apes unit 1 review
1/51
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
predator-prey
one eats, one gets eaten
mutualism
both species benefit by being in the relationship
mutualism example
clown fish and sea anemone
commensalism
one species benefits and the other is unaffected
commensalism example
Remoras attach themselves to a shark's body, feeding on scraps leftover from the shark's meal. The remoras neither hurt nor harm the shark.
parasitism
one species benefits and one species is harmed
parasitism example
flea and dog
competition
2 species competing for the same resources- includes intraspecific and interspecific
interspecific competition
competition between members of different species
intraspecific competition
competition between members of the same species
principle of competitive exclusion
when two or more species coexist using the same resource, one must displace or exclude the other
biome
A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms
ecosystem
A system formed by the interaction of a community of organisms with their physical environment
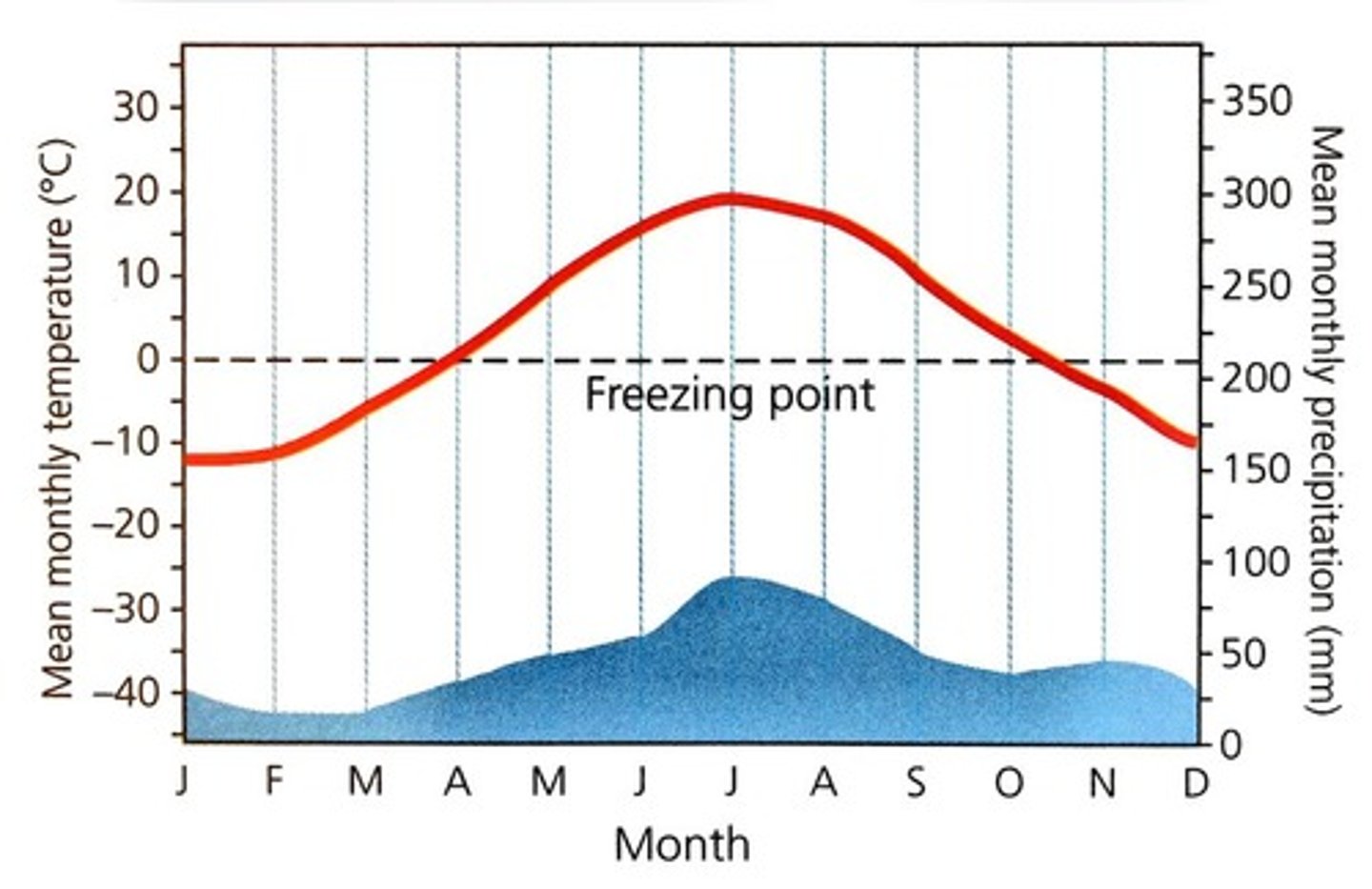
Taiga (Boreal Forest)
Has a short growing season, the soil quality is poor, the biodiversity is low, has conifers such a cedar, spruce, pine, and fir; it has insects, birds mainly in the summer, no amphibians or reptiles, and mammals such as rodents, rabbits, minks, raccoons, bears, and moose live there
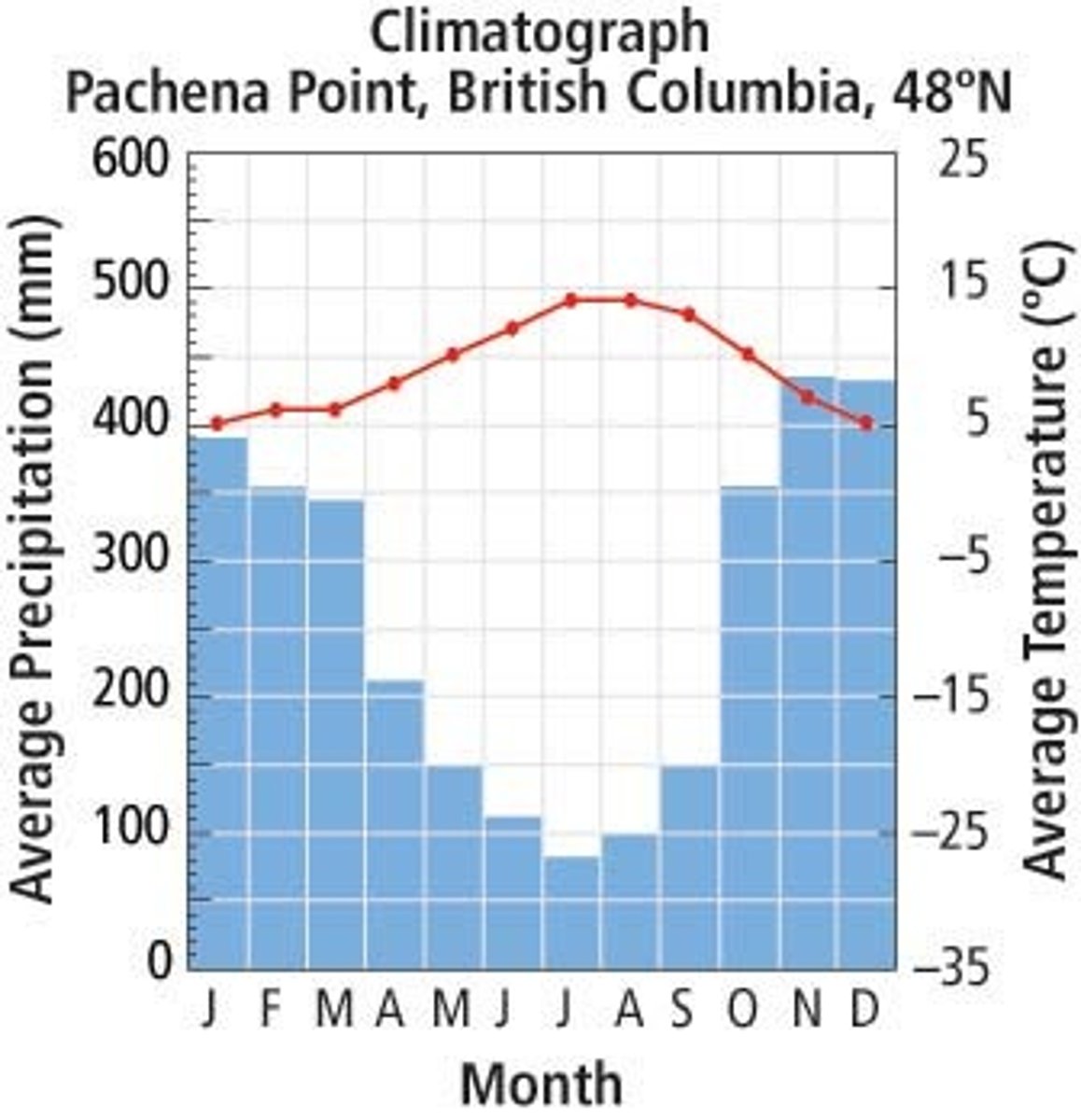
temperate rainforest
a coastal biome typified by moderate temperatures and high precipitation; coniferous and broadleaf trees
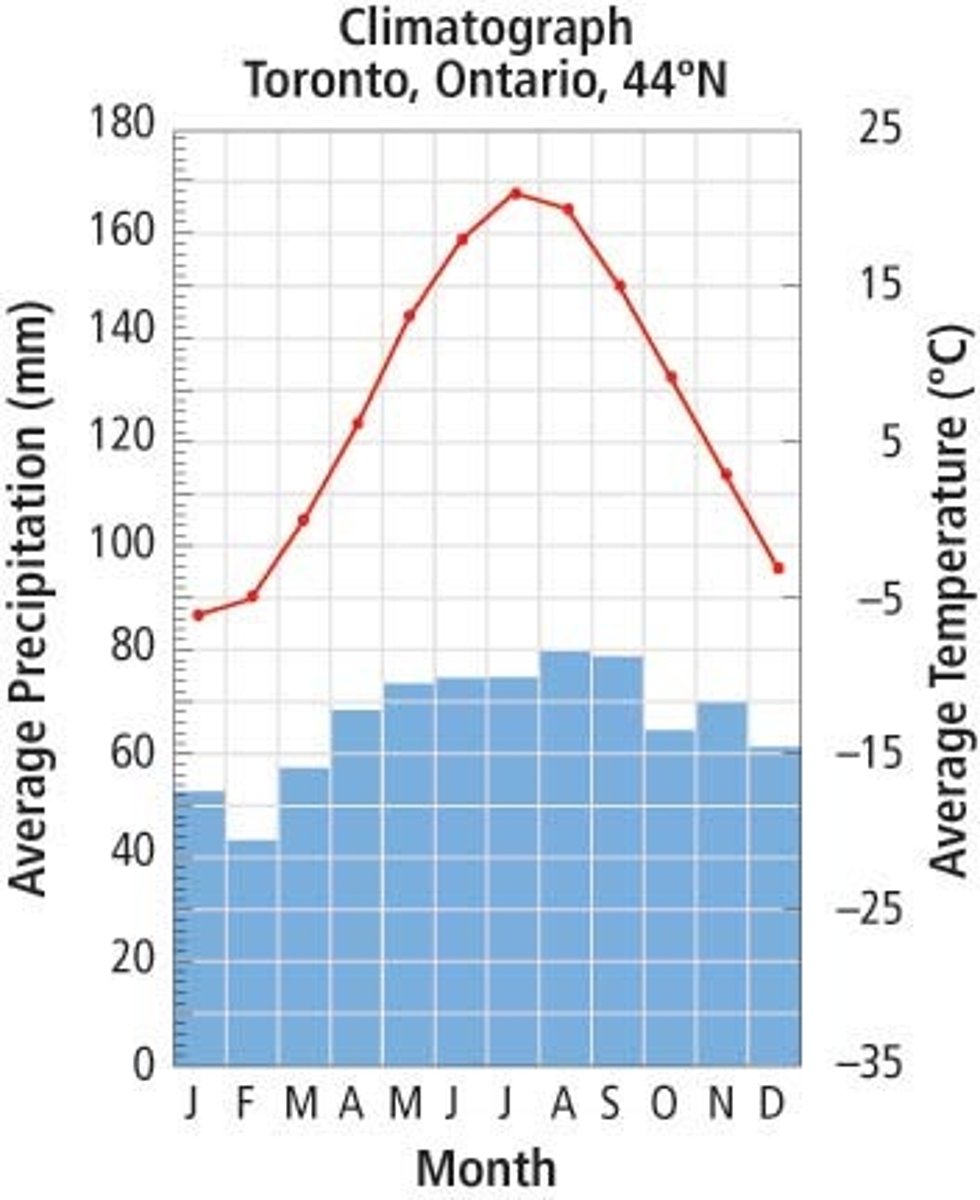
temperate seasonal forest
A biome with warmer summers and colder winters than temperate rainforests and dominated by deciduous trees. 4 seasons: warm, wet summers and cold winters
most dominated by humans
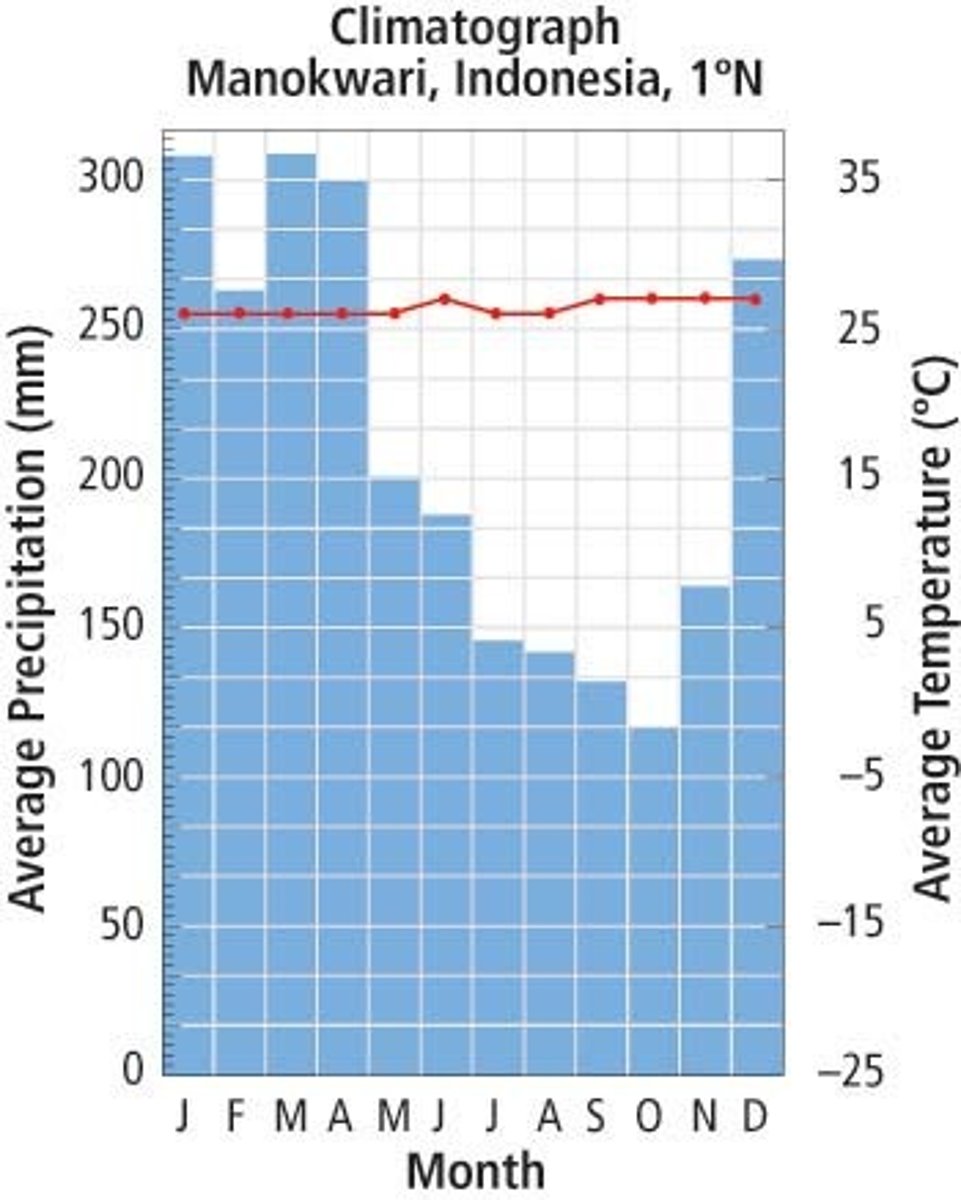
tropical rainforest
Forests in which rainfall is abundant - more that 200 cm (80 in) per year - and temperatures are warm or hot year-round; near the equator; greatest diversity of species with rain all year and warm all year
soil is thin, acidic, and nutrient poor with rapid decomposition and nutrient cycling
shrubland
hot,dry summers and cool, moist winters; found near coasts with short trees and grasses; chaparral; subject to fires
temperate grassland
a community (or biome) that is dominated by grasses, has few trees, and is characterized by cold winters and low rainfall that is intermediate between that of a forest and a desert
savanna
An area of grassland with scattered trees and bushes; wet season and a dry season; wildfires are common
desert
An extremely dry area with little water and few plants
tundra
a vast, flat, treeless Arctic region of Europe, Asia, and North America in which the subsoil is permanently frozen.
permafrost
permanently frozen layer of soil beneath the surface of the ground- found in tundra
freshwater biome
Aquatic biomes that include lakes, streams, rivers and ponds. Salt concentration of less than 1%.
marine biomes
oceans, coral reefs, estuaries, salt marshland
intertidal zones
where the ocean meets the land and the shore is pounded by waves during high tide and exposed to the sun and drying winds during low tide; many nutrients but the organisms must be adapted to avoid drying out or breaking (hard shells, etc)
benthic zone
bottom of an aquatic ecosystem; consists of sand and sediment and supports its own community of organisms nutrients found here
estuary
A habitat in which the fresh water of a river meets the salt water of the ocean; nutrient rich from ocean and river deposition
coral reef
The most diverse marine biome on Earth, found in warm, shallow waters beyond the shoreline.
carbon cycle
the series of processes by which carbon compounds are interconverted in the environment, chiefly involving the incorporation of carbon dioxide into living tissue by photosynthesis and its return to the atmosphere through respiration, the decay of dead organisms, and the burning of fossil fuels.
nitrogen cycle
the series of processes by which nitrogen and its compounds are interconverted in the environment and in living organisms, including nitrogen fixation and decomposition. Bacteria are important
carbon
element found in all living things
nitrogen
Most abundant gas in the atmosphere- atmospheric nitrogen is not 'usable' by living things so it must be 'fixed'
element found in protein and DNA
phosphorus
element that makes up DNA
phosphorus cycle
the cyclic movement of phosphorus in different chemical forms from the environment to organisms and then back to the environment; does not have an atmospheric component
hydrologic cycle
The cycle through which water in the hydrosphere moves; includes such processes as evaporation, precipitation, and surface and groundwater runoff
transpiration
Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant
percolation
The downward movement of water through soil and rock due to gravity.
primary productivity
the rate at which food energy is generated by photosynthesis. It is measured in units of energy per unit area per unit time (ex. kcal/m2/year)
gross productivity
The total rate of photosynthesis in an area, or the full amount of food produced by the producers.
net productivity
the difference between gross productivity and the energy lost by producers for respiration
trophic levels
The hierarchical levels of the food chain through which energy flows from primary producers to primary consumers, secondary consumers and so on. The shape is a pyramid because energy is 'lost' as it goes up to each higher level
the 10% rule
90% of energy is used by the organisms and only 10% moves up the pyramid because the organism below it used up the energy to heat its body, move, reproduce, etc.
food chains
Energy links between different organisms in an ecosystem based on feeding habits; simple and linear
food web
A community of organisms where there are several interrelated food chains
photosynthesis
process by which plants and some other organisms use light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and high-energy carbohydrates such as sugars and starches
photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
cellular respiration equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
biomass
total amount of living tissue within a given trophic level
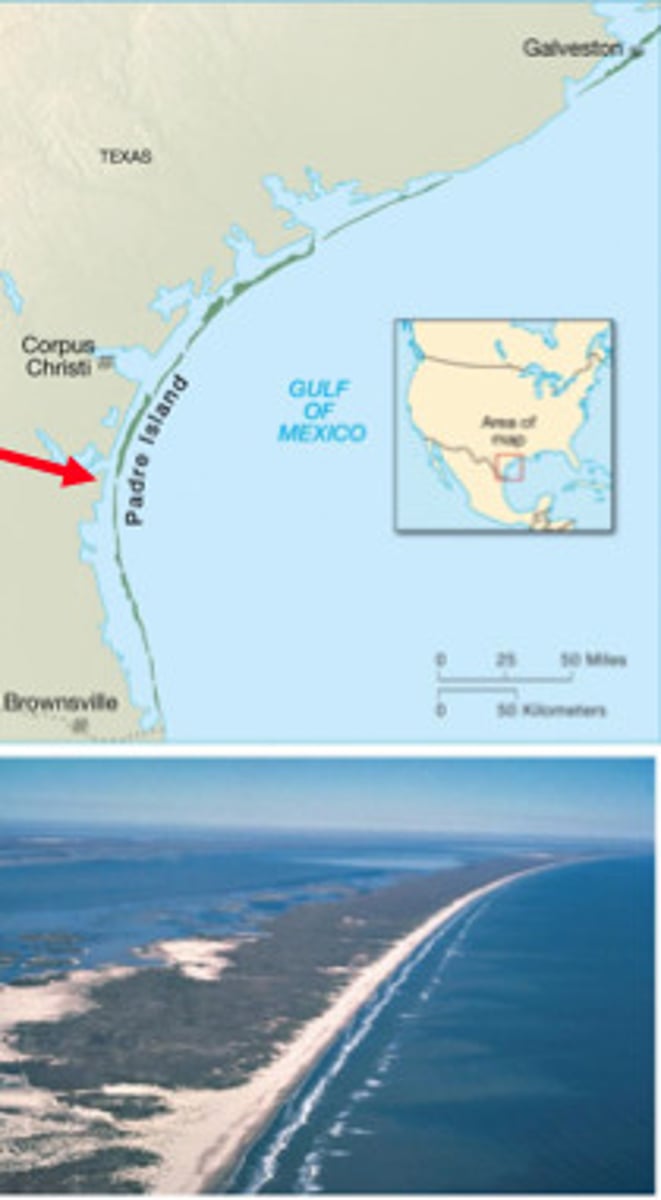
barrier islands
Long, thin, low offshore islands of sediment that generally run parallel to the shore along some coasts.
provide protection from storms, waves, tides
Since they are made of sand, they shouldn't be built on because storms destroy buildings, about 20% in the US have been developed
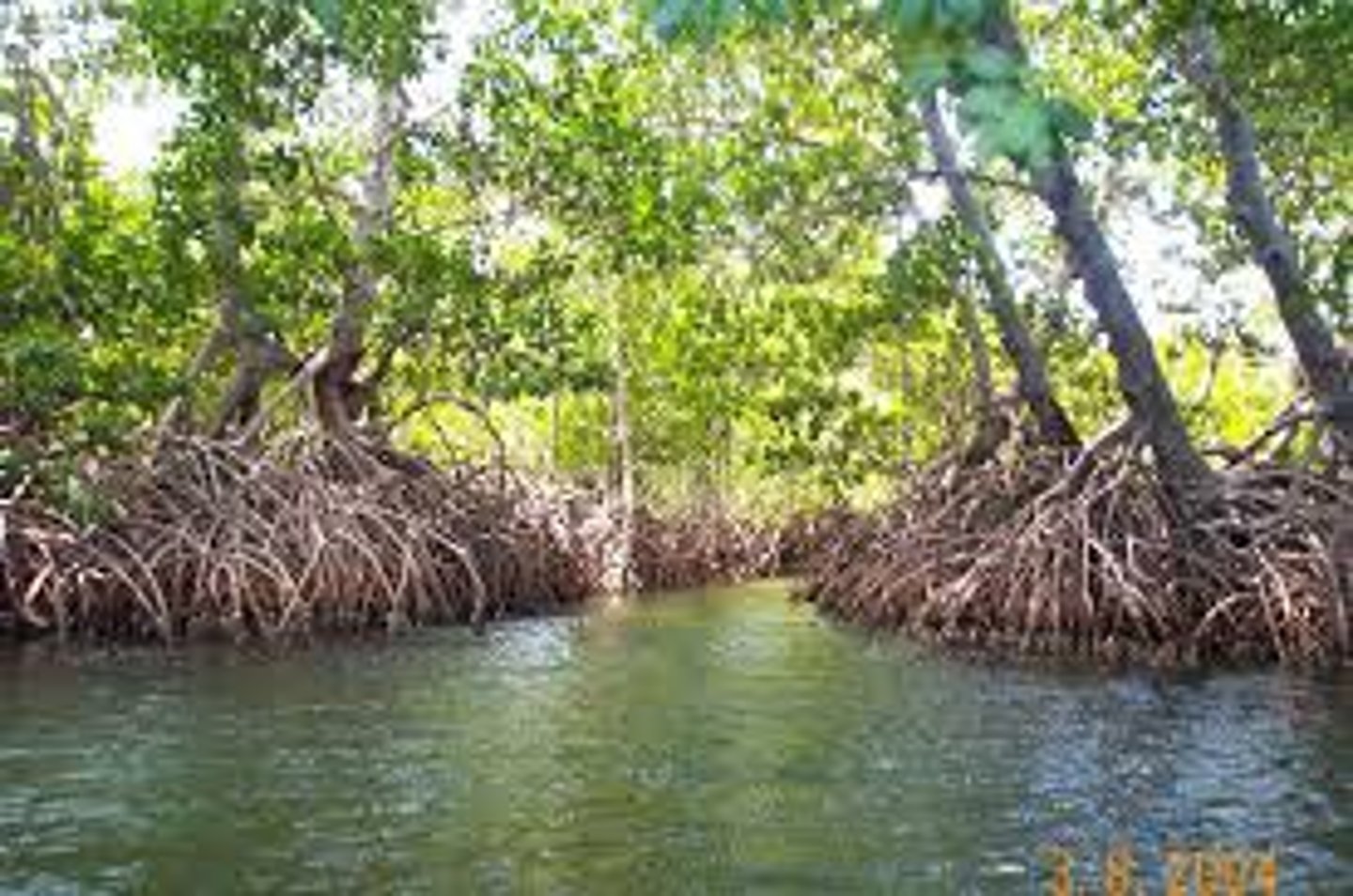
mangroves
tropical trees that grow along coasts and help maintain the health of tropical, coastal environments
stabilize shoreline; nurseries for fish/shrimp
threats: shrimping, development, cut for timber, tourism
