PCCR Peripheral Vascular System
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
arterial, venous, lymphatic system
what comprises the peripheral vascular system?
intima
single continuous lining of epithelial cells
regulates immune/inflammatory rxns, moderates vasoconstriction and vasodilation, location where plaque forms
functions of intima
media
smooth muscle cells with elastic properties
media
surrounded by internal and external laminae
adventitia
connective tissue outer layer
advenitia
contains nerve fibers and vasa vasorum
chronic inflammation of vascular endothelial cells resulting plaque formation
what is atherosclerosis?
vessel injury
what is plaque formation initiated by?
changes in cardiac output during systole and diastole
what do arteries respond to?
large, medium, small, arterioles, capillaries
order of arterial branching
brachial, radial, ulnar, vascular arches in hand
upper extremity arterial pulses
bend of elbow, medial to biceps tendon
location of brachial artery
lateral flexor surface, bt radial styloid and flexor carpi radialis tendon
location of radial artery
medial flexor surface, bt flexor carpi ulnaris and flexor digitorum superficialis
location of ulnar artery
epigastrium
where can you palpate aortic pulsations?
femoral, popliteal, posterior tibial , dorsalis pedis
lower extremity arterial pulses
below inguinal ligament, midway bt the anterior superior iliac spine and pubic symphysis
location of femoral pulse
popliteal fossa
location of popliteal pulse
behind medial malleolus
Location of posterior tibial pulse
dorsum of foot, lateral to extensor tendon of great toe
location of dorsalis pedis
bounding
3+ pulse
brisk, normal
2+ pulse
diminished, weaker than expected
1+ pulse
absent
0 pulse
small weak pulse

large, bounding pulse
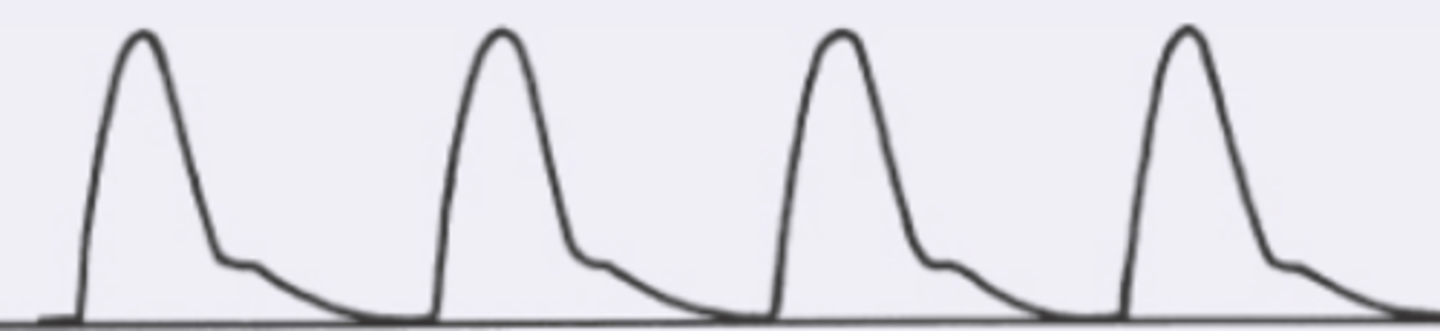
diminished pulse pressure, slow upstroke, prolonged peak
what is a small, weak pulse?
decreases SV, increased PVR
what is a small weak pulse caused by?
increased pulse pressure, rapid rise and fall with brief peak
what is a large, bounding pulse?
increased SV, decreased PVR, increased vascular stiffness/resistance
what are the causes of a large, bounding pulse?
bisferiens pulse

Pulsus alternans
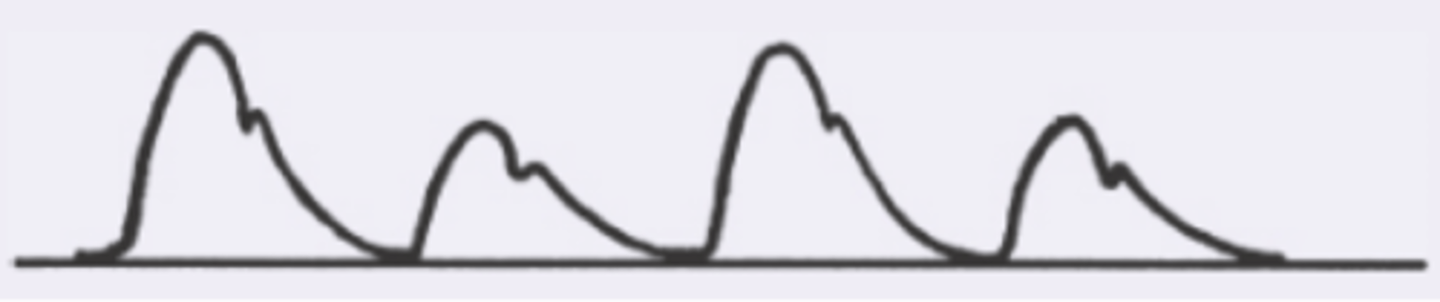
increased arterial pulse with double systolic peak
what is a bisfiens pulse?
HOCM, AR, AR+AS
what are the causes of a bisferiens pulse?
regular, but force of pulse alternates bt weak and strong
what is pulsus alternans?
severe left ventricular dysfunction
what is pulsus alternans indicative of?
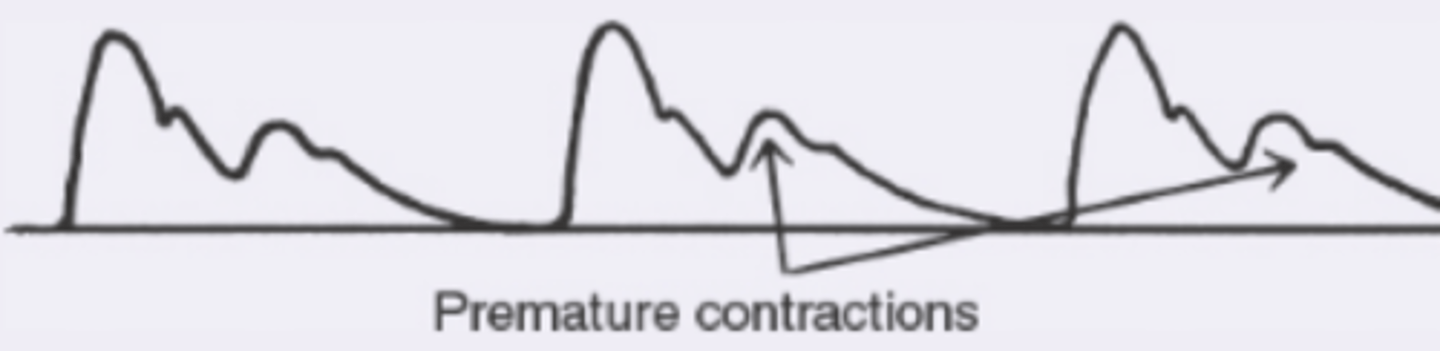
bigeminal pulse
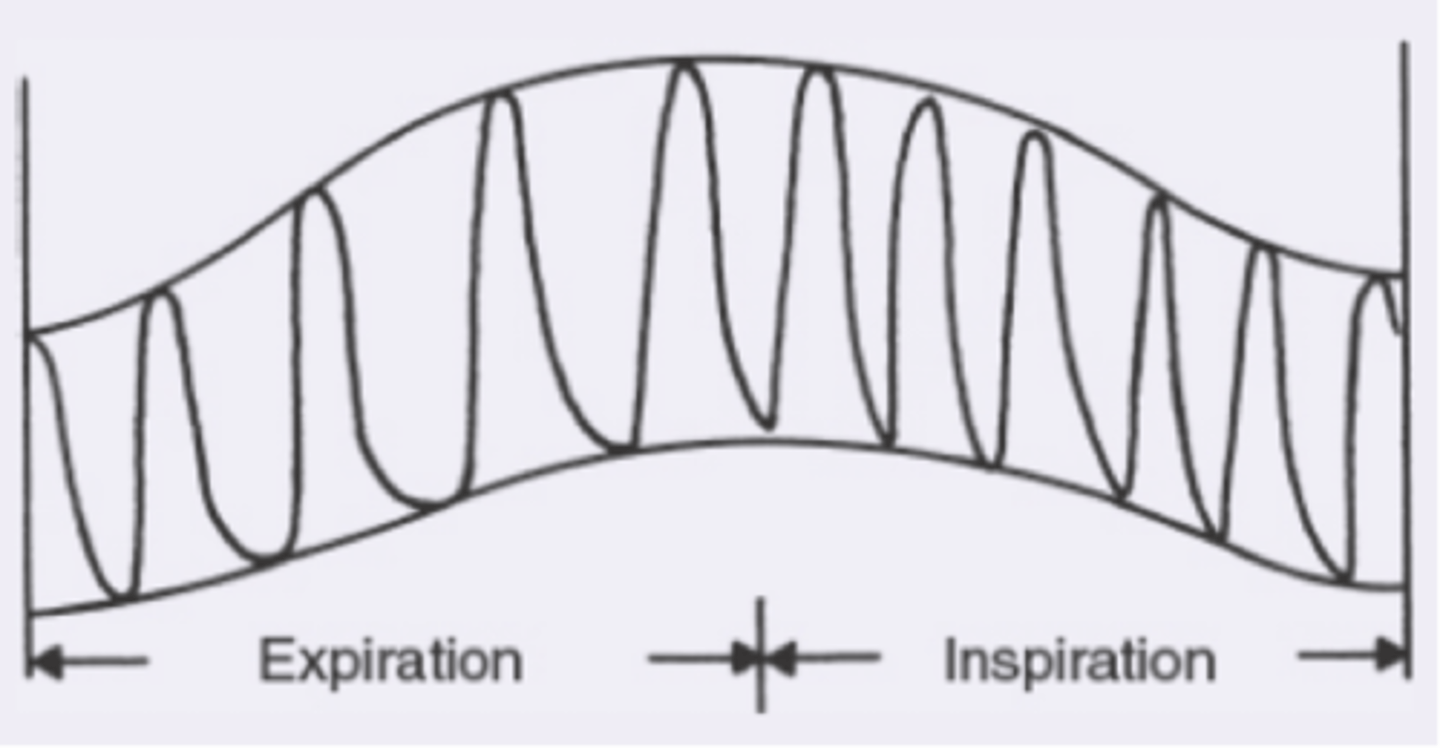
pulsus paradoxus
normal beat alternating with premature contraction with varying amplitude dt diminish stroke volume of premature contraction
what is a bigeminal pulse?
greater than normal drop in systolic pressure during inspiration, varying amplitude with respirations
what is pulsus paradoxus?
pericardial tamponade, constrictive pericarditis, obstructive pulmonary disease
what is pulsus paradoxus found in?
thin walled, holds 2/3 of circulating blood, unidirectional valves
characteristics of veins
capillaries, venules, superficial and deep veins to either the portal vein of venas cavas
venous blood flow
abdominal viscera, inferior vena cava after hepatic veins
what does the portal vein drain and empty into?
inferior vena cava
LE drained into:
superior vena cava
UE drained into:
deep veins
carries 90% of venous blood from lower extremity
deep veins
well supported by surrounding tissue
backflow, pooling, venous stasis
unidirectional valves prevent:
caudally
contraction of the calf muscle pumps blood:
superficial veins
poorly supported by surrounding tissue:
great and small saphenous veins
superficial veins of LE
dorsum of foot, anterior to MM, medially up leg, joins femoral vein of deep venous system below inguinal ligament
great saphenous vein
lateral foot, superiourly along posterior calf, joins deep venous system in popliteal fossa
small saphenous vein
extensive vascular network that drains lymph from body tissues and returns it to venous circulation
what is the lymphatic system?
porous endothelium
what is the lymphatic system comprised of?
tissue fluid, cellular debris, plasma proteins, cells
what does the lymphatic system collect?
networks of lymphatic capillaries in EC space that collect tissue fluid, cellular debris, plasma proteins, and cells
what are lymphatic plexuses?
lymphatic plexuses, vascular channels, collecting ducts, veins in neck
what is the pathway of the lymphatic system?
right side of head, neck, thorax, right upper limb
what does the right lymphatic duct drain fluid from?
right jugular vein and right subclavian vein
what does the right lymphatic duct empty into?
rest of the body
what does the thoracic duct drain fluid from?
left internal jugular vein and left subclavian vein
what does the thoracic duct empty into?
round, oval, bean shaped structures that vary in size based on location
what are lymph nodes?
engulf cellular debris and bacteria and produce antibodies
what is the function of lymph nodes?
ulnar surface of forearm and hand, 3/4 fingers, adjacent surface of middle finger
what do the epitrochlear lymph nodes drain?
rest of the upper extremity
what do the axillary lymph nodes drain?
infraclavicular node
where does some lymph fluid go directly to?
anterior thigh below inguinal ligament
where is the horizontal group of inguinal LN located?
superficial lower abdomen and buttocks, external genitals, but not the testes, anal canal, perianal area, lower vagina
what does the horizontal group of inguinal LN drain?
dorsum of foot, medial aspect of leg
what does the vertical group of inguinal LN drain?
small saphenous vein and joins deep system in the popliteal space
where is the heel, outer aspect of the foot, and posterior calf follow?
filtered fluid returned to circulation as lymph
what is transcapillary exchange?
hydrostatic pressure
what is the arteriolar end dominated by?
forces fluid into tissue spaces
what does hydrostatic pressure do?
colloid osmotic pressure of plasma proteins
what is the venous end dominated by?
pulls fluid back into vascular tree
what does colloid osmotic pressure do?
increased interstitial fluid or edema
what does lymph dysfunction or disturbances in hydrostatic or osmotic forces can disrupt the equilibrium cause?
increased plasma volume from sodium retention, altered capillary dynamics, inadequate removal of filtered lymph fluid, obstructions, increased capillary permeability
what are the causes of lymph dysfunction that can lead to edema?
Extracellular fluid that become clinically apparent as swelling
what is edema?
Edema that is compressible or lessens with external pressure
what is pitting edema?
Edema caused by obstructive lymph drainage, usually not compressible
what is lymphedema?
barely detectable when pressing skin
1+ pitting edema
slight indentation, 15 sec to rebound
2+ pitting edema
deeper indentation, 30 sec to rebound
3+ pitting edema
>30 to rebound
4+ pitting edema
Enlarged lymph nodes with or without tenderness
what is lymphadenopathy?
Causative lesion in drainage area causing focal enlargement
what is local lymphadenopathy?
Enlarged nodes in at least three non-contiguous lymph regions
what is generalized lymphadenopathy?
pain/swelling, coldness, numbness, pallor, discoloration of legs, hair loss, ab/flank/back pain, claudication, leg cramps, sensitivity to cold, ulceration
ROS peripheral vascular system
cold or pale extremity
red flag peripheral vascular system
acute arterial occlusion
what is a cold or pale extremity a concern for?
pain, pallor, pulselessness, poikilothermia, paresthesia, paralysis
SS PAD
pain that limits walking, ED, unhealing wounds, ab pain after eating, first degree relatives with AAA
warning signs of PAD
buttocks or hip
location of pain for aortoiliac
ED
location of pain for aortoiliac-pudental
thigh
location of pain for common femoral or aortoiliac
upper calf
location of pain for superficial femoral
lower calf
location of pain for popliteal