5 Microscopy of urine (cells, etc)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
RBC normal
7 micron
0-2/hpf
Crenated RBC
occurs in concentrated urine
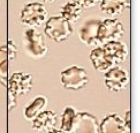
Ghost cells
in dilute urine
Not included in microscopic count
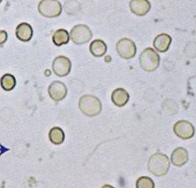
Acetic acid
used to distinguish RBC from oil, air bubbles, yeast, WBC
Will lyse RBC only
Hematuria
RBC in urine
Strip Blood neg limit of RBC
>4 RBC/hpf (possible negative RBC on strip)
Dysmorphic RBC
Cellular protrusions, vary in size, fragmented
Associated with Glomerular bleeding (RBC squeezing through glomerulus)
Second tech/or specialist must review and confirm
Rarely seen due to strenuous exercise
WBC normal
12 micron
0-5/hpf
usually PMN
WBC in hypertonic solution
Shrunk cells
False negative for leukocyte esterase on strip
WBC in hypotonic solution
Glitter cell (swollen WBC with granules)
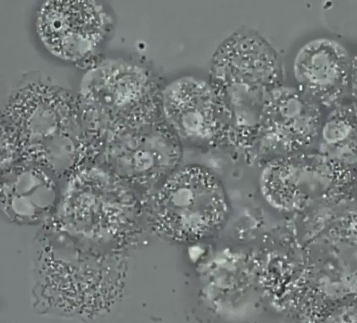
Pyuria
increase in WBC’s in urine
WBC in urine cause
infection or inflammation
Lymphocytes
Small, may resemble RBC - but has nucleus
Seen in early stages of renal transplant rejection
Eosinophils
Usually not in urine
>1% of WBC is clinically significant
Causes
Drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis (AIN) (primary reason)
UTI
Parasitic infection
renal transplant rejection.
Eosinophil stain
Wrights stain or Hansel stain
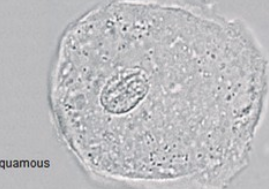
Squamous cell
Epithelial cell from urethra
largest of epithelial cell
no pathology if found in urine
Transitional cell
Epithelial cell from renal pelvis, calyces, ureters, bladder, and upper portion of the male urethra
smaller than squamous, similar to RTE but usually with more defined cell edge and central nucleus
Normal <0-2 /hpf
Nonpathological increase: invasive procedures like catheter
Pathological: cells w/ abnormal morphology from malignancy or viral infection
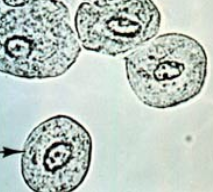
Renal tubular cell (RTE)
Epithelial cell from inside kidney (renal tubules)
Usually smallest epithelial cell, but bigger than WBC
size and shape variation: cuboidal, columnar or round (usually not round and has flattened side)
eccentric nuclei
Reabsorbs material from glomerular filtrate, can cause them to die and slough off
0-2/hpf = normal
>2/hpf = damage or necrosis to renal tubules
Infection, drug toxicity, heavy metals, allergic reactions
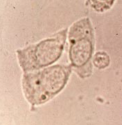
Clue cells
Squamous epithelial cells covered in Gardnerella vaginalis
from bacterial vaginosis
usually not reported in Urine results
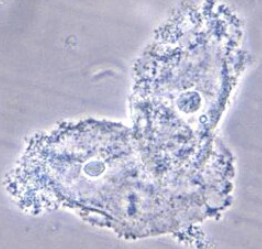
Yellow RTE
RTE reabsorbed bilirubin from glomerular filtrate and sloughed off into urine
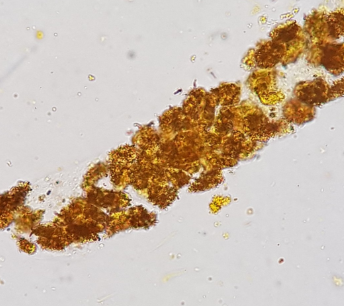
Yellow brown RTE
RTE reabsorbed hemosiderin from glomerular filtrate and sloughed off into urine
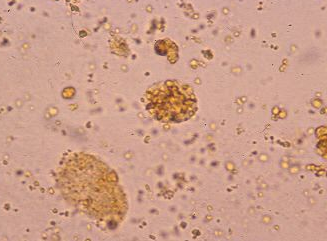
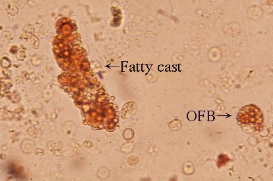
Oval fat bodies
RTE reabsorbed lipids from glomerular filtrate and sloughed off into urine
seen in lipiduria, free fat droplets and/or fatty casts also seen
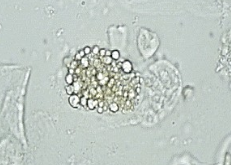
Lipiduria
Lipid (cholesterol or triglyceride) in urine
Causes:
Nephrotic syndrome: damage to glomerulus (most common)
Tubular necrosis (most common)
Diabetes melitus (rare)
Trauma (bone marrow fat leak)
Oval fat bodies from histocytes (instead of RTE) are seen in lipid storage diseases
Oil Red O or Sudan III
lipid stain that only stains triglycerides and not cholesterol
Maltese cross
Polarized cholesterol will show this pattern. Triglycerides will not.
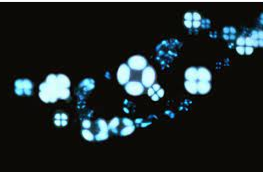
Confirmation of oval fat bodies
Both Sudan stain and polarized light check must be done to check for triglyceride and/or cholesterol
Oval fat bodies can be confused with starch or crystals
Cause of bacteria in urine
sample left in RT >2h
Collection method bad
UTI !!
tests that coincide with bacteria in urine
Leukocyte esterase +
Nitrite +/=
follow up with urine culture
Yeast in urine
can be confused with RBC —> use acetic acid
If INFECTION. Leukocyte esterase should be + or WBC should be observed
more common in patients with diabetes mellitus, immunocompromised patiernt
Usually contaminant from bad collection or vaginal yeast infection
Mucus in urine
produced by glands and RTE cells
major constituent: tamms-horsfall protein
More in female sample > male sample
NOT CLINICALLY SIGNIFICANT
Increased amounts of semen may produce a ____ protein on the reagent strip test
Positive