Chapter 9 (Horizontal Gene Transfer) & Chapter 7 (Gene Regulation & Lac Operon)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
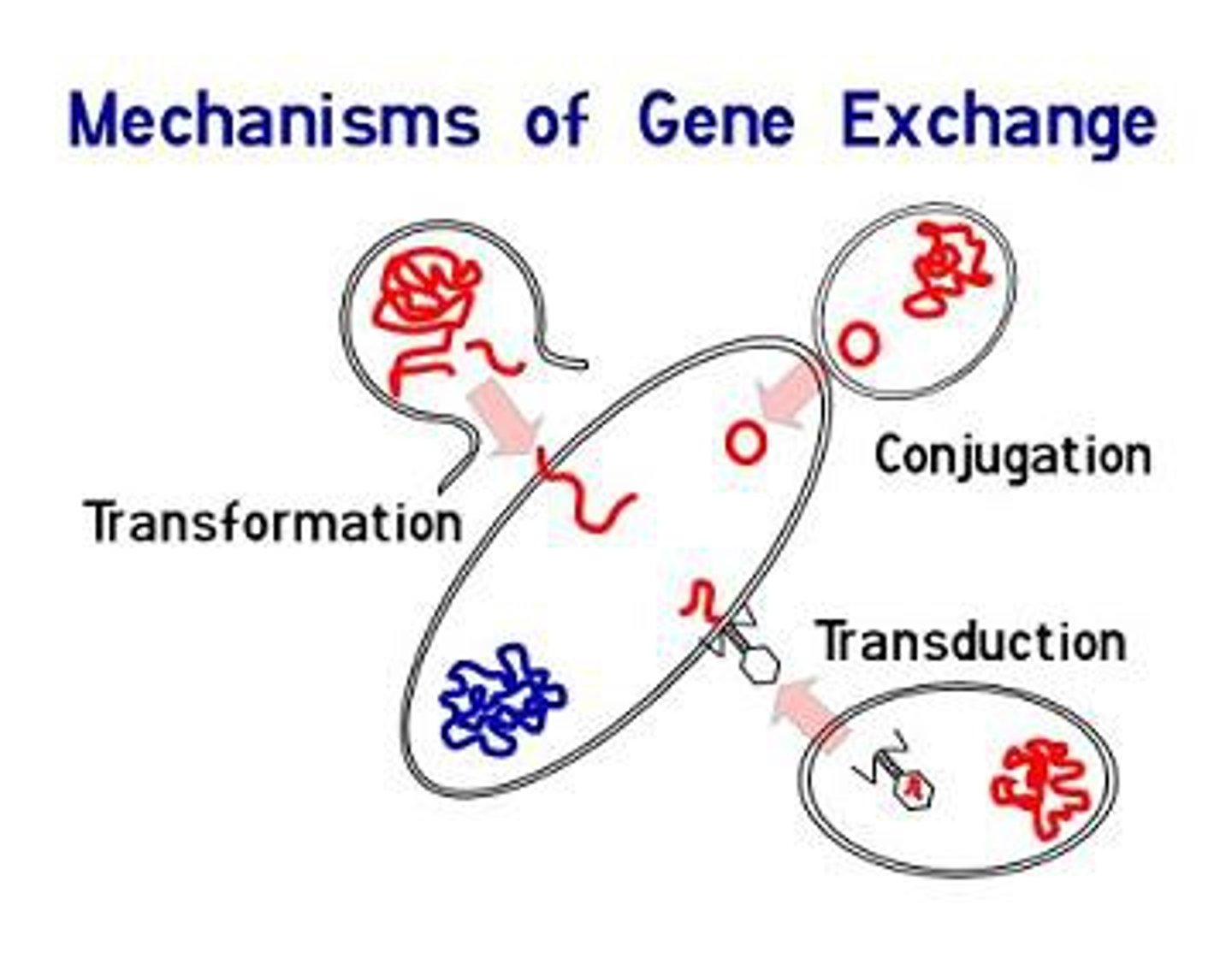
horizontal gene transfer
transfer of genetic information between bacterial cells of similar age
vertical gene transfer
transfer of genetic information from parent to offspring
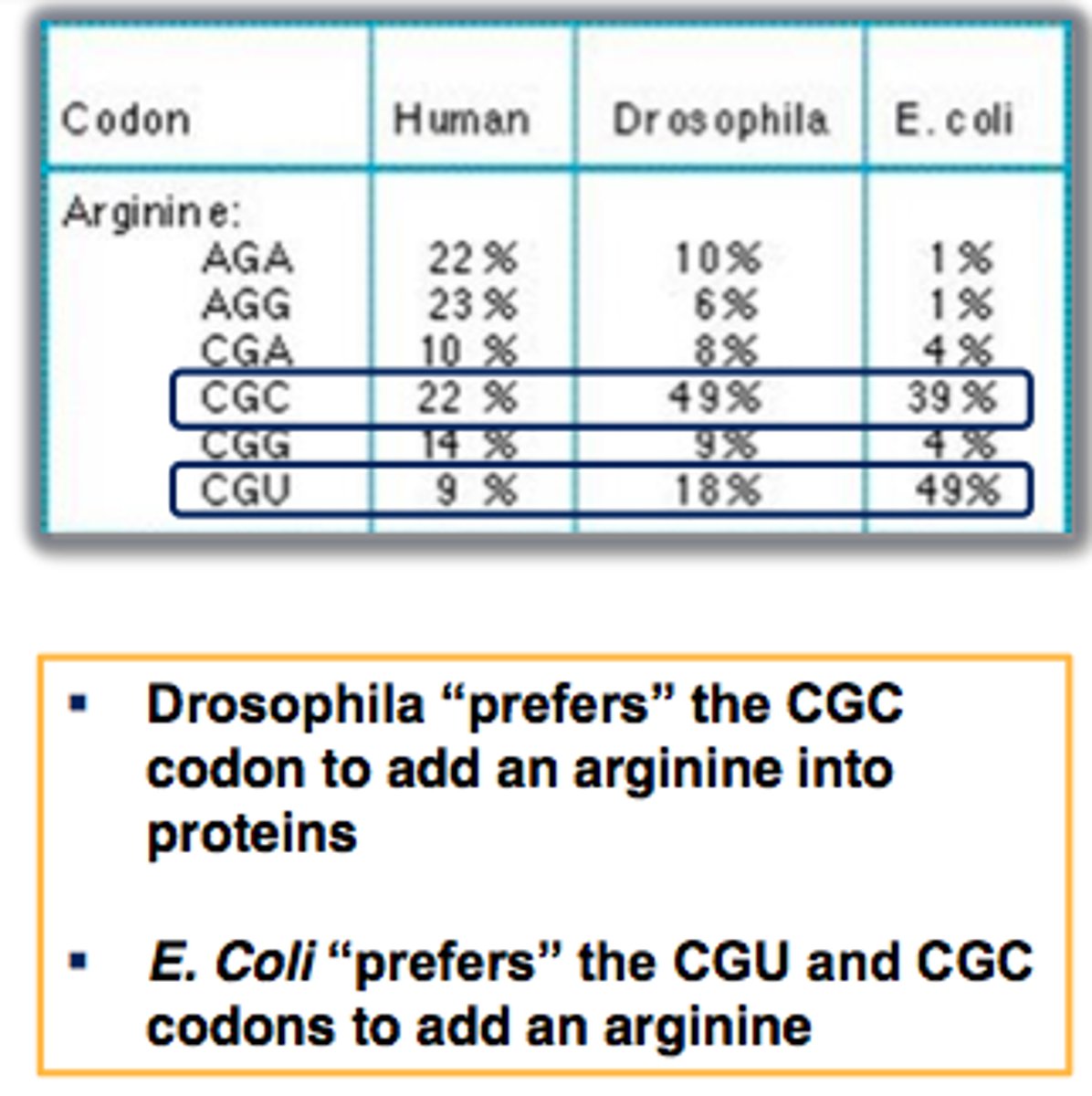
codon bias
the preference for one codon of a set vs others
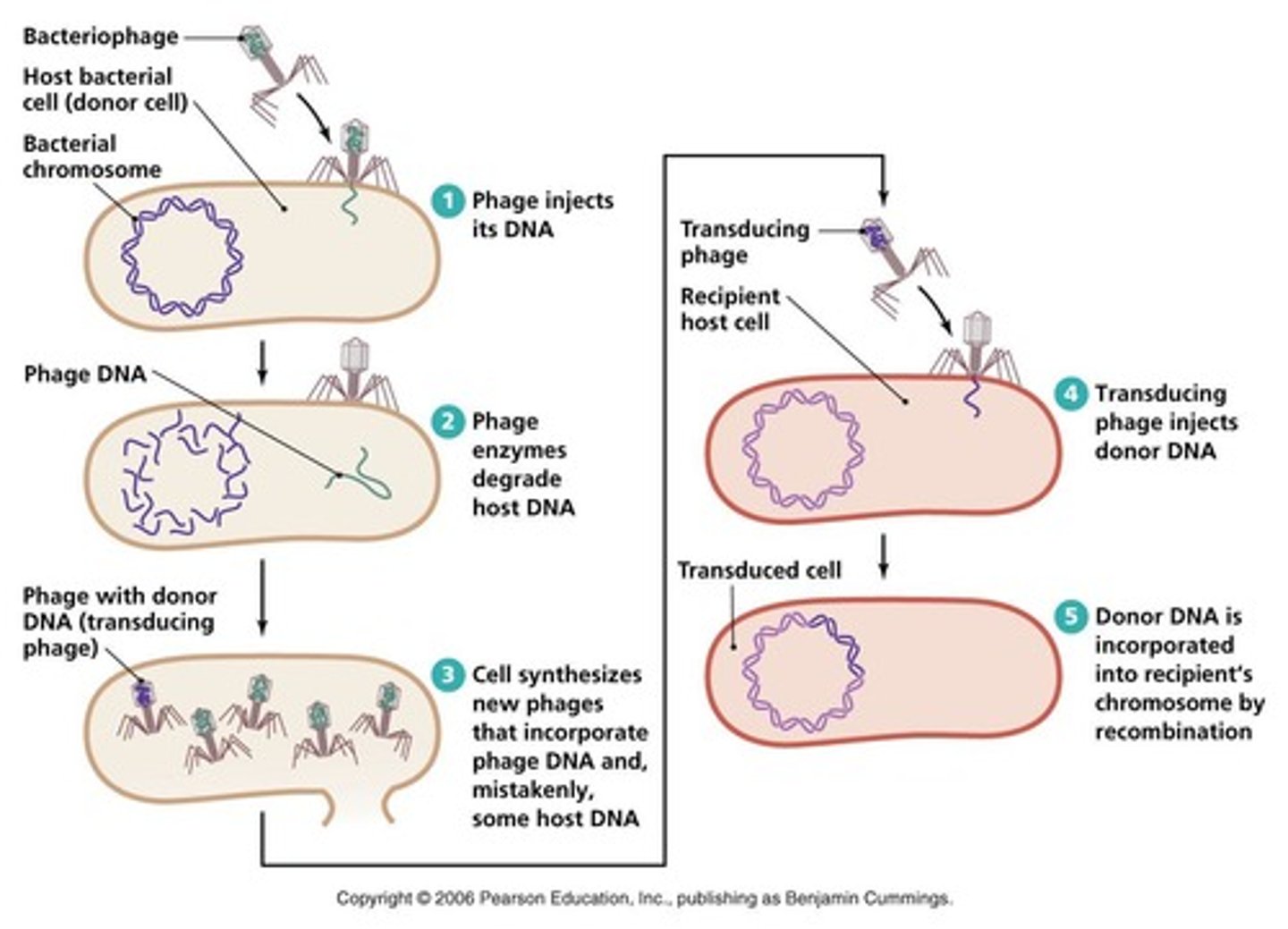
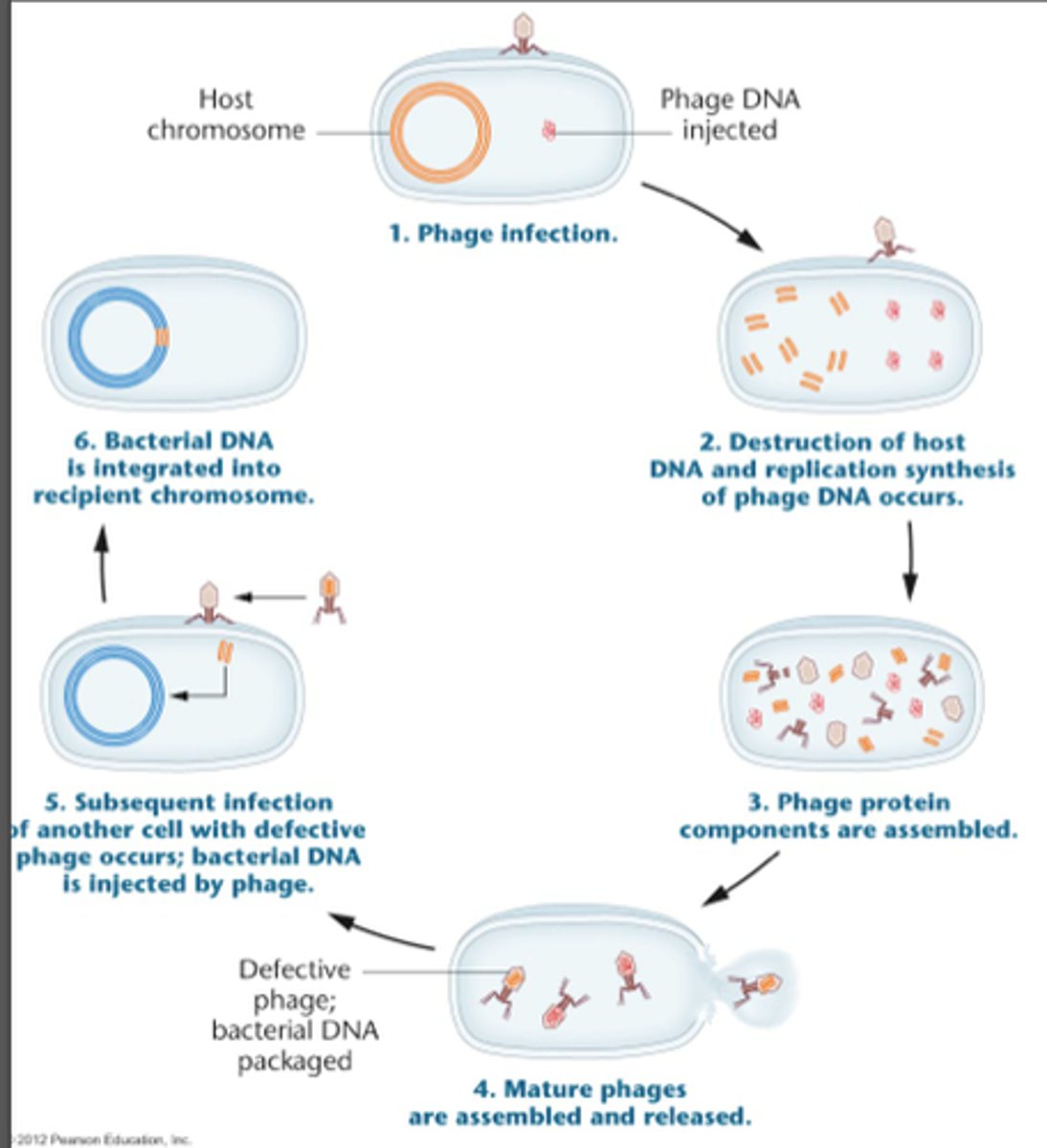
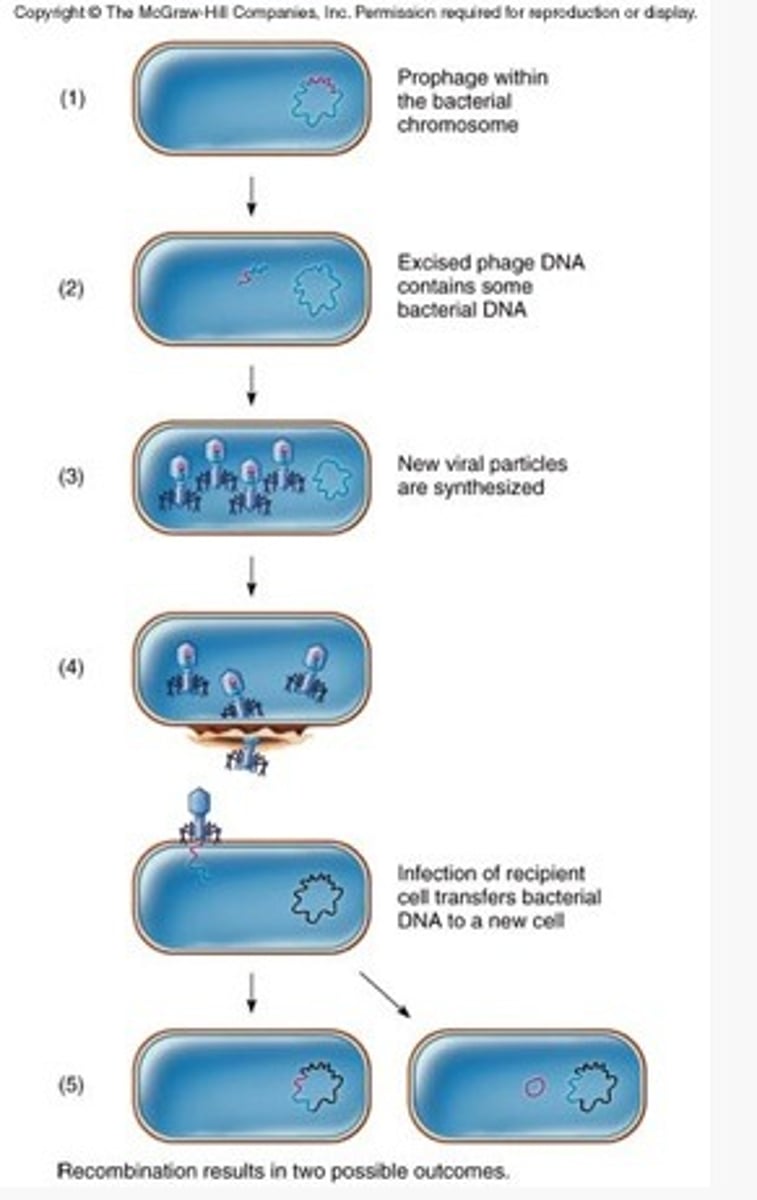
transduction
host DNA gets "mispackaged" into a virus, then injected into another bacterial cell when the virus attaches to it.
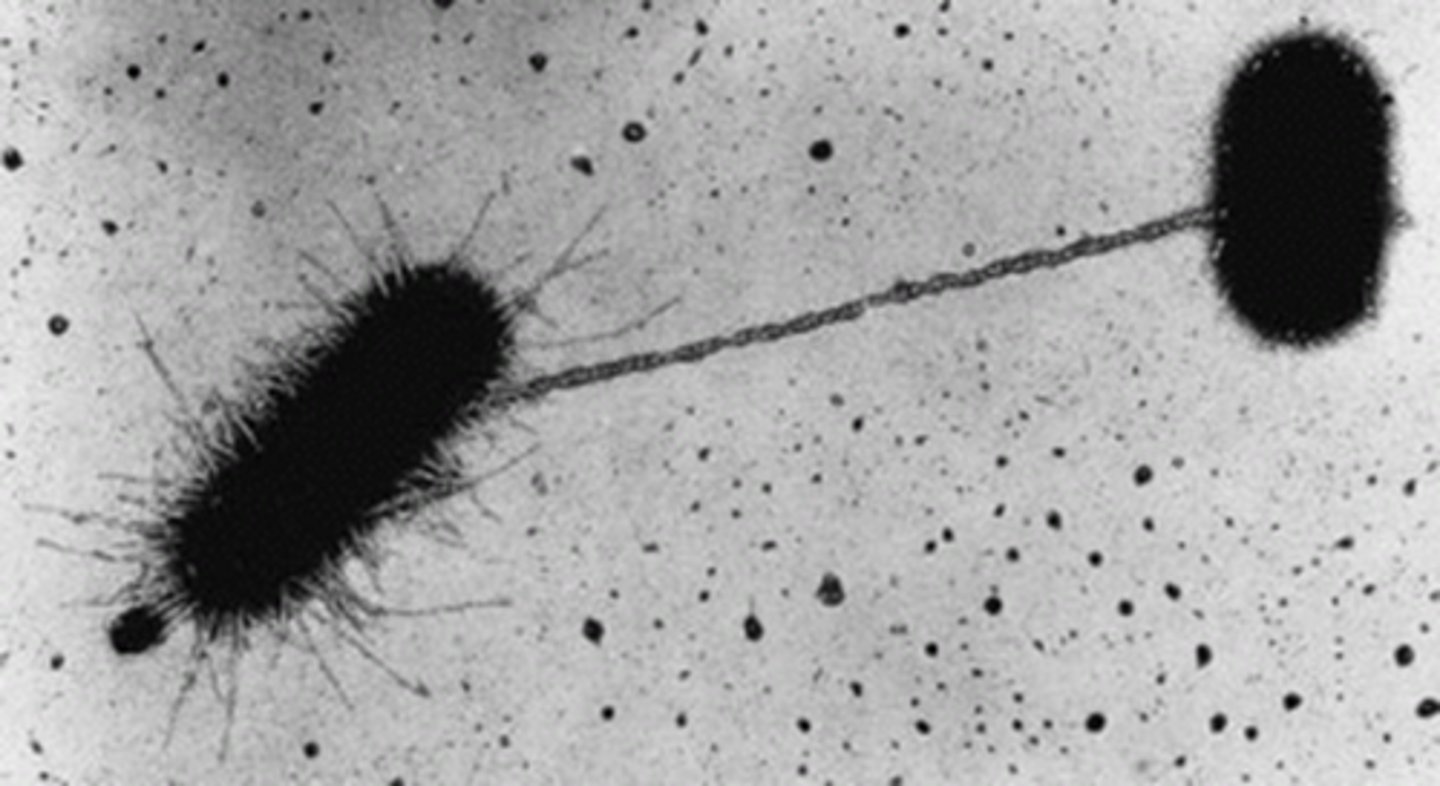
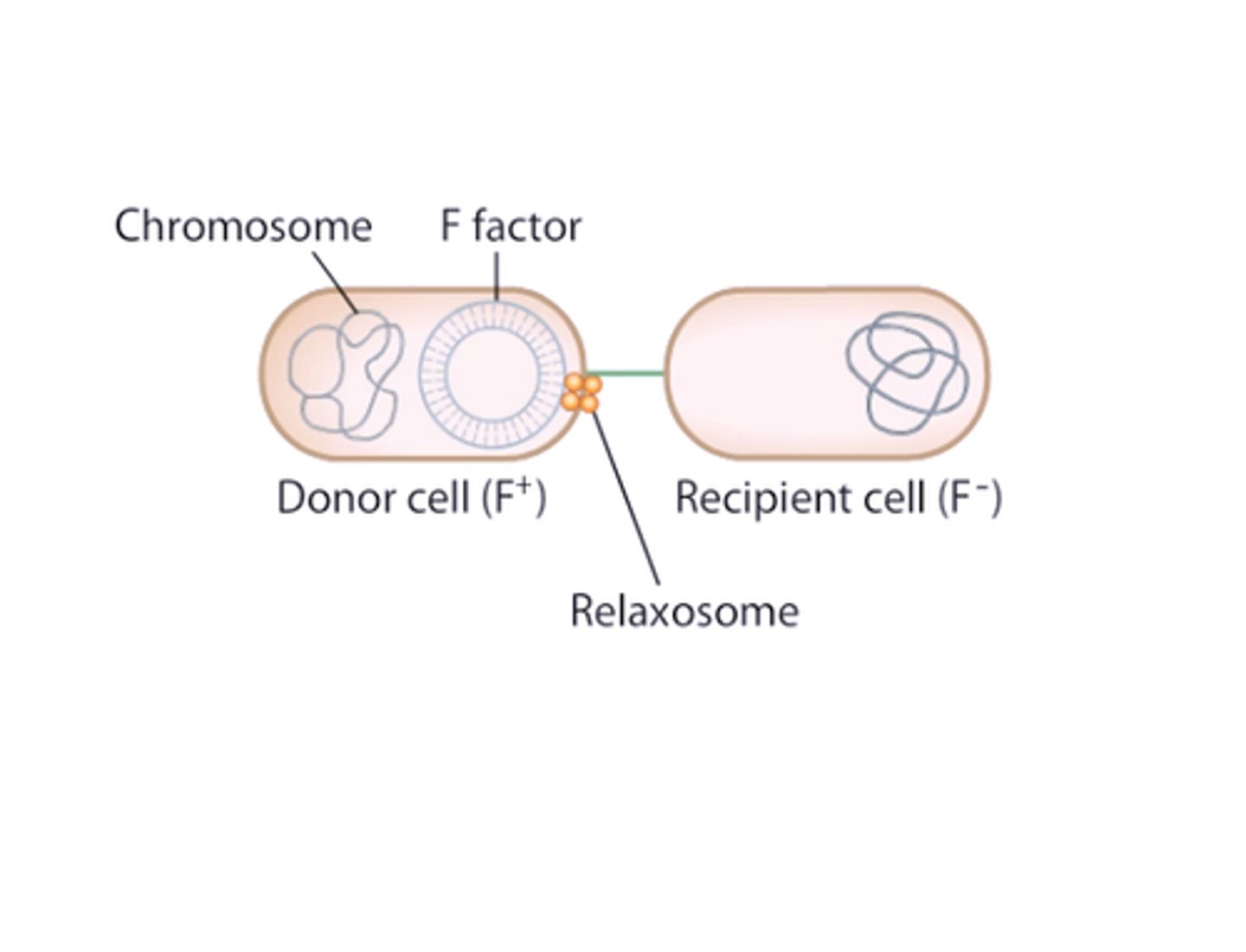
conjugation
bacterial cell-to-cell transfer of genetic material, mediated via a pilus
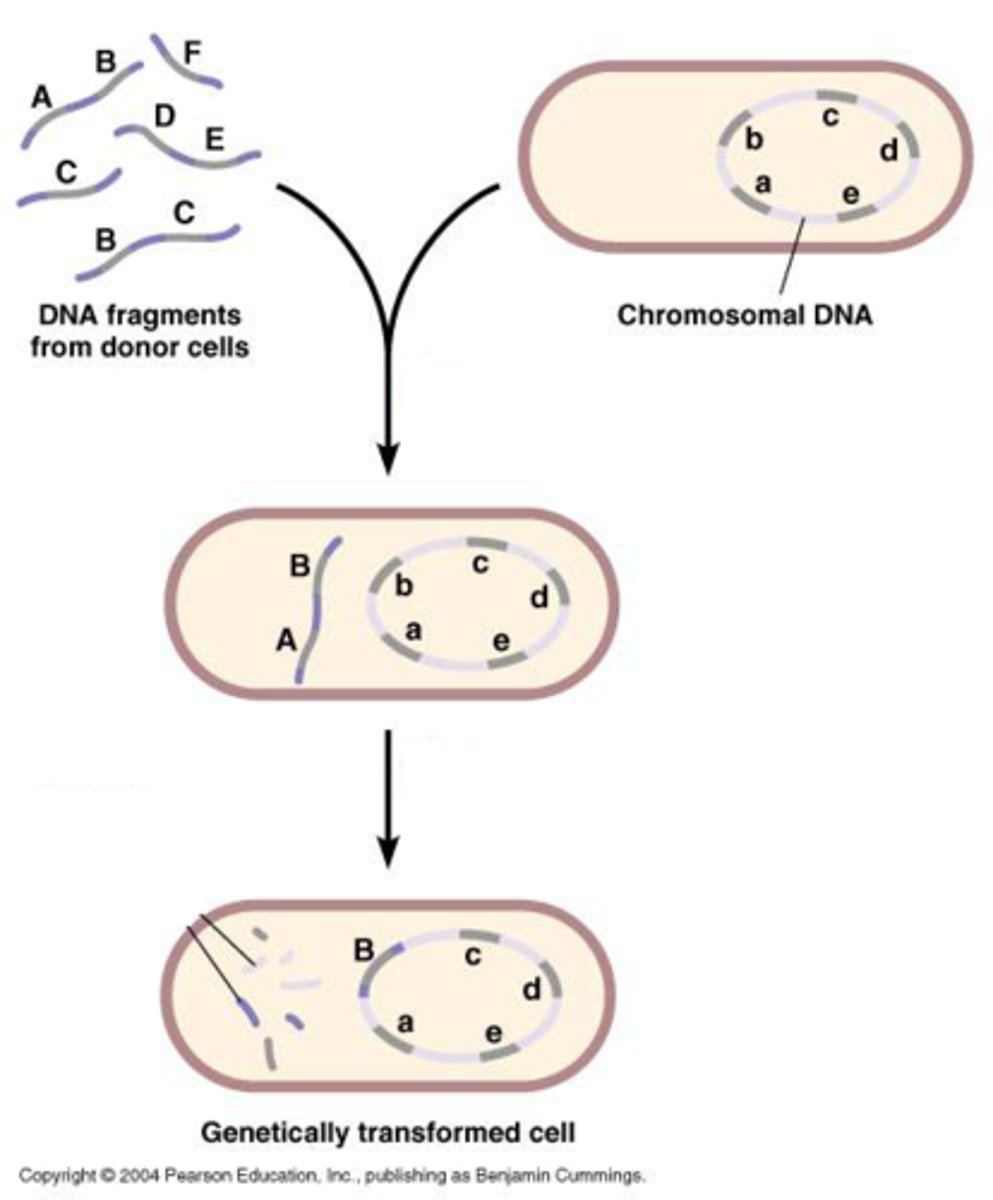
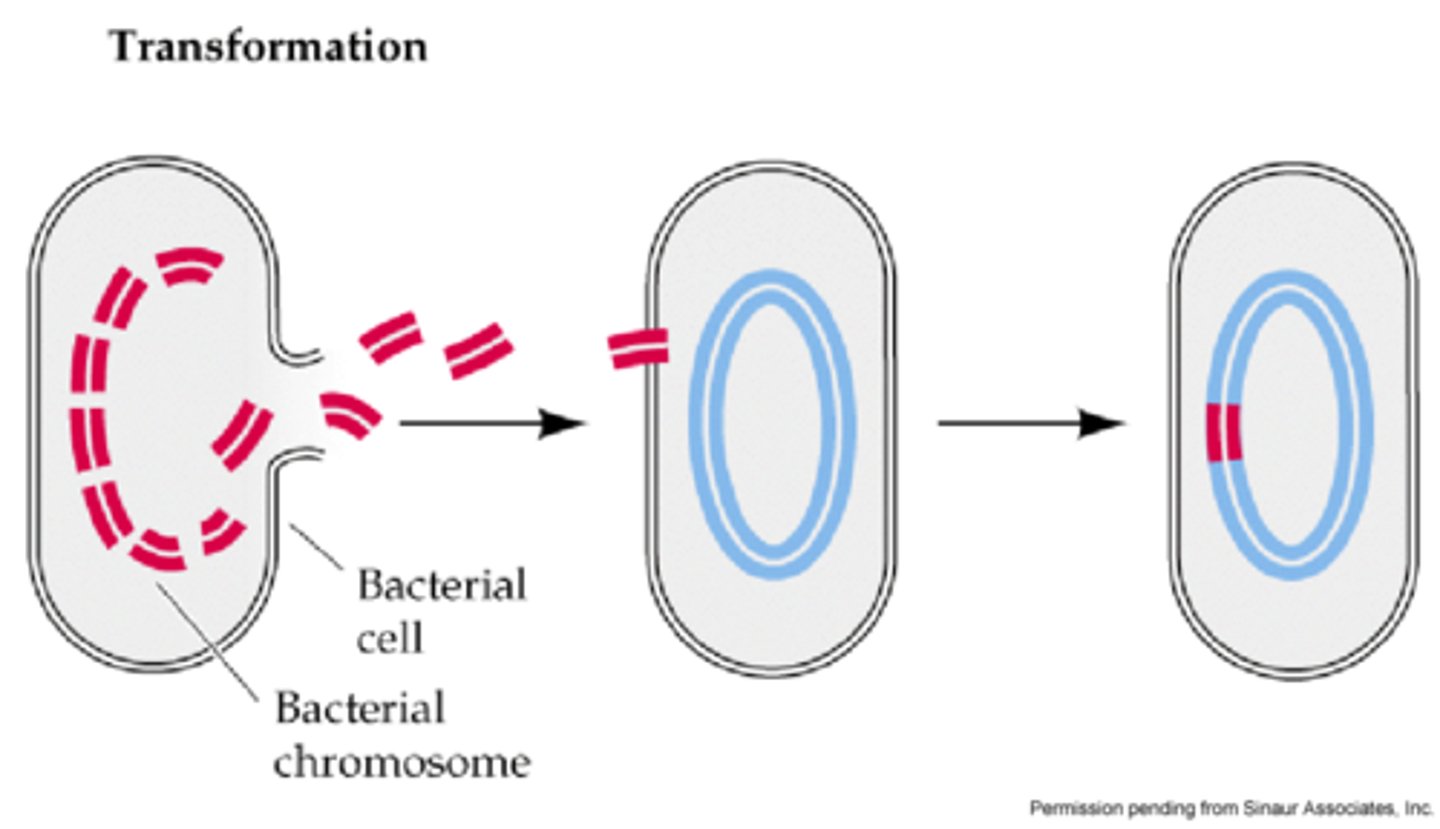
transformation
free DNA is taken up by a bacterial cell from its environment
competent cells
cell that are capable of taking up DNA from their environment. some are naturally this way, others can be made this way through chemical or electrical means.
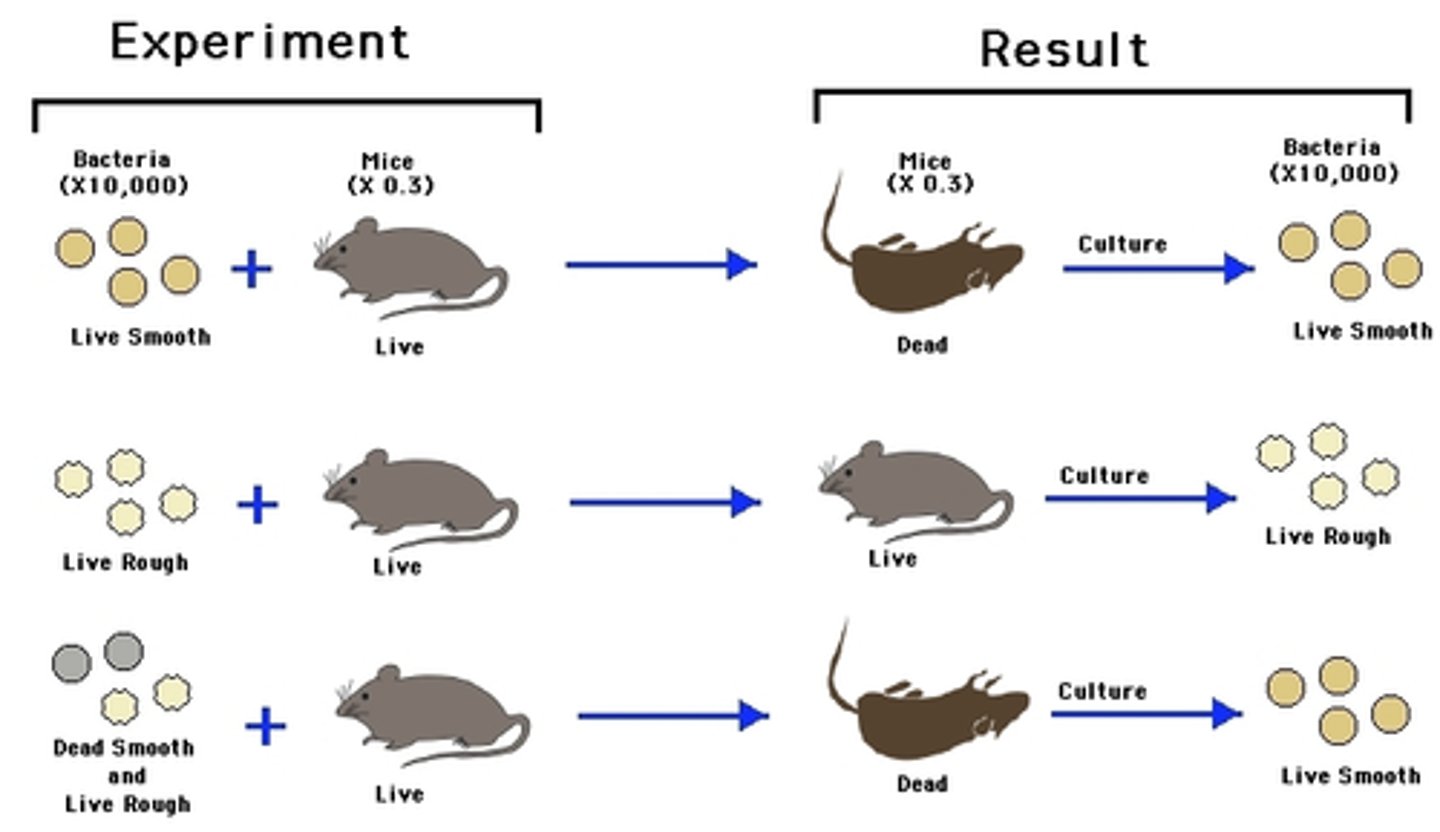
Griffith experiment
experiment in which mice treated with killed S strain (deadly strain) and live R strain (non-pathogenic) caused mice to die. Live S strain was recovered from the mice, and the phenomena was named transformation
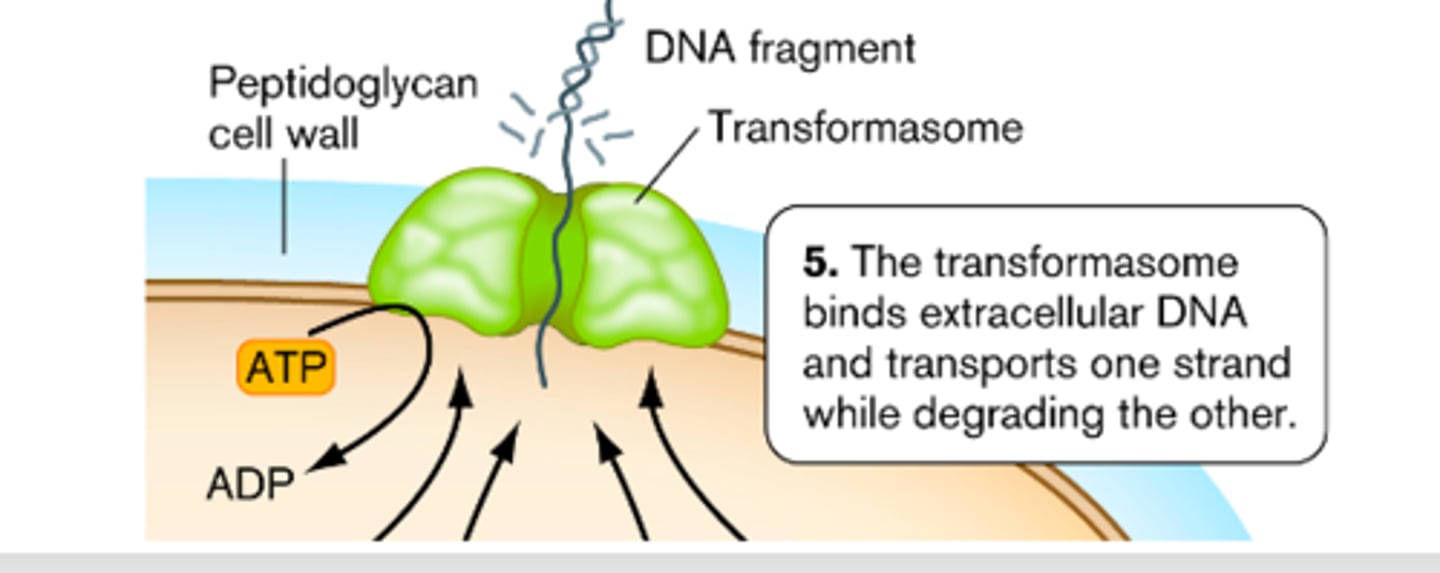
transformasome
a complex formed by Gram-positive bacteria in order to transform bacteria
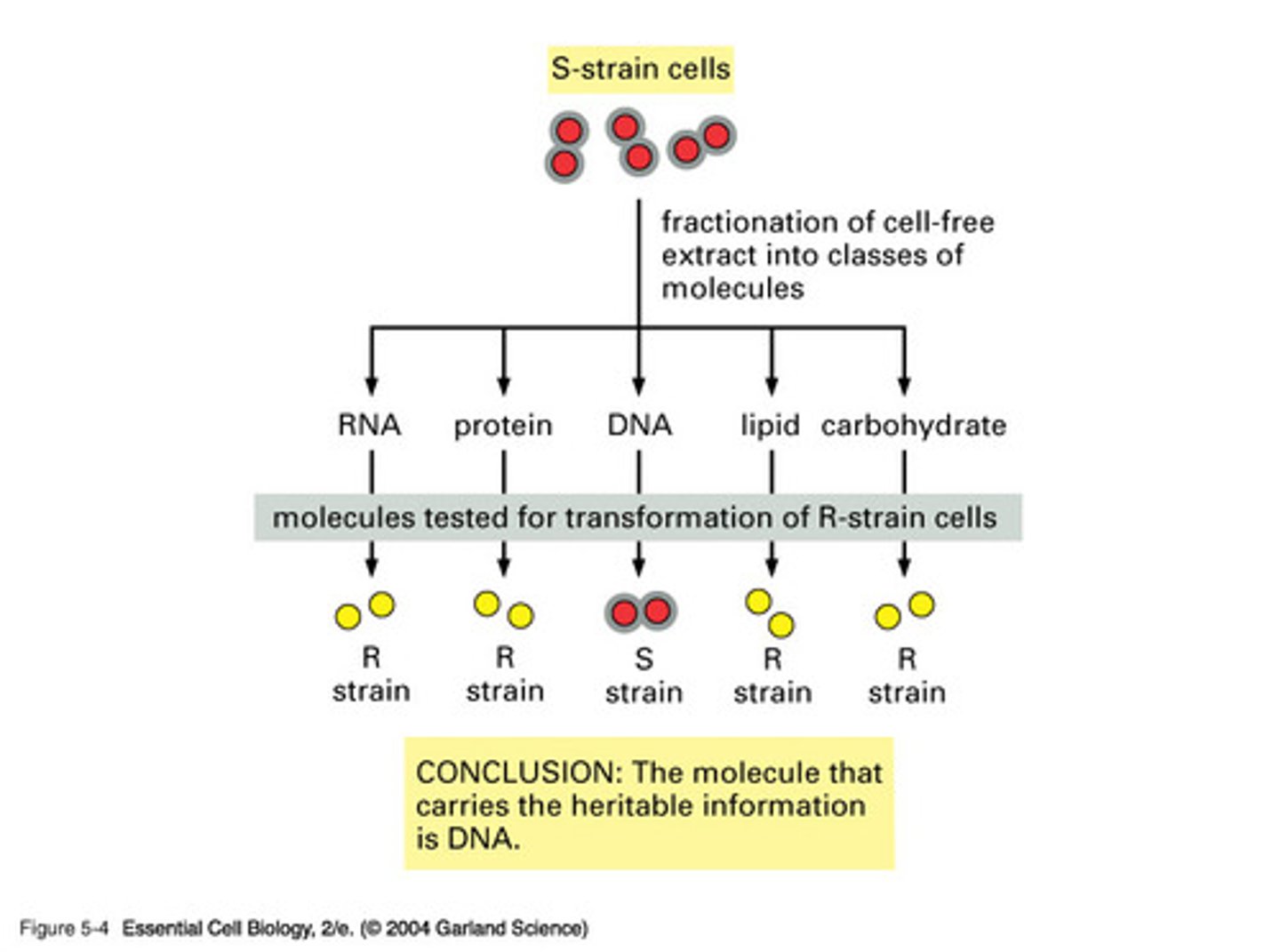
Avery experiment
Experiment in which the transforming material was revealed to be DNA
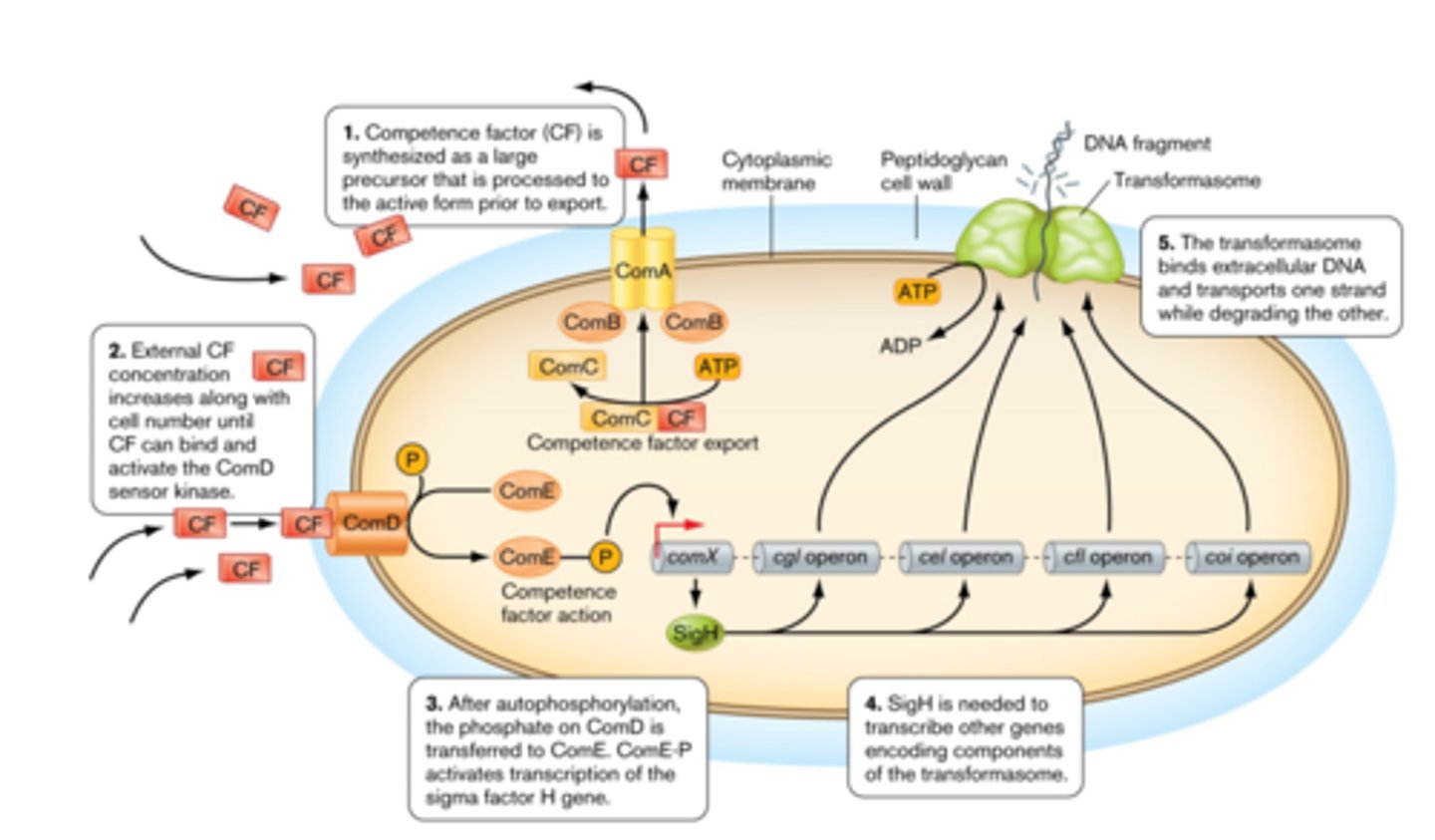
quorum sensing regulated competence
some bacteria become capable of taking up DNA from the environment in response to sensing the presence of other bacterial cells
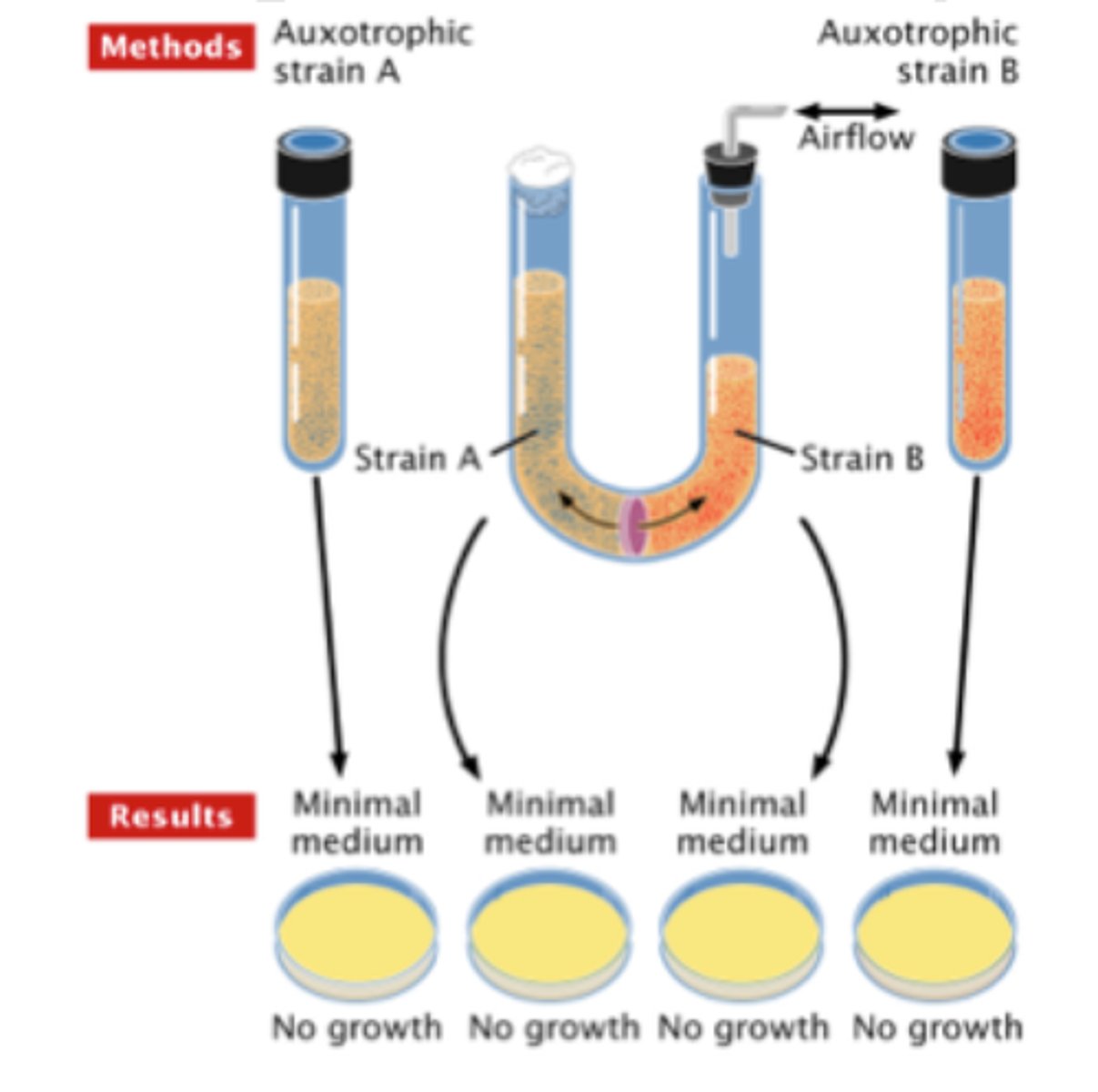
Davis U-Tube Experiment
an experiment that revealed that cell to cell contact was required for conjugation
F factor
A gene contained on a plasmid that allows a bacterial cell which possesses it to synthesize a sex pilus for conjugation
generalized transduction
type of transduction where DNA from any random part of host genome is packaged into the viral host. low efficiency.
specialized transduction
type of transduction where DNA from a specific region of host genome is integrated directly into the viral genome. can be high efficiency.
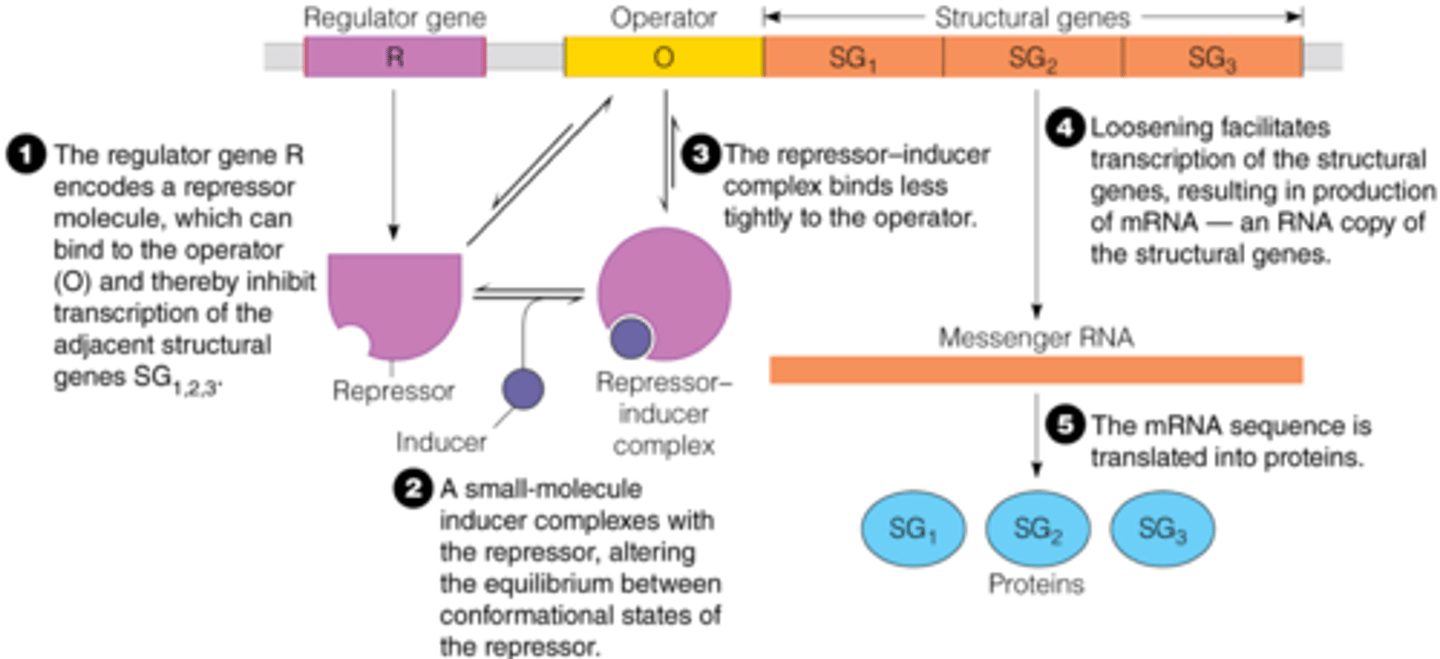
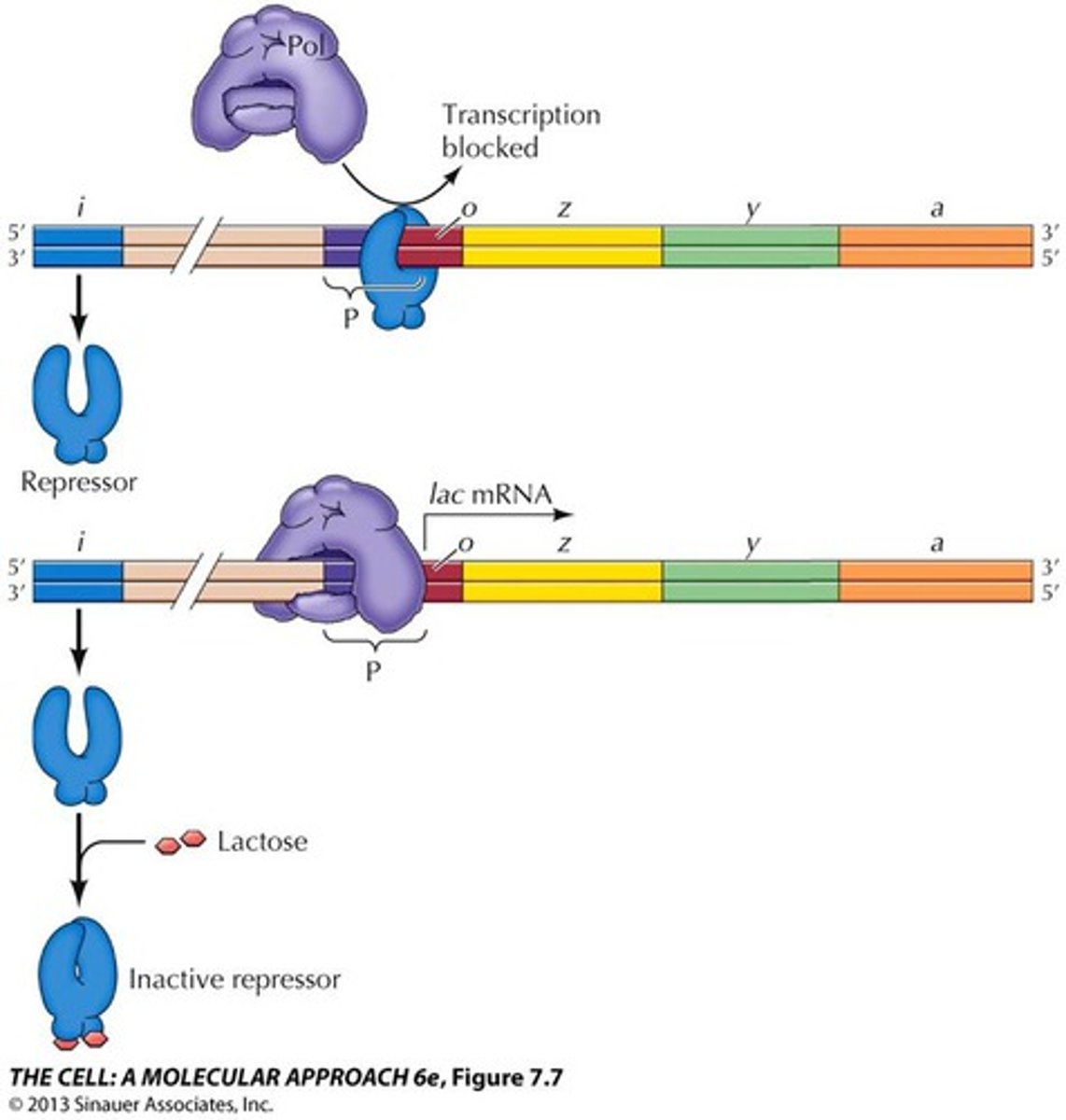
repression
gene control based on negative feedback, once the product of a pathway is made, that product shuts down production of the genes that synthesized it.
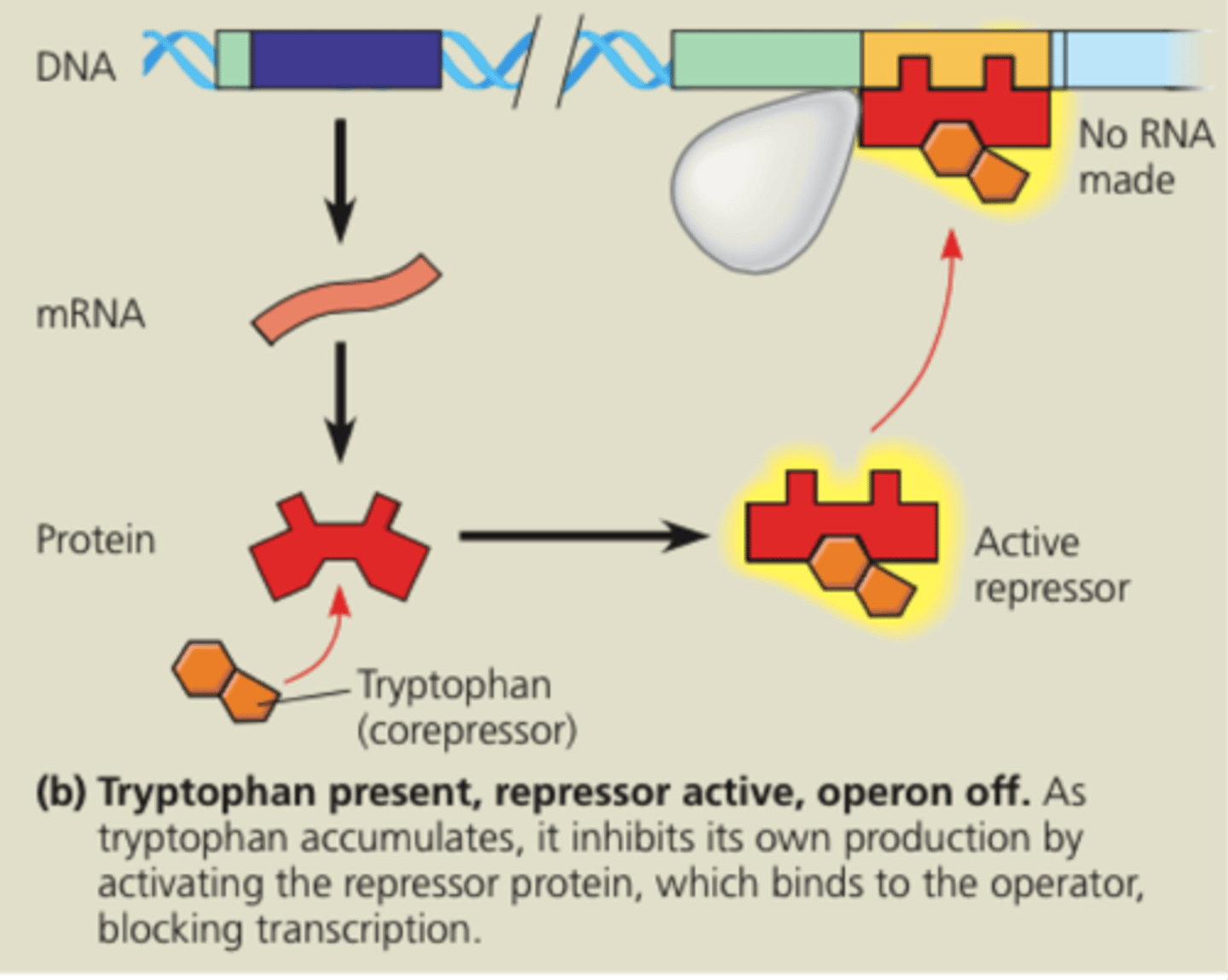
induction
gene control where proteins/enzymes are made in response to the presence of their substrate.
post-translational control
type of control where transcription of gene occurs, translation of mRNA occurs, and then the protein's activity is regulated
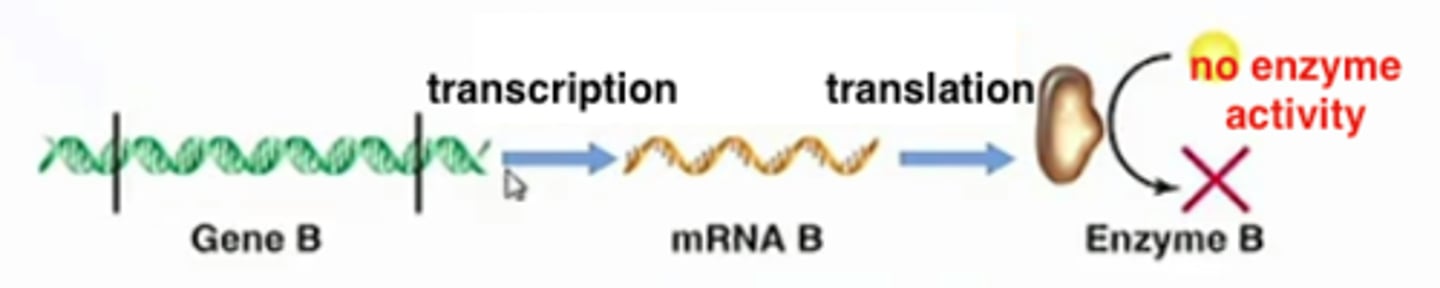
transcriptional control
type of control where gene is not transcribed into mRNA. regulates the amount of protein made.

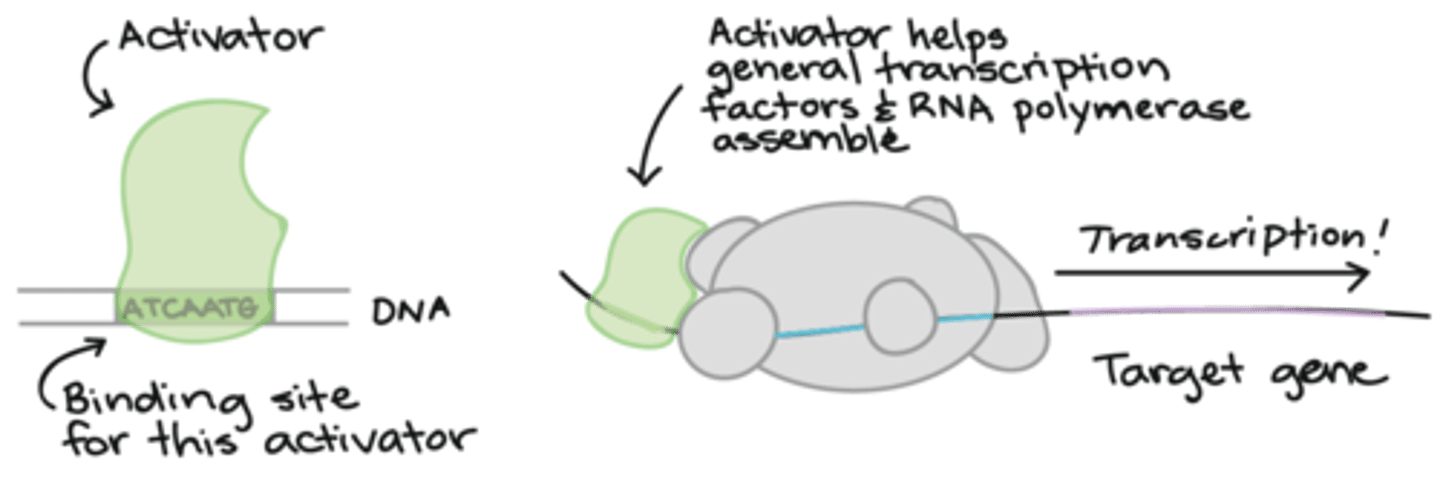
positive control
DNA + protein = transcription is made possible, increased
negative control
DNA + protein = transcription is decreased
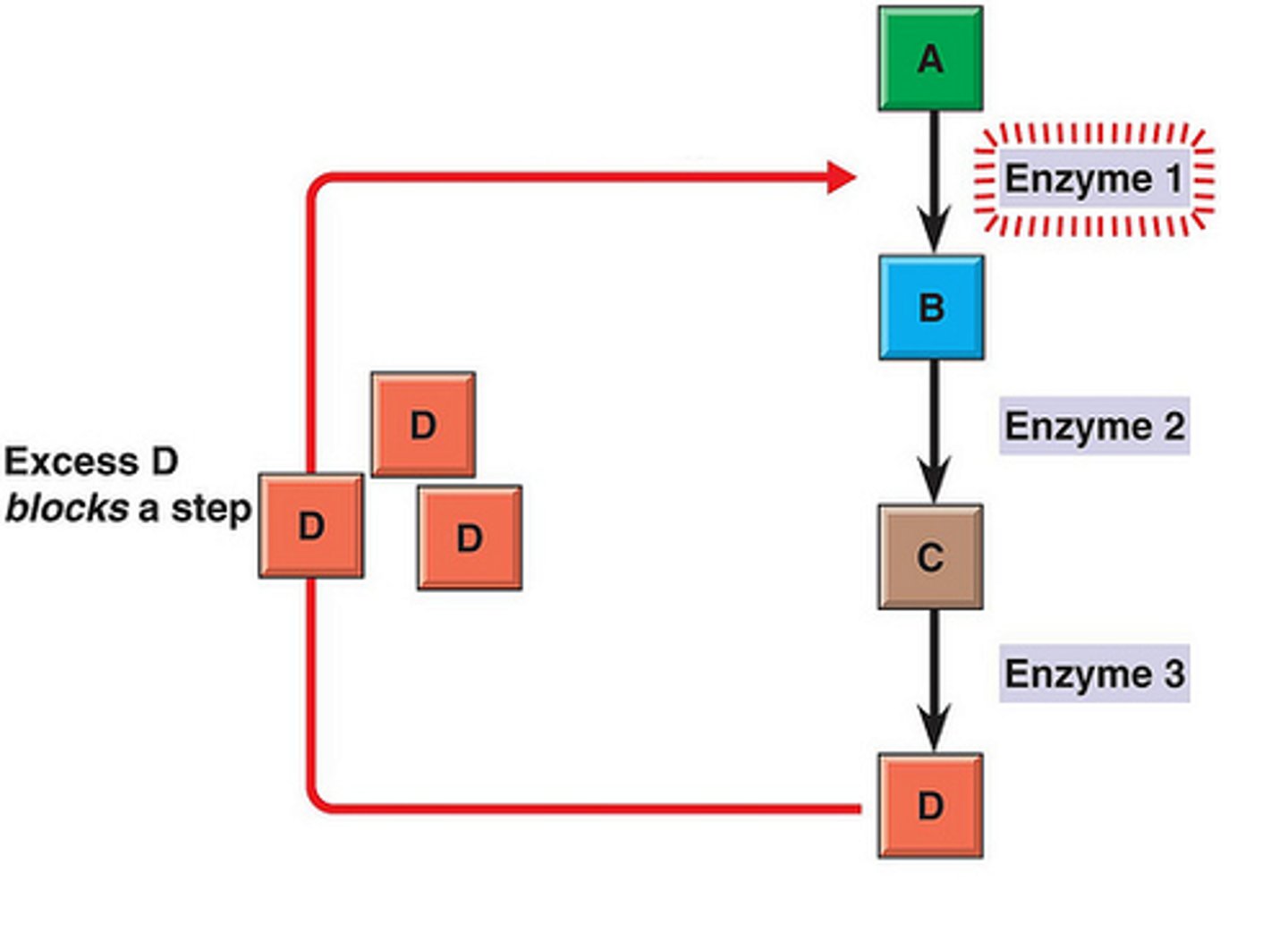
feedback inhibition
type of post-translational modification. once the product of an enzymatic reaction reaches high enough concentrations, it binds to the enzyme and blocks further activity.
repressor
proteins which bind DNA and decrease or prevent transcription
activator
proteins which bind DNA and increase or enable transcription
constitutive expression
gene is transcribed to mRNA, mRNA is translated to protein, and protein is active-- no control is being exerted.
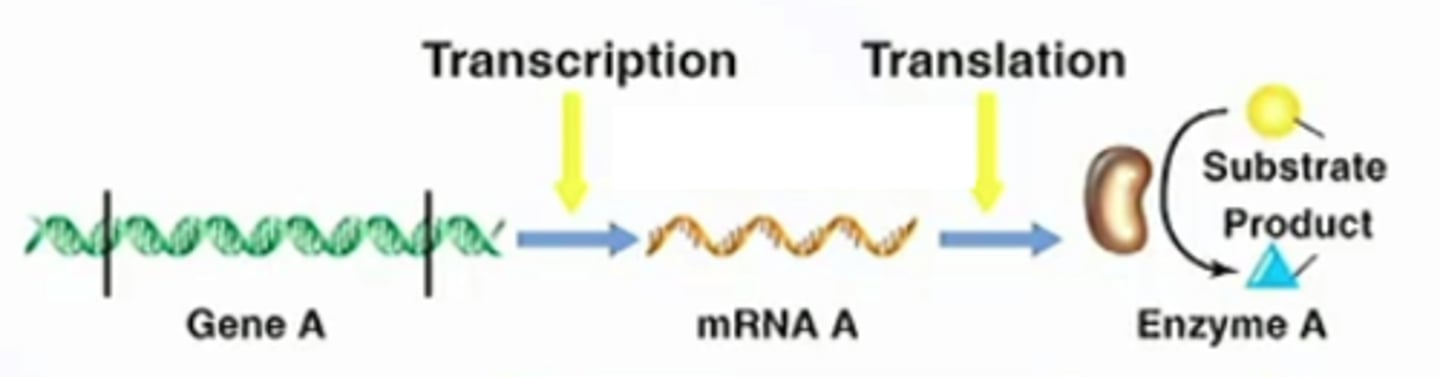
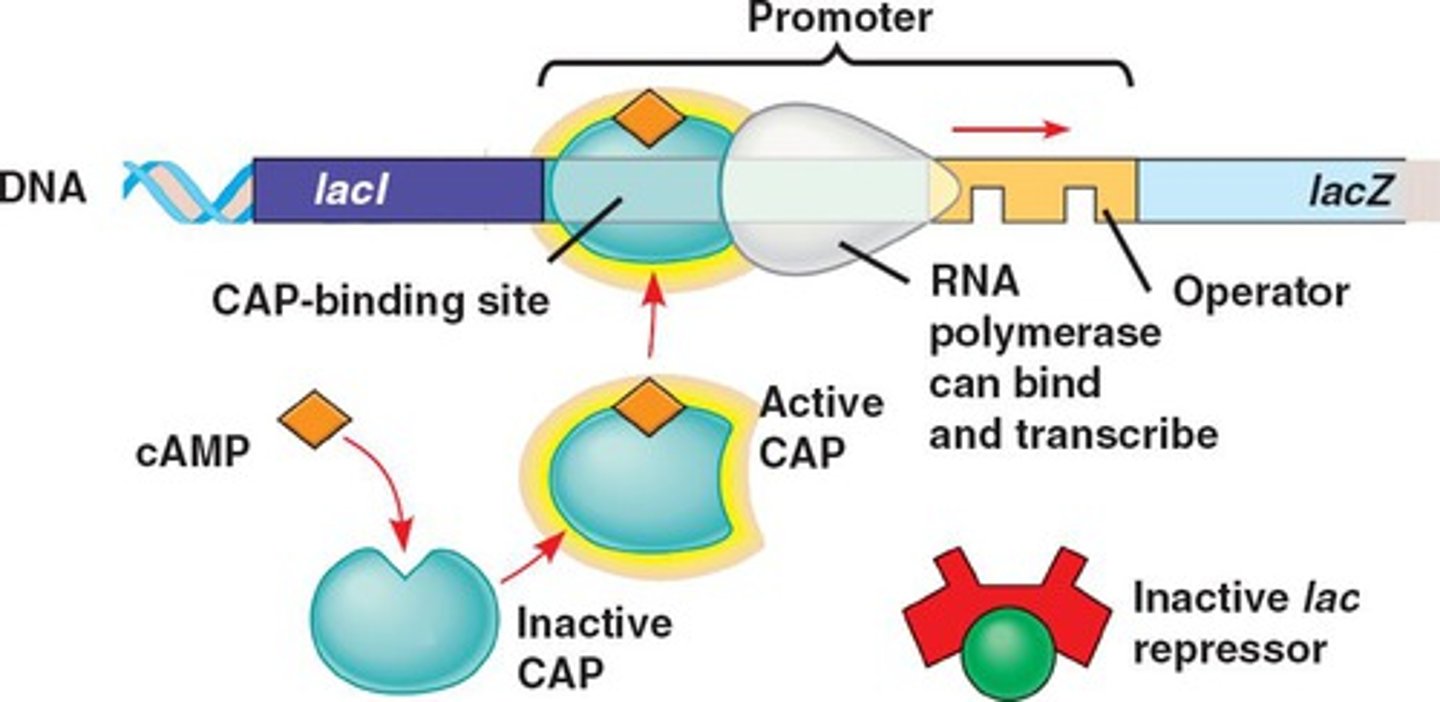
promoter
a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene
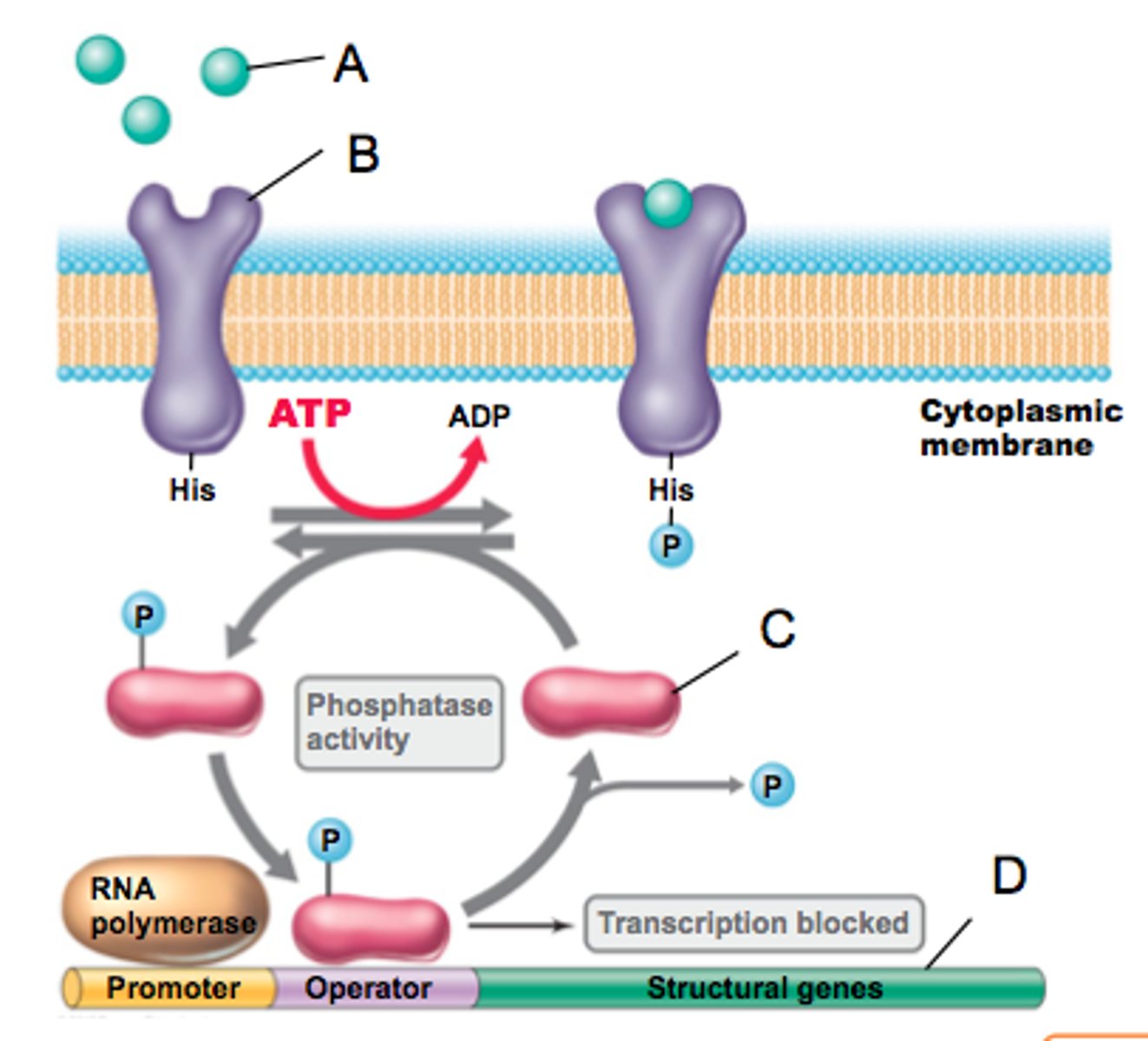
sensor kinase
a protein in a cytoplasmic membrane which serves as a receptor for environmental signals and subsequently activates the response regulator via phosphorylation (B in this figure)
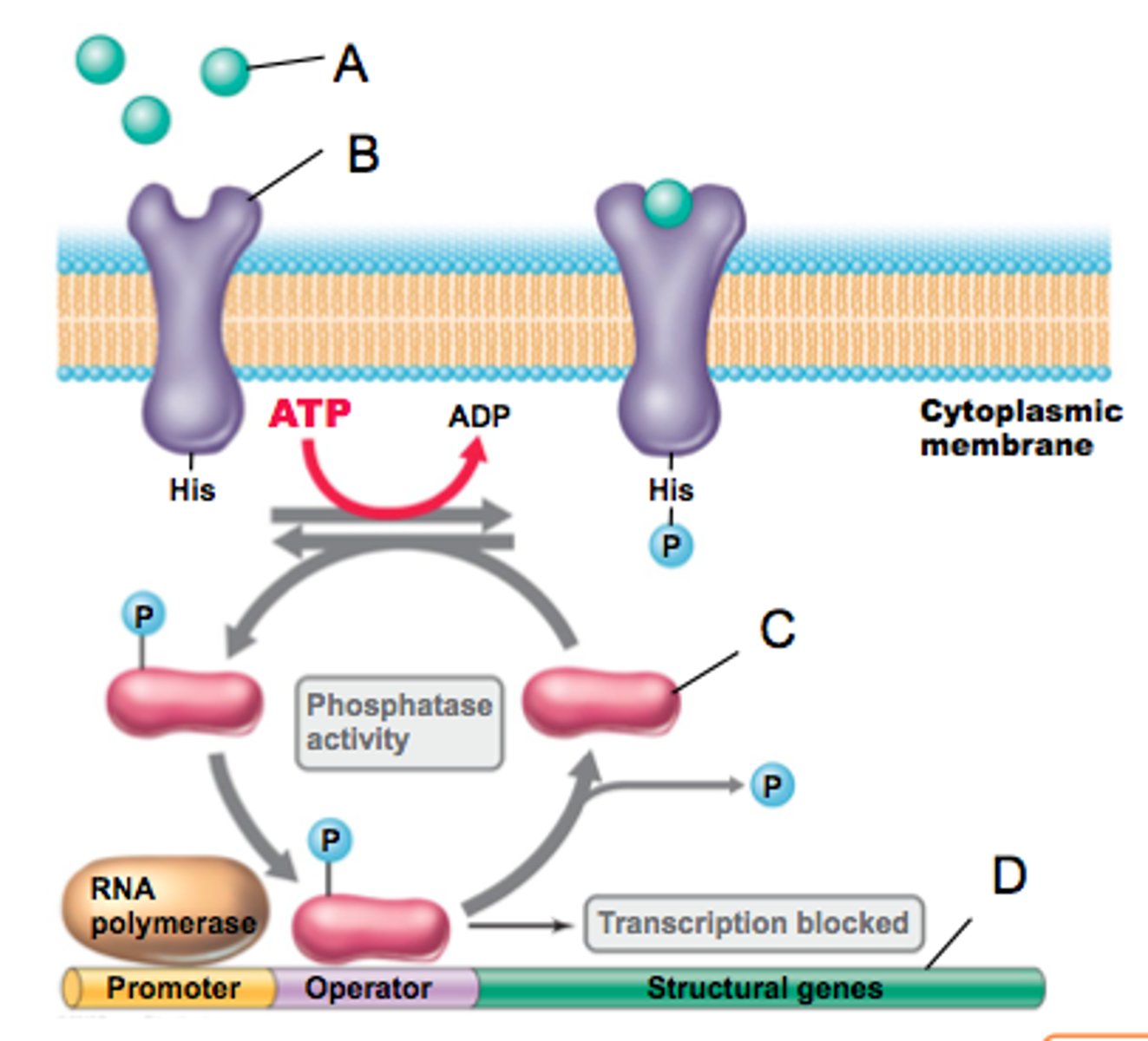
response regulator
protein acted upon by sensor kinase. it binds DNA at operator after phosphorylation to control transcription (can either allow or block transcription) (C in this figure)
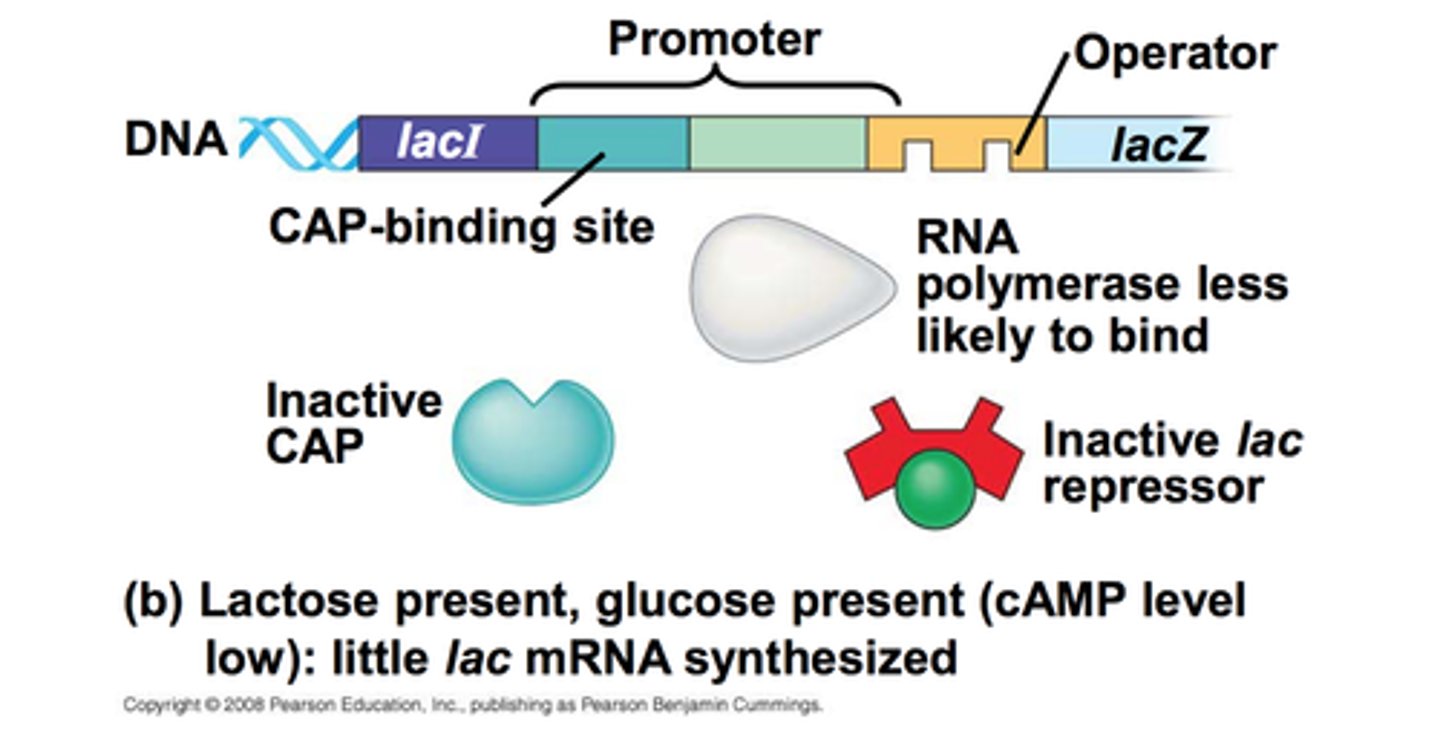
catabolite repression
method for gene expression control which ensures that bacterial cells use up their preferred energy sources first
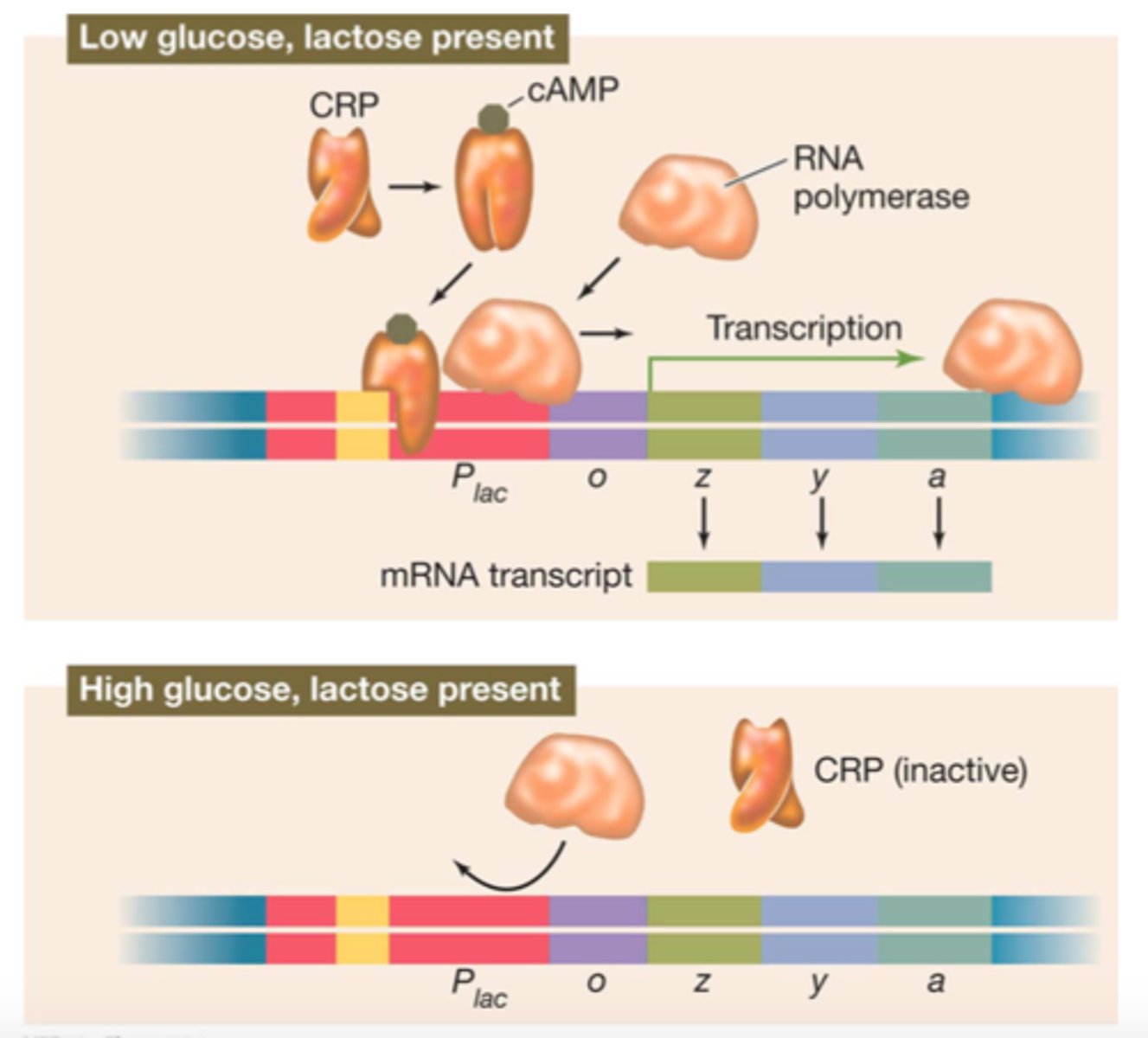
cyclic AMP (cAMP)
regulatory molecule whose concentration is decreased as a cell brings in glucose
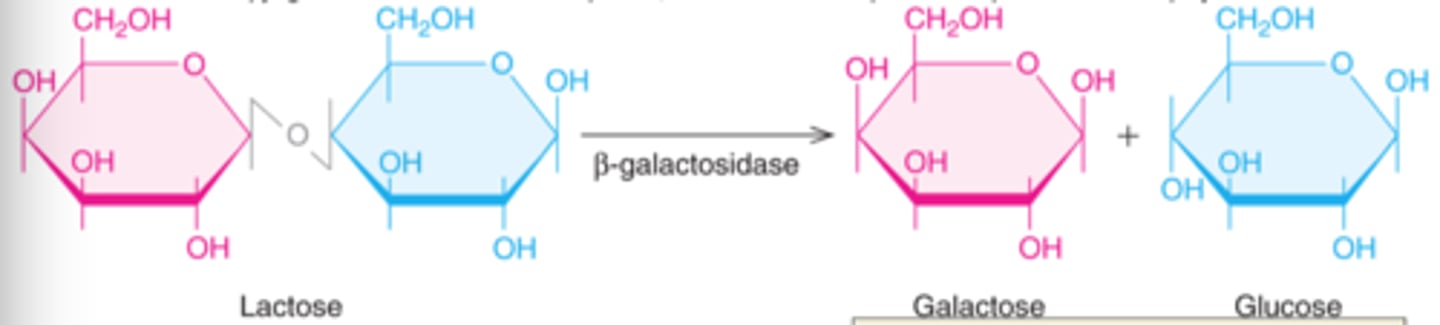
LacZ
The gene that encodes beta-galactosidase, an intracellular protein that breaks down lactose into gluclose and galactose
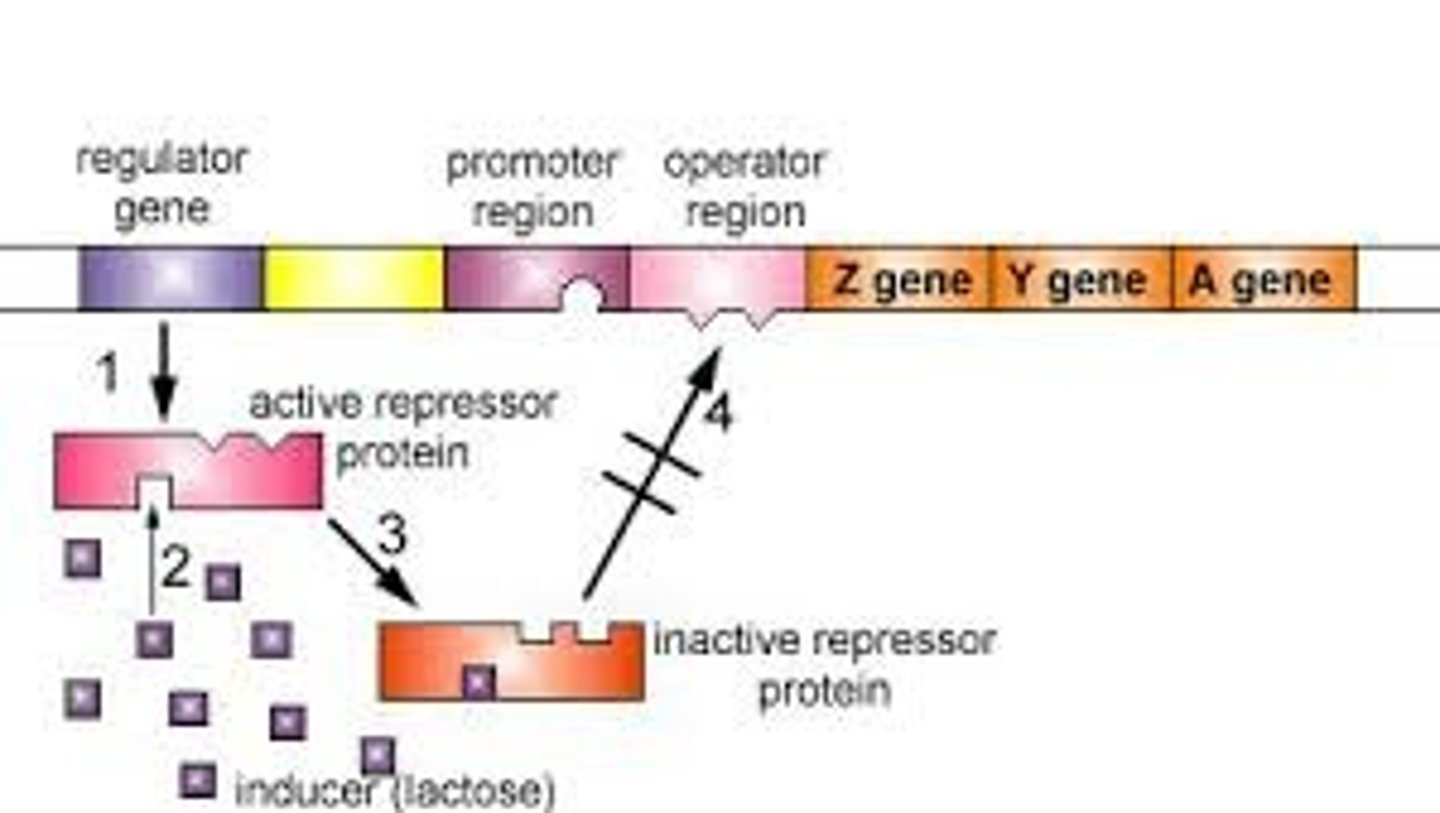
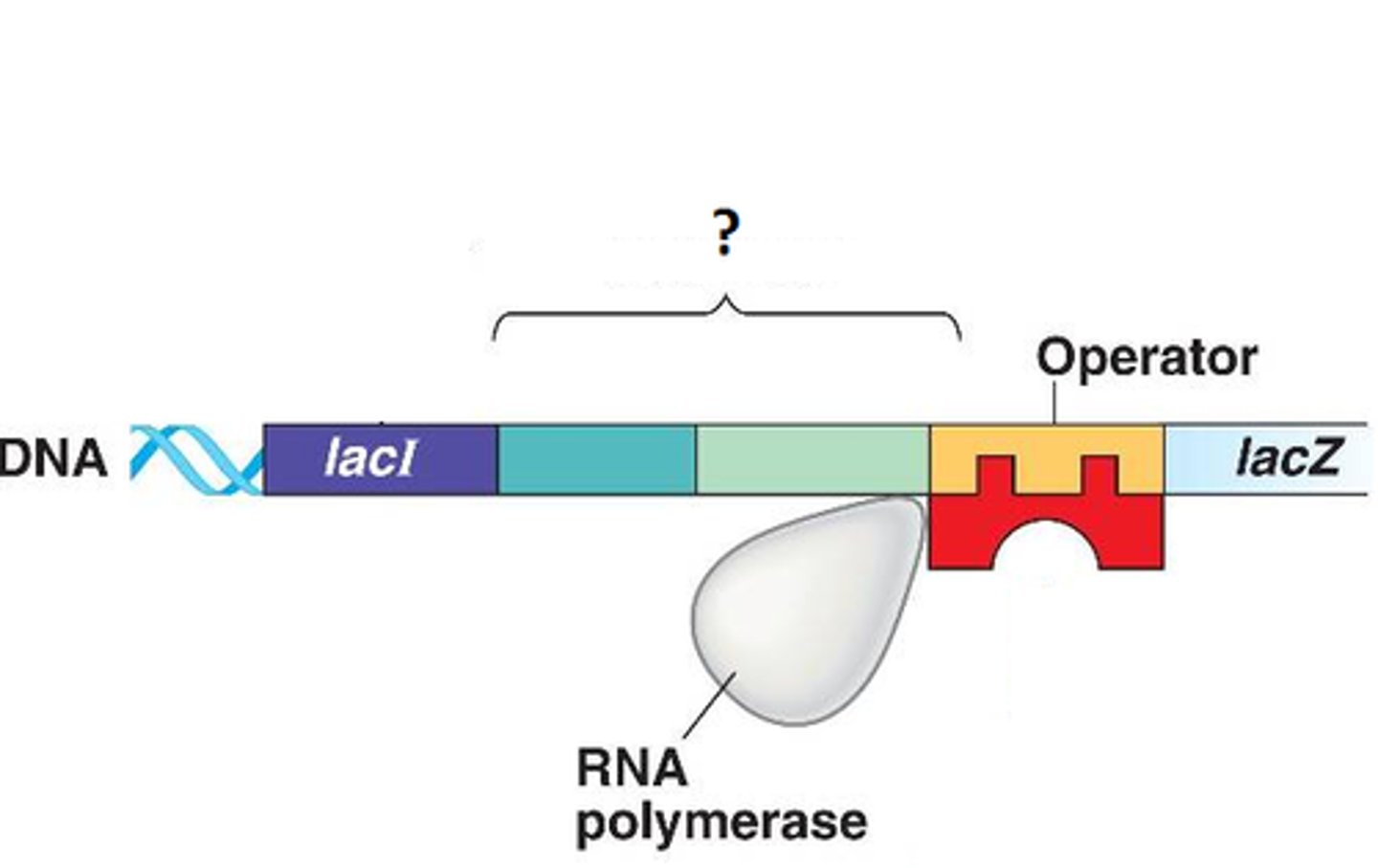
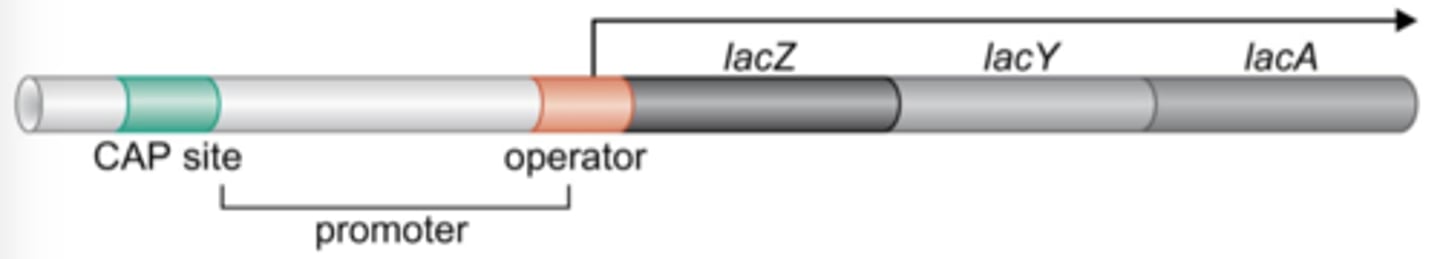
Lac Operon
a number of genes that are grouped together and regulated together related to the use of lactose by E. coli and other bacteria.
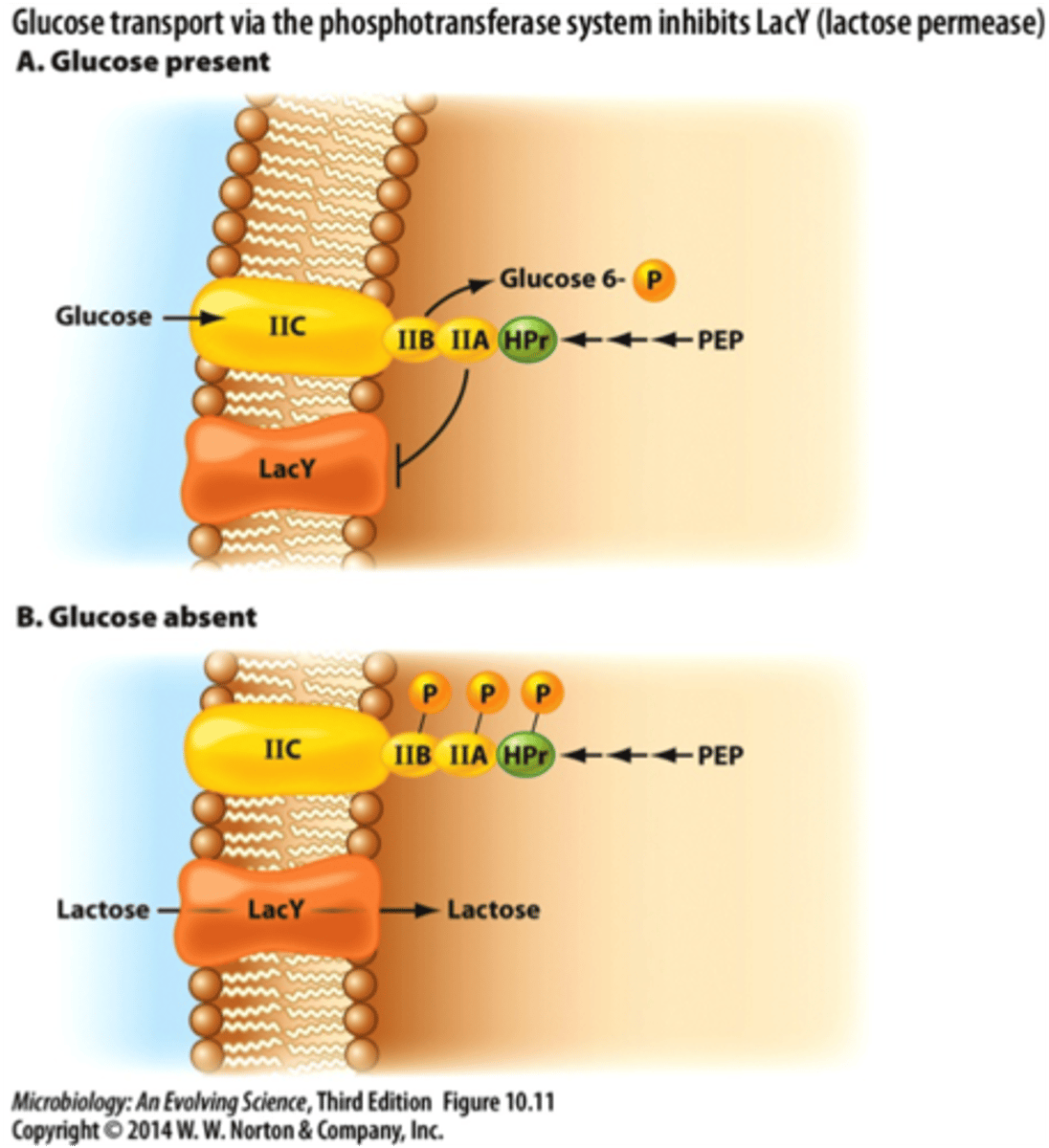
inducer exclusion
method for gene expression control which involves keeping an inducer of transcription out of the cell. Seen in the lac operon, where glucose limits the activity of lacY (permease)
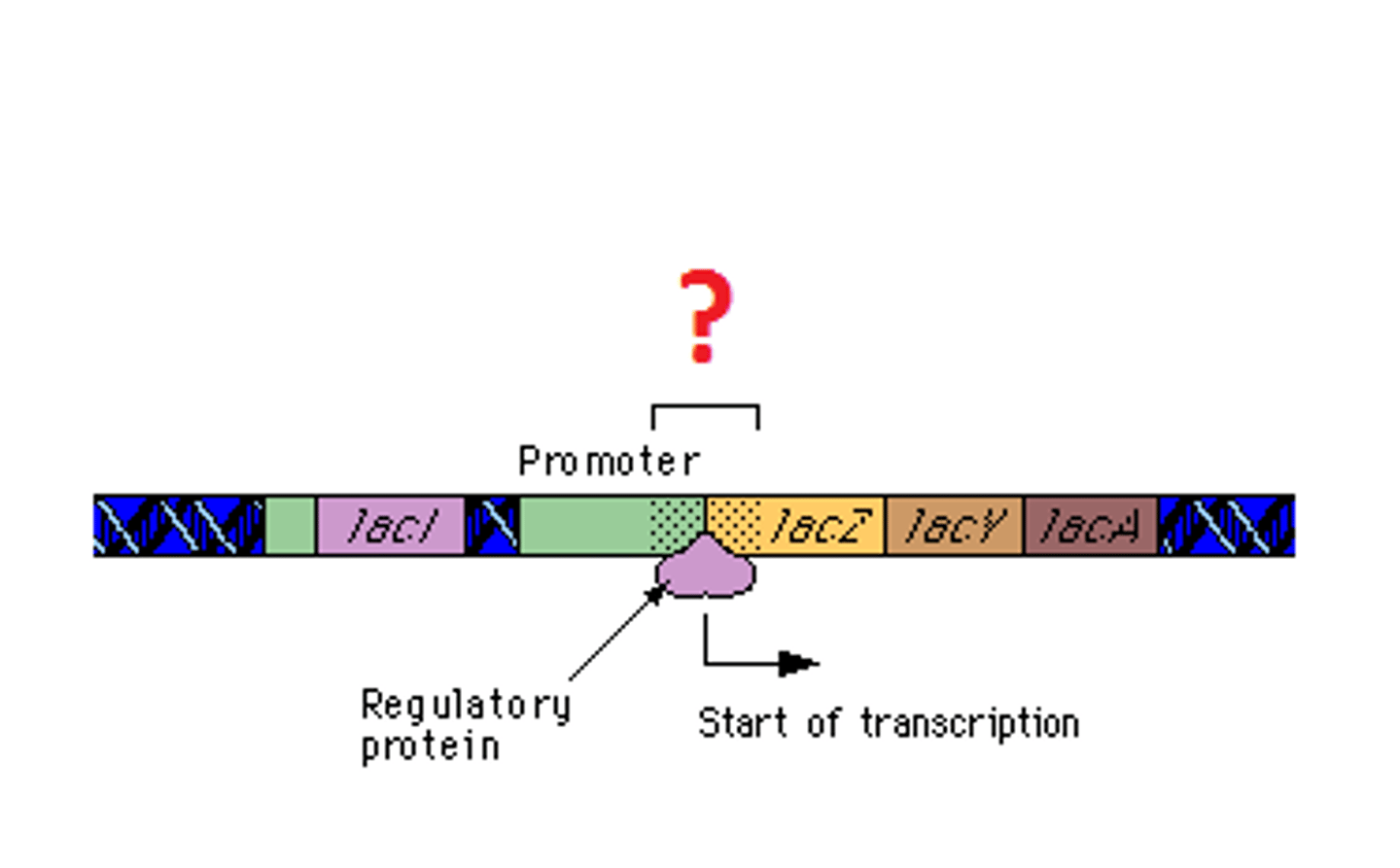
operator
a segment of DNA that a transcription factor binds to in order to regulate gene expression (via repression)
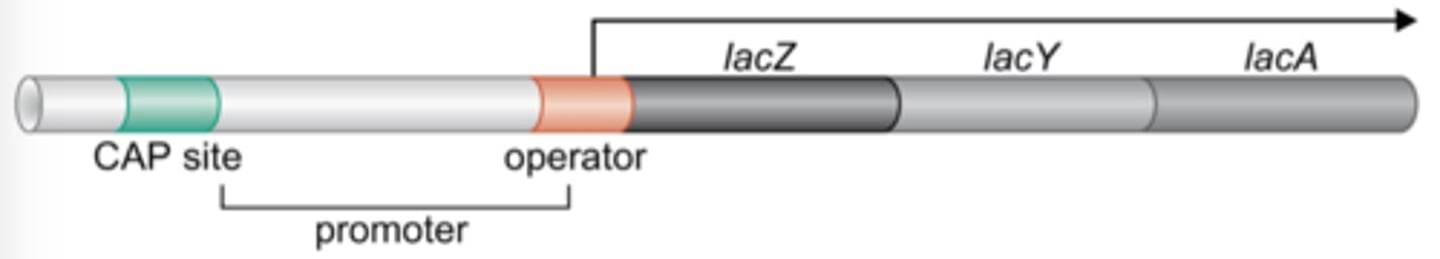
Lac Y
the gene that encodes lactose permease, a membrane bound protein that allows lactose into the cell.
cis-acting elements
changes to DNA itself that alter expression (ex: removing LacO, removing CRP binding site)
trans-acting elements
changes to the proteins which bind DNA that alter expression (ex: removing LacI, removing CRP)