AQA Sociology Methods in Context
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Quantitative data
numerical data
qualitative data
descriptive data
Primary data
Collected first hand by the researcher e.g. field experiments
Advantages and disadvantages of primary data
ADV- gather precise information that they need
DISAV- costly and time-consuming
Secondary data
Collected by previous researchers e.g. school reports
Advantages and disadvantages of secondary data
ADV- quick and cheap
DISAV- may not provide the exact information needed
Theoretical factors of research
Validity
Reliability
Representativeness
Validity
Actually measuring exactly what you intend to measure
Reliability
consistency of measurement
Representiveness
Reflects the characteristics of the population that is being studied
Positivism
Social institutions guiding society
Scientific approach
Prefer quantitative data
Methods with strong reliability
Interpretivism
Individuals interacting and creating the world
Humanistic
Prefer qualitative data
Methods with strong Validity
Aim
Identifies what we hope to achieve, its open-ended so not tied to a particular statement
Interpretivists prefer this as they like to find out what is important to them
Hypothesis
A testable prediction, gives a direction to the research and focus to the question
Positivists prefer as they like to find out the cause and effect
Operationalising concepts
The process of turning a sociological concept into something measurable
The pilot study
A draft version of a study usually questionnaires, to ensure the chosen people are Representative of the whole population we want to study
Sampling Techniques (RSSQSO)
Random sampling
Systematic sampling
Stratified random sampling
Quota sampling
Snowball sampling
Opportunity sampling
Random Sampling
Simple- Pulling names out of a hat or random generator
Stratified- sample frame
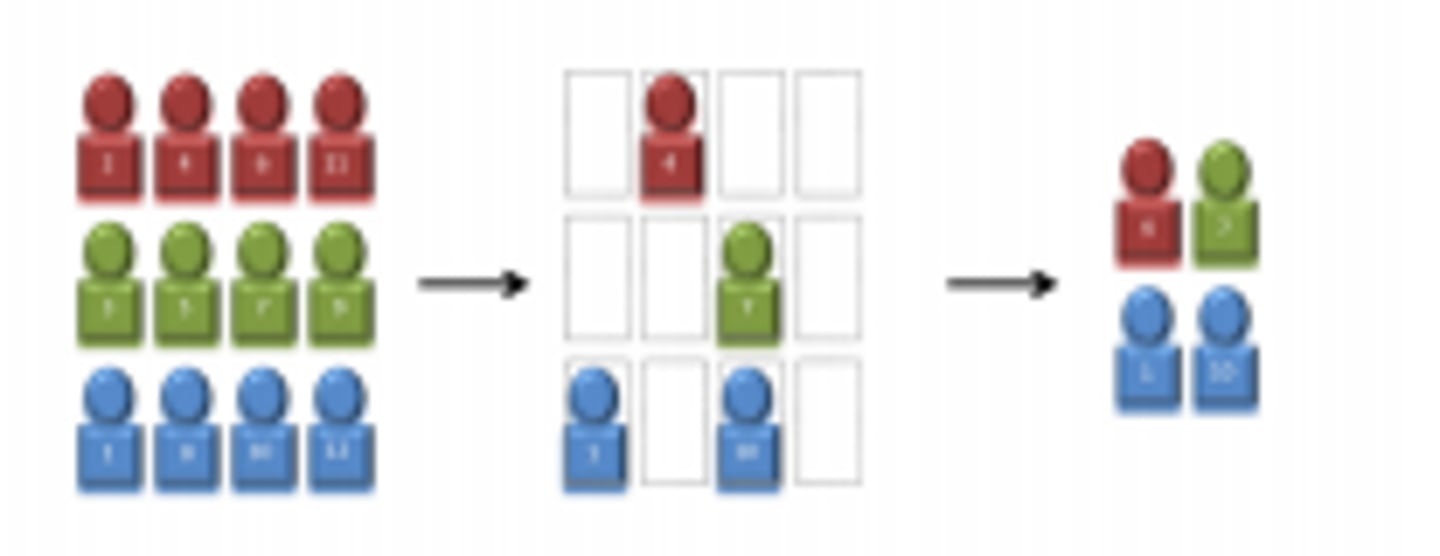
Systematic sampling
selecting names from a sampling frame at regular intervals
Snowball sampling
identifying a person with the desired characteristic and asking them to introduce you to more
Quota Sampling
picking people who fit into specific categories
cluster sampling
clusters of participants that represent the population are used
Oppertunity sampling
Choosing individuals who are the easiest to access
Pupils - Power and Status
-Children have less power than adults making it more difficult for them to state their attitudes openly
-Hierarchical institutions in schools giving teachers power over students
-Sociologists need to think of ways to overcome the power and status differences
-Pupils who resent the power of the teachers may be less likely to cooperate in the research
-On the other hand pupils may feel empowered by getting involved
Pupils- ability and understanding
-Pupils vocabulary, powers of self-expression and confidence are likely to be more limited than adults
-Sociologists will need to word questions carefully to make sure the pupils understand
-Limitations in understanding also makes it difficult to gain informed consent
-Young people use different language to adults
-Young peoples memories are less developed
-Pupils are not homogeneous, they are all different and class, age and ethnic variations create differences
Pupils- Vulnerability and ethical issues
-Young people are more vulnerable to physical and psychological harm than adults
-Consider whether the participation of young people is necessary
-Gain consent from parents teachers AND the pupil themselves who might not understand making it difficult
-Child protection issues= personal data kept private
-Consider stress of participation
-More 'gatekeepers' means it is more difficult to carry out research
Pupils-Laws and guidelines
-Child protection laws such as safeguarding requires researchers to have Disclosure and Barring service checks which may delay research or prevent it
-Ethical concerns, special codes of practice developed for researching young people
-Easy to find target researcher group because they are required to go to school
-Pupils are only in school in term time and for a certain number of hours a day
Researching teachers
Power and Status
Impression management
Teachers - Power and Status
-Teachers have more power and status due to age, experience and responsibility
-They have legal responsibilities for a duty of care
-Nature of the classroom reinforces power and the researcher may be viewed as a 'trespasser'
-Heads, governors, parents and pupils may constrain what the teacher does
-Researcher may have to appear as an assistant teacher
Teachers - Impression Management
-Teachers used to being observed so may be more willing
-'impression management' manipulating the impression others have of us
-Some researchers study teachers in the staff room in their 'backstage' setting
-However a newcomer will be questioned in the staff room due to small spaces
-Teachers may be dishonest or not answer because critical comments could ruin their career
-Head teachers may pick staff who convey a favourable image of the school
Researching classrooms
Closed social setting
Gatekeepers
Peer groups
Classrooms - Closed social setting
-Clear boundaries, less open and highly controlled environment
-Easier to control pupils time, activities, noise and language etc.
-Confined space so straightforward to observe
Classrooms - Gatekeepers
-Headteachers
-Teachers
-Child protection laws
-Difficult to gain access and maintain it
Classrooms - Peer groups
-Sensitive to peer pressure due to insecurities
-Affect how they respond
-Supervise pupils when filling in questionnaires so there is no influence from other students
Researching parents
Parental influence
Access to parents
Impression management
Parents - Parental influence
-How children are brought up
-Involvement in school e.g. parents evenings
-Marketisation policies = parents see themselves as consumers
Parents- Access to parents
-Can't observe how the parents help their children at home
-More difficult to research
-Sending letters/questionnaires home doesn't mean they will complete them
Parents- Impression management
-Parents may present themselves in a positive light
-They may lie about attending parents evenings
Researching schools
Schools own data
The law
School organisation
Gatekeepers
Schools - Schools own data
-Lots of secondary data produced by the schools
-Schools are 'data-rich' and sociologists may be able to make use of some of the resources
-School resources are confidential and it may be hard to gain access
-Some schools may falsify their information if they have problems to maintain a positive image
-Schools also may make changes in the curriculum to improve results and create the image that the school is improving
Schools - The law
-Young people are required to go to school in the law
-The researcher will know where everyone is most of the time or where they should be at given times
-The role of schools is education and the head may see involvement of research as interfering with this
-Schools are required to keep reports of attendance and achievement which is useful to sociologists
-Legal duty of care for students would mean access is restricted
Schools - Gatekeepers
-Headteachers and governors have the right to deny the researcher access to the school if they believe it will interfere or undermine teachers authority
-Some situations and school settings may be 'off limits' to the researcher making it hard to get the full picture
Schools - School organisation
-Schools are formal organisations with rules and hierarchy
-The researcher may be seen to get in the way of the hierarchy e.g pupils may see them as teachers whilst teachers see them as inspectors
-Lots of schools are single sex which may pose problems if the researcher is a different gender to the pupils
-Schools are large and highly organised with timetables which may affect when a study can be carried out for example holidays and exam periods
-Size and complexity could take time for the researcher to 'understand' the school
The researchers experience of education
-Researchers experience of schools can dull their awareness of how different educational environments are from other social settings
-They will have spent years being educated so need to be aware of their taken for granted assumptions
-They are probably successful so may not be able to empathise with those who are not
-The researcher has to be aware their investigations could lead to a wider political and media debate