignment, bones, cartilage, and soft tissue
what are the ABCS of reading radiographs?
subluxation
an incomplete dislocation when some contact between the joint surfaces remains
dislocation
the total displacement of a bone from its joint
diastasis
separation of normally joined parts
- SI joint and cranial sutures
lucency
decreased opacity
sclerosis
increased opacity
osteoblasts
osteoclasts have the capability of reabsorbing bone about 20x faster than _____ can lay it down
- leads to net bone loss and decreased opacity (increased lucency)
lucent line
fracture
focal lucency
common causes: bone tumor, osteomyelitis
appears less dense on an X-ray or CT scan compared to the surrounding tissues, resulting in a darker appearance
diffuse lucency
drugs
endocrine/metabolic (osteoporosis)
tumor
- usually a global process
- metabolic disorder is most common
- a wide area of decreased density or less dense tissue, resulting in a darker appearance on the image
increased opacity (sclerosis)
bone impaction or rotation --> fracture
bone production (reactive sclerosis)
- fracture --> callus
- tumor --> tumor bone formation or periosteal rxn
- infection --> periosteal rxn
- osteoarthritis --> subchondral sclerosis
fracture callus
some fractures are so subtle that they might be missed at first
can only be seen once they have started to heal with ____ ____ formation
solid; aggressive
periosteal reactions:
- benign processes = _____ pattern
- malignant processes = _____ pattern
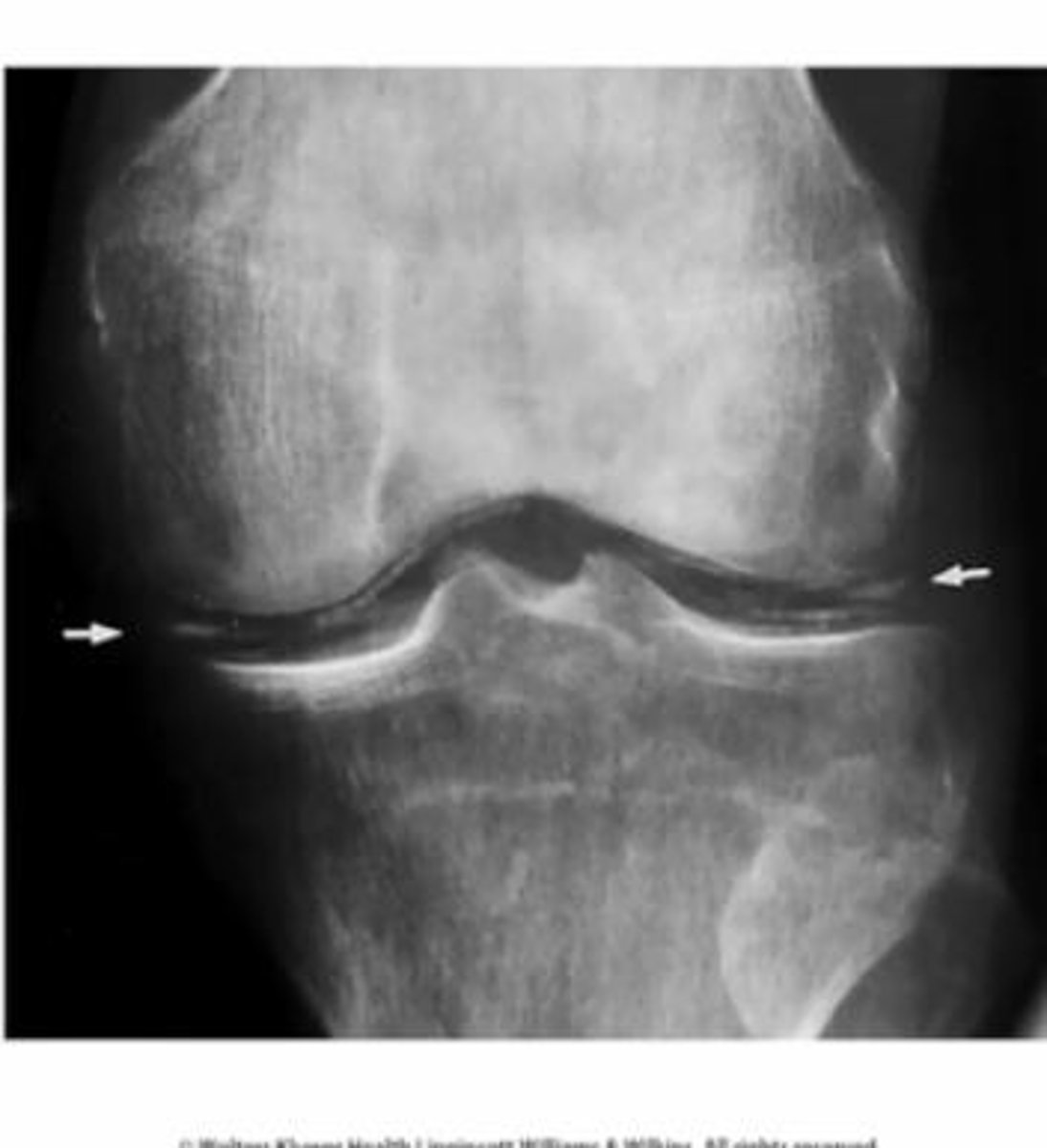
decreased joint space
infers arthritis (OA most common and then RA)
increased joint space
acromegaly or joint effusion
chondrocalcinosis
Radiographic finding of fine, linear calcifications in cartilage diagnostic of pseudogout
- most commonly due to CPPD in the joints
swelling
usually not very diagnostically helpful
gas
penetrating injuries, following surgery, soft tissue infections due to gas-forming organisms
calcification
usually non-specific
mass
hematoma, abscess, tumor
MRI is more helpful imaging choice for most masses
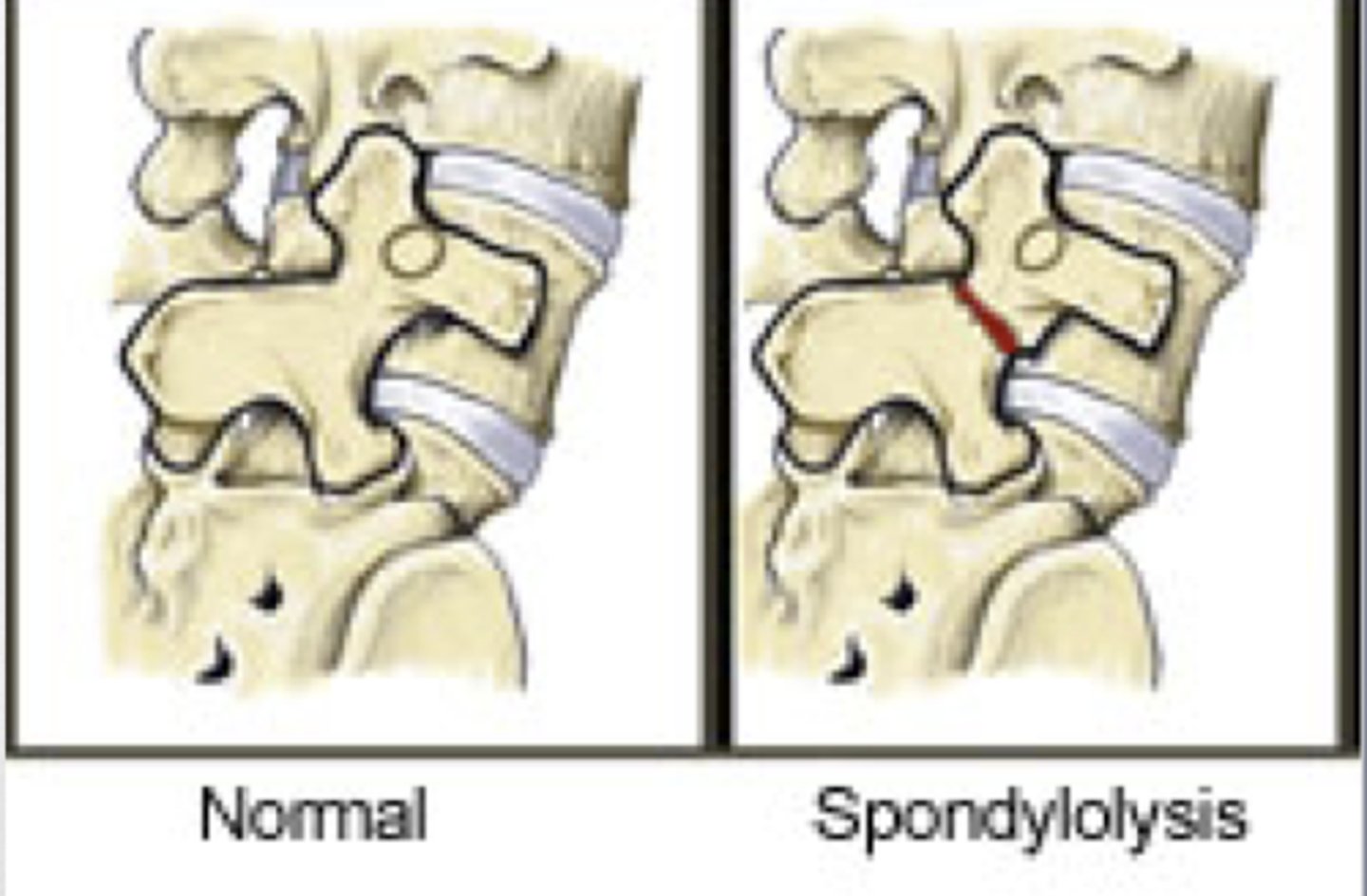
scotty dog fracture
Fracture of Pars Interarticularis, = spondylolysis. Could lead to spondylolisthesis. Head = TP, Body = Lamina & SP, Ear = SAP, Forefoot = IAP
ultrasound
doesn't use ionizing radiation
- imaging using sound waves
- diagnostic and therapeutic uses
- generally considered cheapest and safest imaging modality
- real time
evaluates
ultrasound ______
- lesions to muscles, tendons, ligaments
- detection of cysts
- measurement of blood flow
dynamic
ultrasound images can be _____
- resisted contractions, passive stretching, etc.
limitations
ultrasound _____
- operator dependent
- does not penetrate bone
- does not cross air interfaces
- obese patients not imaged well
nuclear imaging
tracer is absorbed by specific tissue in varying amounts, based on metabolic activity within that tissue
- pathologies identified by variations in the uptake of tracer
- gamma rays emitted from body are detected by gamma cameras
- types: nuclear scintigraphs (bone scan), PET, SPECT and SPECT CT
SPECT
lower cost
uses gamma emitting radioisotope
provides metabolic and functional information
PET
very expensive
uses positron emitting radioisotope
better contrast and spatial resolution
bone scan
used for stress fractures
- early indicator of increased bone activity
- abnormal conditions show increased uptake of the tracer
- tracer Technetium 99m
CT
X-rays on steroids
- merges X-ray and computer technology
- provides detailed cross sectional images
- same imaging principles as radiology
- radiodense structures are bright white
MRI
magnetic resonance imaging
magnetic field and radiofrequency signals
- hydrogen nuclei emit signals
- different tissues = different signals
- converted to image
best
MRI is _____ for:
- bone marrow changes
- soft tissue
- disc herniations
- nerve root impingements
- neoplasms
- bone METs (more sensitive than bone scan)
T1
best for soft tissues
T2
best for fluid (H2O)