Final Exam Study Guide for RTE1000, Exam #1 on Intro to Radiography and Student Success Skills combine, Introduction to Clinical Education: Module 4 Exam #2 combine, Exam #1 on Intro to Radiography and Student Success Skills, Ethical & legal Issues:…
1/506
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
507 Terms
Define the term radiation
Radiation is energy that is transmitted by waves through space or through a medium (matter). It has permeated the universe since the beginning of time and is a natural part of all of our lives. For example, the sun radiates light energy, and a stove radiates heat energy.
Describe ionization
Ionization is any process by which a neutral atom gains or loses an electron, thus acquiring a net charge. This process has the ability to disrupt the composition of the matter and, as a result, is capable of disrupting life processes.
When were x-rays discovered?
November 8, 1895
Which imaging modalities use x-rays to produce images of the body?
-Radiography
-Computed Tomography (CT)
-Mammography
-Bone Densitometry (DEXA or DXA)
Identify members of the imaging healthcare team
-Radiologic Technologists (RTs)
-Radiologists (physicians specializing in the use of x-rays and other forms of radiation)
-Radiologist Assistants (RAs)
-Medical physicists (often supporting radiation therapy teams)
What organization provides programmatic accreditation of radiography schools?
The Joint Review Committee on Education in Radiologic Technology (JRCERT) provides programmatic accreditation for radiography programs.
What is required to gain ARRT certification?
-Complete an ARRT-recognized educational program.
-Earn an academic degree (required for certifications starting January 1, 2015).
-Meet ethical standards.
-Pass the ARRT certification examination in the chosen specialty.
Identify ways to deal with stress
-Change: Plan positive activities to balance negative events, e.g., take walks, relax, or watch favorite shows.
-Language: Use positive, in-control phrases like "I choose to" instead of "I have to."
-Worry: Focus on actionable tasks and avoid procrastination. Most worries never happen.
-Time Management: Schedule tasks realistically and include time for relaxation.
-Exercise: Engage in aerobic activity 3-5 times a week.
-Nutrition: Eat balanced meals rich in Vitamin C, B-complex, and magnesium.
Identify study skills that promote success
-Schedule study blocks (50-60 minutes with breaks).
-Use mnemonics, visualization, and summarization for retention.
-Study in advance and join study groups.
What are the elements of time management?
-Know peak productivity times.
-Prioritize tasks and responsibilities.
-Plan for relaxation alongside work.
-Avoid distractions like social media and unnecessary calls.
-Address indecision quickly.
Identify test taking tips
-Avoid last-minute cramming for exams.
-Wear bright, colorful clothes the day of exams.
-Avoid a heavy, high-carbohydrate meal before exams.
-Get a good night's sleep the night before an exam.
-Arrive for a test early to prepare mentally.
-Scan the entire test to develop a test strategy.
-Answer questions you know first.
-Tackle remaining questions requiring deeper thought.
-Review the test carefully and make corrections after additional thought.
-Check test answer sheet and correlate with test numbering.
-After the test is done, put it behind you!
What are the steps in problem solving & critical thinking?
-Identify the Problem: Define it clearly.
-Investigate: Assess factors and gather relevant information.
-Formulate Solutions: Develop viable options based on knowledge and standards.
-Select the Best Solution: Implement and reflect on outcomes for future learning.
What is meant by the term competencies?
Competencies refer to the observable and documented successful achievement of performance objectives. They involve demonstrating proficiency in various clinical skills, procedures, or treatments relevant to medical imaging or radiologic sciences. For radiography, this includes procedural competencies in areas such as chest and thorax imaging, musculoskeletal system and trauma, cranium, spine, pelvis, and specialized studies like fluoroscopic, surgical, and pediatric procedures. Meeting and documenting these are prerequisites for eligibility to sit for the ARRT credentialing examination
Identify radiography program officials
-Program Director: Responsible for organizing, administering, and assessing the program, ensuring both didactic and clinical effectiveness.
-Clinical Coordinator: Works closely with the program director to maintain program effectiveness through regular coordination, instruction, and evaluation.
-Clinical Instructor: Directly supervises and evaluates students in the clinical setting, possessing knowledge of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
-Clinical Staff: Health care professionals employed at clinical sites who provide supervision and guidance to students
Teamwork is critical to improve what aspects of health care?
Teamwork is critical in improving quality, safety, and efficiency in health care. Highly effective teams, as supported by programs such as TeamSTEPPS, are necessary to assure positive patient outcomes. Key aspects include structured communication, leadership, situation monitoring, and mutual support
What is one of the most important elements related to teamwork & quality patient care?
One of the most critical elements is effective communication. Structured communication ensures clarity and accuracy among team members, enabling better coordination and support for patient safety and quality care.
Differentiate between direct & indirect clinical supervision of radiography students
Direct Supervision: Requires the qualified radiographer to:
1. Review the examination request in relation to the student's competence.
2. Evaluate the patient's condition relative to the student's knowledge.
3. Be physically present during the procedure.
4. Review and approve the procedure or images. Unsatisfactory images must always be supervised under direct supervision.
Indirect Supervision: The qualified radiographer:
1. Reviews and approves the procedure as in direct supervision.
2. Is immediately available to assist the student physically, adjacent to the room or location where the procedure is performed.
Describe aspects of the HIPAA privacy rule
The HIPAA privacy rule mandates confidentiality of patient information, requiring students and professionals to uphold ethical standards of privacy during clinical education and practice. Failure to comply can result in disciplinary actions, including reprimands, probation, or dismissal from the program. It highlights the necessity for professional behavior in handling patient data
What are the parts of an x-ray tube?
-The x-ray tube's primary components are the anode and cathode... The anode is the positive electrode, and the cathode is the negative electrode
-It is made of Pyrex glass and encased in a sturdy, lead-lined metal housing with large high-voltage electrical cables attached at each end
-The cathode filament is typically a tightly wound tungsten wire helix, similar to the filament in an incandescent light bulb
-A tube stand or overhead tube crane (OTC) suspension supports the x-ray tube and allows the radiographer to position it as needed over and around the patient
Define the term primary beam
The primary beam is the x-ray beam that exits the x-ray tube and travels toward the patient before interacting with any object or body tissue. It represents the initial radiation emitted directly from the source
What items are contained in a Bucky of a radiographic table?
Grid: Reduces scatter radiation to improve image contrast.
Cassette Tray: Holds the image receptor (cassette).
Radiographic Grid Movement Mechanism: Moves the grid during exposure to prevent grid lines from appearing on the image
What part does an upright Bucky have for specific exams?
An upright Bucky is designed to hold the image receptor in a vertical orientation, which is particularly useful for chest x-rays, upright abdomen exams, and certain orthopedic studies requiring weight-bearing positions
What does the x-ray generator cabinet contain?
Electronics Cabinet: Houses the components necessary to generate and control high voltage for x-ray production.
Operator Console: The interface where the radiographer selects exposure factors such as kilovoltage peak (kVp), milliamperage (mA), and exposure time
What are the parts & function of an x-ray collimator?
Adjustable Radiopaque Blades: Define the dimensions and shape of the x-ray field.
High-Intensity Light Bulb and Mirror: Projects a visible light field to indicate the exposure area.
Controls for Width and Length: Adjust the x-ray field size.The collimator minimizes unnecessary radiation exposure by restricting the x-ray beam to the area of interest
Define tube movement controls
Tube movement controls refer to the mechanisms that allow the radiographer to manipulate the position and angulation of the x-ray tube. These controls enable adjustments for vertical, longitudinal, transverse, and rotational movements to achieve proper alignment with the patient and image receptor
What type of IR does a CR system use?
A CR (Computed Radiography) system uses a Photostimulable Storage Phosphor (PSP) Plate housed in a cassette. This plate captures and stores x-ray energy, which is later processed into a digital image
Describe DR digital technology
Direct Capture DR: Converts x-ray photons directly into electrical signals using amorphous selenium.
Indirect Capture DR: Converts x-rays to light using a scintillator, and then into electrical signals via photodiodes or TFT arrays. Both systems use flat-panel detectors to create digital images that can be viewed almost instantly. DR eliminates the need for cassettes and provides superior image quality and efficiency
What type of imaging does fluoroscopy allow?
Fluoroscopy allows for dynamic imaging, enabling real-time visualization of patient motion, such as organ movement or the flow of contrast material through vessels and organs. This technique is commonly used for gastrointestinal studies, angiography, and orthopedic procedures
How is the primary beam attenuated?
Attenuation refers to the process where the primary radiation is changed (partially absorbed or scattered) as it travels through the patient. The x-ray beam's attenuation depends on the type of body tissue irradiated. Different materials absorb radiation energy differently based primarily upon density and atomic number. For instance, denser bone tissue attenuates the beam more than soft tissue of the same thickness. The degree of attenuation can be high or low. High attenuation occurs in radiopaque matter. Low attenuation occurs in radiolucent matter.
Describe mAs & its effect on exposure
Milliampere-seconds (mAs) control the number of electrons flowing from the cathode to the anode in the x-ray tube, which determines the number of x-ray photons produced. This directly influences the image receptor (IR) exposure. An increase in mAs results in increased IR exposure, while a decrease reduces it. The relationship between mAs and IR exposure is directly proportional
Describe kV & its effect on exposure
Kilovoltage peak (kVp) defines the electrical pressure forcing the current through the tube, controlling the x-ray beam's penetrating ability. Higher kVp increases penetration and IR exposure but not proportionally. According to the 15% rule, increasing kVp by 15% approximately doubles IR exposure, while decreasing it by the same percentage halves the exposure
Describe SID & its effect on exposure
Source-to-image distance (SID) is the distance from the x-ray tube's focal spot to the IR. As SID increases, radiation intensity decreases due to the divergence of the beam, reducing IR exposure. This relationship is explained by the inverse square law, where doubling the SID reduces beam intensity to a quarter
What is the purpose of filtration?
Filtration involves placing attenuating materials (like aluminum) between the x-ray tube and the patient. It removes low-energy nondiagnostic photons, reducing patient dose and enhancing image quality. The required material to reduce beam intensity by half is called the half-value layer
How does collimation affect scatter & IR exposure?
Collimation confines the primary x-ray beam to the area of interest, reducing the production of scatter radiation. This results in a decrease in IR exposure and enhances image contrast by minimizing non-diagnostic scatter photons
What is the main purpose of a grid?
A grid is used to absorb scatter radiation before it reaches the IR, thereby improving image contrast. It contains thin lead strips to intercept scattered photons
What are grids designed to "trap"?
Grids are designed to trap scattered photons that deviate from their original paths after interacting with the patient's tissues
How does part thickness affect IR exposure?
Thicker or denser tissues attenuate more x-rays, reducing IR exposure. This differential attenuation is key for image contrast. Bone tissue, for example, appears lighter due to its higher attenuation compared to soft tissues
Define the terms short & long-scale contrast
Short-scale contrast: Produces high contrast with few gray tones, typically achieved with lower kVp.
Long-scale contrast: Produces low contrast with many gray tones, achieved with higher kVp
How does changing kV affect contrast?
Increasing kVp reduces contrast by producing more gray tones (long-scale contrast), while decreasing kVp enhances contrast with fewer gray tones (short-scale contrast)
What is the purpose of contrast media?
Contrast media are substances like barium or iodine compounds that enhance image contrast by attenuating the beam differently than surrounding tissues. They are used to visualize structures such as the gastrointestinal tract or urinary system
What does an exposure index (EI) number represent?
The exposure index (EI) reflects the amount of exposure the IR receives. Proper exposure ensures diagnostic-quality images while minimizing patient dose
Define size & shape distortion
Size distortion: Also called magnification, occurs when the image size differs from the object size, influenced by SID and object-to-image distance (OID). It is minimized by using longer SIDs and minimum OIDs.
Shape distortion: Misrepresentation of an object's shape, caused by improper alignment of the x-ray beam, patient's anatomy, and IR
How do changes in SID affect magnification (size distortion)?
Increasing SID reduces magnification by minimizing the beam's divergence, while decreasing SID increases magnification
How does beam angulation affect shape distortion?
Beam angulation can cause elongation or foreshortening of the object, leading to shape distortion. Proper alignment is crucial to minimize this effect
How does focal spot size affect detail?
Smaller focal spots provide better image sharpness and detail by reducing penumbra (unsharpness). Larger focal spots are used for general imaging to handle higher exposure loads
What unit is used to measure the energy of an x-ray beam?
The energy of an x-ray beam is measured in kiloelectron volts (keV).
What interaction contributes greatly to occupational exposure?
Compton scattering is the primary interaction responsible for a majority of occupational worker exposure to radiation
Which interaction contributes greatly to patients' x-ray exposure?
The photoelectric effect contributes significantly to patient exposure, as it results in complete energy absorption in tissues during diagnostic radiography
Define & identify the units of radiation exposure, absorbed dose, & dose equivalent
Radiation Exposure: Measured in Roentgen (R) or coulombs per kilogram (C/kg).
Absorbed Dose: Measured in rad (radiation absorbed dose) or gray (Gy), where 1 Gy = 100 rad.
Dose Equivalent: Measured in rem (radiation equivalent man) or sievert (Sv), where 1 Sv = 100 rem
Define air KERMA
Air Kerma (Kinetic Energy Released in Matter) measures energy transferred from radiation to a material, like air or a patient's body. It is measured in joules per kilogram (J/kg) and is replacing traditional exposure units
Define ALARA
ALARA stands for "As Low As Reasonably Achievable," a principle used to minimize radiation exposure to both patients and workers while achieving diagnostic image quality
What is the annual whole-body effective dose limit for workers?
The annual whole-body effective dose limit for occupational workers is 50 mSv (5 rem)
What advisory group recommends dose limits for those exposed to radiation?
The National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP) recommends dose limits for radiation exposure
Define acute radiation syndrome
occurs only when the organism is exposed fully (total body) to an external source of radiation given in a few minutes. Only then does the organism develop the full set of signs and symptoms that define each syndrome, which depends on the dose received
Differentiate between genetic & somatic effects of radiation exposure
Somatic Effects: Affect the individual exposed, involving cells other than germ cells.
Genetic Effects: Affect future generations by altering germ cell DNA, with effects manifesting only if the mutated cells are fertilized
Describe patient protection measures in terms of time, distance & shielding
Time: Minimize the duration the patient is exposed to radiation by using appropriate techniques and avoiding repeat exposures.
Distance: Maintain a safe distance between the radiation source and the patient.
Shielding: Use devices like lead aprons and collimators to limit exposure to non-target areas
Describe radiographer protection measures in terms of time, distance & shielding
Time: Reduce the time spent near active radiation sources.
Distance: Maximize distance from the radiation source to reduce exposure using the inverse square law.
Shielding: Employ lead aprons, barriers, and thyroid shields
Explain the purpose of radiation monitoring
Radiation monitoring is used to track the quantity of radiation exposure received by occupational workers, ensuring compliance with safety limits and identifying potential overexposure
Describe where radiation dosimeters are to be worn
Radiation dosimeters are worn at collar level, outside leaded apparel, and facing forward to measure exposure accurate
How often are dosimeters for students in a radiography program read?
Dosimeters are typically read monthly, and exposure reports are maintained as part of the student's permanent record
What unit is used for the dose received by a worker for OSL & TLD dosimeters?
The dose received by a worker using Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL) and Thermoluminescent Dosimeters (TLD) is measured in sieverts (Sv)
Differentiate between verbal & nonverbal communication
Verbal Communication: Messages sent using spoken words; it includes vocabulary, clarity, tone, and organization of sentences. Effective verbal communication involves face-to-face interactions, polite attention, and ensuring the vocabulary level is appropriate for the listener.
Nonverbal Communication: Includes the exchange of information, thoughts, or messages using tone of voice, speed of speech, facial expressions, and body language. Examples are paralanguage (cadence and rhythm of speech) and body positioning
Describe the 3 types of touch used by radiographers
-Touching for Emotional Support: A gentle pat on the hand or shoulder can convey understanding and empathy.
-Touching for Emphasis: This is used to highlight instructions or locations, e.g., gently touching a shoulder to indicate direction for positioning.
-Touching for Palpation: Light pressure with the fingertips to locate bony landmarks for positioning. Permission should always be obtained to ensure patient comfort
Identify best practices for communicating with pediatric & geriatric patients
Pediatric Patients:
-Squat to the child's eye level to create a positive environment.
-Use a calm and friendly voice, and never separate them from security objects unless necessary.
-Familiarize the child with the environment by explaining procedures in simple terms.
Geriatric Patients:
-Be patient and respectful.
-Adjust communication to account for sensory impairments like hearing loss.
-Engage in clear, straightforward explanations and use touch when appropriate
Differentiate between objective & subjective data collection
Objective Data Collection: Includes observable and measurable facts, such as vital signs, laboratory results, or physical conditions.
Subjective Data Collection: Relates to what the patient says about their condition, including feelings, symptoms, or personal experiences
Identify the leading causes of injury to health care workers
The leading causes of injury to health care workers typically stem from physical demands, such as lifting or transferring patients improperly, leading to musculoskeletal injuries
Identify practices for good body mechanics
-Keep the back straight and use the legs for lifting.
-Maintain a wide base of support.
-Avoid twisting movements while lifting or transferring patients
Identify devices used to move a patient from a stretcher onto an x-ray table
Devices such as sliding boards, transfer sheets, and mechanical lift systems are commonly used to safely transfer patients
Define the term morals
Morals are generally accepted customs, principles, or habits of right living and conduct in a society and the individual's practice in relation to these"
When do ethical dilemmas occur?
Ethical dilemmas occur in situations requiring moral judgment between two or more equally problem-fraught alternatives; two or more competing moral norms are present, creating a challenge about what to do
Describe the ethical principles
Also known as moral principles, are general, universal guides to action that are derived from so-called basic moral truths. Examples include:
-Beneficence: Performing actions that benefit others.
-Nonmaleficence: Avoiding harm to others.
-Justice: Fair and equitable treatment of all individuals.
-Autonomy: Respecting a person's independence and individual choice
How do you maintain professional relationships toward other health professionals?
Maintaining professional relationships involves loyalty, faithfulness, and fairness. Radiologic technologists should exercise professional discretion, recognize their limitations, and prioritize patient safety while balancing professional duties
What is the main purpose of the law?
The law serves to:
-Protect individual autonomy.
-Protect the patient's status as a human being.
-Avoid fraud and duress.
-Encourage healthcare practitioners to make careful decisions.
-Foster rational decision-making by patients.
-Involve the public in medicine
Differentiate between criminal & civil law
Criminal Law: Involves offenses against the state or society as a whole.
Civil Law: Involves disputes between individuals or organizations where compensation may be awarded to the victim
What is tort law?
Tort law refers to a private or civil wrong or injury, other than breach of contract, for which the court provides a remedy in the form of an action for damages
Define the term standard of care
The standard of care is the degree of skill (proficiency), knowledge, and care ordinarily possessed and employed by members in good standing within the profession
Define the term negligence
Negligence is the failure to do something that a reasonable person guided by the ordinary considerations that ordinarily regulate human affairs would do, or the doing of something a reasonable and prudent person would not do
When is an incident report used?
Incident reports are used to document events that deviate from the standard of care or procedures, especially when harm to a patient or staff has occurred or is a potential risk. This ensures accountability and helps prevent future incidents
Differentiate between implied & informed consent
Implied Consent: Agreement inferred from a person's actions or inactions, rather than explicitly stated.
Informed Consent: Explicit agreement based on full disclosure of the risks, benefits, and alternatives involved in a procedure
The term ________________ is defined as energy transmitted through matter.
-ionization
-radiation
-electromagnetic
-non-ionizing
radiation
Ionization occurs when an atom gains or loses an electron.
True
False
True
Which of the following forms of energy are used for medical imaging? (Choose all that apply)
-sound waves
-x-rays
-gamma rays
-sound waves
-x-rays
-gamma rays
All of the following are classified as EM radiation, except:
-visible light
-microwaves
-x-rays
-sound waves
sound waves
All forms of electromagnetic energy are harmful to humans because they produce biologic changes. True
False
False
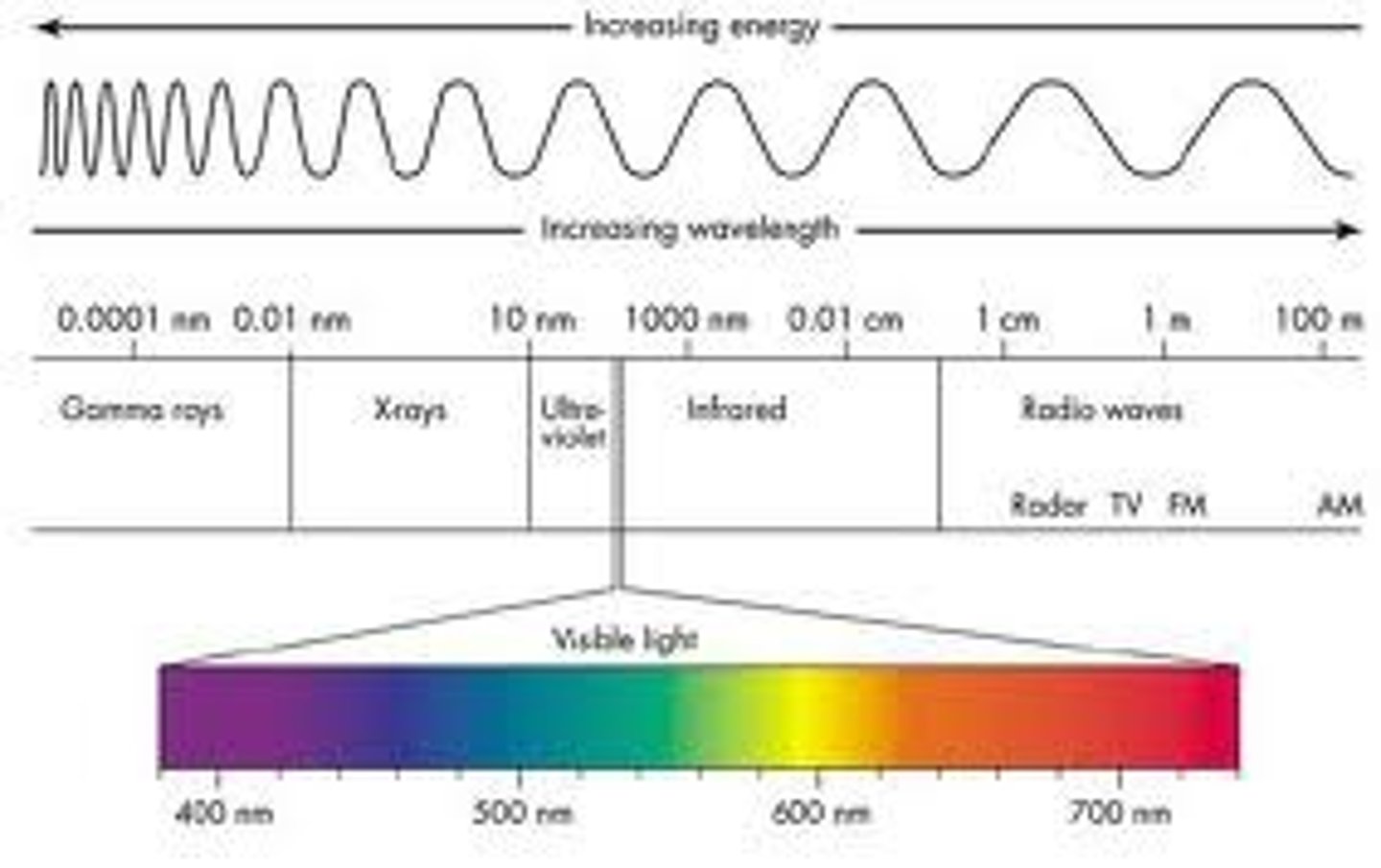
The electromagnetic spectrum (know what graph looks like)
Which of the following utilizes x-rays to produce images of the body? (Choose all that apply)
-CT
-MRI
-radiography
-bone densitometry
-CT
-radiography
-bone densitometry
Which of the following is considered a valuable diagnostic tool used to detect osteoporosis & osteopenia?
-sonography
-CT
-bone densitometry
-MRI
bone densitometry
Mammography is a sub-specialty of radiography that uses sound waves to create medical images of the breast.
True
False
False
________ utilizes radiopharmaceuticals to assess physiological function & create images of the body.
-Radiation therapy
-Nuclear medicine
-Bone densitometry
-Magnetic resonance imaging
Nuclear medicine
Interventional & cardiovascular technology involves the use of x-rays, catheters, & contrast media to visualize blood vessels & heart anatomy.
True
False
True
Both MRI & CT are non-ionizing imaging modalities.
True
False
False
Radiation therapists work with oncology team members such as dosimetrists to treat cancer.
True
False
True
Who is noted for their study of cathode rays using electric current sent through gas in a sealed tube?
-Crooks
-Rontgen
-Edison
Crooks
Rontgen discovered x-rays in
1895
What does the "x" in x-rays stand for?
-extra
-radiation
-unknown
-times
Unknown
Rontgen received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1901 for his work.
True
False
False
The first known x-ray of a human was Roentgen's wife's arm.
False
The initials "PA" after a health care worker's name would indicate what profession?
-nurse practitioner
-physician assistant
-pharmacist
-none of the above
physician assistant
A medical physician (doctor) may have which of the following abbreviations listed after his or her name? (Choose all that apply)
-NP
-MD
-DO
-PA
-MD
-DO
The initials RT(R)(CT) would indicate that this is a technologist registered in both radiography & computed tomography.
True
False
True