basic concepts of organic chemistry
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
structure and bonding in organic molecules - the formula of organic compounds
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
p orbitals
dumbbell shaped
three types oriented along three diff axes : x y and z
what are the diff types of covalent bonds ?
sigma and pi bond
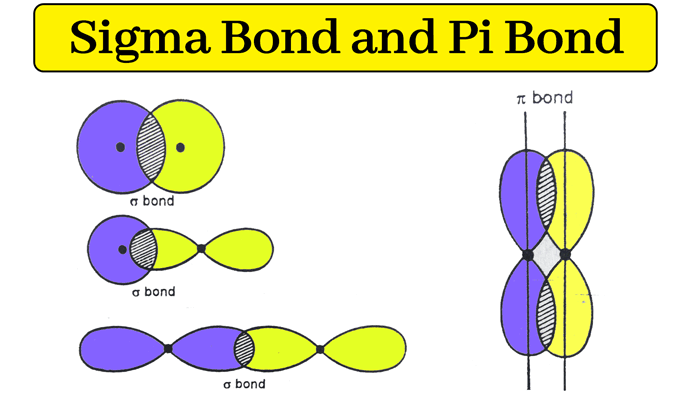
sigma bond
single bonds
head to head overlap of either :
S orbitals
S+P orbitals
P+P orbitals
P orbitals horizontal along x axis
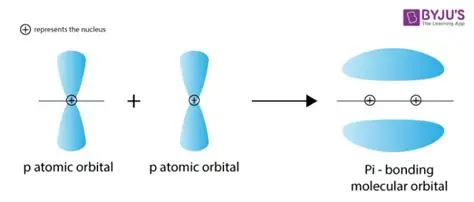
Pi bond
formed when the overlap between two p orbitals occurs sideways . you get two electron clouds above and below the plane
why is the C=C bond in ethene not twice as strong as the C-C bond in ethane?
a single bond is made of one sigma bond while the double bond is made of a sigma and pi bond
double bond is not double the strength of a single bcs a pi bond is weaker than the sigma

aliphatic
have straight or branched chains of C atoms
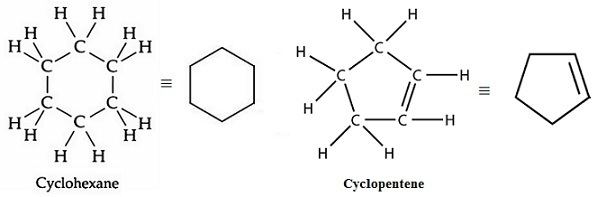
Alicyclic
have rings of C atoms w/ normal C-C and C-H bonds e.g. cyclobutene
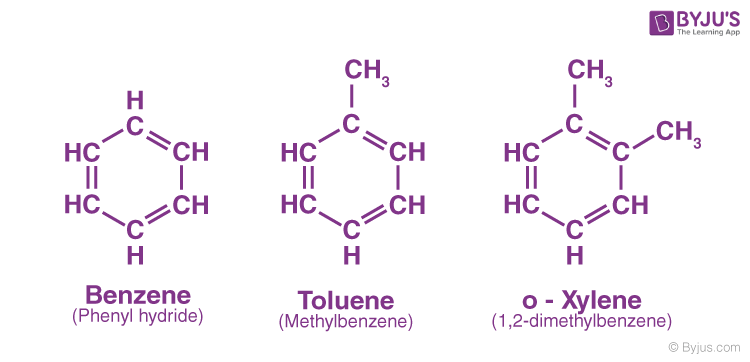
aromatic
contains a benzene ring - benzene C6H6 consists of a ring of 6 C-H grps joined tg by delocalised pi bonds
empirical formula
simplest whole num ratio of atoms
molecular formular
actual num of atoms in a formula
three types of organic reactions?
addition
substitution
elimination
homolytic fission
equal splitting of a covalent bond to form a free radical
heterolytic fission
unequal splitting of a covalent bond where one atom takes both the electrons
free radical
a vv reactive species w/ an unpaired electron
electrophile
electron pair acceptor
neutrophile
electron pair donor
homologous series
series of organic compounds having the same functional grp but w/ each successive member differing by CH2
functional grp
grp of atoms responsible for the characteristic reactions of a compound
structural isomer
compounds w/ the same molecular formula but diff structural formulae