Weather and Water Cycle: Humidity, Apparent Temperature, and Atmospheric Stability
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Apparent temperature
The temperature it feels like, not the actual air temperature.
Dew point temperature
Temperature at which condensation occurs; also a measure of moisture in the atmosphere.
Heat Waves
Periods of excessively hot weather, which can lead to increased mortality.
Hydrologic Cycle
The continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
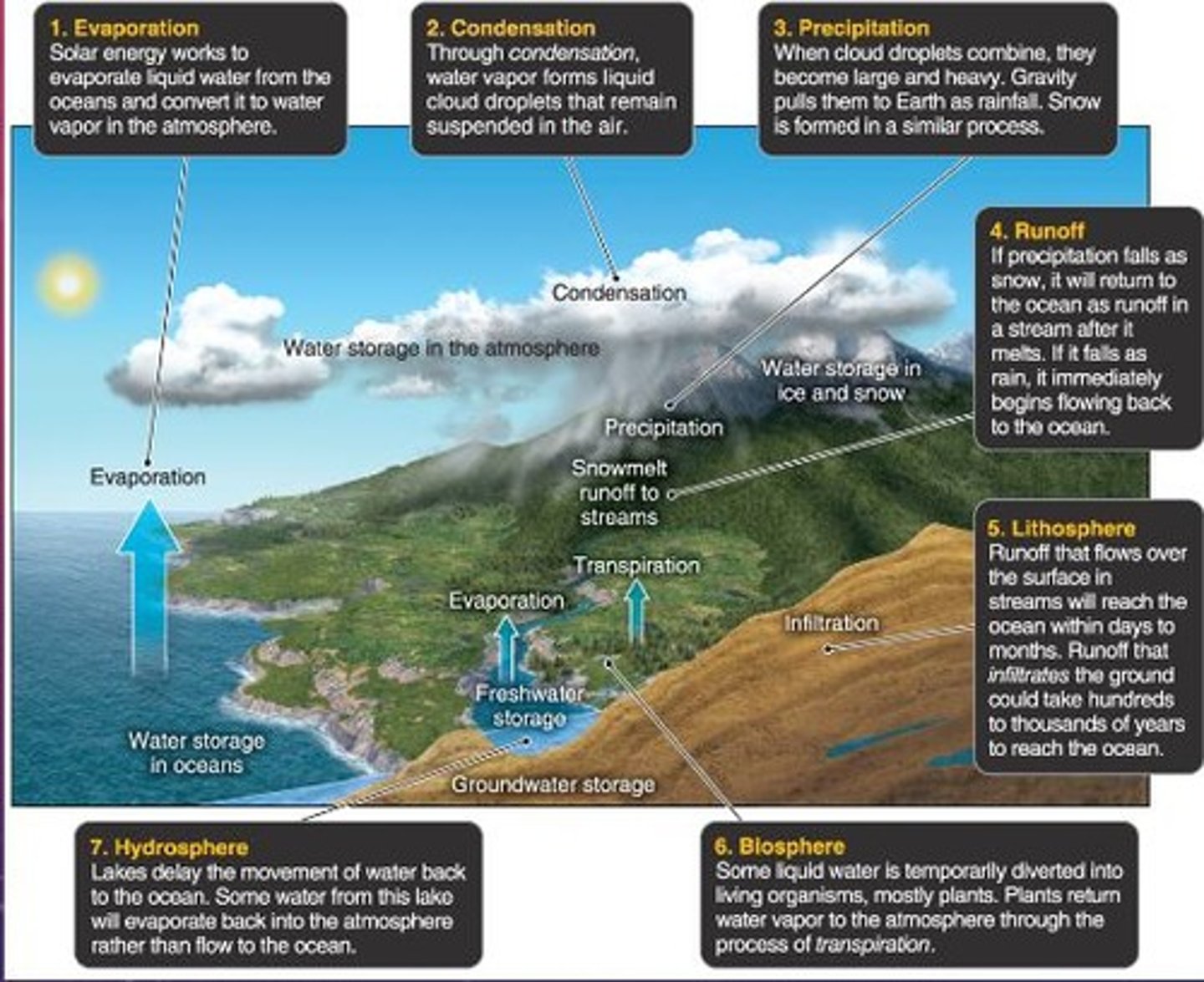
Evapotranspiration
The sum of evaporation from the land and transpiration from plants.
Properties of Water
Key component of Earth-Atmosphere System; absorbs, transports, and releases energy.
Hydrogen bonds
Weak bonds between hydrogen and oxygen atoms in water molecules.
Cohesion
Water molecules join to other water molecules.
Adhesion
Water molecules join to other objects.
Latent heat of water
Energy that is absorbed or released during a state change of water.
Sensible heat
Heat that causes a change in temperature but not a change in state.
Vapor pressure
Portion of air pressure exerted by molecules of water vapor.
Hygrometers
Instruments that measure water vapor in the atmosphere.
Liquid water density
1 kg/L (8.3 lbs./gal).
Record heat temperature
Apparent temperature of 81° C (178° F) recorded on July 8, 2003, in Dharan, Saudi Arabia.
Dew points > 21° C (70° F)
Increases discomfort.
Average deaths from heat-related situations
On average, 400 people die from this situation each year.
Deaths in Chicago and Milwaukee 1995
750 died due to heat-related issues.
Deaths in Europe 2003, 2006, and 2018
73,500 died due to heat-related issues.
Deaths in Russia 2010
56,000 died due to heat-related issues.
Phases of water
Solid, liquid, and gas.
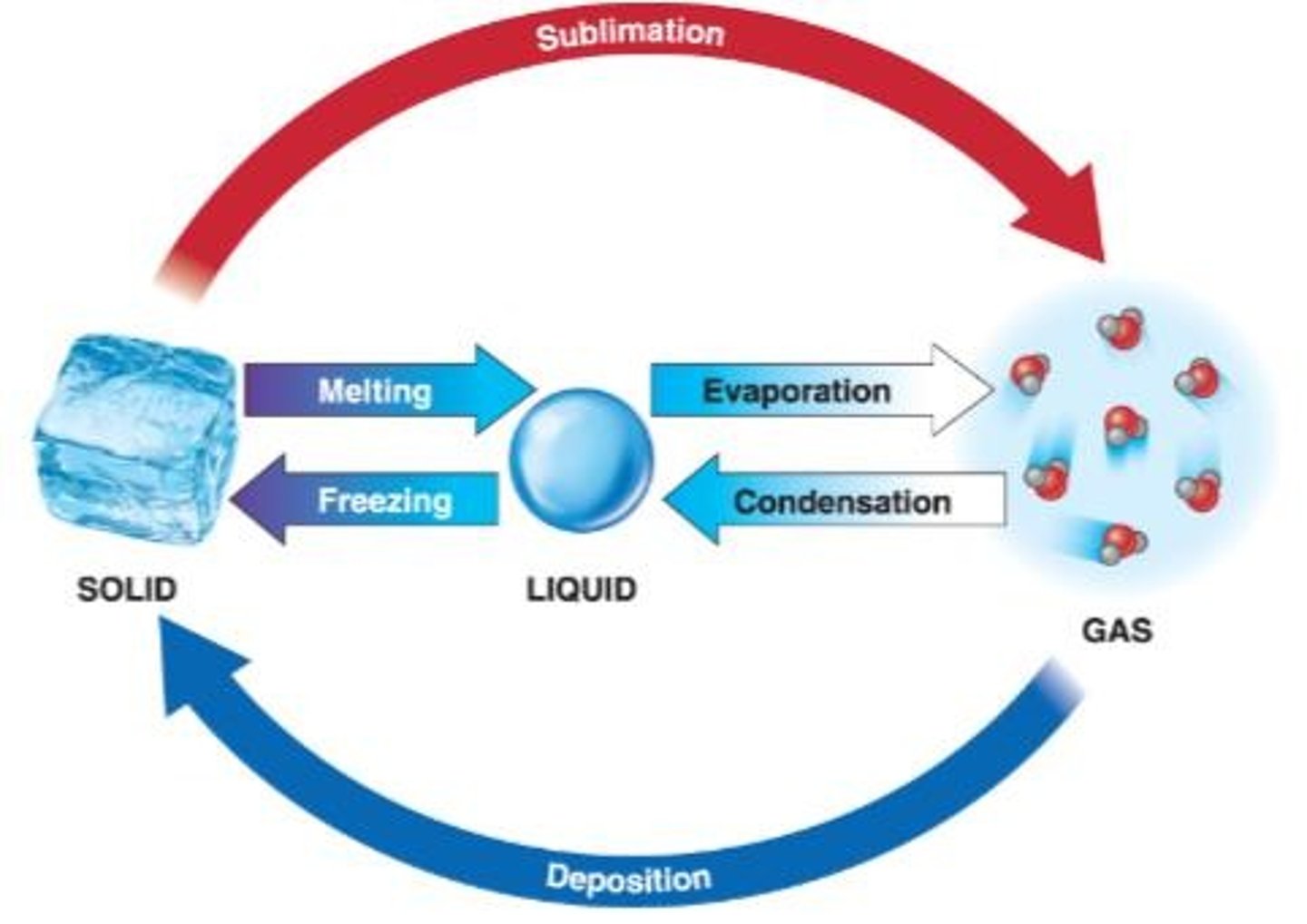
Ice
A solid state of water with a lattice of hydrogen bonds.
Liquid water
Weaker bonds that stretch, break, and re-form.
Gas state of water
Few bonds, move freely.
Average Sea Level Pressure
1013.25 mb
Saturation Vapor Pressure
Vapor pressure at which saturation occurs
Specific Humidity
Mass of water vapor in grams per kilogram
Relative Humidity
Ratio of water vapor content to water vapor capacity expressed as percentage
100% Relative Humidity
Net condensation
Dew Point
Temperature at which the air becomes saturated
Dew-Point Depression
Difference between air temperature and the dew point
Unstable Air
Air moves higher in the atmosphere
Atmospheric Instability
Transports heat from Earth's surface
Adiabatic Temperature Change
Temperature change due to rising or sinking air
Dry Adiabatic Rate
10° C/1000 m (5.5° F/1000 ft)
Environmental Lapse Rate
6.5° C/1000 m (3.6° F/1000 ft)
Moist Adiabatic Lapse Rate
6° C/1000 m (3.3° F/1000 ft)
Atmospheric Stability
Measure of atmospheric buoyancy
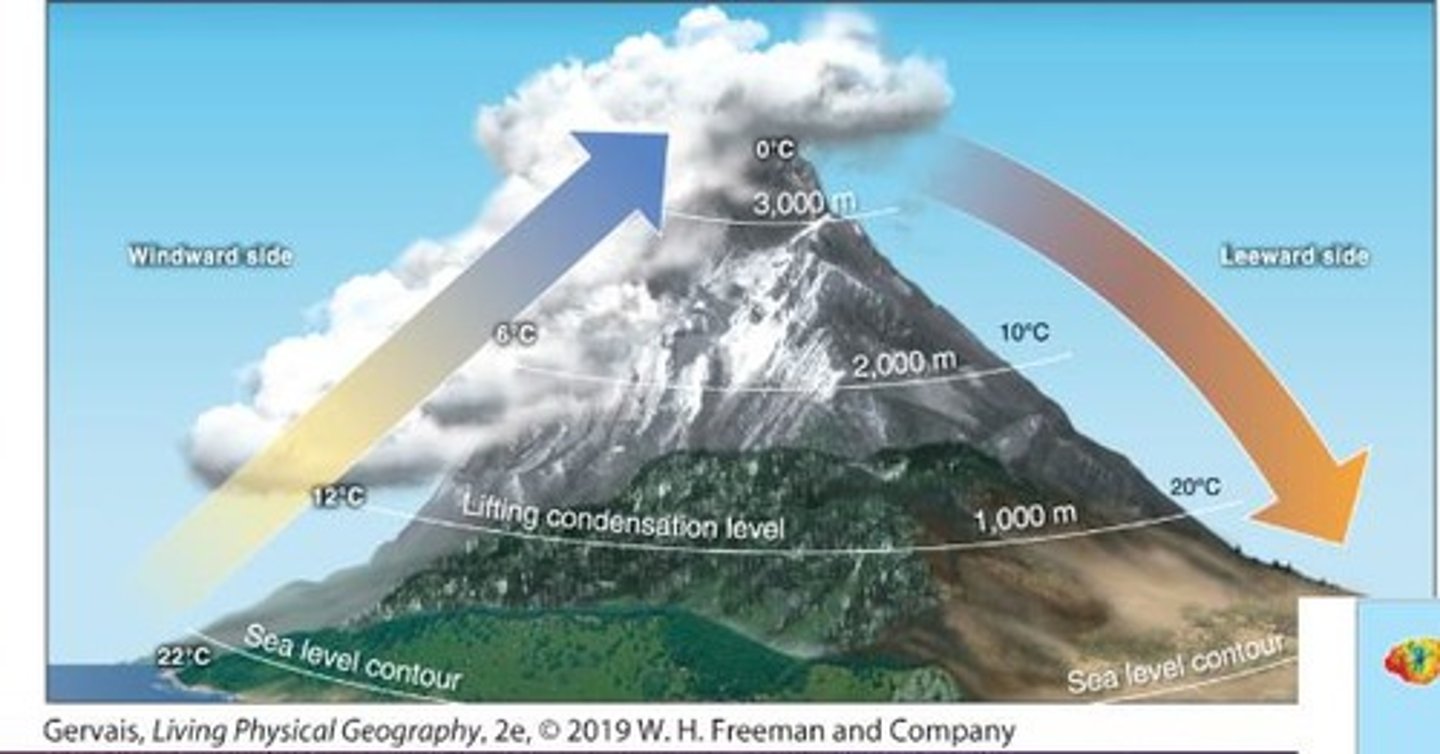
Rain Shadow
Leeward side of mountains with sinking air, creating a desert
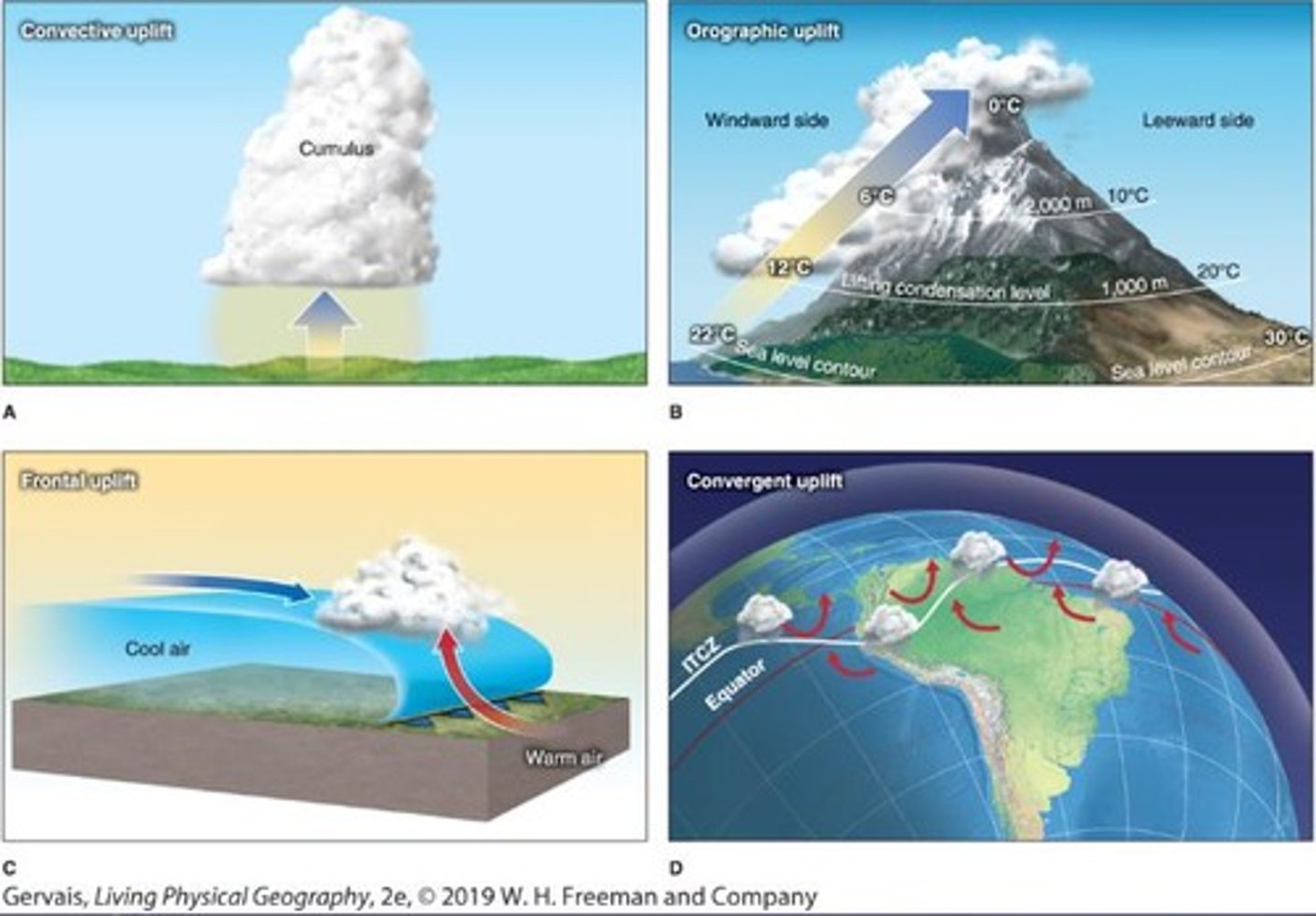
Lifting Mechanisms
Processes such as orographic, convection, frontal, and convergence that lift air
Lifting Condensation Level
Altitude where air temperature equals dew point temperature, resulting in 100% RH