OB Exam 2
1/229
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch 16,17,18,19,27
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
230 Terms
how are contractions described?
involuntary and intermittent
what is the period between the end of one contraction and the beginning of the next?
an interval or resting tone of the uterus
time when most fetal exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products occurs
what does intermittent contractions do for the fetus?
allows placental blood flow and exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between maternal and fetal circulation during the interval
what is the strongest part of the uterus?
the fundus; it contracts actively during labor as it pushes the fetus down
when is the best time to check vitals during labor?
in between contractions
what are the three phases of contractions?
increment: occurs as the contraction begins in the fundus and spreads throughout the uterus
peak: or acme is the period during which the contraction is most intense
decrement: the period of decreasing intensity as the uterus relaxes
what happens to your GI system during labor?
gastric motility is reduced; most women are not hungry, but are often thirsty or have dry mouth
ice chips can be provided in small amounts
popsicles, clears, or hard candy
what happens to your urinary system during labor?
decrease in sensing a full bladder because of intense contractions or the effects of an epidural
foley catheter is usually inserted for pts. with an epidural
after birth, urine is excreted in large quantities
what occurs to the hematopoietic system during labor?
WBCs increase; averages around14000-16000
may go up to 25000 or higher (this level might suggest an infection)
during strong labor contractions, maternal blood supply stops intermittently, what protective mechanisms does the fetus have against this?
fetal hemoglobin
high hematocrit
high cardiac output
what is effacement?
the thinning and shortening of the cervix
what are the components of the birthing process?
powers, passage, passenger, psyche, and position
what are the two powers of labor?
uterine contractions and the maternal pushing efforts
what is the passage component of the birthing process?
the bony pelvis and soft tissue
gynecoid and anthropoid
what is the best pelvic shape for vaginal birth?
gynecoid
what pelvic shapes are not favored in vaginal births?
platypelloid and android
why might c-section babies become tachypneic after birth?
they are not able to absorb the lung fluid like naturally born babies
what intensifies the absorption of fetal lung fluid?
labor
thoracic compression during labor aids in the expulsion of additional fluids
what is the passenger component of the birthing process?
fetus and placenta
how are the bones of the fetal head connected?
by sutures composed of strong but flexible fibrous tissue and the wider spaces at the intersections of sutures are called fontanels
these move together, slightly changing the shape of the head called molding
what is fetal lie?
the relationship to how the baby is lying compared to the mother’s spine
longitudinal or parallel
transverse
oblique
what is longitudinal lie?
either the head or the buttocks of the fetus enters the pelvis first
in more than 99% of pregnancies
what is transverse lie?
“right angle”
the long axis of the fetus is at right angles to the woman’s long axis
lying horizontal rather than vertical
what is an oblique lie?
at an angle between the longitudinal lie and transverse lie
what is fetal attitude?
the relation of fetal body parts to each other
what is normal fetal attitude?
one of flexion, with the head flexed toward the chest and the arms and legs flexed over the thorax
the back is curved in a convex C shape as labor starts
what is presentation of a fetus?
the fetal part that enters the pelvis first is the presenting part
cephalic (most common)
breech
shoulder
what are the four variations to cephalic presentation?
vertex, military, brow, and face
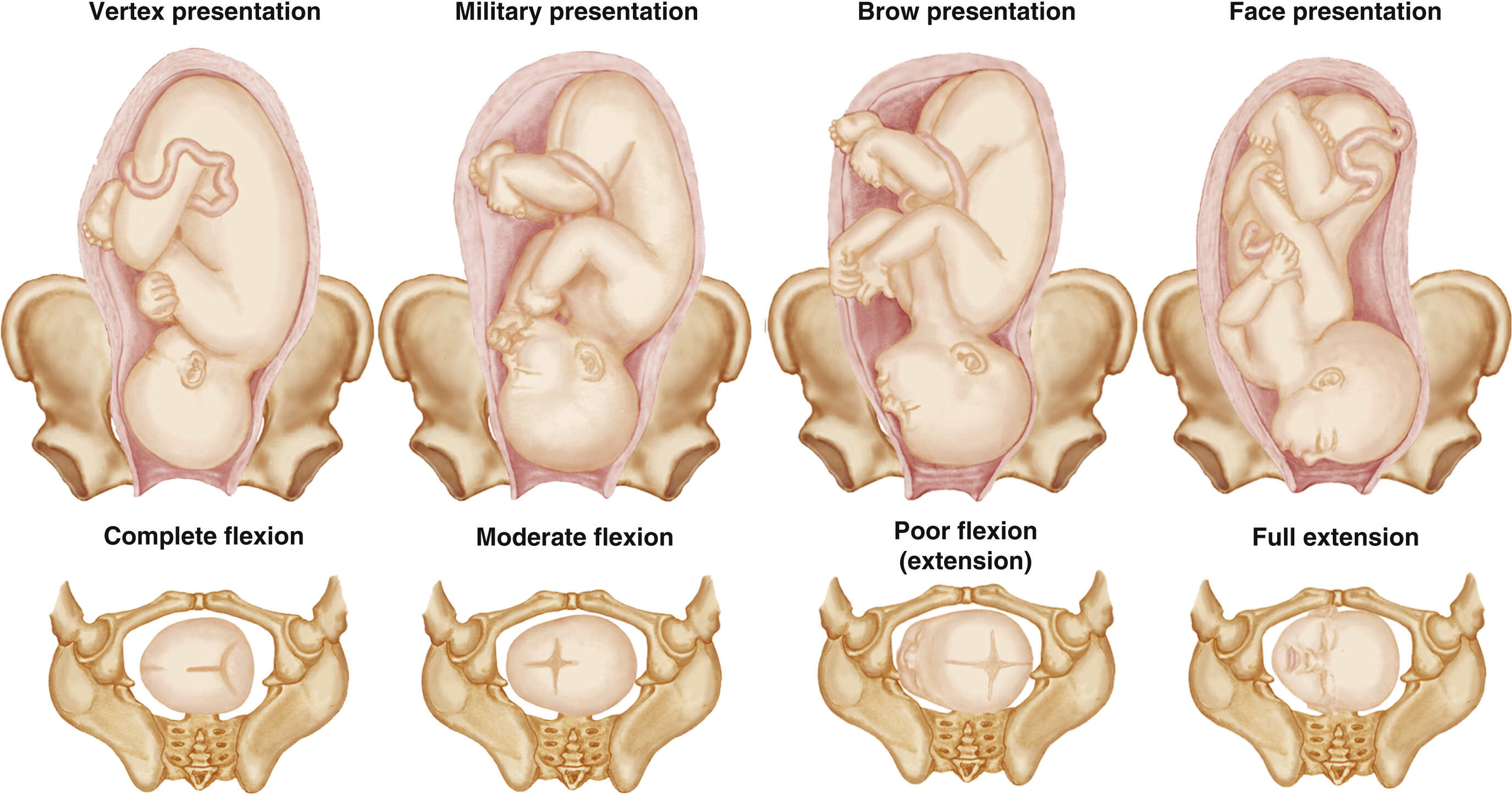
what is the most common and favorable cephalic presentation?
vertex
the fetal head is fully flexed
what are the three variations to breech presentation?
frank, full (complete), or footling
what is frank breech?
the most common, the fetal legs are extended across the abdomen towards the shoulder
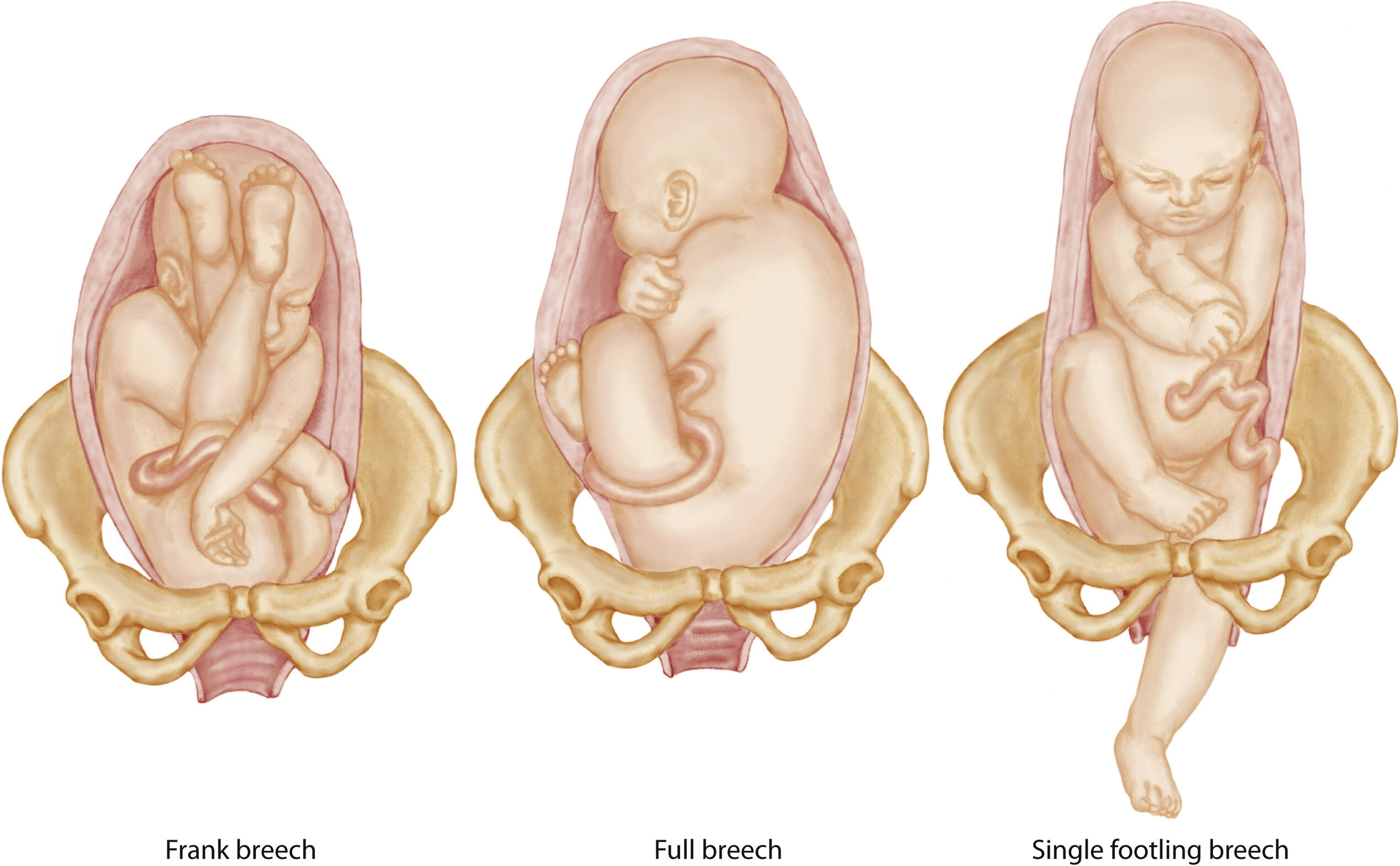
what is complete breech?
reversal of the usual cephalic presentation
the head is flexed, and the knees and hips are also flexed, but the buttocks are presenting
what is footling breech?
occurs when one or both feet are presenting
what is shoulder presentation?
transverse lie
body part may be shoulder, arm, or trunk
c-section is necessary
what is fetal position?
describes the location of a fixed reference point on the presenting part in relation to the four quadrants of the maternal pelvis
position is not fixed but rather changes during labor as the fetus moves downward and adapts to the pelvic contours
what are the four quadrants of the maternal pelvis?
right and left posterior and right and left anterior
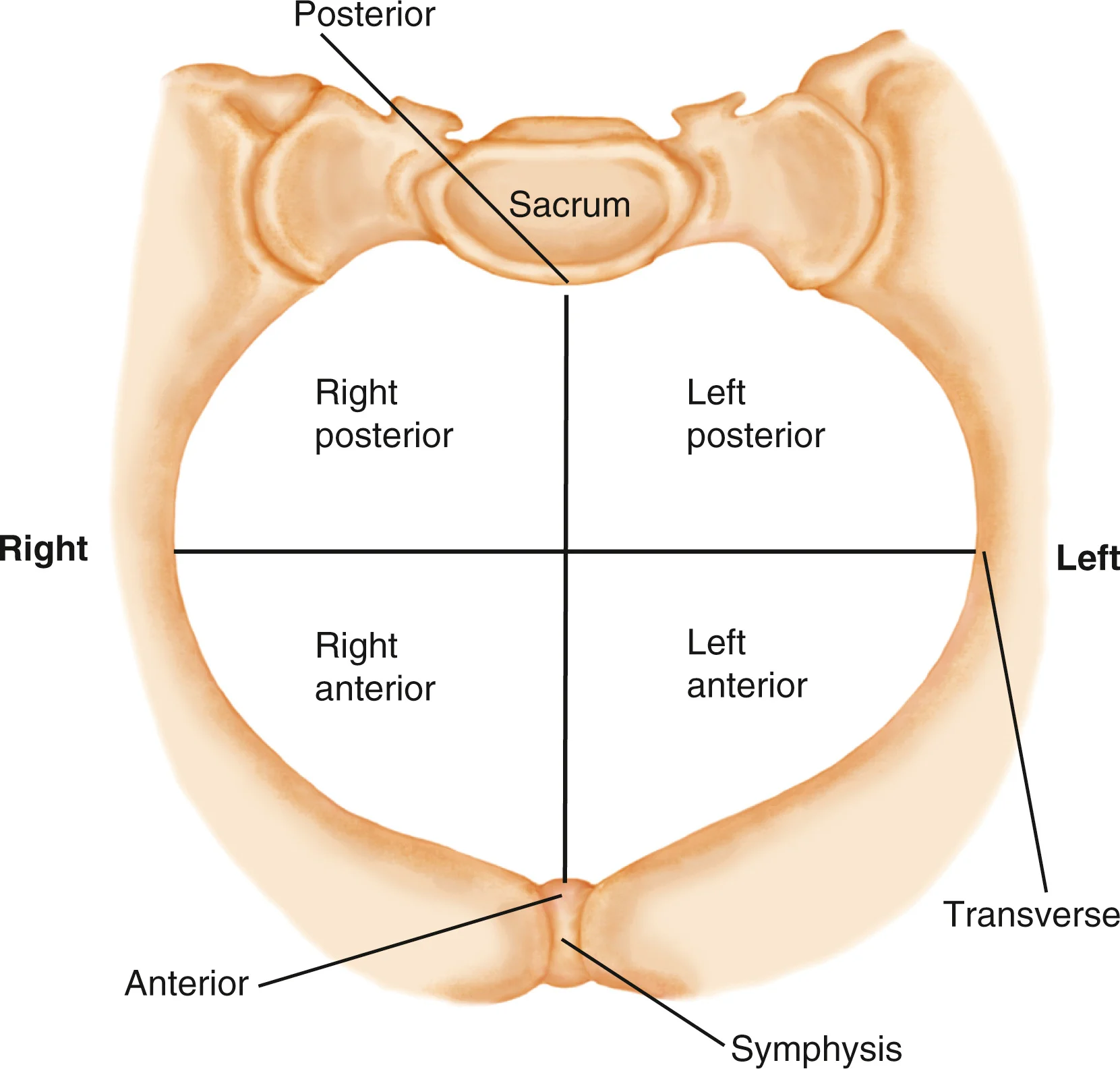
what does the first letter of the abbreviation refer to?
whether the fetal reference point is in the right or the left of the mother’s pelvis
right R or left L
if fetal point is neither, the letter is omitted
what does the second letter of the abbreviation refer to?
the fixed fetal reference point, which varies with the presentation
occiput O- used in vertex presentation
chin or mentum M- used in face presentation
sacrum S- used in breech presentation
fronto F or scapula Sc- for brow presentation
what does the third letter of the abbreviation refer to?
the fetal reference point is in the anterior or the posterior quadrant of the mother’s pelvis
anterior A
posterior P
transverse T
what is the psyche component of the birthing process?
the mother’s mindset
very important because marked anxiety, fear, or fatigue decreases a woman’s ability cope with pain labor
mother should be relaxed
what do maternal catecholamines do?
they are secreted in response to anxiety or fear
causes the inhibition of uterine contractility and placental blood flow
what is the position component of the birthing process?
the position of the mother that should allow for the pelvis to stay open
use a peanut ball
creative positioning
what are the premonitory signs that labor is near?
braxton hicks contractions
lightening
increases in clear and nonirritating vaginal secretions
“bloody show”
energy spurt (nesting)
small weight loss
what happens to the mother’s hormones during labor?
estrogen increases while progesterone decreases
oxytocin receptors in the uterus increase
what are braxton hicks contractions?
irregular mild contractions that occur throughout pregnancy increase in frequency and are sometimes painful
what is lightening?
“dropping”
the fetus descends toward the pelvic inlet
most noticeable in first time mothers (nulliparous)
what is “bloody show”?
a mixture of thick mucus and pink or dark brown blood
this may occur as the cervix begins to soften, dilate, and efface slightly (ripening)
how much weight can a women lose before labor?
small weight such as 1-3 lbs
what is the true difference between true and false labor?
true labor has progressive changes in the cervix (dilation and effacement)
how is false labor described?
also called prodromal labor; contractions are inconsistent in frequency, duration, and intensity
change in activity does not alter contractions
felt in the abdomen and groin, more annoying than painful
no significant changes in cervix
how is true labor described?
contractions are consistent pattern of increasing intensity, duration, and frequency; walking increases the intensity
discomfort begins in the low back and wraps around the abdomen
the cervix will dilate and efface
what is another name for the mechanisms of labor?
cardinal movements
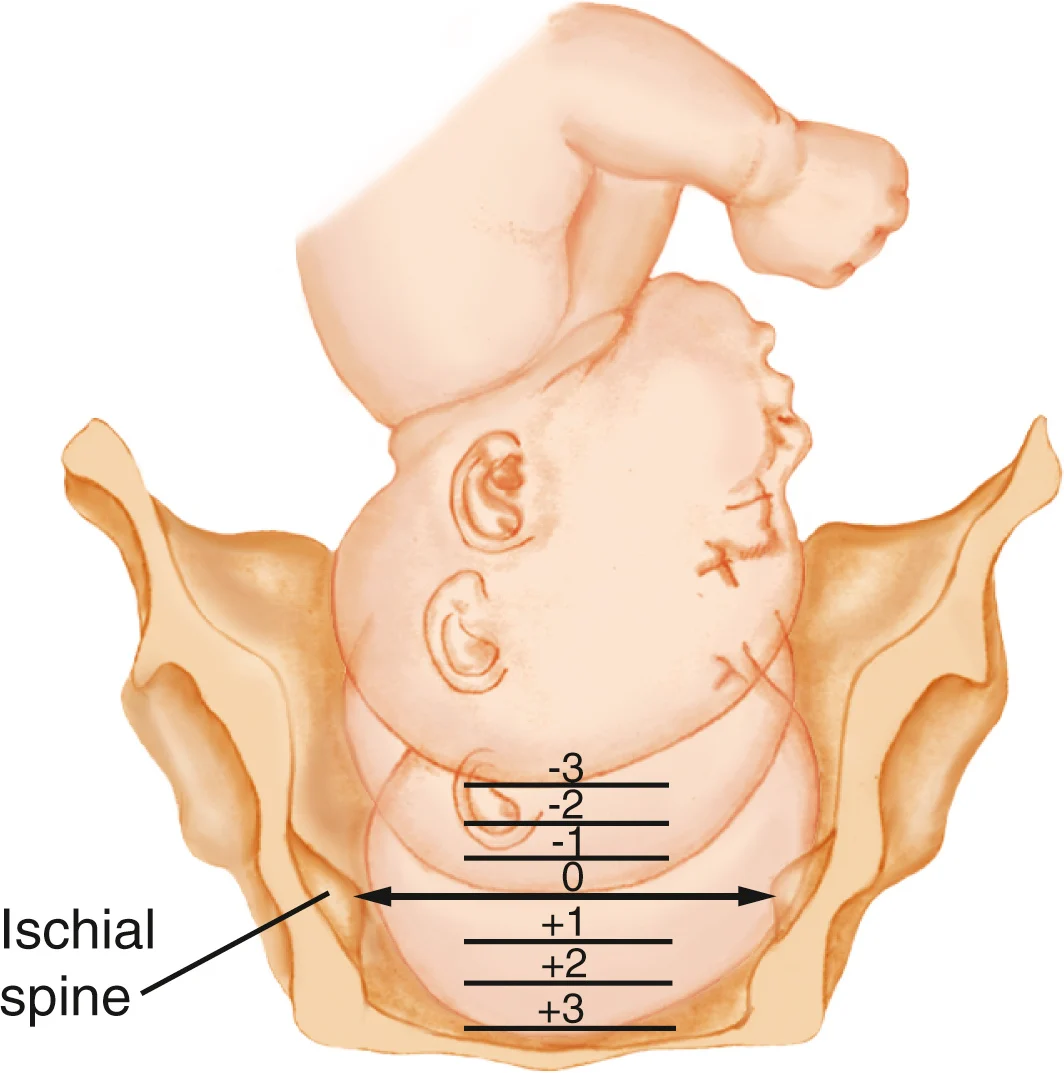
what does station mean?
describes the descent of the fetal presenting part in relation to the level of the ischial spines
the level of the ischial spines is zero station
as the fetus descends it will go from high negatives numbers (-3, -2, -1) to zero to high positive numbers (+1, +2, +3)
how many stages of labor are there?
four
what is the first stage of labor?
three phases: latent, active, and transition
also known as stage of dilation and longest stage
begins with onset of contractions and ends with complete dilation (10 cm) and effacement of (100%)
what is the latent (early) phase of the first stage of labor?
lasts from the beginning of labor until 0-3 cm of cervical dilation (varies among women)
best time to educate the women while she is calm and excited
what is the active phsse of the first stage of labor?
the cervix dilates more rapidly between 4-6 cm (dilation and effacement is complete)
what is the transition phase of the first stage of labor?
used to describe the intense contractions of fetal descent and final cervical dilation, approximately 7 or 8 cm to complete
short but intense
when does bloody show increase?
with the completion of cervical dilation
what is a Friedman curve used for?
identify whether a woman’s cervical dilation is progressing at the expected rate
what is the second stage of labor?
expulsion begins with complete (10 cm) dilation and full (100%) effacement of the cervix and ends with birth of the baby
mother may say she needs to have a BM or “the baby’s coming”
what is the third stage of labor?
placental stage; begins with the birth of the baby and ends with expulsion of the placenta
expelled in two ways: Schultze or Duncan
the placenta should be delivered within how many minutes?
30 mins
what is the Schultze mechanism?
expelled with the shiny, fetal side first
what is the Duncan mechanism?
less common, with the rough maternal side presenting
what should occur with the uterus after birth?
it must contract firmly and remain contracted after the placenta is expelled to compress open vessels
can result in in hemorrhage with inadequate uterine contraction
make sure to check the fundus every hour after birth for any abnormalities!
what are 4 signs that suggest placenta separation?
The uterus has a spherical shape.
The uterus rises upward in the abdomen as the placenta descends into the vagina and pushes the fundus upward.
The cord descends further from the vagina.
A gush of blood appears as blood trapped behind the placenta is released.
what is the fourth stage of labor?
stage of physical recovery for the mother and infant
lasts from the delivery of the placenta through the first 1-4 hours after birth
what is lochia rubra?
vaginal drainage during the 4th stage, usually blood (may have clots)
what can be done for discomfort in the 4th stage of labor?
discomfort usually from birth trauma or afterpains
ice packs on the perineum limit discomfort and hematoma formation
what are the 4 reasons a women should be informed to go to the hospital?
contractions
ruptured membranes
bleeding
decreased fetal movement
how can you promote early family attachment after birth?
skin to skin contact for the first hour after birth
what can excessive pain cause physiologically?
increase in metabolic rate and oxygen demand
increase in production of catecholamines, cortisol, and glucagon
les oxygen/waste exchange for fetus
what can excessive pain cause psychologically?
difficulty interacting with infant
unpleasant memories
partner may feel inadequate
what are the two types of physical pain?
visceral pain
somatic pain
what is visceral pain?
described as throbbing, is related to initially the contractions of the uterus and dilation and stretching of the cervix
what is somatic pain?
described as sharp and localized, is directly related to the stretching of the perineal tissue and adjacent structures
what are the sources of pain with childbirth?
tissue ischemia
cervical dilation
pressure and pulling on pelvic structures
distention of the vagina and perineum
how can medicating a pregnant women affect her pregnancy?
any drug will affect the baby
drugs may have effects in pregnancy they wouldn’t have in a non pregnant person
drugs can affect the course and length of labor
how does an analgesic affect a fetus?
decreases FHR variability
what are the cardiovascular changes in medicating a pregnant women?
cardiac output increase, which indirect affects hepatic and renal blood flow
what are the changes respiratory in medicating a pregnant women?
a full uterus reduces her respiratory capacity
she will breath more rapidly and deeply
more vulnerable to reduced arterial oxygenation
what should you watch for when giving narcotics for pain?
respiratory depression in the neonate
what are the GI changes in medicating a pregnant women?
stomach in displaced upward by her large uterus; the stomach’s interior also has a higher pressure
decrease in gastrointestinal absorption of any oral medications
what are the nervous system changes in medicating a pregnant women?
circulating levels of endorphins and enkephalins, morphinelike natural analgesics, are high
reduce requirements for analgesics
what problems may arise with other substances used for pain?
women who use therapeutic or botanical agents may have fewer options due to interactions between these substances and analgesics
women who have abused substances will also have fewer options
what are the disadvantages to regional pain management?
maternal hypotension
bladder distention
migration of epidural catheter
fever
N/V
pruritis
how should Benadryl be given?
slow IV push
given for pruritis with epidural opioids
what can cloud, yellowish, foul odor amniotic fluid indicate?
chorioamnionitis
what is regional anesthesia?
comfort for 1st stage of labor, but doesn’t provide comfort for 2nd stage
does not effect sensory or labor motor function
what is a pudendal block?
anesthetizes the lower vagina and part of the perineum to provide anesthesia for an episiotomy and vaginal birth
second stage of labor right before delivery
what is local infiltration anesthesia?
infiltration of the perineum with a local anesthetic
for episiotomy/lacerations
what is an epidural block?
local anesthetic in epidural space
can cause slow labor, vasodilation, and hypotension
what actions should you take before giving an epidural?
informed consent
maternal VS, FHR before, during, and after
assess bladder frequently
IV bolus to reduce hypotension
what may happen if a dura is unintentionally punctured?
substantial leakage of CSF, which may result in a spinal headache
what can you do to relieve a spinal headache?
lowering HOB, lying flat, and hydration
if those don’t work, anesthesiologist can perform a blood batch where 10-20 ml of moms blood is removed and injects her own blood back into the epidural space
this will clot and plug the hole in the dura to stop the leakage of CSF
what is a combined spinal-epidural?
injection of an opioid analgesic into the intrathecal space provided labor pain management w/ out sedation
what is a subarachnoid (spinal)block?
local anesthetic combined w/ opioid (fentanyl) in the subarachnoid space
lose sensory and motor function
bladder must be assessed frequently
may need to use intermittent catheter
s/s may include N/V, respiratory depression, and itching
what is duramorph?
type of subarachnoid (spinal) block
commonly used for spinal block for c sections
pain relief for 24 hours but the itching can be intense for 24 hours
pts. may scratch face and nose so much skin it rubs off
what is nitrous oxide?
inhalant via face mask in a mixture w/ 50% O2 - must be self administrated
cleared from body through lungs, so there is minimal risk of overdose
s/s: dizziness, N/V, and dysphoria