Atomic Structure
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Proton
subatomic particles carrying a charge equal to but opposite to that of an electron
Neutron
subatomic particle that has a mass nearly equal to that of a proton but carries no charge
Isotopes
atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
Mass number
identifies each isotope of an element and is the sum of the atomic number (or number of protons) and neutrons in the nucleus.
Radioactivity
When substances emit radiation
Radiation
Rays and partcles emitted by the atoms
Radioactive decay
When unstable nuclei loses energy by emitting radiation in a spontaneous process
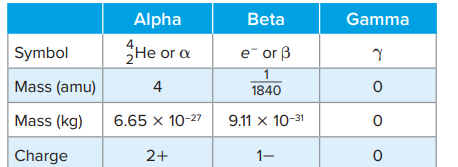
Types of radiation
Alpha radiation
Beta radiation
Gamma radiation
What determines an atom’s stability?
The ratio of neutrons to protons
Atoms containing too many or too few neutrons are unstable and lose energy as they decay to form a stable nucleus.
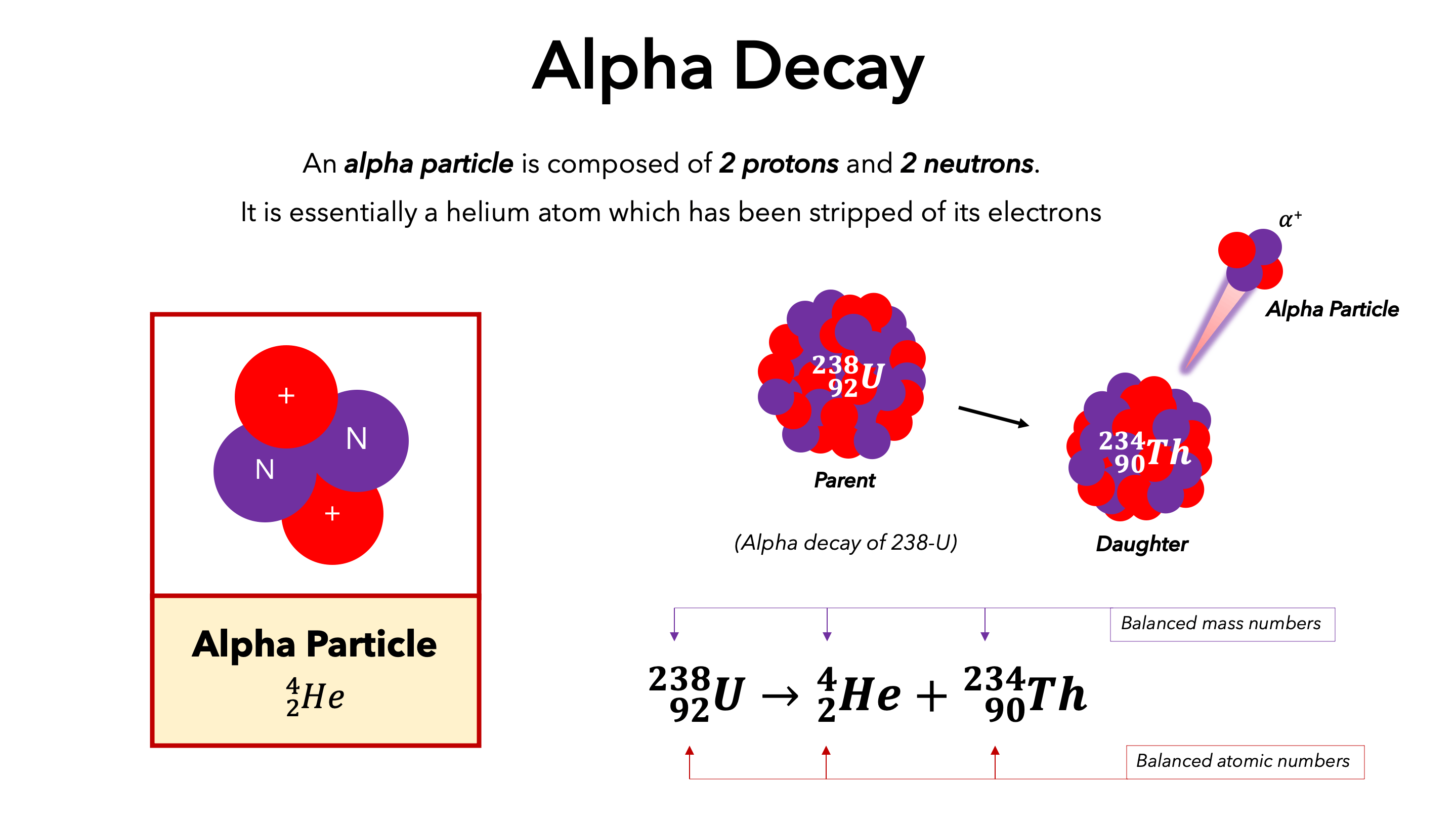
Alpha radiation
involves alpha particles containing two protons and two neutrons and thus has a 2+ charge (don’t have electrons)
Alpha particles are
negatively attracted to the negatively charged plate
Alpha particles are equivalent to
helium-4 nucleus
Beta radiation
Involves beta particles which are electrons with a charge of 1- and no mass
Process of beta radiation
Electrons arent emitted from the atom shells
One of the atom’s neutron’s decay into a proton and electron
The proton stays in the nucleus and the electron is emitted out at a high speed
Gammy rays
not particles, waves of electromagnetic radiation
(lighters, light)
Charge of gammy rays
No mass/charge
When does this radiation happen?
After beta radiation as a way to get rid of the extra energy in the nucleus