Chapter 10: Rotational Kinematics & Energy
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
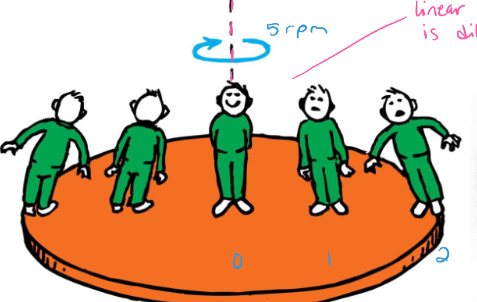
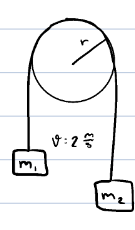
How do the rotational/angular speeds of each person compare?
They all have the same rotational speeds
Same rpm regardless of their position on the rotating system
same ω
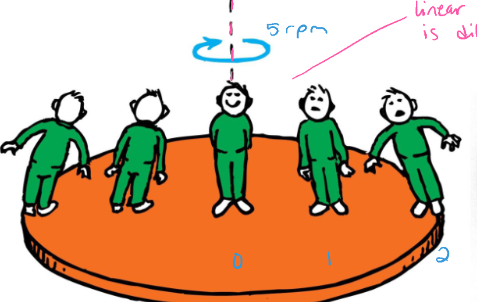
How do the linear speeds of each person compare?
The person farthest from the axis of rotation has the highest linear speed
linear speed increases with distance from the center of rotation
v = ωr
ω is the same, radius increases → v increases
The top of a bike wheel…
rotates 2x faster than the bottom
top of wheel rotating forward, whole bike moving forward (botom of wheel moving backward)
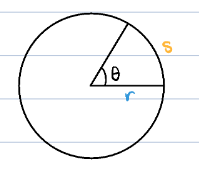
Angular Position
θ = s/r
r = radius: distance from rotational axis
s = arc length
θ in radians
In angular position, the reference line is _______ to the rotational axis.
perpendicular
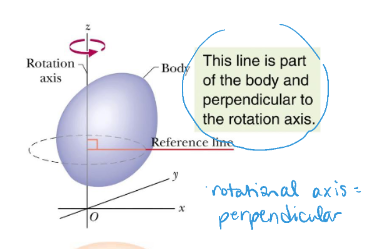
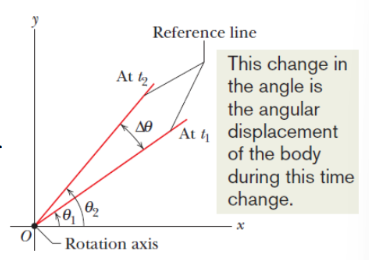
Angular Displacement
If a body rotates about the rotation axis (changes angular position of reference line from θ1 to θ 2 ) the body undergoes angular displacement
Δθ = θ2 - θ1
in the counterclockwise direction = positive
in the clockwise direction = negative
Angular Velocity
how fast something is rotating
how fast the angle is changing in time
ω = Δθ/Δt
Rolling = ?
translation (linear) + rotation
Kroll = Kt + Kr
Kroll = ½ mv² + ½ Iω²
2600 rev/min is equivalent to how many rad/sec?
(2600 rev/min)(1 min/60 s)(2pi rad/1 rev) = 273 rad/s
Angular Acceleration
if the angular velocity is not constant → there is angular acceleration
how fast the angular velocity is changing
speeding up: +, down: -, constant: 0
α = Δω/Δt in rad/s²
If angular velocity (ω) is constant, what is angular acceleration?
constant angular velocity = spinning/angle changing at the same speed all the time, not speeding up or slowing down
there is no angular acceleration
α= dω/dt = 0
Are angular quantities vectors?
Yes, angular quantities are vector quantities because they have both magnitude and direction.
A flywheel is initially rotating at 20 rad/s and has a constant angular acceleration. After 9.0 s it has rotated through 450 rad. Its angular acceleration is…?
ω0 = 20 rad/s
t = 9.0 s
angular displacement: θ = 450 rad
angular acceleration = ?
use kinematic equation:
θ = ω0t + ½ αt²
450 rad = 20 rad/s*9.0 s + ½ (α)(9.0)²
α = 6.67 rad/s²
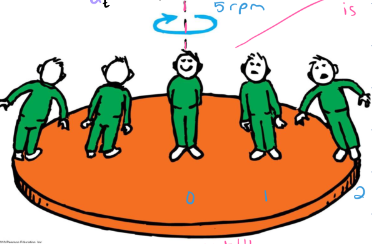
How would you find the person with the highest linear speed?
v = ωr
would convert 5 rpm to rad/s for angular speed
then multiply each by their radius; person 2 will have highest linear speed
Radial Acceleration
ar = ac = v²/r = ω²r
equal to centripetal acceleration
how hard the center-pulling force has to work to keep object moving in a circle
points towards center
arises due to change in direction
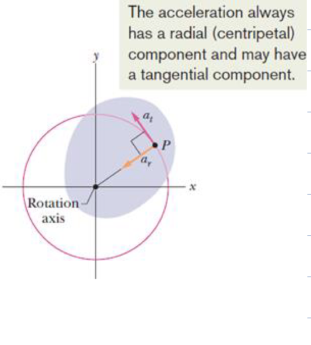
Tangential Acceleration
at = αr
a = sqrt( ar² + at² )
arises due to change in magnitude; points along direction of motion (tangent to the circle)
Tangential & Radial acceleration are…
perpendicular to each other
Calculate the linear speed due to the Earth’s rotation for a person at the equator of the Earth. The radius of the Earth is 6.40×10^6 m.
v = ωr
v = ?
r = 6.40×10^6 m
ω = ?
ω = Δθ/Δt = 2π radians / 24 hours = (2π / 86400) radians per second
v = (2π / 86400) rad/s * 6.40×10^6 m
v = 465 m/s
Kinetic Energy of Rotation
Treat a rotating rigid body as a collection of particles with different speeds and add up the kinetic energies of all particles to find total KE
K = ½ m1v1² + ½ m2v2² + …
K = ½ Iω²
radian measure where I is the moment of inertia of the body
ω is the same for all particles
Moment of Inertia
A measure of an object's resistance to rotational motion
dependent on the mass distribution relative to the axis of rotation
I = ∑ miri²
mi is mass and ri is the distance from the axis
linear: mass resists linear acceleration
rotational: moment of inertia resists angular acceleration
A higher moment of inertia means…
It is more difficult for the object to rotate
inertia = resistance to changes in rotational motion
due to greater mass distribution further from the axis
larger r
A lower moment of inertia means
it is easier for the object to rotate
inertia = resistance to changes in rotational motion
due to less mass distribution closer to the axis
smaller r
Moment of Inertia Equation will…
vary based on the shape
A pulley with a radius of 3.0 cm and a rotational inertia of 4.5×10^-3 kg*m² is suspended from the ceiling. A rope passes over it with a 2.0-kg block attached to one end and a 4.0-kg block attached to the other. The rope does not slip on the pulley. When the velocity of the heavier block is 2.0 m/s, the total kinetic energy of the pulley and blocks is…
r = 3.0 cm = 0.03 m
I = 4.5×10^-3 kg*m²
m1 = 2.0 kg
m2 = 4.0 kg
v = 2.0 m/s
Assign Linear vs. Rotational
Linear = straight line = blocks
Rotational = spinning about an axis = pulley
Connect Linear & Rotational
Given v (linear), we need ω for pulley (rotational)
v = ωr
2.0 m/s = ω(0.03 m) → ω = 66.7 rad/s
Find Total KE
K = K1 + K2 + Kr
K = ½ m1v² + ½ m2v² + ½ Iω²
K = ½ (2.0 kg * 2.0² m/s) + ½ (4.0 kg x 2.0² m/s) + ½ (4.5×10^-3 kg x m²)((66.7 rad/s)²)
K = 22 J
Rolling
combination of translation of the center of mass and rotation of the rest of the object around that center
rolling = linear/translational + rotational motion
Which wheel will win? A: rolling, B: sliding
B: sliding will win
only translational motion, no rotation
All PE goes into linear kinetic energy
mgh = ½ mv²
A: rolling will lose
has both translational and rotational motion
PE splits → some energy goes into spinning in addition to moving forward
mgh = ½ mv² + ½ Iω²
A has less linear velocity/speed in comparison
A rolling object has…
2 types of kinetic energy
a rotational KE due to its rotation about its center of mass: ½ Iω²
a translational KE due to translation of its center of mass: ½ mv²
A bowling ball is rolling without slipping at constant speed toward the pins on a lane. What percentage of the ball’s total KE is translational KE? Moment of inertia of a solid sphere is 2/5 MR².
rolling without slipping: translational & rotational KE
Kroll = Kt + Kr
Kroll = ½ mv² + ½ Iω²
Kroll = ½ mv² + ½ (2/5 mr²)(ω²)
Kroll = ½ mv² + ½ (2/5 m(v²/ω²)(ω²))
Kroll = ½ mv² + 1/5 mv²
factor out mv²
Kroll = mv² * (1/2 + 1/5) = 7/10 mv²
Kt = ½ mv²
Fraction: Kt / Kroll = ½ / 7/10 = 71.4% translational KE
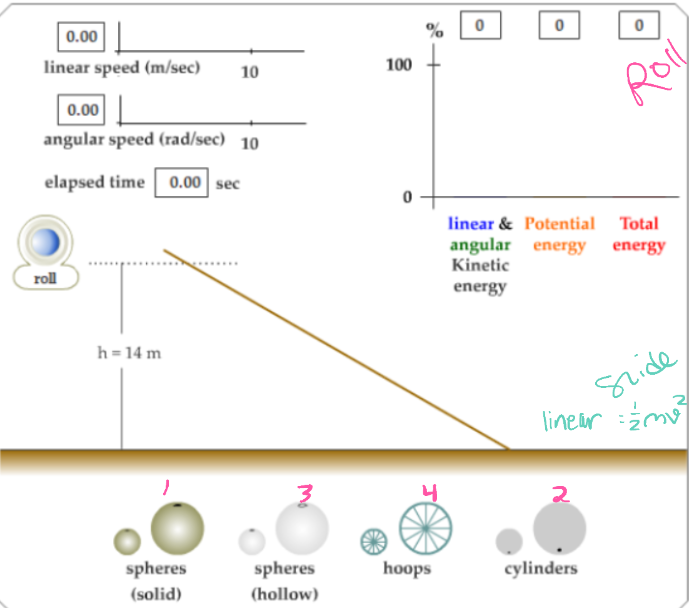
Which roll the fastest? Which slide the fastest?
Roll: Solid sphere
greater mass moves faster due to greater mass distribution
when bigger fraction is rotational (2/3 vs 2/5 mr²) then the center moves slower and it will move slower
smaller I will move faster
Slide: Linear, all the same
½ mv²
all Kt when sliding, equivalent speed when from the same height
v = sqrt(2gh)
A solid sphere of mass 4.0 kg and radius 0.12 m starts from rest at the top of a ramp inclined 15 degrees and rolls to the bottom. The upper end of the ramp is 1.2 m higher than the lower end. What is the linear speed of the sphere when it reaches the bottom of the ramp? I = 2/5 MR² for a solid sphere and g = 9.8 m/s²
m = 4.0 kg
r = 0.12 m
theta = 15 degrees
h = 1.2 m
I = 2/5 MR²
g = 9.8 m/s²
v = ?
Kroll = Kt + Kr
Ei = Ef
(Kt + Kr + Ug)i = (Kt + Kr + Ug)f
Kt & Kr are initially = 0 because the sphere is at rest
Ug final is = 0 because the sphere will not have any more PE
Ugi = ½ mv² + ½ Iω²
Ugi = ½ mv² + ½ (2/5 mr²)(ω²)
Ugi = ½ mv² + ½ (2/5 m(v²/ω²)(ω²))
Ugi = ½ mv² + 1/5 mv²
factor out mv²
Ugi = mv² * (1/2 + 1/5) = 7/10 mv²
mgh = 7/10 mv²
m cancels
(9.8 m/s)(1.2 m) = 7/10 v²
v = 4.1 m/s