Chapter 11
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Nucleic Acid
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Nucleic Acid
A long chain (polymer) made up of many nucleotides linked together
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
RNA (Ribonucleic acid)
Nucleotide
Is the basic building block (monomer) of nucleic acids
Purine
Adenine (A)
Guanine (G)
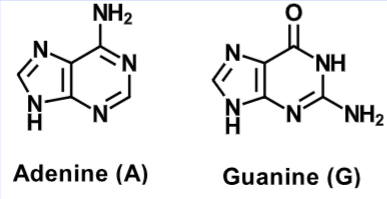
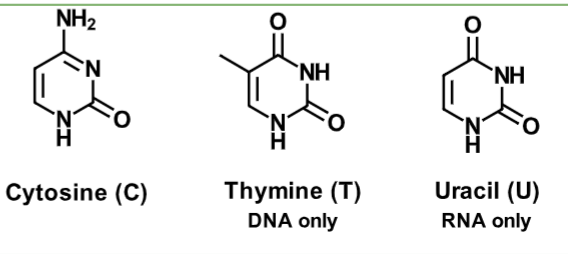
Pyrimidine
Cytosine (C)
Thymine (T)
Uracil (U)
What are Nucleosides made of
Base + Sugar
What are Nucleotides made of
base + sugar + phosphate
How do we name nucleic acid for ribose
(Nucleoside) (prefix)phosphate
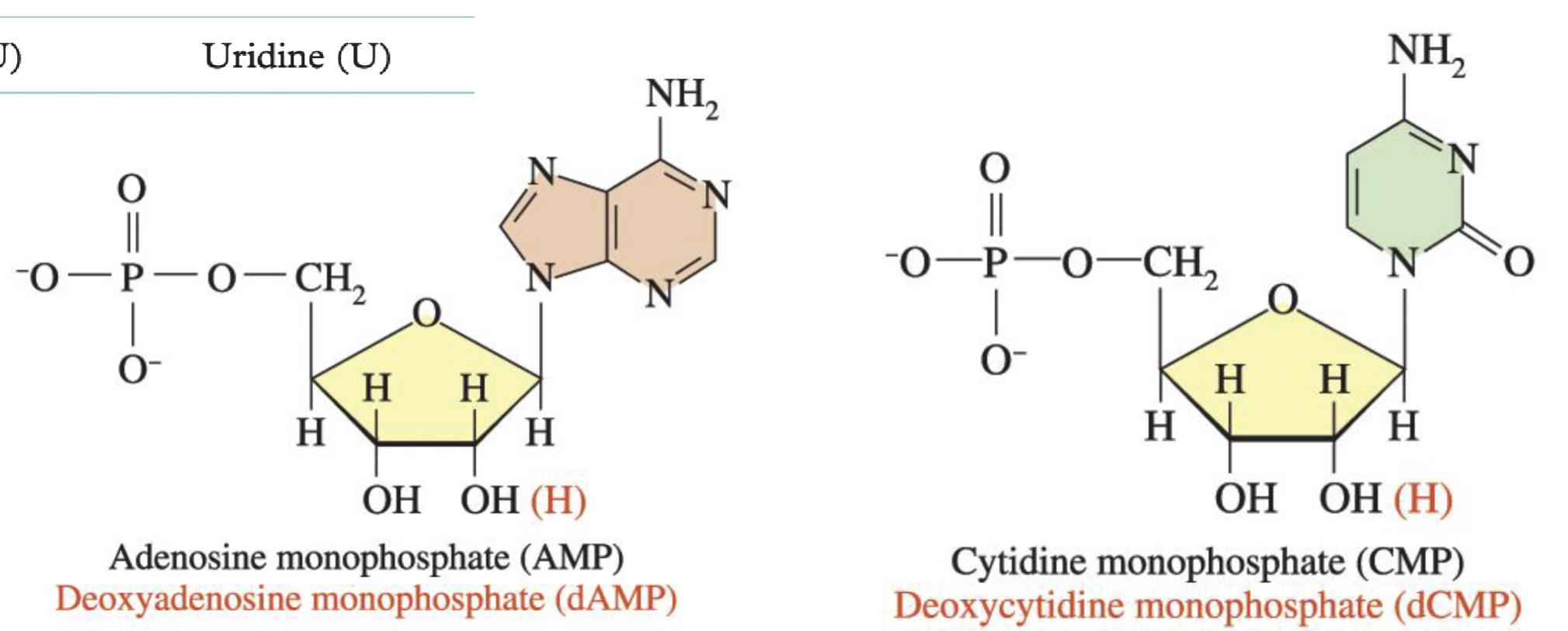
How do we name a nucleic acid for deoxyribose
Deoxy( nucleoside) (prefix)phosphate
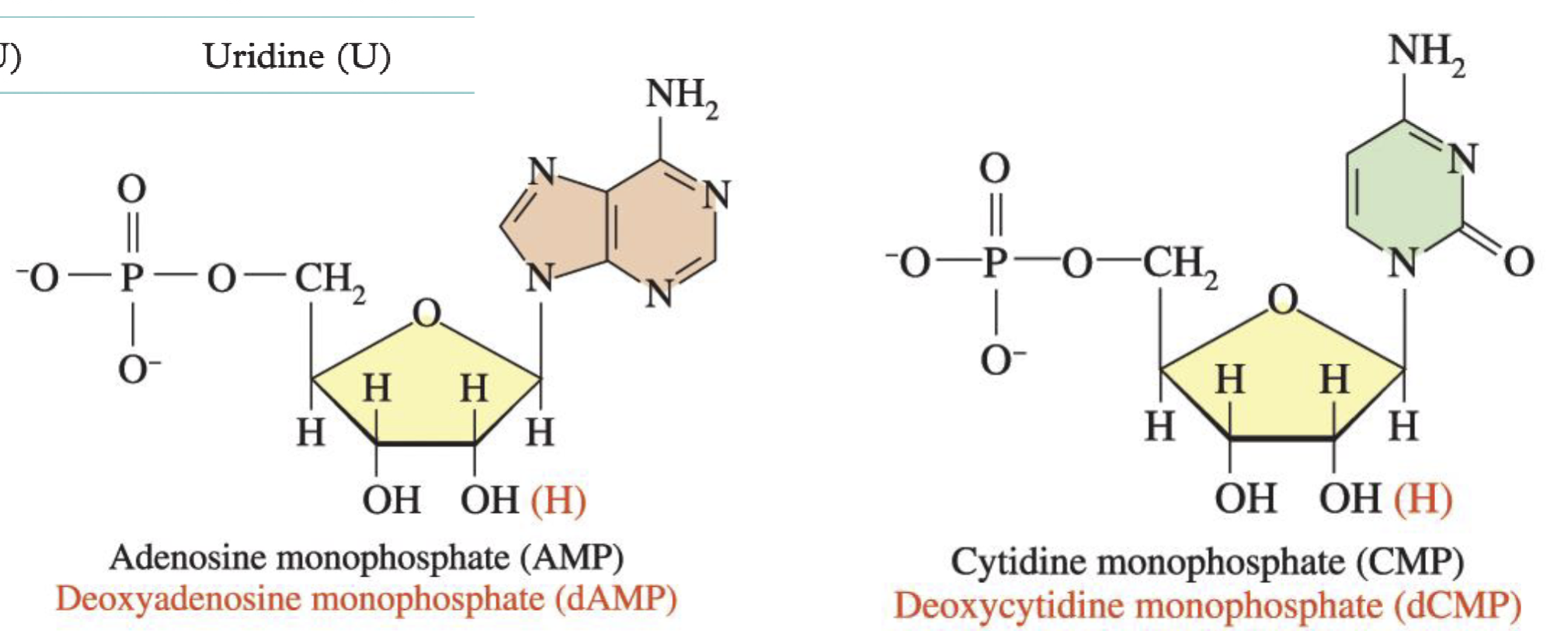
Adenine (A)
Adenosine (A)
Guanine (G)
Guanosine (G)
Cytosine (C)
Cytidine (C)
Uracil (U)
Uridine (U)
Phosphodiester bond
Links nucleotides together to form nucleic acids; oxygen in phosphate group connected between the 3’ and 5’ carbons of sugar molecules
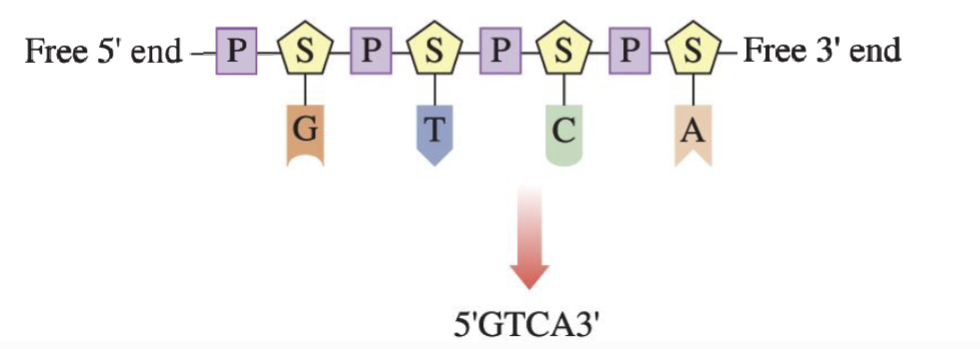
Primary Structure
Nucleotide sequence
read from free 5’ end to free 3’ end
Secondary Structure
Double helix
backbone is antiparallel to each other
one strand in 5’ to 3’ direction; other strand in 3’ to 5’ direction
bases interact through hydrogen bonding
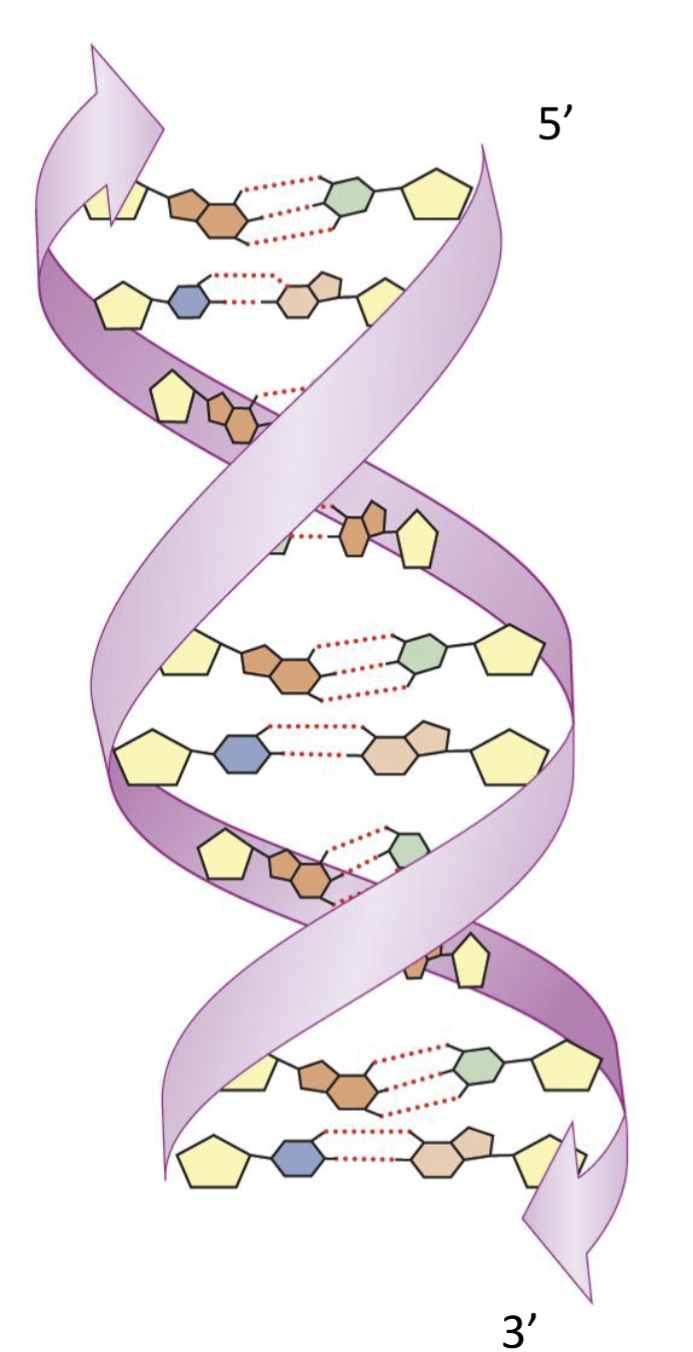
Complementary base pair in DNA
A-T and G-C
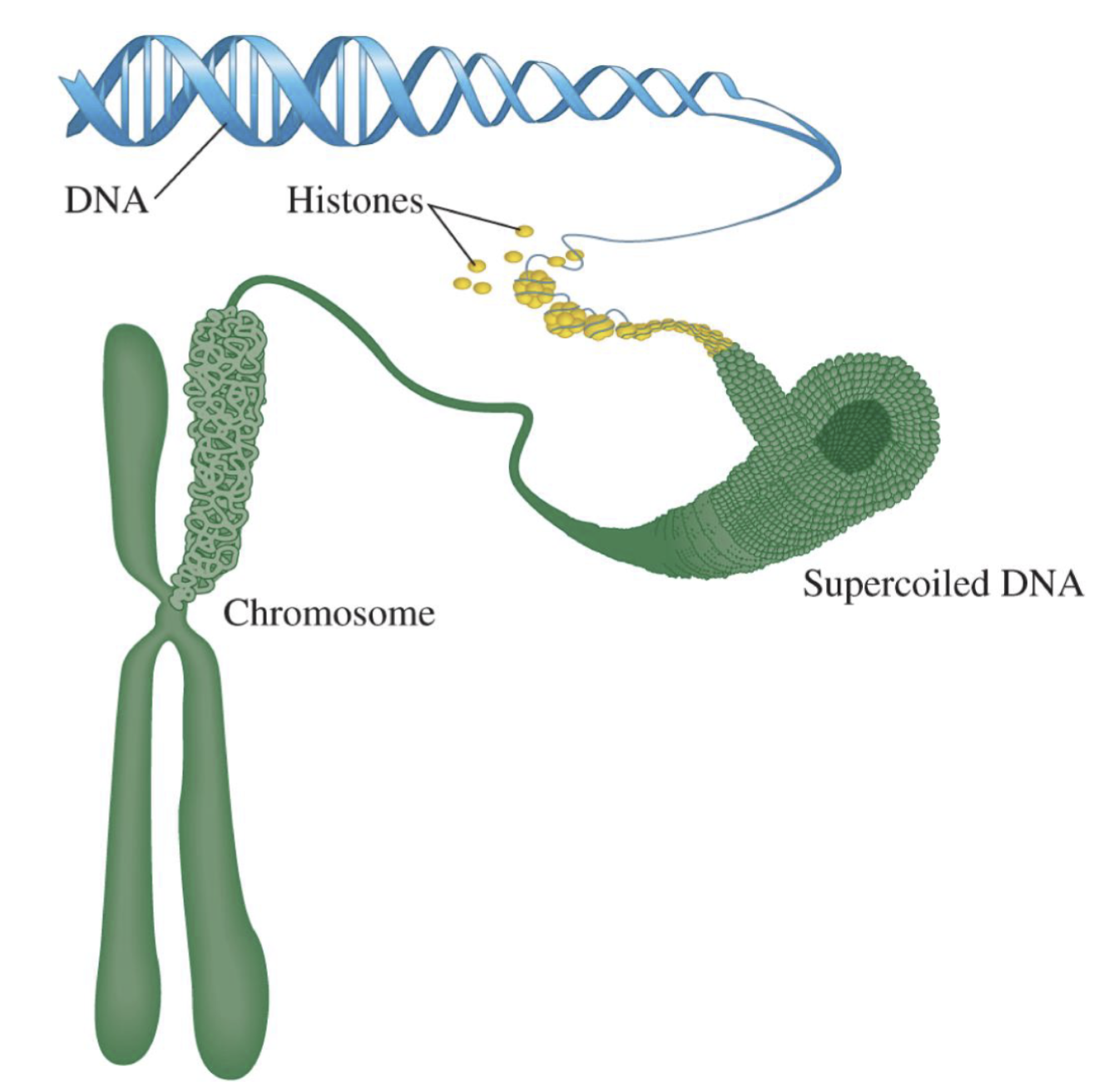
Teriary structure
Supercoiling: further twisting of the DNA double helix structure
DNA is wound around (supercoiled around) proteins - histones
Histones pack together to form chromosomes
Complementary base pair in RNA
G-C and A-U
How many H-bonds does G-C make
3
How many H-bonds does A-T make
2
What is RNA
Single stranded
Usually much shorter than DNA strand
Contains Uracil (U) instead of T
mRNA
Transcription: the process of making a gene copy from DNA
DNA double helix temporarily unwinds, complimentary copy is made from template strand
Catalyzed by RNA polymerase
Notice the 3’ and 5’ designations
Contains codons
3-letter segments
rRNA
Ribosome made of rRNA and proteins
small and large subunits bind mRNA for protein synthesis
tRNA
facilitates translation
What does tRNA help do to mRNA
It helps to “decode” mRNA
Anticodon
three-base sequence, can hydrogen bond to complementary bases on mRNA. “Decodes” mRNA
Codon
Three-base sequence (triplet) that translates to a specific amino acid
Mutation
any change in a DNA nucleotide sequence
Amino acid is replaced with different amino acid (may affect structure and function of protein)
Premature stop codon (terminates protein formation too soon)
inserting or deleting a base. Messes up every codon downstream (frameshift mutation)
Silent Mutations
Results in no change in protein sequence
EX: Codon CAU is changed to CAC- both code for histidine
Change in protein sequence has very little effect on protein function
EX: Isoleucine (AUU) is changed to valine (GUU) - amino acids are similar in size and polarity
Spontaneous mutation
Error that occurs randomly when DNA replicates
Mutagen
Environmental agents that produce mutations in DNA (chemicals, radiation, carcinogens, etc)
Mutation in somatic cells only affects the individual organism
Mutation in germ cells (egg or sperm) can be passed on to future generations - genetic diseases