KIDNEY FUNCTION TEST AND NON-PROTEIN NITROGENS
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Kidney
paired bean shaped organ, located retriperitoneally either of the spinal column
Functional Unit: Nephron
Glomerulus
non selective filter of plasma substances
The main filtering unit of the kidneys
Act as sieve of the kidneys
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Immediate reabsorption of essential substances (e.g glucose, water, peptides and also the other nutrients from the tubule fluid back into the blood)
Loop of Henle
Site of the renal concentration
Water and Sodium Chloride is also reabsorbed from the filtrate
Distal Convoluted Tubule
Final site for the adjustment of the urine composition
Collecting Duct
Final site for the renal concentration, wherein it will collect the urine and later on it will transport it to pelvis to the ureters. And temporary stored in urinary bladder
There is still reabsorption of excess water
CLEARANCE TEST
Tests which measure the rate of glomerular filtration
Usually the unit is mL/min
Cleared or removed the substances from the plasma to urine
CREATININE CLEARANCE TEST
Creatinine occurring through metabolic production is eliminated from the plasma by glomerular filtration and therefore a measurement of its rate of clearance affords a measure of the process
Excellent measure of renal function
It is freely filtered by the glomeruli but not reabsorbed
Daily the creatinine excreted is 1.2 to 1.5g per day
INCREASED CREATININE CLEARANCE
Increased in URINE
Decreased in the PLASMA
High cardiac output
Pregnancy
Burns
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
DECREASED CLEARANCE TEST
Decreased in URINE
Increased PLASMA
Impaired kidney function
Shock, Dehydration
. Hemorrhage
Congestive heart failure
INULIN CLEARANCE TESTS
freely passes the glomeruli but is neither secreted nor absorbed by the tubules
Considered to be the most accurate measure of GFR
This is the reference method
Not commonly/routinely used
Good Measure for Clearance
Not excreted and not reabsorbed
UREA CLEARANCE TEST
Urea is freely filtered by the glomeruli but variably reabsorbed in the tubules depending upon the transit time (rate of urine flow along the course of tubules) of urea filtrate
CYSTATIN C
Produced at a constant rate by all nucleated cells
Not secreted but completely reabsorbed
Serum Cystatin C Levels- Increases more rapidly than creatinine in the early stages of GFR involvement
B2-MICROGLOBULIN
Easily filtered and reabsorbed
Usually elevated in cases of there is increased cellular turnover
Increased in inflammation and in renal failure
MYOGLOBIN
Associated with acute skeletal and cardiac muscle injury
Rhabdomyolysis → acute renal failure
Continuous breaking down of muscles
Myo = muscles (associated with muscle injuries)
Myoglobin released from the skeletal muscle is enough to overload the PCT and later on cause acute renal failure
MICROALBUMINURIA
Small amount of albumin in the urine
Trace amount of albumin in the urine
Can lead to kidney damage
EXCRETORY TEST
Both utilizes dye
PARA-AMINO HIPPURATE TEST (PAH) OR DIODRAST TEST
Measures the renal plasma flow
REFERENCE RANGE: 600 to 700 mL/min
PHENOLSULFONAPHTHALEIN (PSP) DYE EXCRETION TEST
Dye excreted will be proportional or equal to tubular mass
REFERENCE RANGE: 1200 mL/min
CONCENTRATION TEST
Reflect the function of collecting tubules and Loop of Henle
More on assessing the quantity of solutes in urine
Assess the ability of those parts to produce a concentrated urine
Prevalent solute are the urea, chloride, sodium
Preferred Sample: First Morning Urine Sample
SPECIFIC GRAVITY
Measurement is affected by the solute number and mass
The simplest
REFERENCE RANGE: 1.005 to 1.030
OSMOLALITY
Only affected by the number of solute present
Serum osmolality (Due to Sodium and Chloride)
Urine osmolality (Due to Urea)
Useful for assessing water deficit or excess
REFERENCE RANGES (Serum): 275 to 295 mOsm/kg
REFERENCE RANGES (Urine): 300 to 900 mOsm/kg
DIRECT METHODS
Freezing Point Osmometry
More on common
Procedure using super cooling temperature (-70oC)
Quality check the solution/freezing point osmometer you can use Sodium Chloride (QC reference solution)
Vapor Pressure
INDIRECT METHODS
Osmolal Gap
Difference between the measured and calculated plasma osmolality
A sensitive indicator of alcohol and drug overdose
Utilizes a computation
Subtract the measured and calculated by the machine
NON-PROTEIN NITROGEN (NPN
Test for measuring renal blood flow
NPNs are the waste products of the body as a result of degradation (amino acids, proteins, or muscle metabolism)
UREA
Major excretory product of protein metabolism
Formed in the liver from amino groups (NH2) and free ammonia generated during protein catabolism
Check/Verify the adequacy of dialysis
Protein Content of the Diet
Rate of Protein Catabolism
90% Excreted, 10% Remains in the bloodstream
BLOOD UREA NITROGEN (BUN)
In severe liver damage = Decreased Levels of Urea
It is also the first metabolite to increase in KIDNEY DAMAGE or DISEASES
It is used as a SCREENING TEST for kidney disease
Urea is readily removed by DIALYSIS
CHEMICAL METHODS – DIRECT METHODS
A. DIACETYL MONOXIME METHOD (DAM)
Also known as Fearon’s Reaction
Urea + Dam → yellow diazine derivative
Arsenic thiosemicarbazide is added to enhance color reaction and has the ability to exclude protein interferences
ENZYMATIC METHOD – INDIRECT METHOD
Indirect – have to generate a compound first or a different reaction
PRIMARY STEP – hydrolysis of urea by urease
A. UREASE-NESSLER METHOD
Urea + Urease → NH3 + CO2
NH3 + Nessler’s reagent → Dimercuric Ammonium Iodide (yellow)
Ammonia will continue on the reaction
B. UREASE BERTHELOT METHOD
Urea + Urease → NH3 + CO2
NH3 + phenol hypochlorite → indophenol (blue)
Phenol hypochlorite is phenol + sodium chlorite
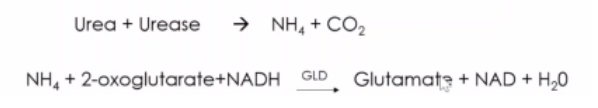
C. COUPLED UREASE/ GLUTAMATE DEHYDROGENASE (GLD)
Method – UV Enzymatic Method
In lab, we usually use reagents either GLD or Berthelot . If we use UV enzymatic method, colorless solution.
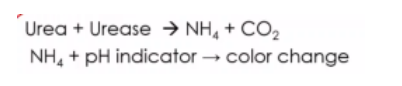
D. INDICATOR DYE
E. CONDUCTIMETRIC
Conversion of unionized urea to NH4 and CO3
Results in increased conductivity (Electrode)
ISOTOPE DILUTION MASS SPECTROPHOTOMETRY
REFERENCE METHOD
Expensive so not recommended for routine purposes
REFERENCE VALUE: 8-23 mg/dL (2.9 – 8.2 mmol/L)
CONVERSION FACTOR: 0.357
UREMIA
defined as the increased in urea and creatinine (azotemia) with accompanying clinical signs and symptoms of renal failure like
METABOLIC ACIDOSIS
Acidic environment in the body because we cannot excrete acidic products in the body. It only retains in the bloodstream
HYPERKALEMIA
Increased potassium. We cant excrete potassium, it increases in the blood.
EDEMA
One of general function of kidney is to regulate water volume balance, if we cant reabsorb and excrete water properly. Water will retain in the body, there will be generalized edema
If px have kidney problem, manas si patient
AZOTEMIA CAN BE DIFFERENTIATED INTO THREE
Pre-Renal
circulation through kidneys is less efficient than usual
AZOTEMIA CAN BE DIFFERENTIATED INTO THREE
Renal
characterized by lesions on the parenchyma (tubular injury)
AZOTEMIA CAN BE DIFFERENTIATED INTO THREE
Post-Renal
obstruction in the urinary tract
CREATININE
Creatinine is the principal waste product of muscular metabolism derived mainly from creatine (alpha-methyl guanidoacetic acid)
Directly proportional to muscle mass
Compared to urea, this is not easily removed by dialysis
DIRECT JAFFE METHOD
Formation of red tautometer of creatinine picrate when creatinine serum is made to react with a freshly prepared alkaline sodium picrate solution
Product is red or red-orange. Dependent on concentration, higher concentration yields darker product
FOLIN WU METHOD
Sensitive but not specific
LLOYD OR FULLER’S EARTH METHOD
Both sensitive and specific
Lloyd’s reagent = Sodium aluminum silicate
Fuller’s reagent = Aluminum magnesium silicate
Not routinely used because it is time-consuming and not readily automated
DIRECT REDOX METHODS
Uric acid is oxidized to allantoin and CO2 by phosphotungstic acid reagent
In the process, phosphotungstic acid is reduced to tungsten blue under alkaline condition
KINETIC JAFFE METHOD
Requires equipment for precision
Serum is mixed with alkaline picrate solution and the rate of change in absorbance is measured between 2 points
CARAWAY METHOD
Oldest method of uric acid determination
MODIFICATION OF CARAWAY
Henry’s Method
ENZYMATIC METHOD – INDIRECT METHOD
BLAUNCH AND KOCK (URICASE METHOD)
Differential or Absorption Spectrophotometry
BERTHELOT'S REACTION
The ammonia formed reacts with phenol and alkaline hypochlorite using sodium nitroprusside as catalyst to form indophenol blue
NESSLERIZATION
yellow in color nitrogen is present in low to moderate concentration
orange brown - nitrogen is present in high concentration