Conduction disorders pt. 1 - Clin Med
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
What does this refer to “Orderly passage of electrical current sequentially through the heart muscle”
Depolarization
What is the Process allowing the muscle cells of the ventricles to regain their ability to depolarize again
Repolarization
What does this refer to
Cell is more negative inside
Na+ outside/ K+ inside
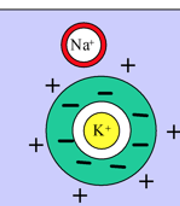
Rest
What does this refer to
Na+ enters
K+ exits
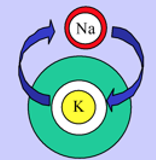
Depolarization (contraction)
What does this refer to
Na+ exits
K+ returns
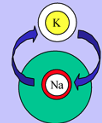
Repolarization (relaxation)
What is the direction of movement of depolarization
Measured in degrees, from 0 (horizontal) to +90 (vertical) and -90 (inverted)
Remember – the ventricles depolarize simultaneously
Contraction = QRS
Look at leads I and aVF
EKG Axis
What does this refer to
Represents an average of the instantaneous electrical charge during the sequence of ventricular depolarization
Movement of electrical charge
Tells us the average direction of the depolarization wave
Spreading wave of electrical activity in the heart
Causes ventricular activation
QRS Axis
What does this refer to? R>S
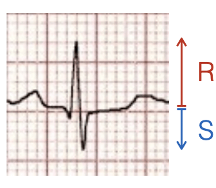
Positive
What does this refer to ? R = S
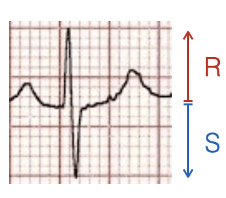
Equiphasic
What does this refer to S > R
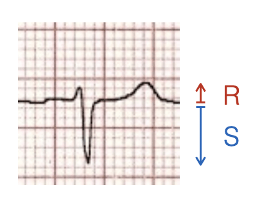
Negative
What is the Axis if Lead 1 is positive and aVF is positive
Normal
What is the Axis if Lead 1 is positive and aVF is negative
LAD
What is the Axis if Lead 1 is Negative and aVF is positive
RAD
What is the Axis if Lead 1 is negative and aVF is negative
Extreme RAD or extreme LAD
What does this refer to
Normal variant in young, healthy people
Often due to changes in vagal influence on the sinus node
Irregularity of the normal heart rate
Variation in the PP interval of > 120 ms
Sinus arrhythmia
What does this refer to
Heart rate slower than 60 beats per minute
May be due to vagal influence on the SA node
May be due to organic disease of the sinus node
Significance
Young people?
Elderly?
Severe bradycardia
AV node or Bundle of His take over
Rates 35-60
Sinus Bradycardia
What does this refer to

and TSH
Workup for Sinus Bradycardia
What does this refer to
Event monitoring
What are you looking at
Loop recorder
What does this refer to
Varies based on etiology BUT important question to ask is MEDICATION LIST?
May be as simple as stopping a medication that has SE of bradycardia OR
May require pacemaker or other device
Clinical management of Sinus Bradycardia
What does this refer to
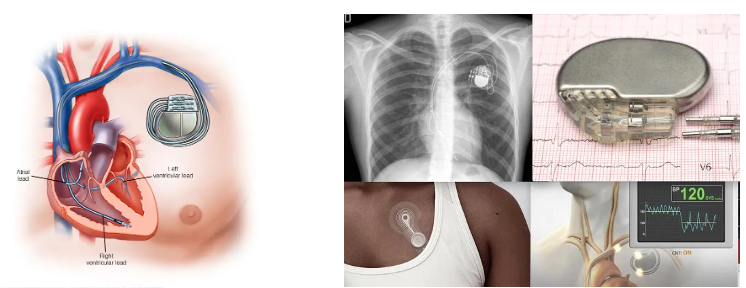
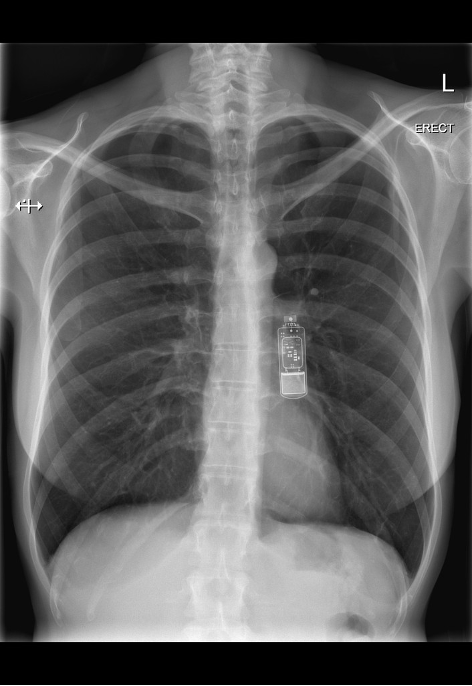
Pacemaker
What does this refer to
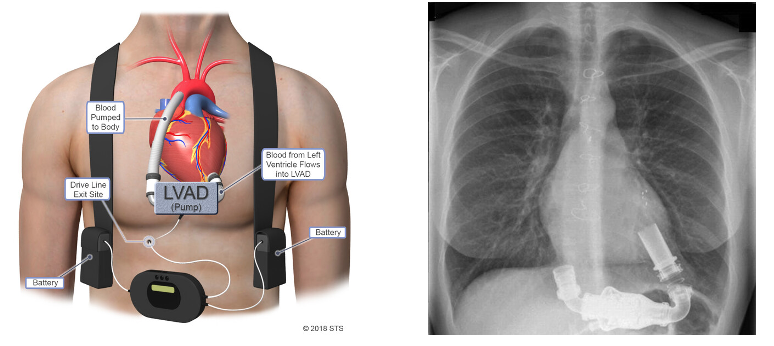
Left ventricular assist device (lvad)
What does this refer to
Heart rate faster than 100 beats per minute
Due to rapid impulse formation from the SA node
In line with physiologic demands —> appropriate
Inappropriate
Sinus Tachycardia
What does this refer to

Appropriate tachycardia triggers
What does this refer to
Sensation of a rapid heartbeat (palpitations), which may be uncomfortable
Shortness of breath
Dizziness
Fainting
Chest pain
Anxiety
Headaches
Decreased ability to exercise
Clinical history of Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia
What does this refer to
EKG
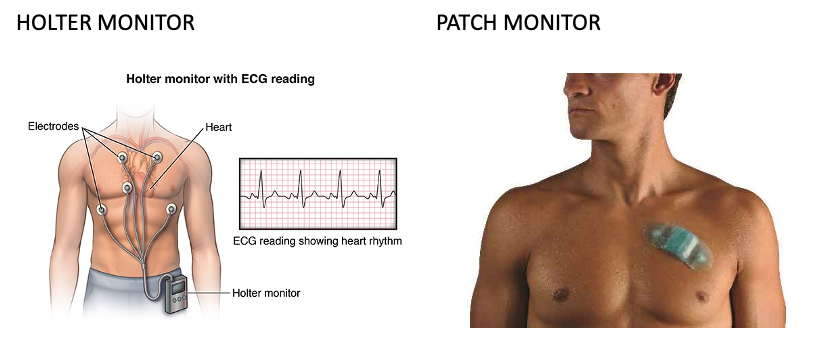
Continuous monitoring of the heart rhythm (Holter/patch)
CBC w. diff, CMP, thyroid panel
Echocardiogram
Chest X-ray
Workup for Sinus Tachycardia
What does this refer to
Eliminate potential triggers or stimulants —> lifestyle changes
Beta-blockers
Metoprolol 1st line
Catheter ablation
Refractory cases - persistent symptomatic inappropriate sinus tachycardia despite optimal pharmacologic therapy, radiofrequency catheter ablation
Rarely performed
Clinical management of Sinus tachycardia
What does this refer to
Not a specific disease, but rather a group of signs or symptoms + EKG changes that indicate the sinus node, the heart's natural pacemaker, is not functioning properly
Bradycardia
Sinus pauses
Sinus arrest
Sick Sinus Syndrome
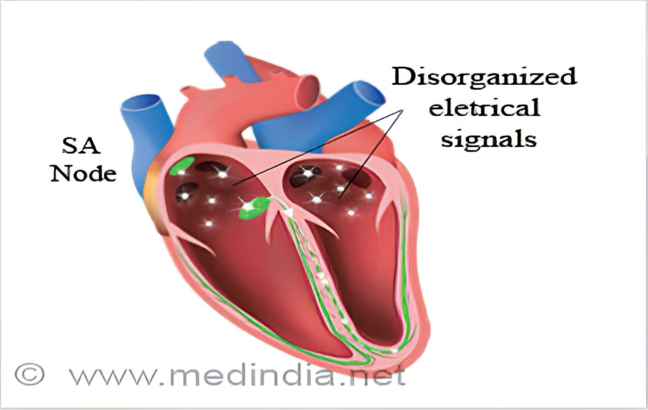
What does this refer to
Sick Sinus Syndrome
What does this refer to
Occurs as a result of disease in the sinoatrial (SA) node
May cause tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome
Rate varies from fast to slow and back again
May manifest as syncope
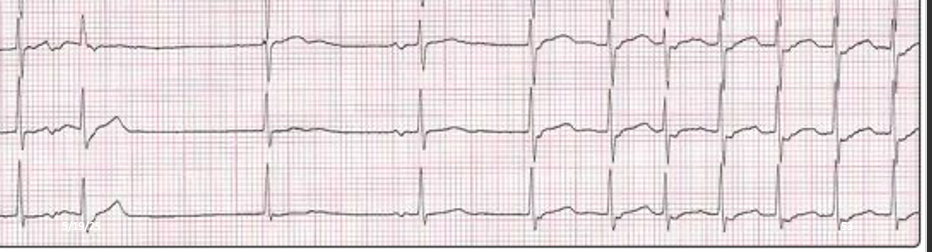
Sick Sinus Syndrome
What does this refer to
Age greater than 65
1/600 patients
Accounts for one-half (1/2) of all pacemaker implantations
Epidemiology Sick Sinus Syndrome
What does this refer to
Sinus Node Disease
Scarring
Etiology of Sick Sinus Syndrome
What does this refer to
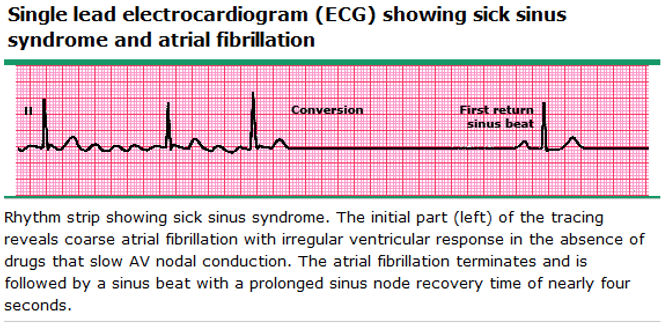
Periods of inappropriate, and often severe bradycardia
Sinus pauses, arrest, and sinoatrial (SA) exit block with, and often without, appropriate atrial and junctional escape rhythms
Failure of escape pacemakers may lead to symptoms including syncope
Alternating bradycardia and atrial tachyarrhythmia in over 50% of cases
Atrial fibrillation is most common
Atrial flutter and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (ie, due to atrial tachycardia) may also occur
EKG of Sick Sinus Syndrome
What does this refer to
Sick Sinus Syndrome (no consistent P waves)
What does this refer to
Sick Sinus Syndrome
What does this refer to
Fatigue
Lightheadedness
Palpitations
Presyncope/syncope
Clinical history of Sick Sinus Syndrome
What does this refer to
CBC w/ diff
CMP
Magnesium
Cardiac biomarkers and EKG
CXR
Echocardiogram
Stress Test
Left heart cath
Workup for Sick Sinus Syndrome
What does this refer to
Cardiology referral
Holter Monitor
Event Recorders
Clinical intervention of Sick Sinus Syndrome
What does this refer to
Remote monitoring
Records electrical activity of the heart
Sx should correlate with arrhythmias
Event recorders for Sick Sinus Syndrome
What does this refer to
No tx for asx patients
Bradycardia
Atropine
Emergent tx for symptomatic patient
Chronic bradycardia
Pacemaker
Tachycardia
Beta-blockers OR CCB
Antiarrhythmic if symptomatic
Clinical Management of Sick Sinus Syndrome
What does this refer to
____________
Extra heart beat
Originates in the atria
P wave is present and the QRS is narrow
P wave usually has a different morphology from sinus node beats
Premature Atrial Contraction (PAC)
What does this refer to
_____________________
Extra heart beat
Begins in either the Right or Left Ventricle
Also known as
Ventricular Premature Beats
Extrasystoles
Premature Ventricular Complexes
Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC)
What does this refer to
1-4% of the general population
More common (up to 69%) of patients 75 yo or older
MC African Americans with HTN
Males > Females
Epidemiology of Premature Beats
What does this refer to
Alcohol/Tobacco/Illicit drug use
Anemia
Anxiety
Caffeine
Exercise
Heart disease/Hypertension
Some medications → decongestants
Hypercalcemia/Hypokalemia
Hypomagnesemia
Etiology of Premature Beats
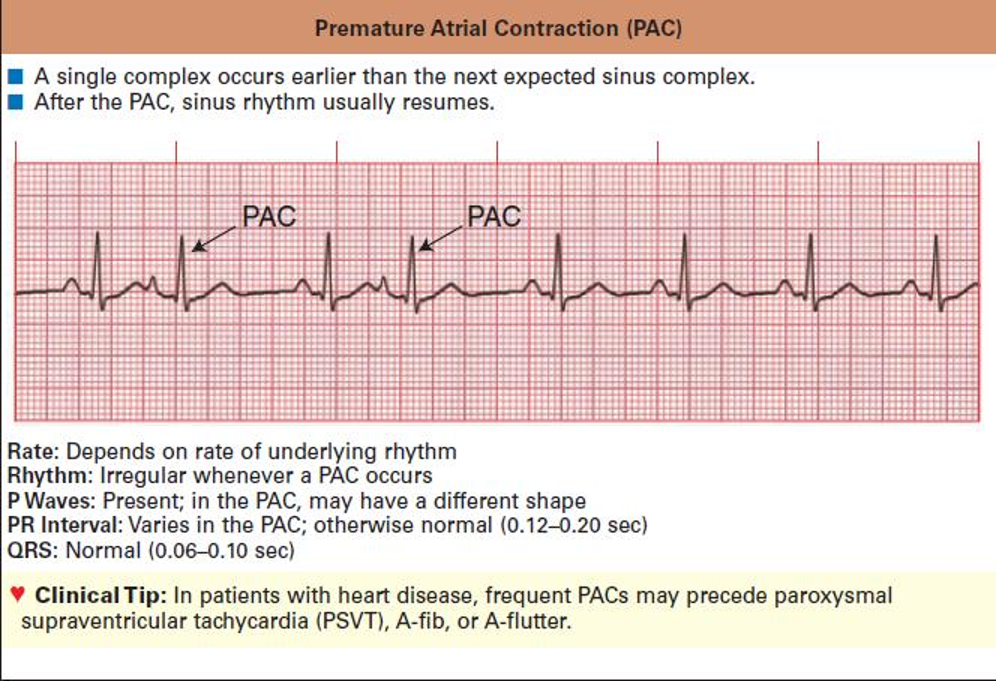
What does this refer to
Premature Atrial Contraction (PAC)
What does this refer to
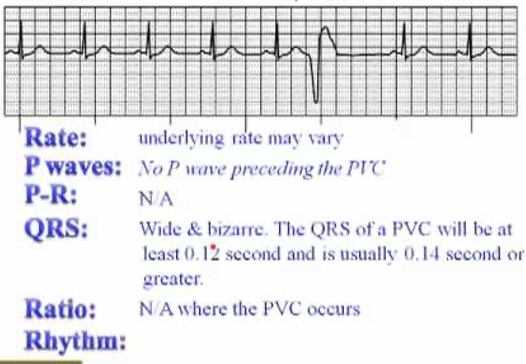
Premature ventricular complex
What does this refer to
Characterized by Frequency
Isolated
Bigeminy
Trigeminy
“Runs of V-Tach”
Characterized by location of origin = morphology
Monomorphic PVC
Polymorphic PVC
Classification of Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVC)
What does this refer to
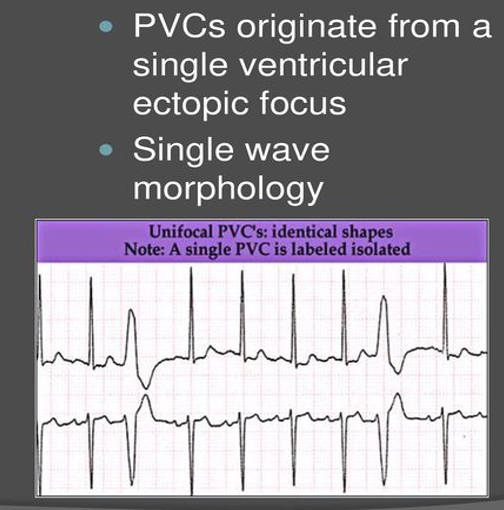
Monomorphic PVC
What does this refer to
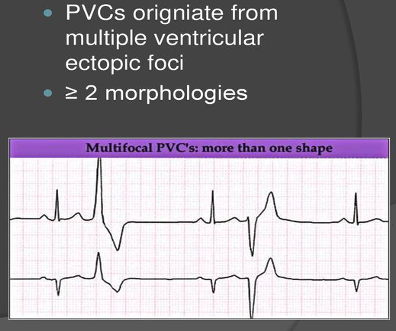
Polymorphic PVCs
What does this refer to
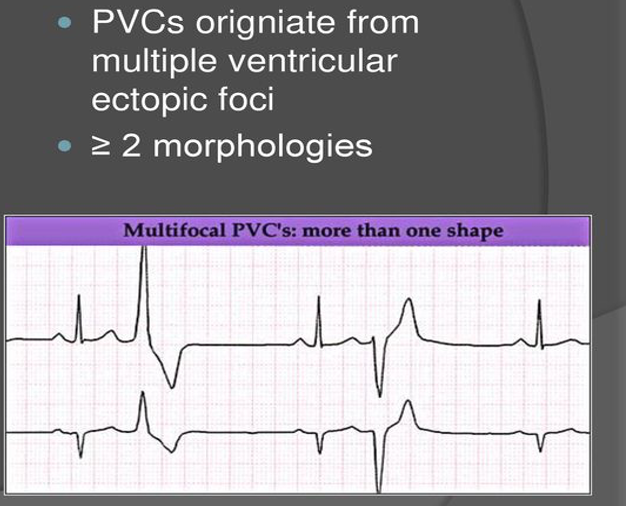
Polymorphic PVC
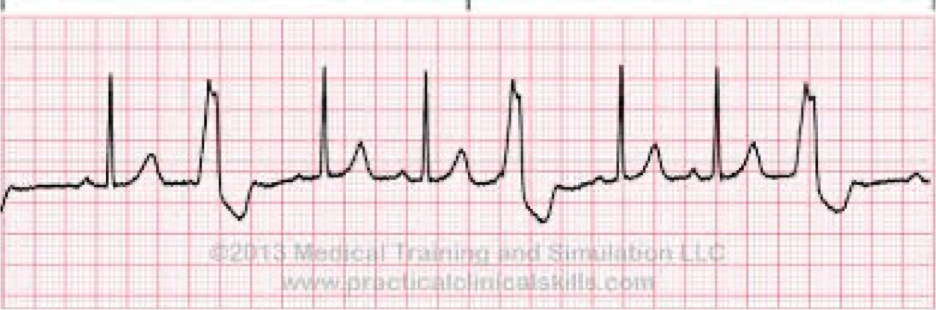
What does this refer to
Trigeminy PVC
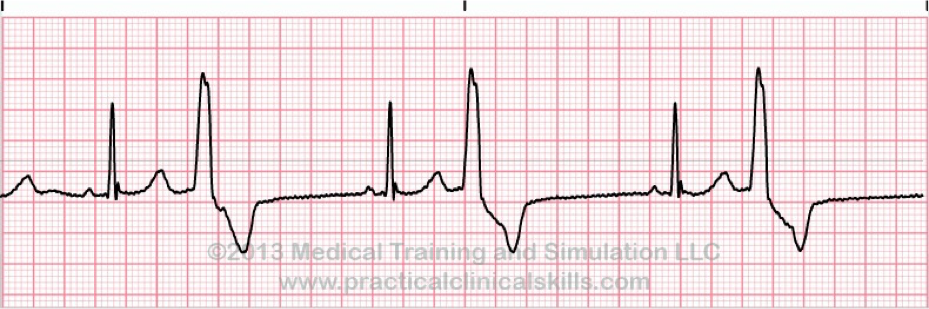
What does this refer to
Bigeminy PVC
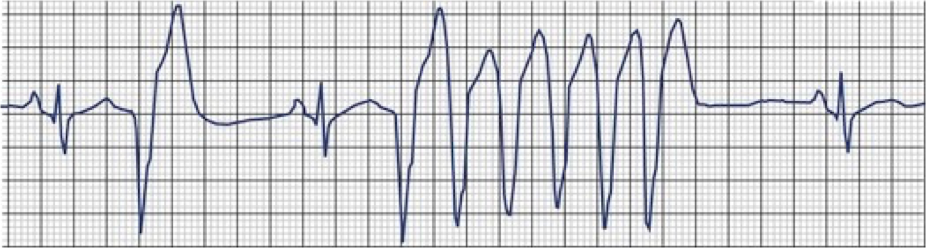
What does this refer to
Run of V-tach (VT) PVC
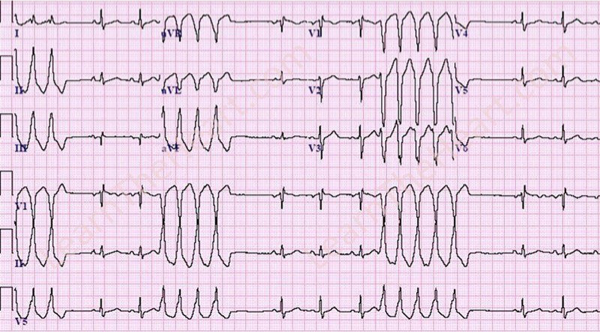
What does this refer to
Non-sustained V-tach
What does this refer to
Skipped beat/Palpitations
Lightheadedness
Chest Pain
Near Syncope
Generalized fatigue
Clinical history of Premature beats
What does this refer to
May be symptomatic if increased frequency of PVCs
Pale
Diaphoretic
Occasionally irregular heart rate
Physical exam for Premture Beats
What does this refer to
12 lead EKG
CBC with Diff
CMP
Cardiac Biomarkers
Drug Screen
CXR
Holter Monitor
24-48 hours
Workup for Premature Beats
What does this refer to
Elimination of triggers
Caffeine/Alcohol/Drugs
Electrolyte Replacement
Antiarrhythmics
Beta-blockers
Calcium Channel Blockers
Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation
Clinical management for Premature beats
What does this refer to
In the absence of severe heart disease/Morbidities
Excellent recovery/prognosis
Asymptomatic with decreased EF have 3.5% increased incidence of sudden cardiac arrest/death
Prognosis of Premature beats
What does this refer to
“If the R is far from P”
1st degree AV Block
What is the max the distance of R and P should be
0.20
What does this refer to
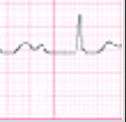
First degree block
What does this refer to
A 20-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for an annual exam.
He is currently feeling well but has some concerns since he occasionally has palpitations.
Medical history is unremarkable and he takes a daily multivitamin.
He denies any alcohol or smoking history.
Family history is significant for his paternal grandfather expiring from a fatal arrhythmia.
He is a college student and part of the school's basketball team, which he continued since he was a student in high school.
He says that his caffeine intake has increased in these past few weeks due to upcoming final examinations.
He is requesting an electrocardiogram (ECG) to ensure his heart is healthy since this worry is interfering with his schoolwork.
An ECG demonstrates a PR interval of 0.25 sec and is otherwise unremarkable.
First degree block
What does this refer to
Depolarization waves are not conducted normally to the ventricles through the atrioventricular node.
Types of Blocks
First (1st) degree (1°)
Second (2nd) degree (2°)
Third (3rd) degree (3°)
1st degree block
What does this refer to
Up to 1.6% of young adults affected
Higher prevalence in trained athletes
5% of persons > 60 yo affected
AA > Caucasians
M > F
Epidemiology of 1st Degree Block
What does this refer to
Physiologic OR Pathologic
Damage to the AV node
Ischemia/infarction
Inflammatory disorders
Infiltrative disorders
Postoperative
Generally associated with organic heart disease
May also be seen in Inferior MI Patients
Medication induced
Digoxin/BB/CCB
Electrolyte imbalance
Etiology of 1st degree block
What does this refer to
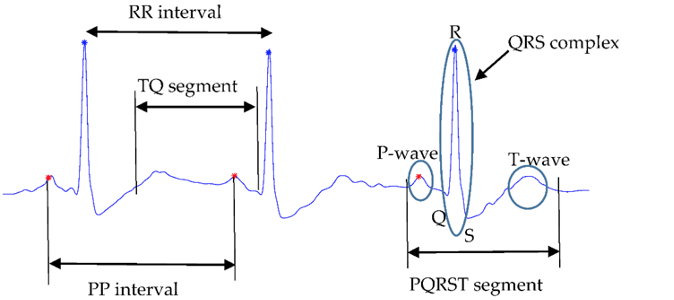
P wave
atrial depolarization
Upright and rounded
Normal duration-0.04-0.11 seconds (definitely not greater than_____?)
P waves that have normal size and shape signal to us that the impulse is originating in the SA node
P wave review of 1st degree block
What does this refer to
PRI (PR interval)
Time to travel from atria through AV node, bundle of His and bundle branches to Purkinje fibers
Measured from beginning of P wave to beginning of QRS
Normal duration 0.12-0.20 seconds
PR Interval of 1st degree block
What does this refer to
May be asymptomatic
Symptoms usually vague, including palpitations and dizziness
Bradycardia may present with lightheadedness or syncope
History and physical exam of 1st degree block
What does this refer to
No pathognomonic physical findings
Occasional irregular pulse
Loss of atrial and ventricular synchronization
Pertinent physical exam findings of 1st Degree Block
What does this refer to
Sinus bradycardia
Sick sinus syndrome (tachy-brady syndrome)
Effects of negative chronotropic substances (i.e. beta-blockers)
Differential Diagnosis of 1st degree block
What does this refer to

Workup for 1st degree block
What does this refer to
EKG is usually diagnostic of atrioventricular conduction disorders.
1° block
Delayed conduction through the AV node
Produces a PR interval greater than 0.20 seconds.
PR-I should be < 0.20 seconds
Rate: Typically 60-100
Rhythm-Typically regular
QRS-follows each p wave and is typically normal
Diagnostic evaluations of 1st degree block
What does this refer to
First Degree AV Block
What does this refer to
Consult/referral to cardiology
Asymptomatic
Treatment typically not required
Observation of patient???
Clinical Intervention of 1st degree block
What does this refer to
May be viewed as a warning signal to future development of more serious AV Blocks
Prognosis of 1st degree block
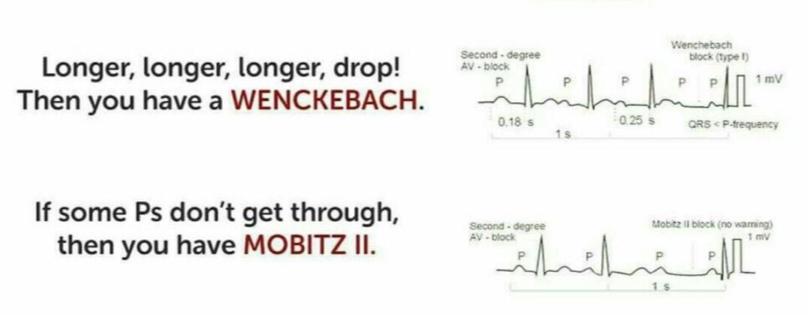
What does this refer to
2nd degree AV Block
What does this refer to
Conduction through the AV node is intermittent
Divided into two subclasses
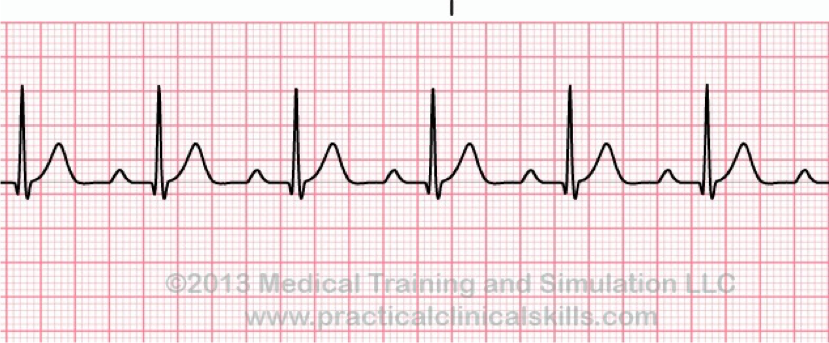
Mobitz I —> Wenckebach
Mobitz II
Rate: 30-55 beats a minute
2nd degree block
What does this refer to
M = F
3% of patients with structural heart disease will develop 2nd degree AV block
Epidemiology of 2nd Degree Block
What does this refer to
Cardioactive drugs are an important cause of AV block
MS drug Fingolimod (Gilenya)
Various inflammatory, infiltrative, metabolic, endocrine, and collagen vascular disorders have been associated with AVblock
Etiology of 2nd Degree Block
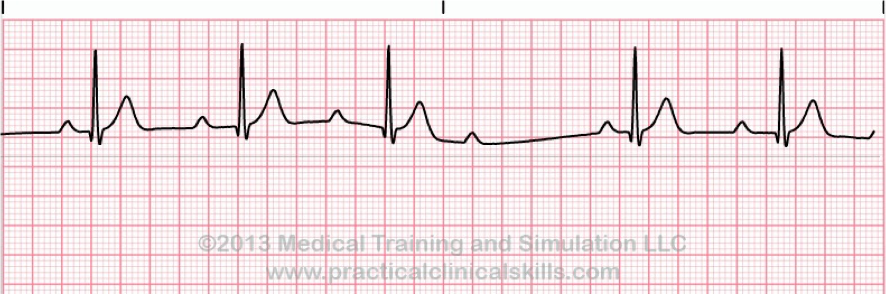
What does this refer to
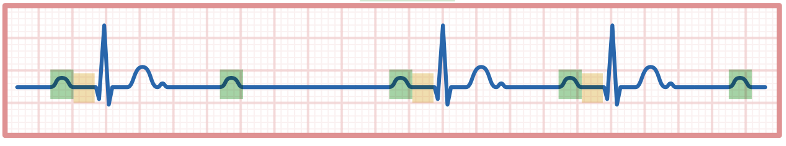
Characterized by a cycle of increasingly lengthened PR intervals followed by a missed QRS complex
Each P wave gets farther away from its QRS till eventually a P wave is not conducted thru the AV node (Blocked) and a QRS is lost
Lone wolf P Wave
2nd Degree Mobitz I (Wenckebach)
What does this refer to

Workup for 2nd Degree Mobitz I (Wenckebach)
What does this refer to
Clinical Management for 2nd Degree Mobitz I (Wenckebach)
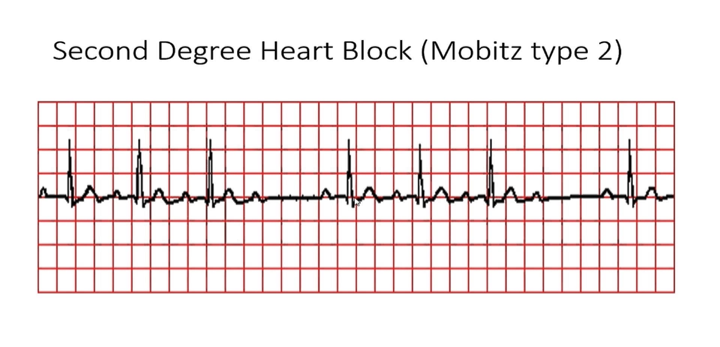
What is characterized by occasional non-conducted P waves not preceded by lengthened PR intervals
2nd Degree Block Mobitz II
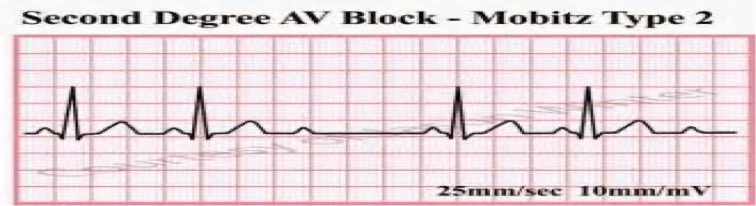
What does this refer to
PRI prolonged but constant
Dropped QRS
Everything seems to be going fine then wham
2nd Degree Block Mobitz II
What does this refer to
1st degree AV Block
2nd degree AV Block
3rd degree AV Block
SSS
Sinus bradycardia
Differential Diagnosis of 2nd Degree Block Mobitz II
What does this refer to
Serious as may lead to Syncope
Management:
Cardiology Consult
Atropine
Temp. Pacing
Definitive Treatment: Pacemaker Implantation as may progress to 3rd degree
2nd Degree Block Mobitz II
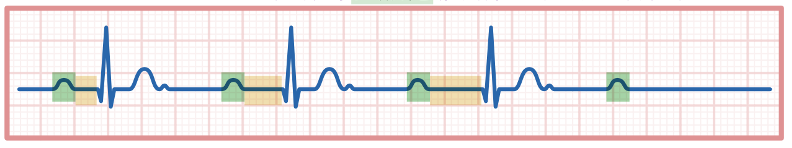
What does this refer to
“PR intervals gradually elongate until a P-wave is completely blocked
Mobitz Type 1
What does this refer to
“PR Intervals are consistent but some P-waves don’t conduct”
Mobitz Type II

What does this refer to
3rd Degree AV Block
What does this refer to
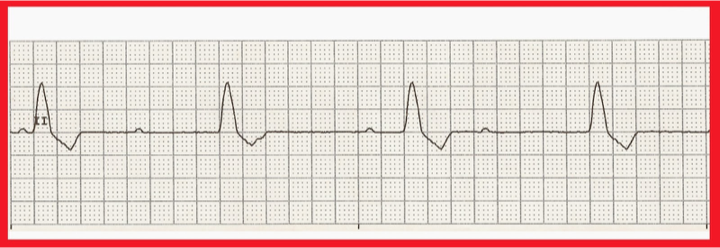
No conduction is taking place through the AV node.
Typically, atrial and ventricular depolarizations take place at their intrinsic firing rates with no relation to one another.
P waves are not associated with QRS—cardiac output insufficient
3rd Degree AV Block
What does this refer to
Atria continued to be paced by their respected SA node
See a typically normal P wave rate but, a slower QRS rate.
3rd Degree AV Block
What does this refer to
Patients may present with hemodynamic instability secondary to bradycardia.
Transcutaneous or transvenous pacing should be initiated until a permanent pacemaker can be placed.
Emergency management of 3rd degree AV block
What does this refer to
Acute Symptomatic-Temporary Pacing until Permanent Pacemaker placedDefinitive Treatment: Implantable pacemaker
Clinical Management of 3rd Degree AV Block
What does this refer to
“________ carry the signal from just below the AV node (the junction between the top and bottom chambers of the heart) through the ventricles (bottom of the heart).”
Bundle branches
What does this refer to
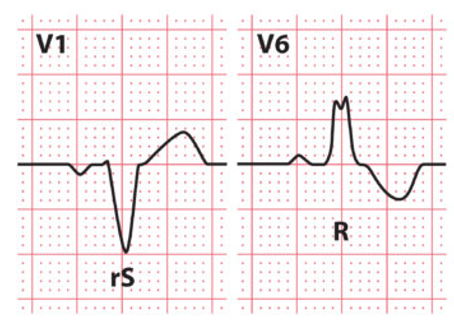
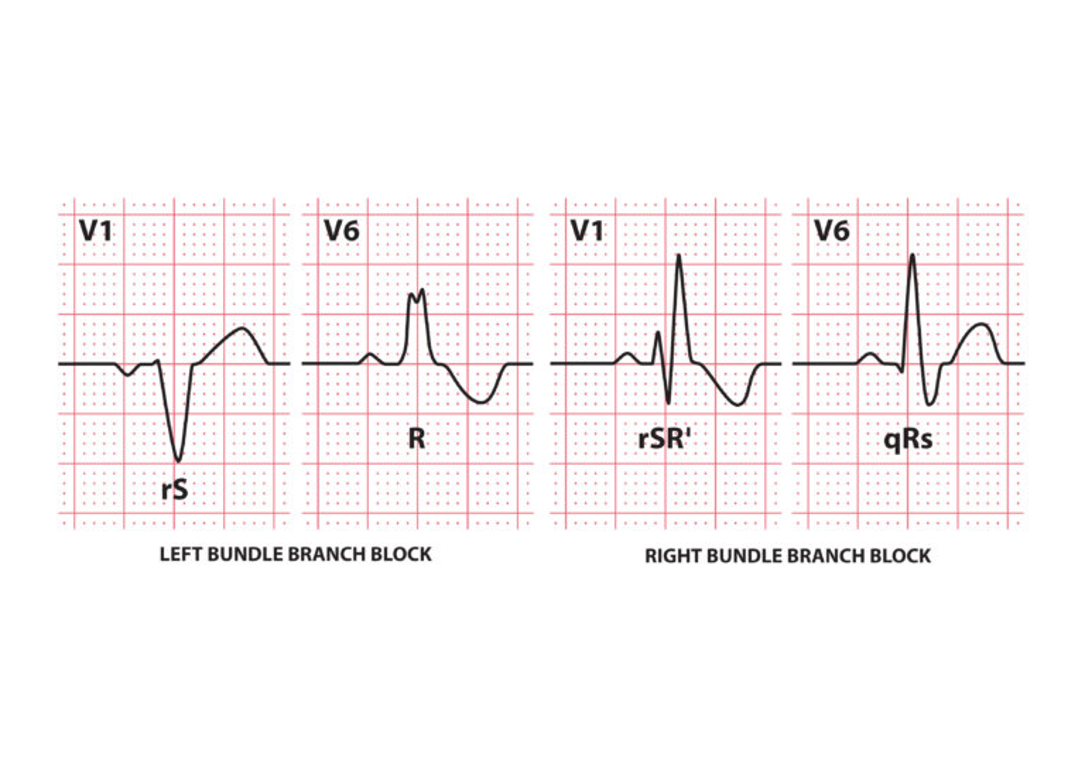
Left bundle branch block
What does this refer to
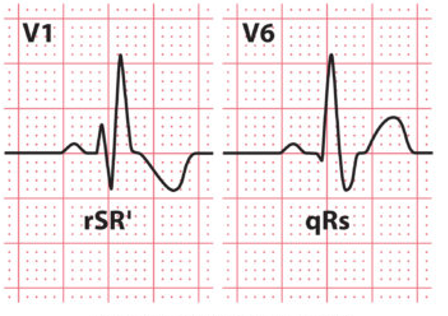
Right bundle branch block
What does this refer to
Problem with the right branch of the conducting system that sends the electrical signal to the RV
Impulse still gets to the RV but it has to travel to the left side before getting to the RV
Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
What does this refer to
The sino-atrial node acts as the initial pacemaker
Depolarization reaches the atrioventricular node
Depolarization through the bundle of His occurs only via the left bundle branch.
Left branch still depolarizes the septum as normal.
The left ventricular wall depolarizes as normal.
The right ventricular walls are eventually depolarized by the left bundle branch, this occurs by a slower, less efficient pathway.
Pathophysiology Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
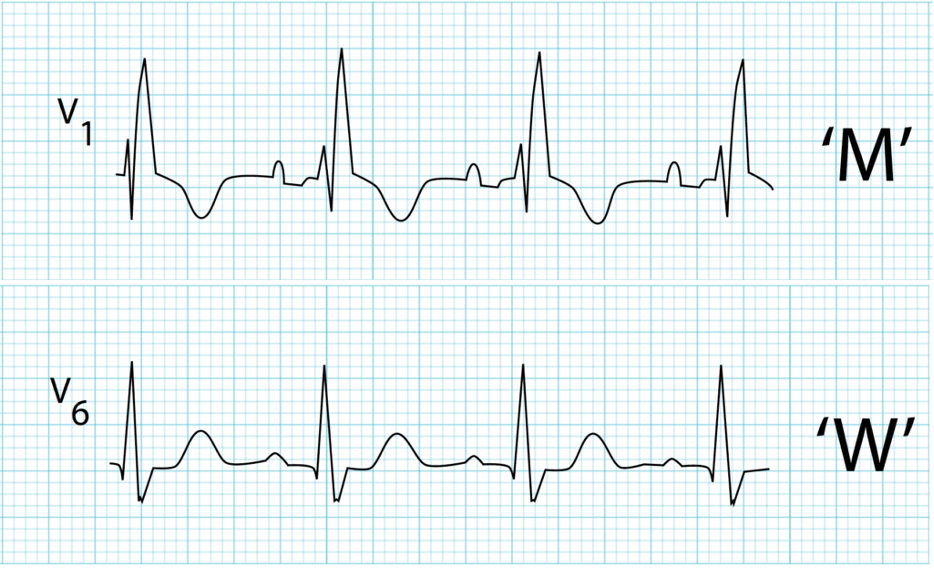
What does this refer to
EKG Diagnostic Criteria
QRS duration > 120ms
RSR’ pattern in V1-3 (“M-shaped” QRS complex)
Wide, slurred S wave in lateral leads (I, aVL, V5-6)
EKG Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)