Lecture 1: The Overlapping Generations Model
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Which economic view applies in the short run?

What do we know about production, output and unemployment in the short-run?

Which economic view applies to the long-run?
Neoclassical
What do we know about markets and unemployment in the long-run?

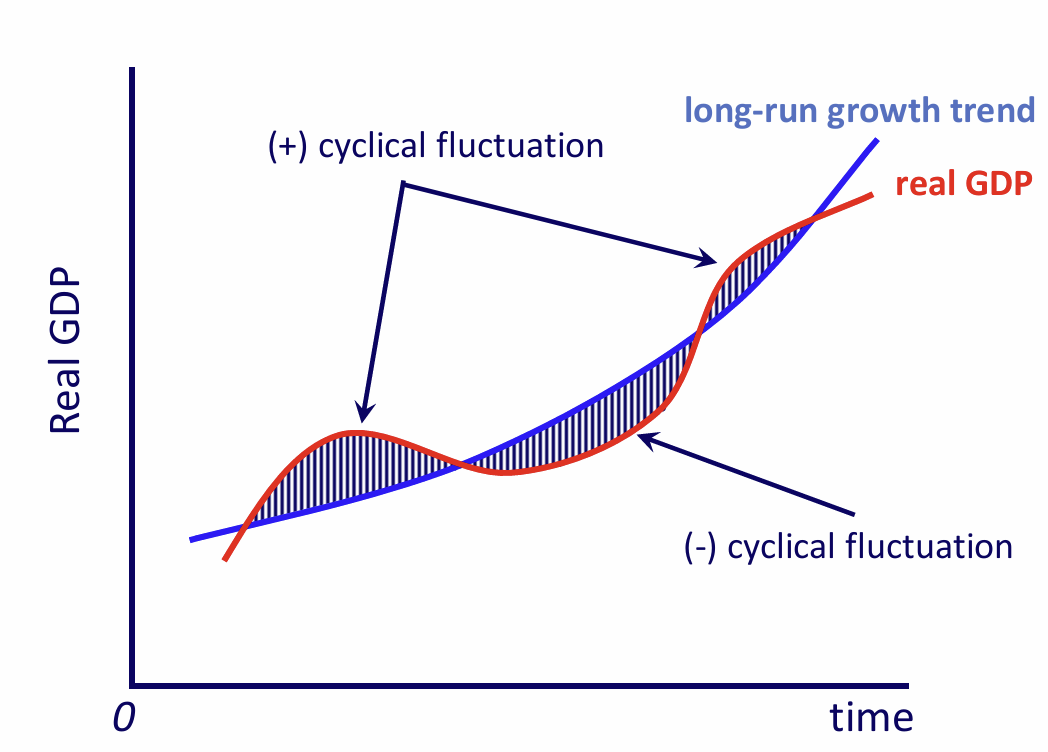
How do Keynesian policies alter the cycles?

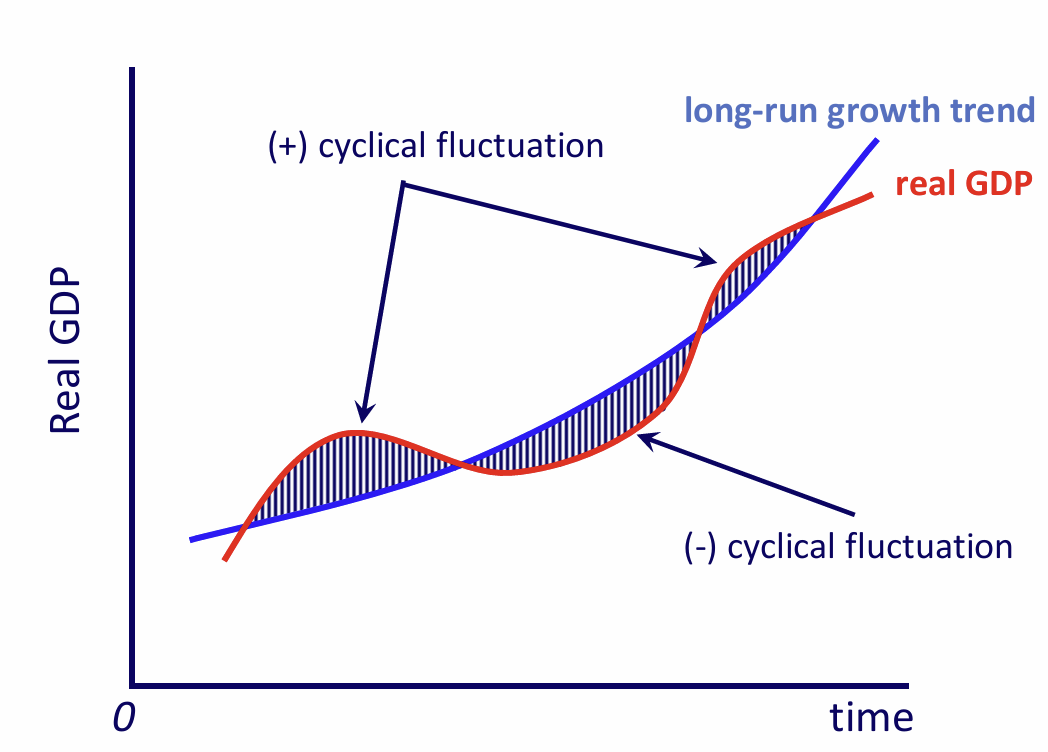
How can we increase the long-run growth trend?

How has macroeconomic theory evolved over time?


What is Y equal to and what leads to an increase in Y?
Neoclassical production function
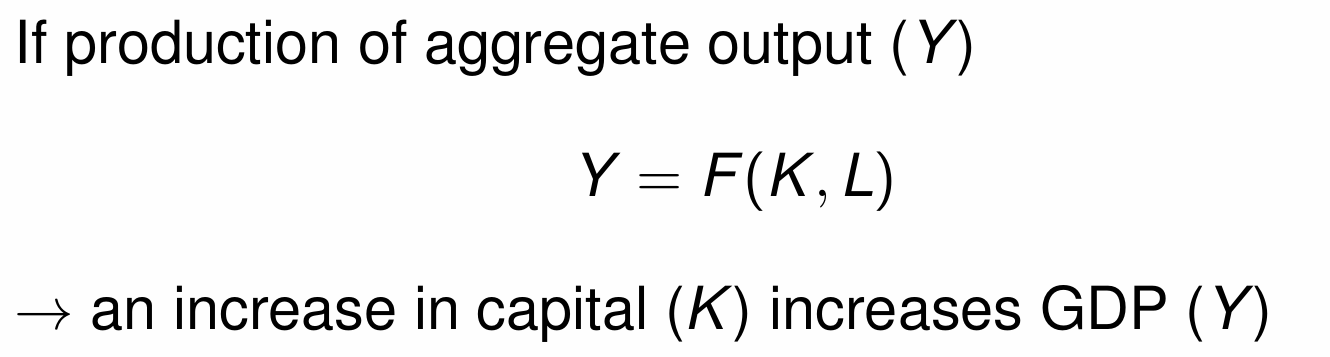
What time period are savings made by households based on?
Future periods (forward looking)
What are the main two models used to analyse the savings decisions of households?


What is the main difference between the models?
We choose OLG as it is easier to analyse and manipulate

In the Diamond OLG model, how many periods do individuals live for and how long is each period?

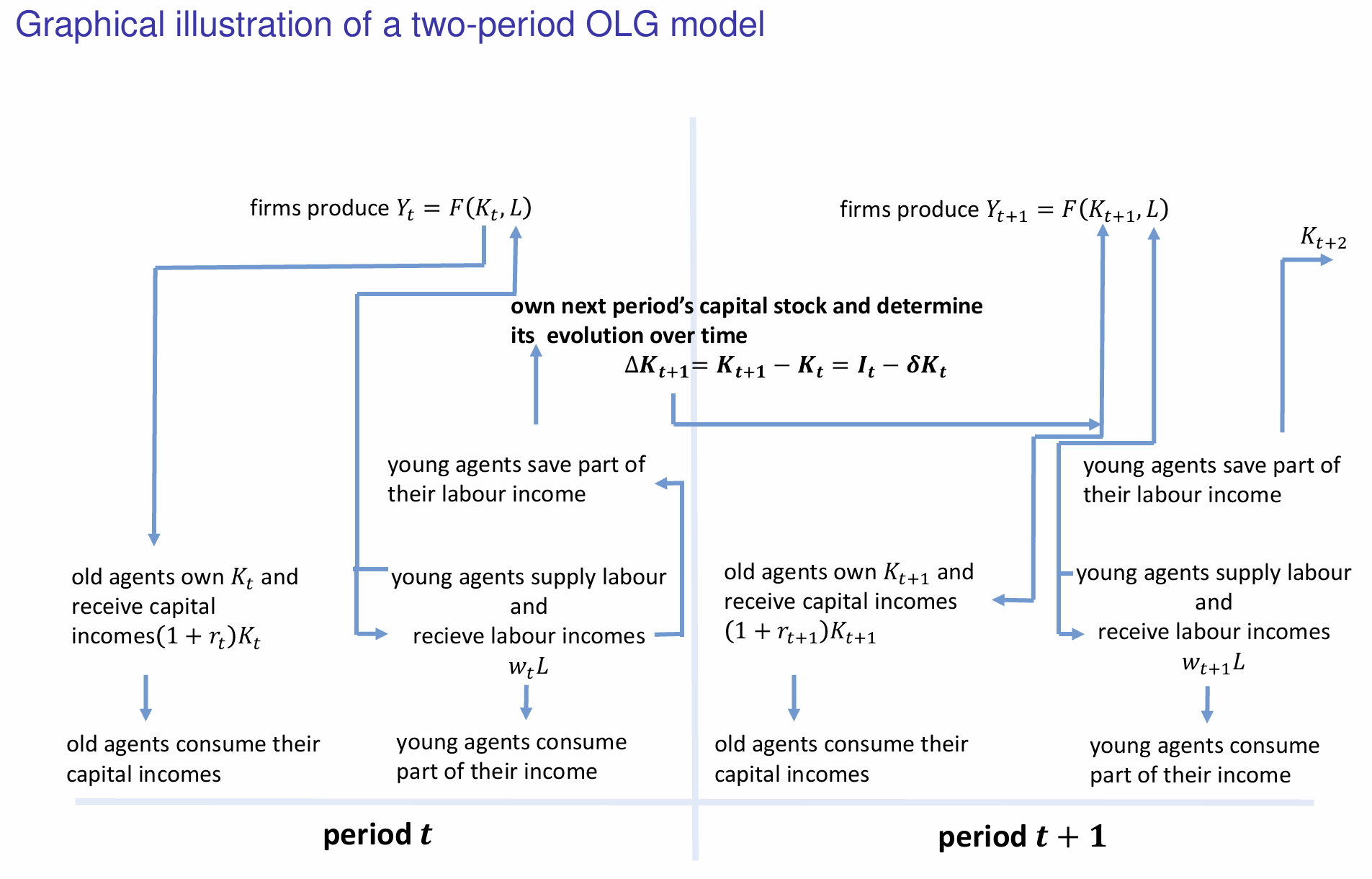
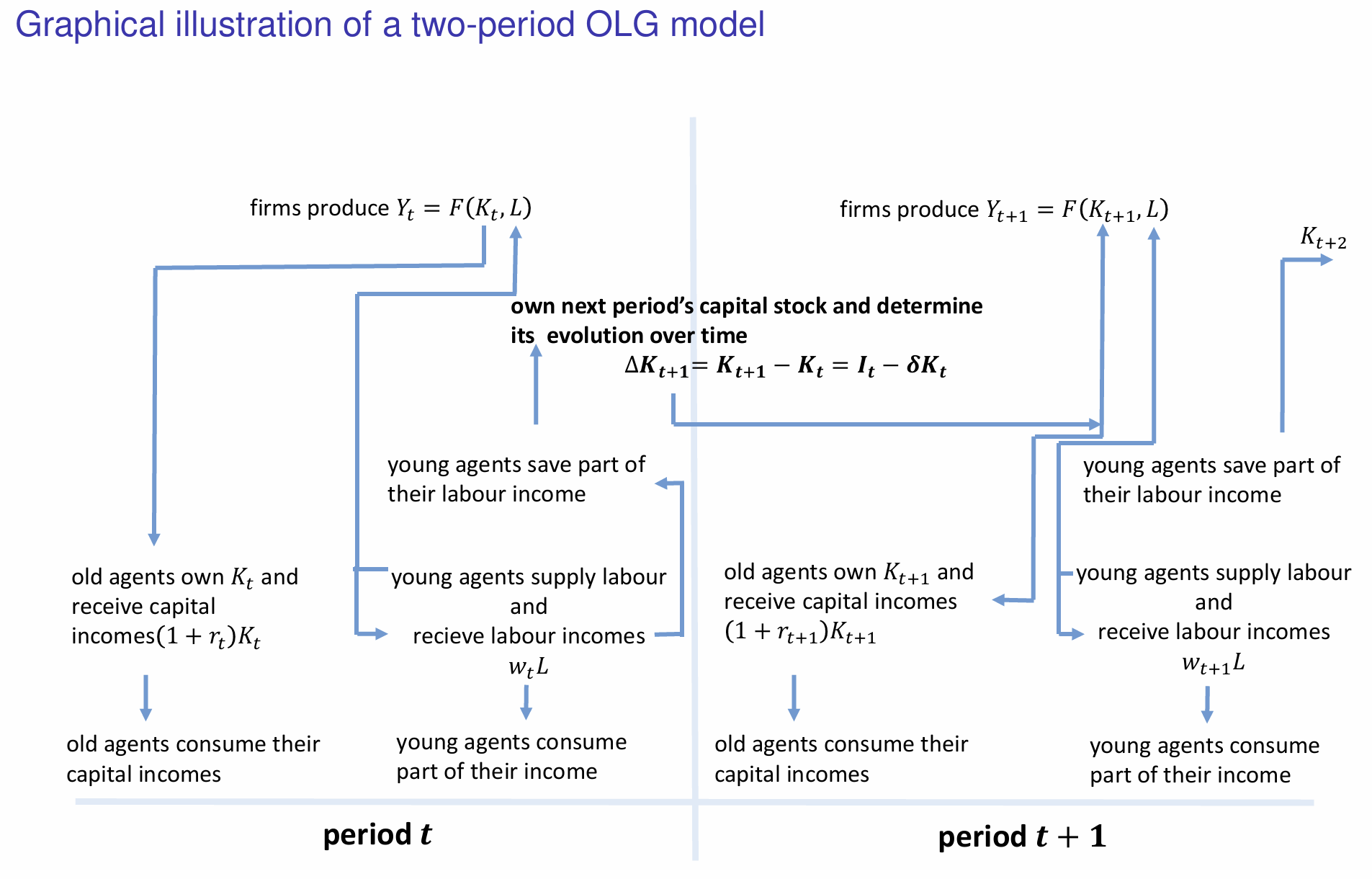
At any point in time, the economy exists of two generations. What are they?
Young and old
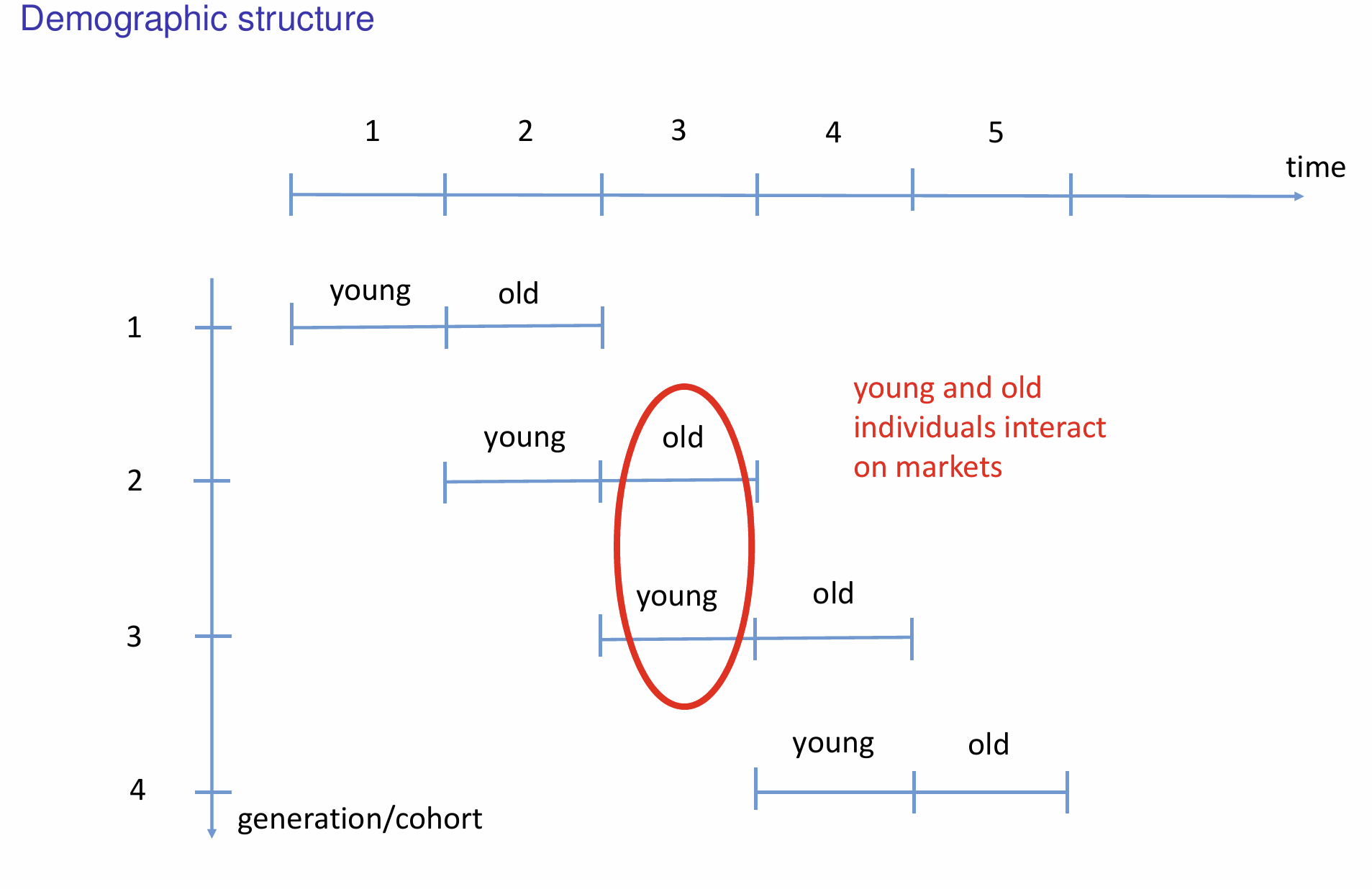
What do individuals do when young?

What do individuals do when old?

In the general equilibrium structure of the Diamond OLG model, is time discrete or continuous?
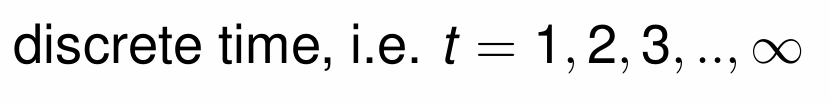
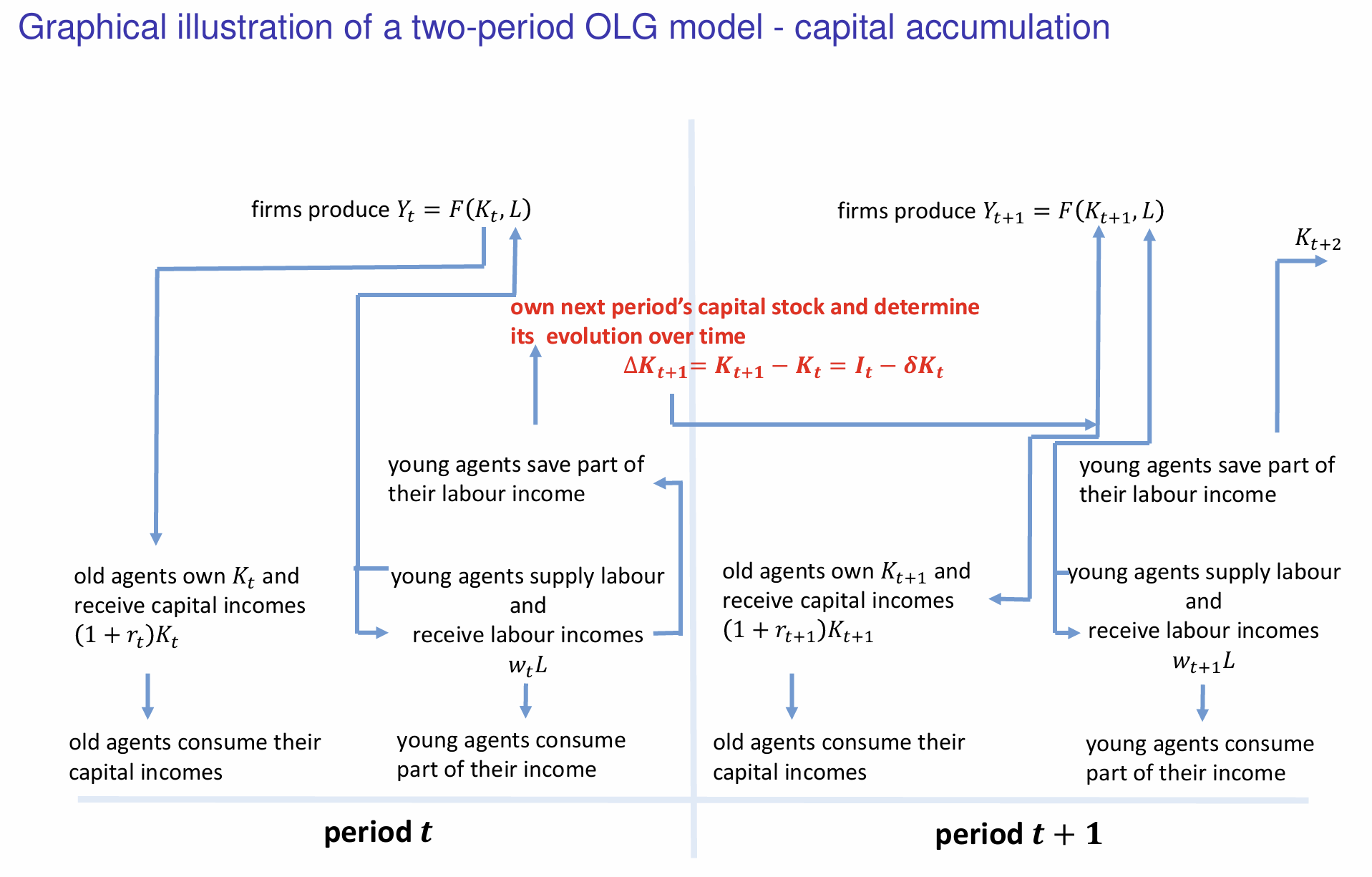
How do we denote the change in capital stock and when is it positive?
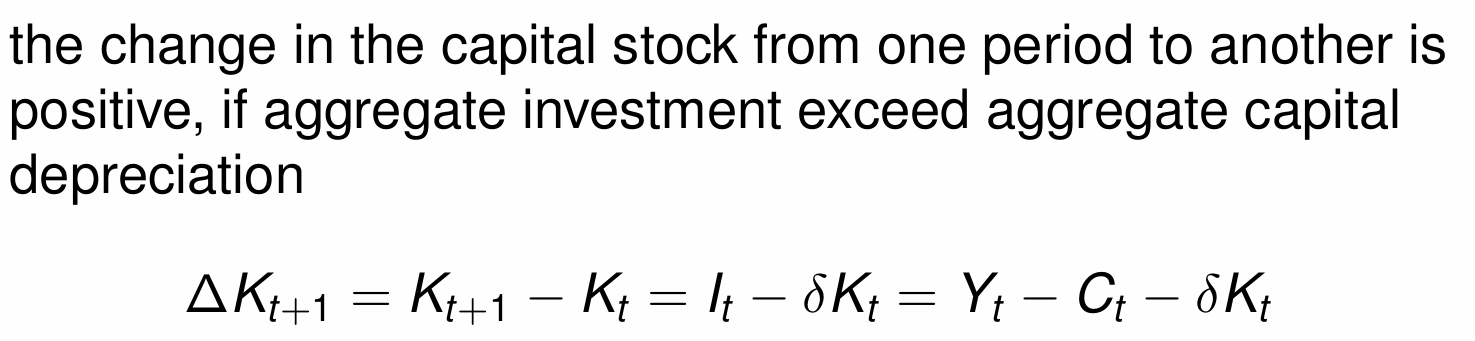
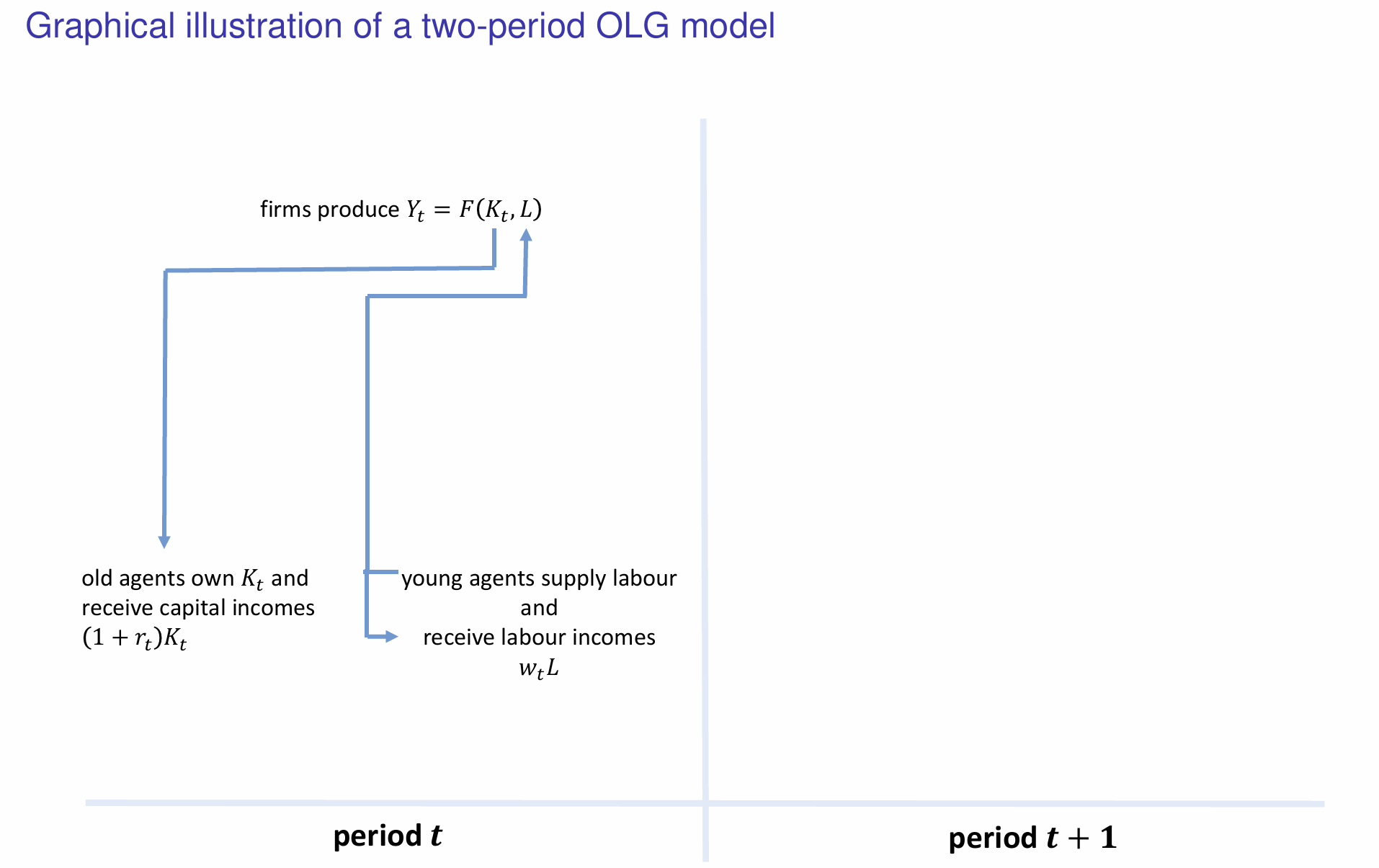
What happens to capital and labour incomes?
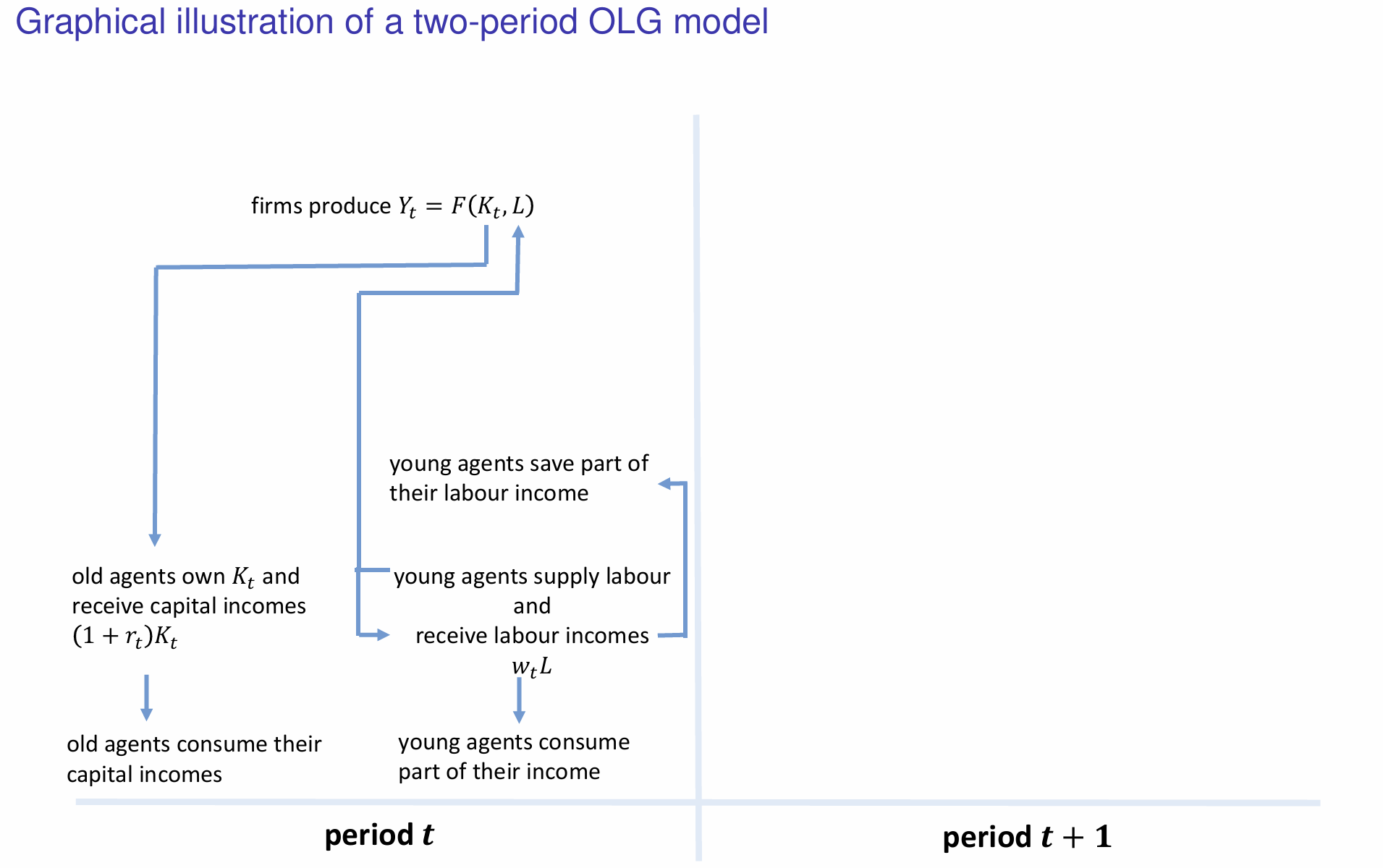
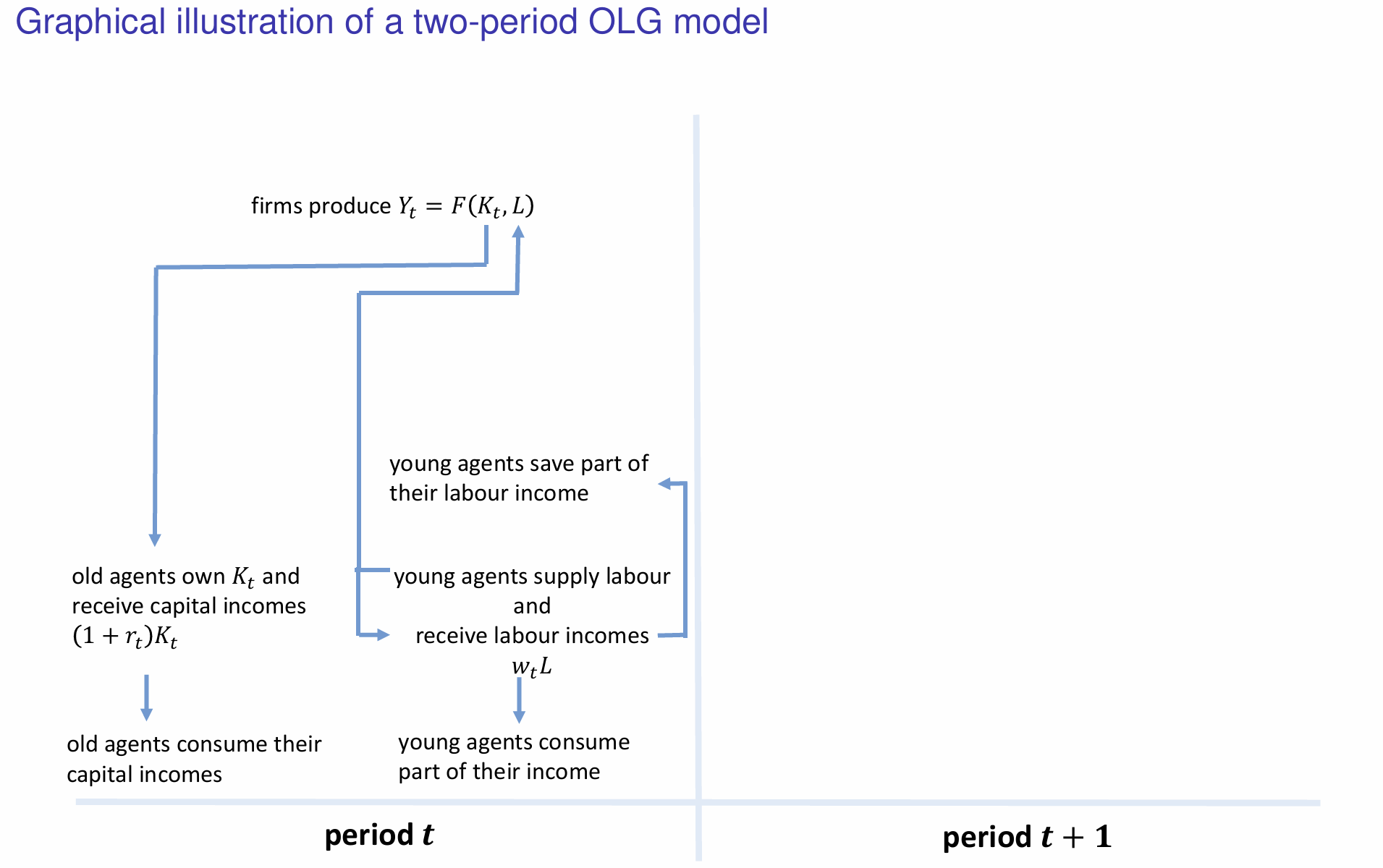
How do the savings made by young individuals influence the capital stock and evolution of capital in the next period?
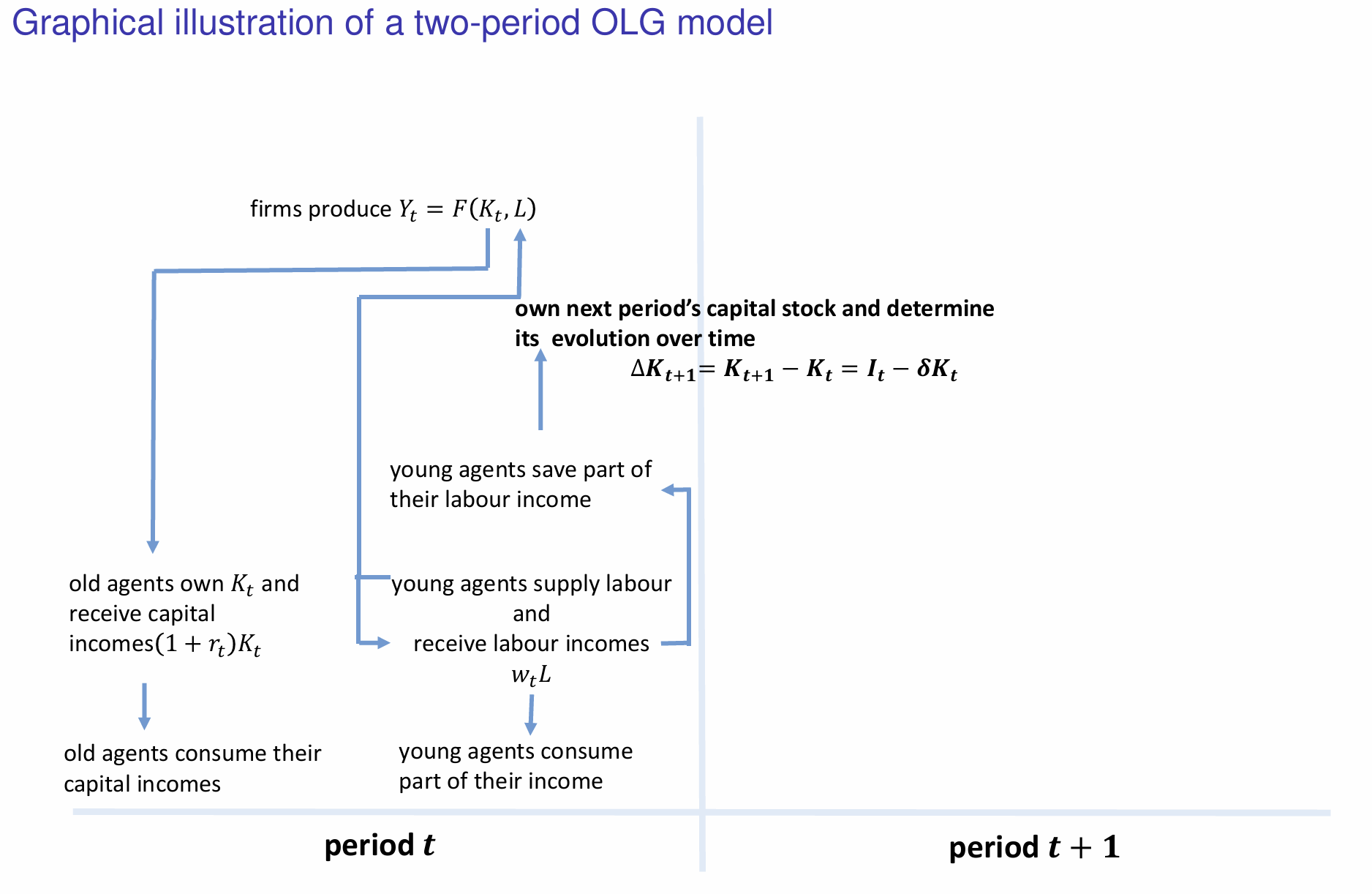
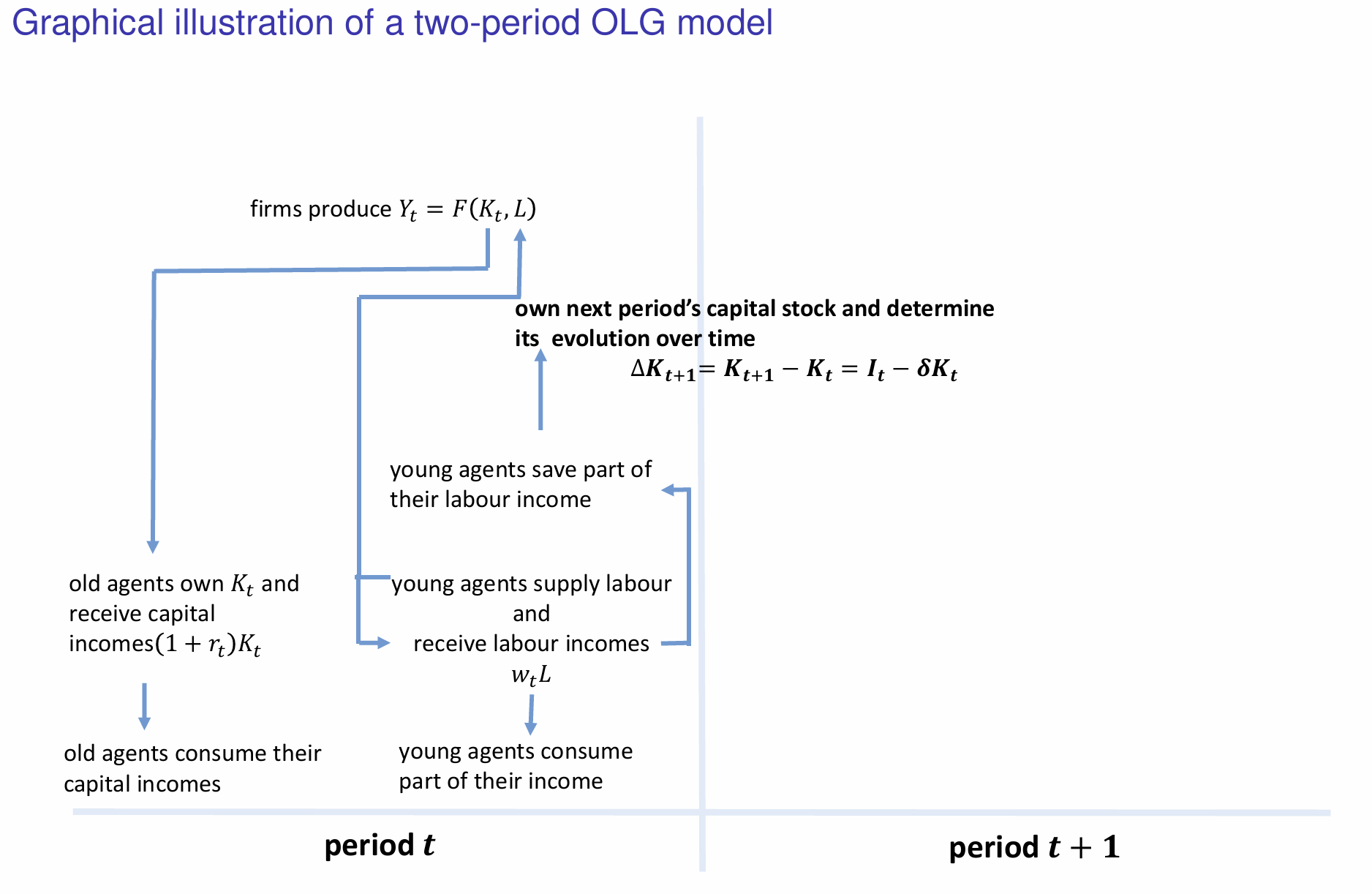
How is the new capital stock utilised in the next period (t+1)?
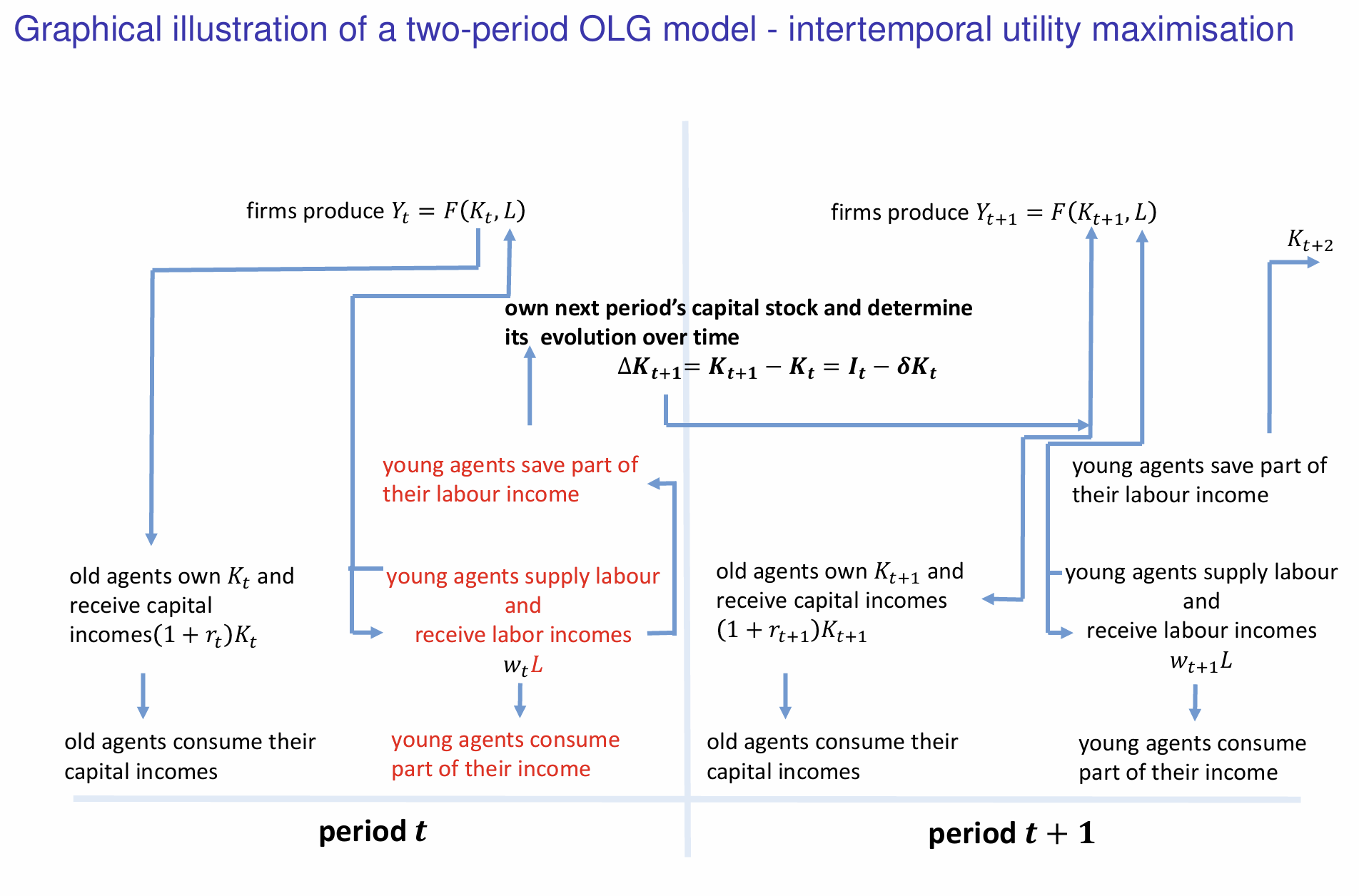
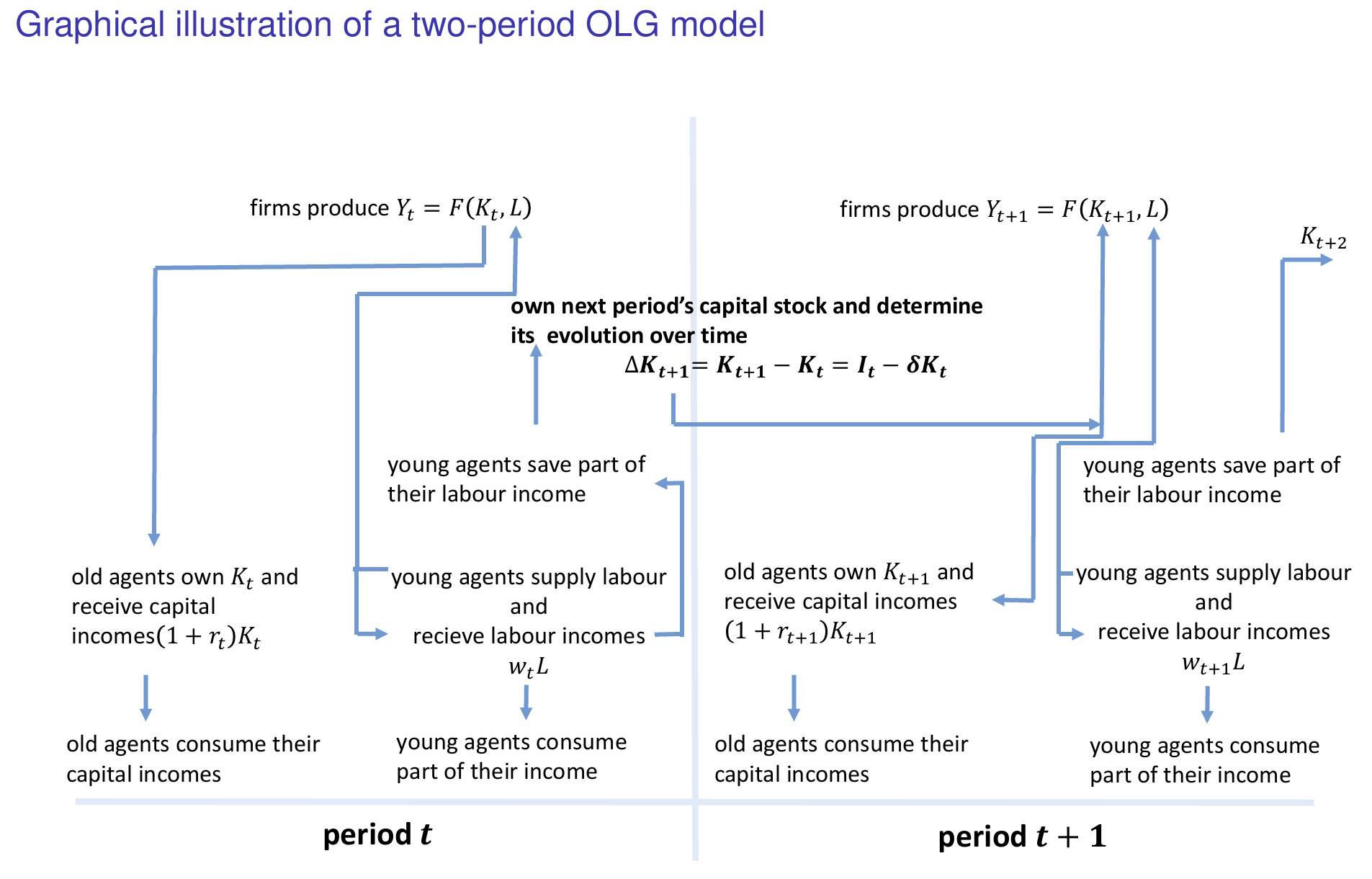
Which components represent the intertemporal utility maximisation decision?
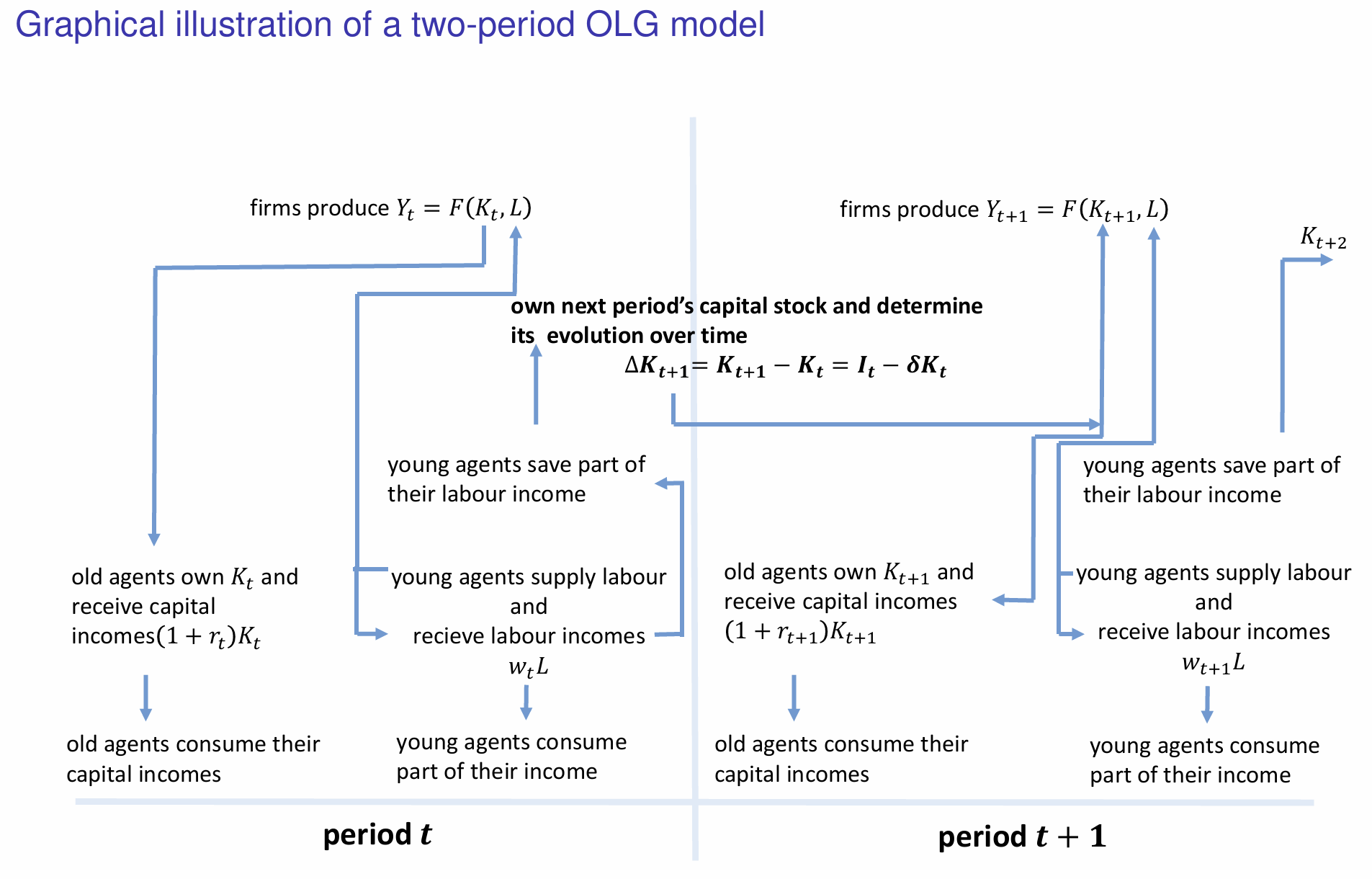
Which components represent the profit maximisation decision?
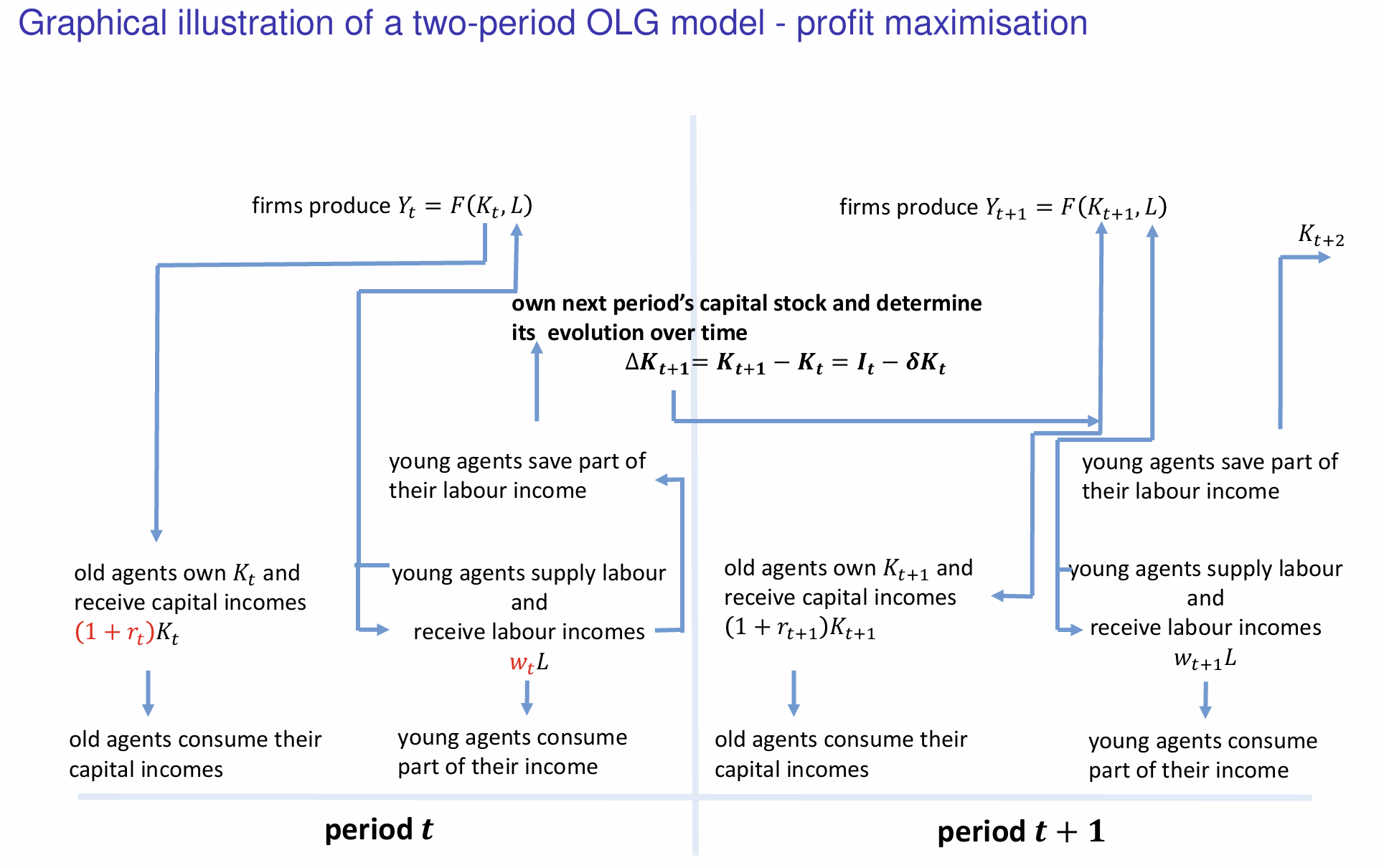
Which component represents how capital accumulates over time?
What is the total utility function for consumption when young and old?
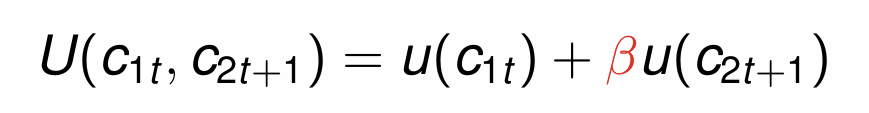
What values can the discount factor (β) take and how is it calculated?

What assumptions do we make about the utility functions when young and old?
Diminishing marginal returns
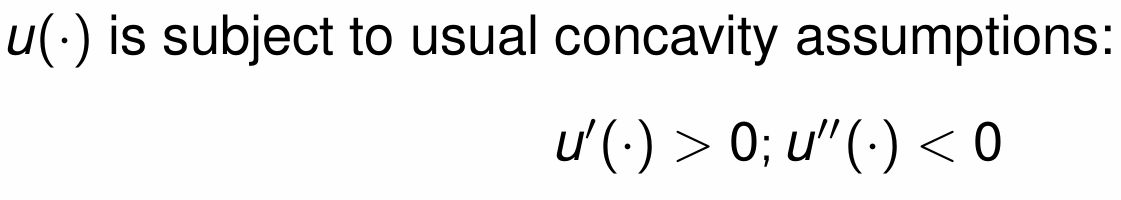
What do we assume about labour supply when young?

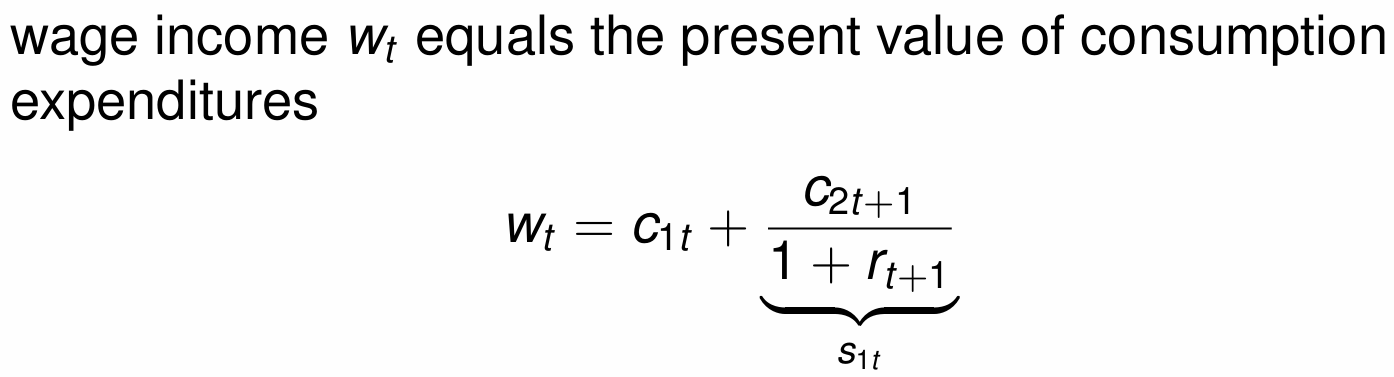
How do we calculate wage income and what does it represent?
What is the equation for the evolution of the population?
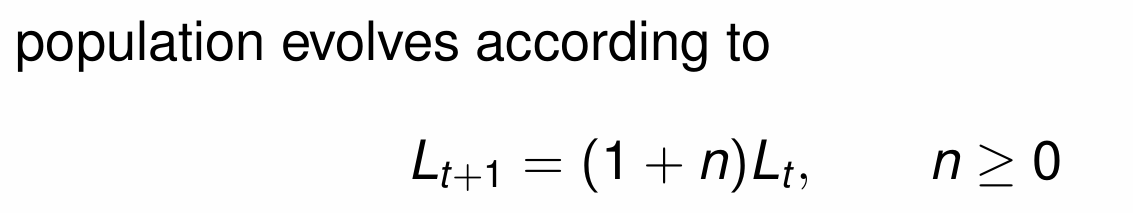
What is the equation for output?
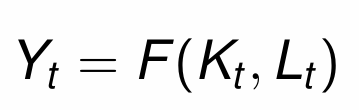
What form of the OLG model has just been derived?
Canonical OLG model
How is the lifetime utility of an individual in generation t calculated?
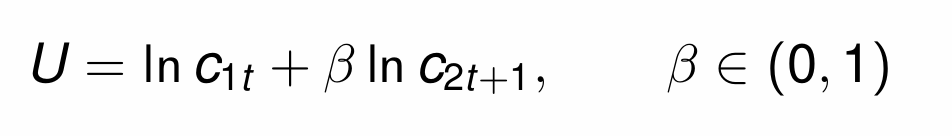
What are the budget constraints for the individual in generation t? (i.e. wt and st)
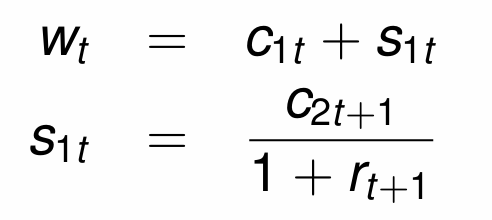
How do we calculate the production function in generation t?
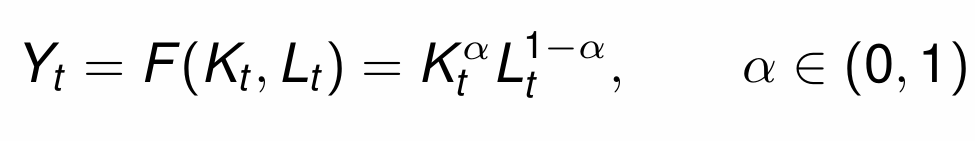
How do we write the Euler equation?
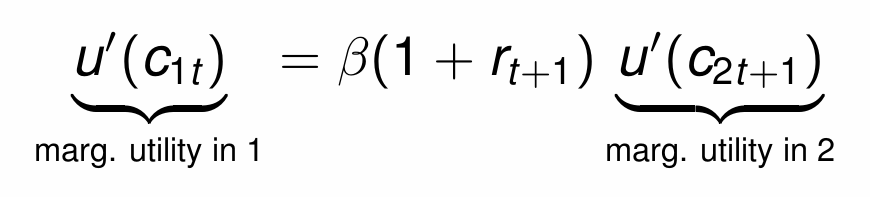
How do we calculate consumption when old in t+1?
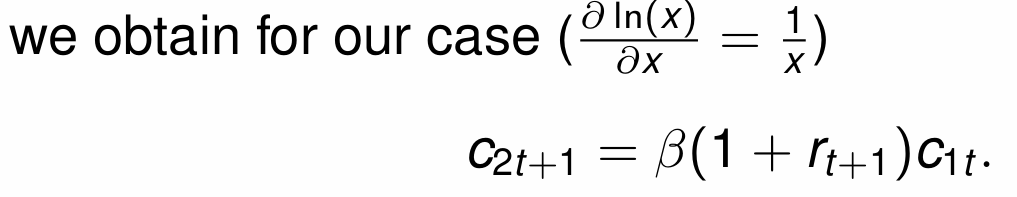
When we combine the Euler equation and the budget constraints, what are the equations for c1t and s1t?
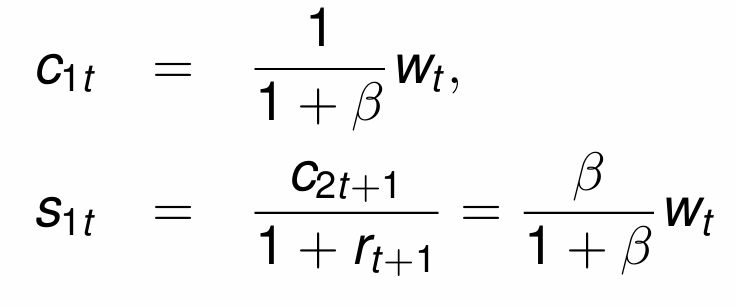
What causes s1t to increase?


Firms aim to maximise profits
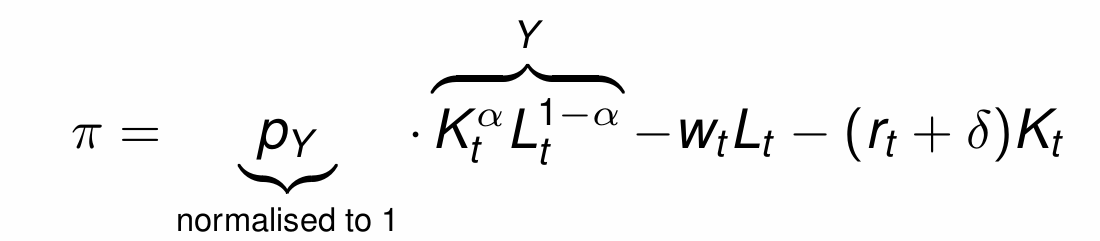
What does the assumption of perfect competition in goods and factor markets mean firms do with prices?
Firms are price takers rather than price setters
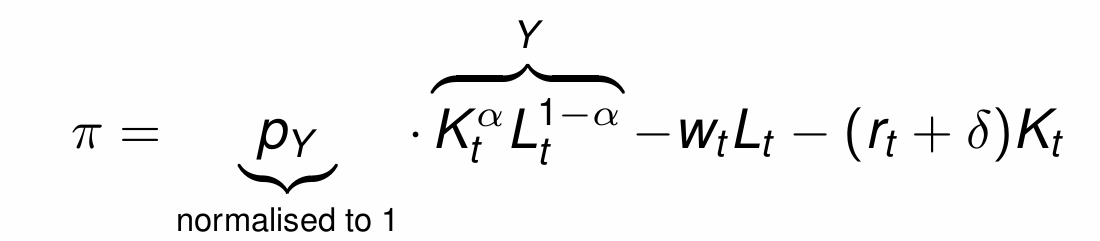
Maximising profits wrt capital in period t gives what equation?
Marginal Product of Capital (MPK)
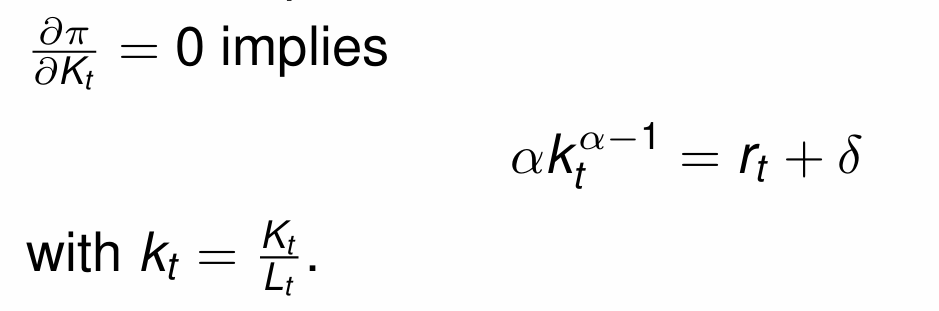
If we assume that the rate of depreciation of capital is equal to 1, what does the equation become?

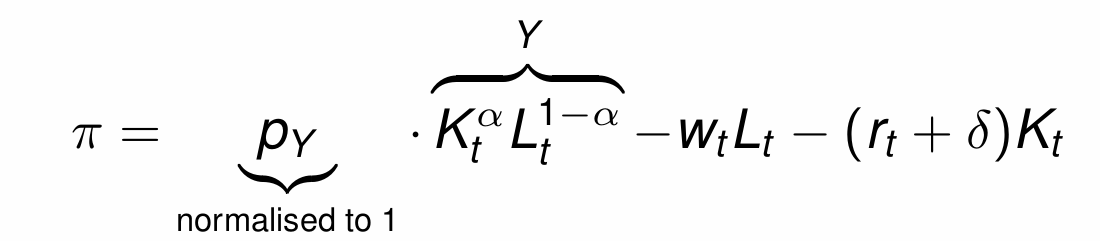
Maximising profits wrt labour in period t gives what equation?
Marginal Product of Labour (MPL)

When does aggregate investment increase the aggregate capital stock?
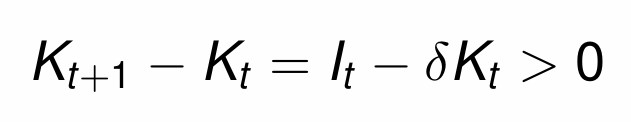
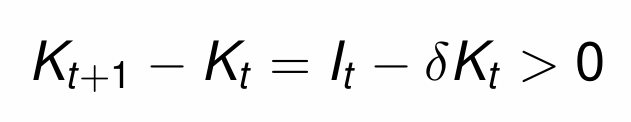
How does this change given the assumption of δ = 1?
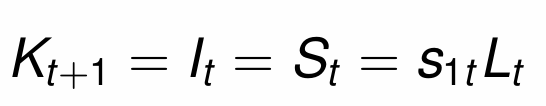
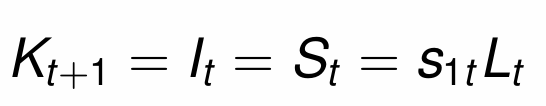
Substitute in s1t from the household optimisation problem
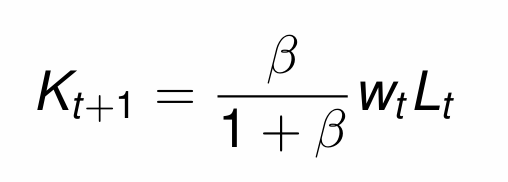
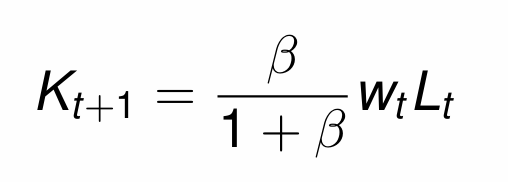
Substitute in the MPL
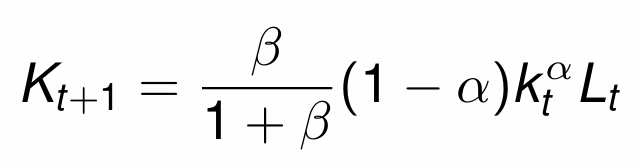
How do we express the capital intensity (capital per worker)?
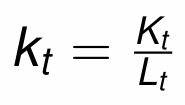
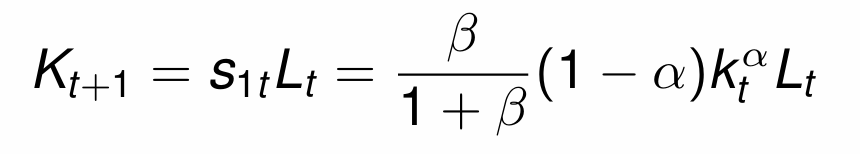
Divide by Lt and simplify to get the fundamental equation governing the evolution of kt
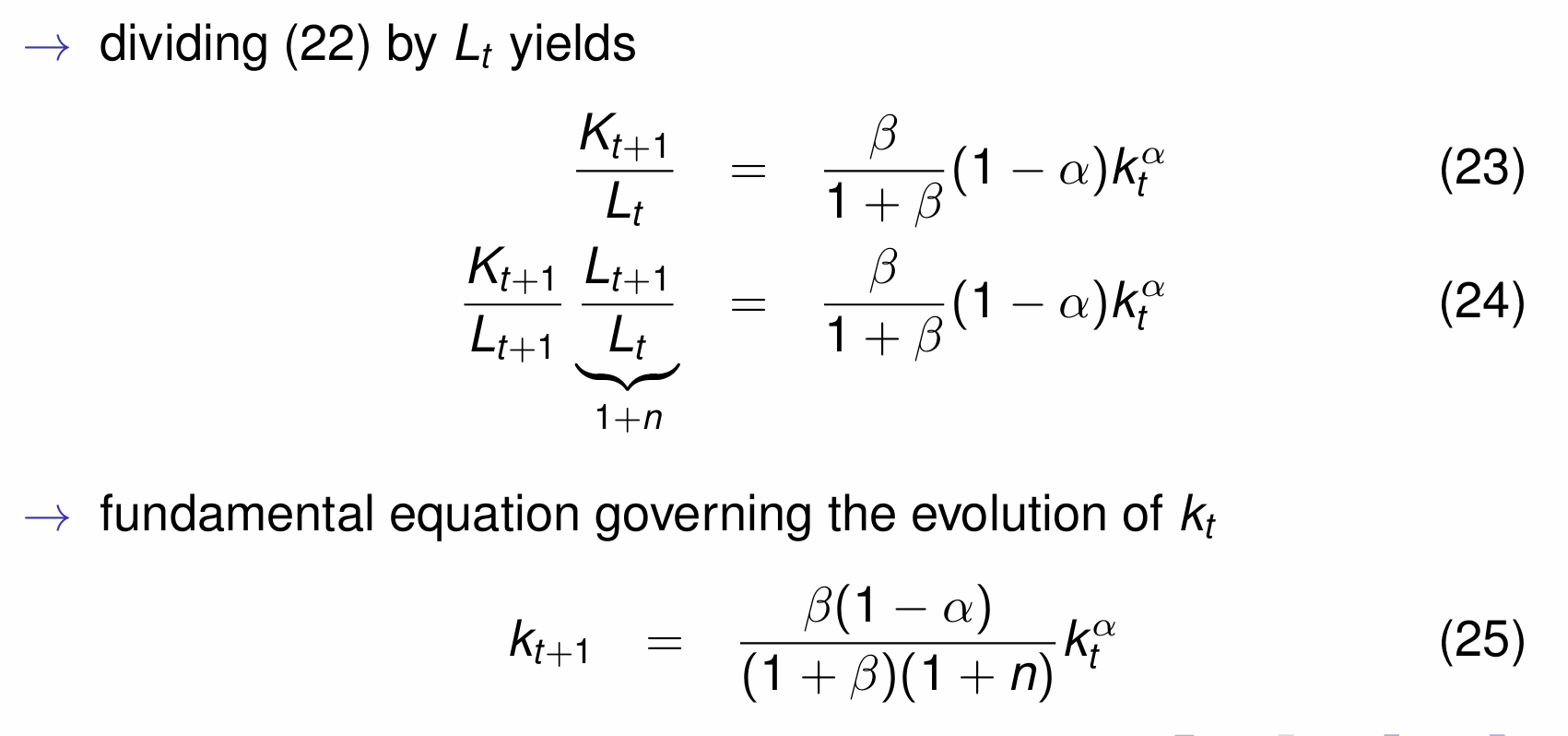
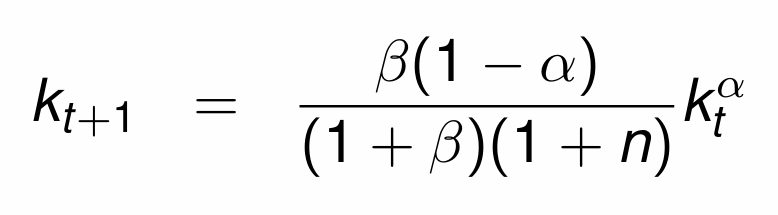
Obtain the steady state (stationary) solution
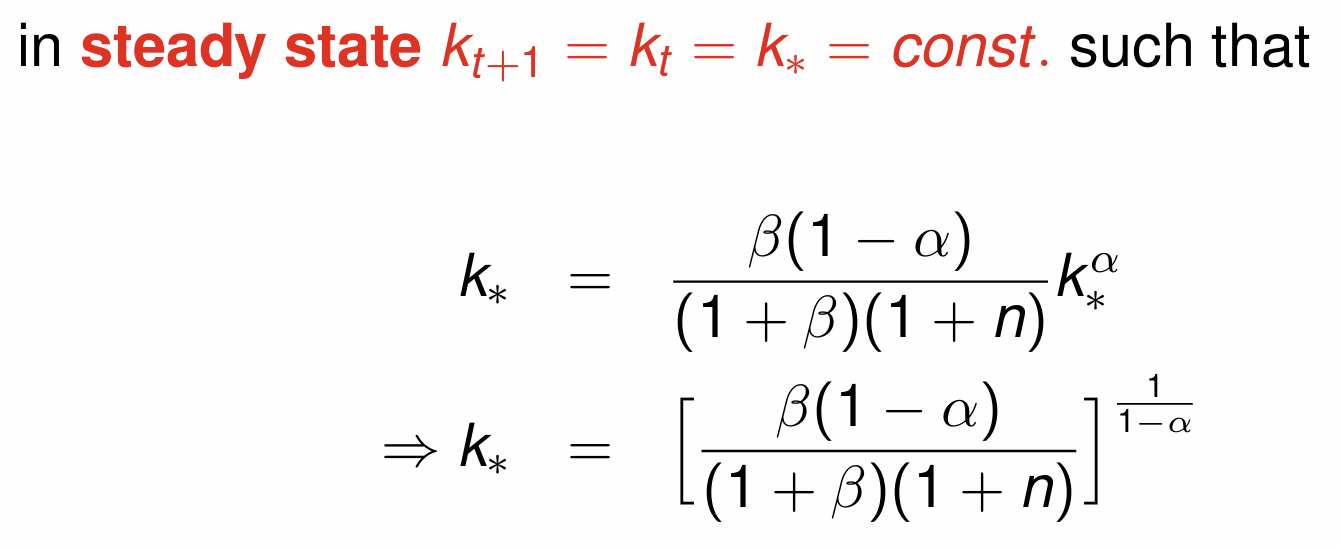
What do we assume about the variables that are functions of k at steady state?

Are the steady state assumptions realistic? And when is it appropriate to model in this way?

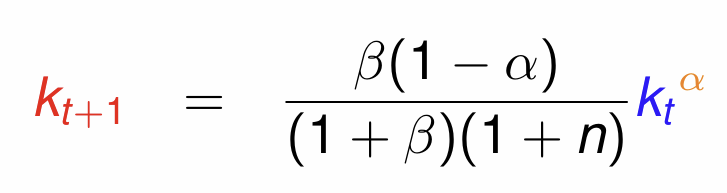
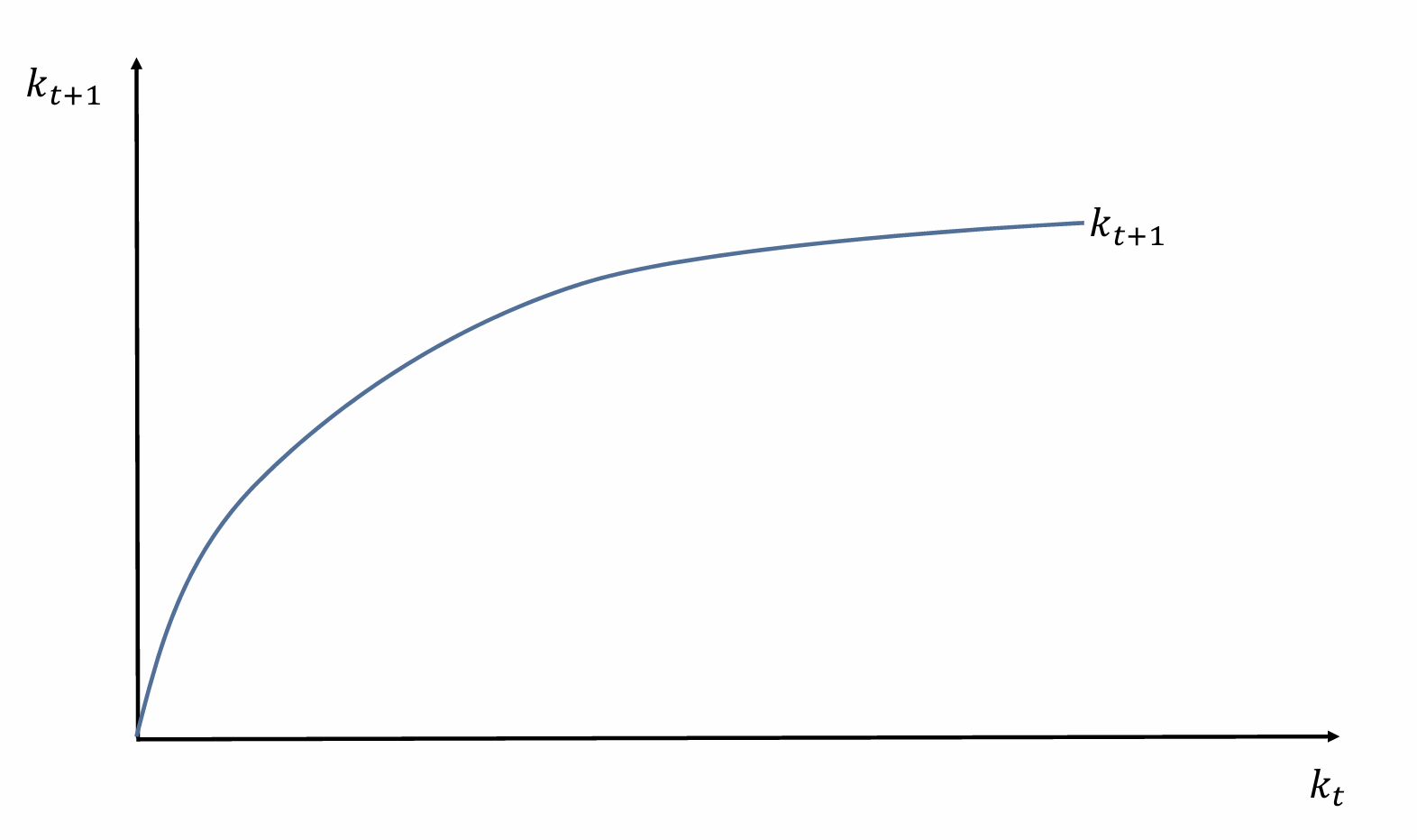
If kt = 0, what does that mean for the starting point when plotting kt+1?
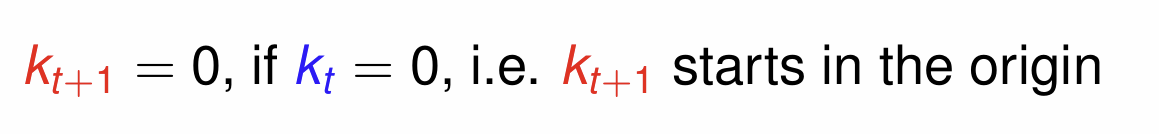

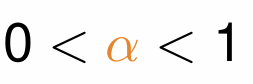
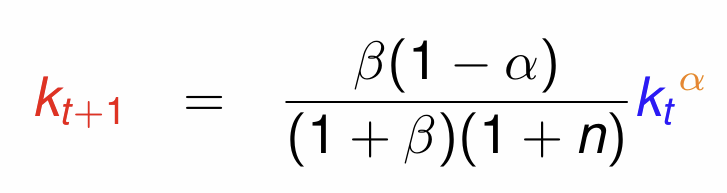
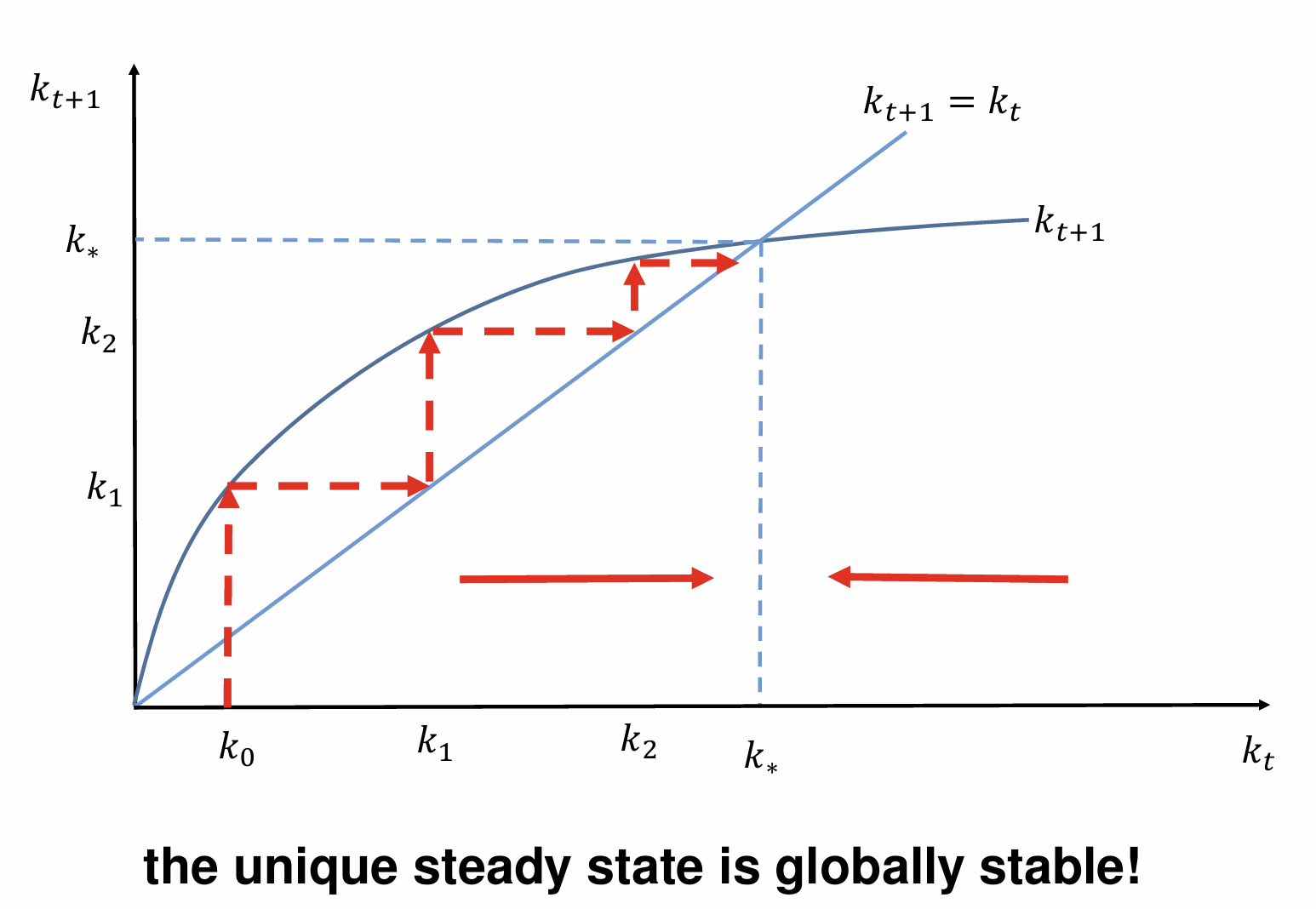
Draw the evolution of k
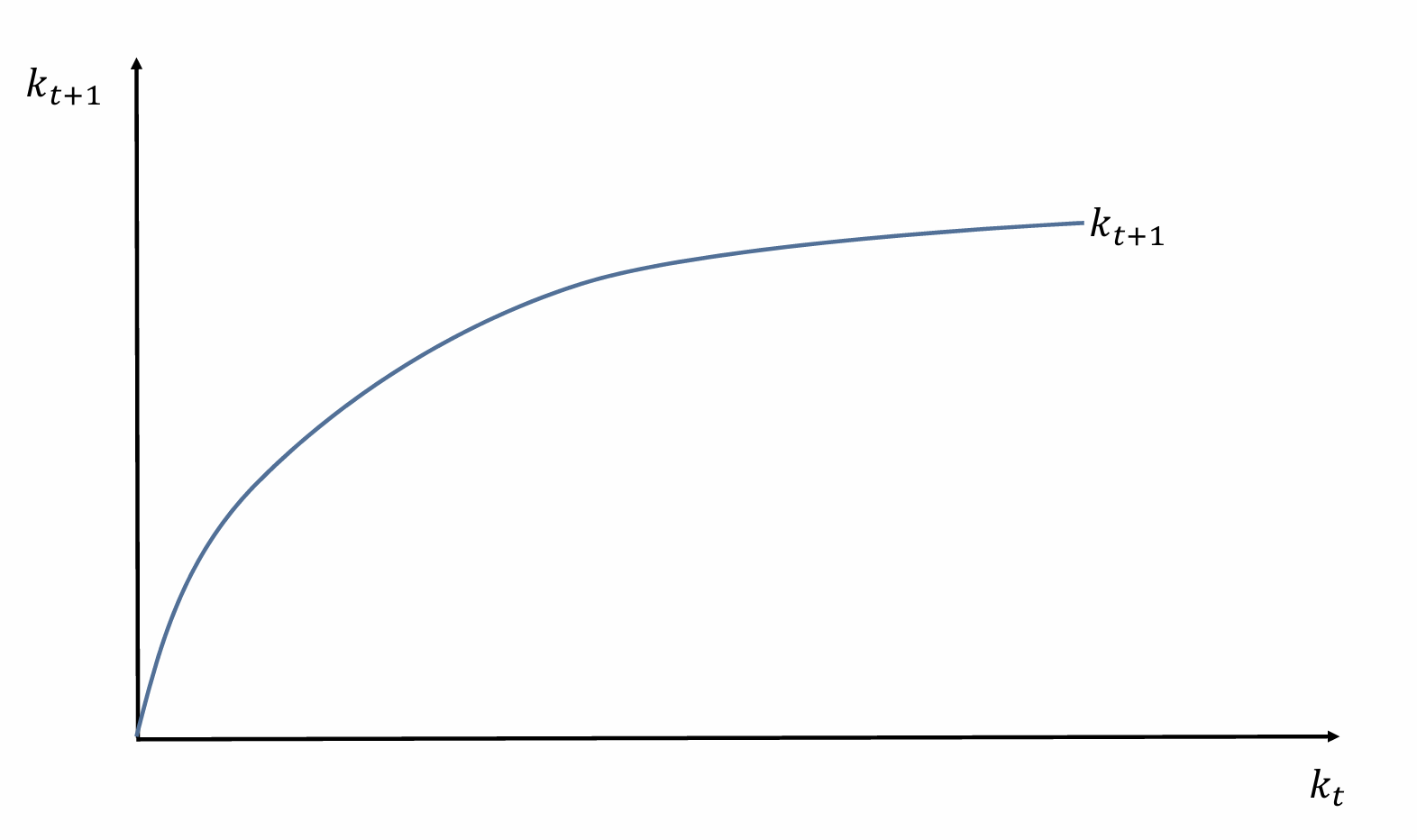
Add in the steady state solution
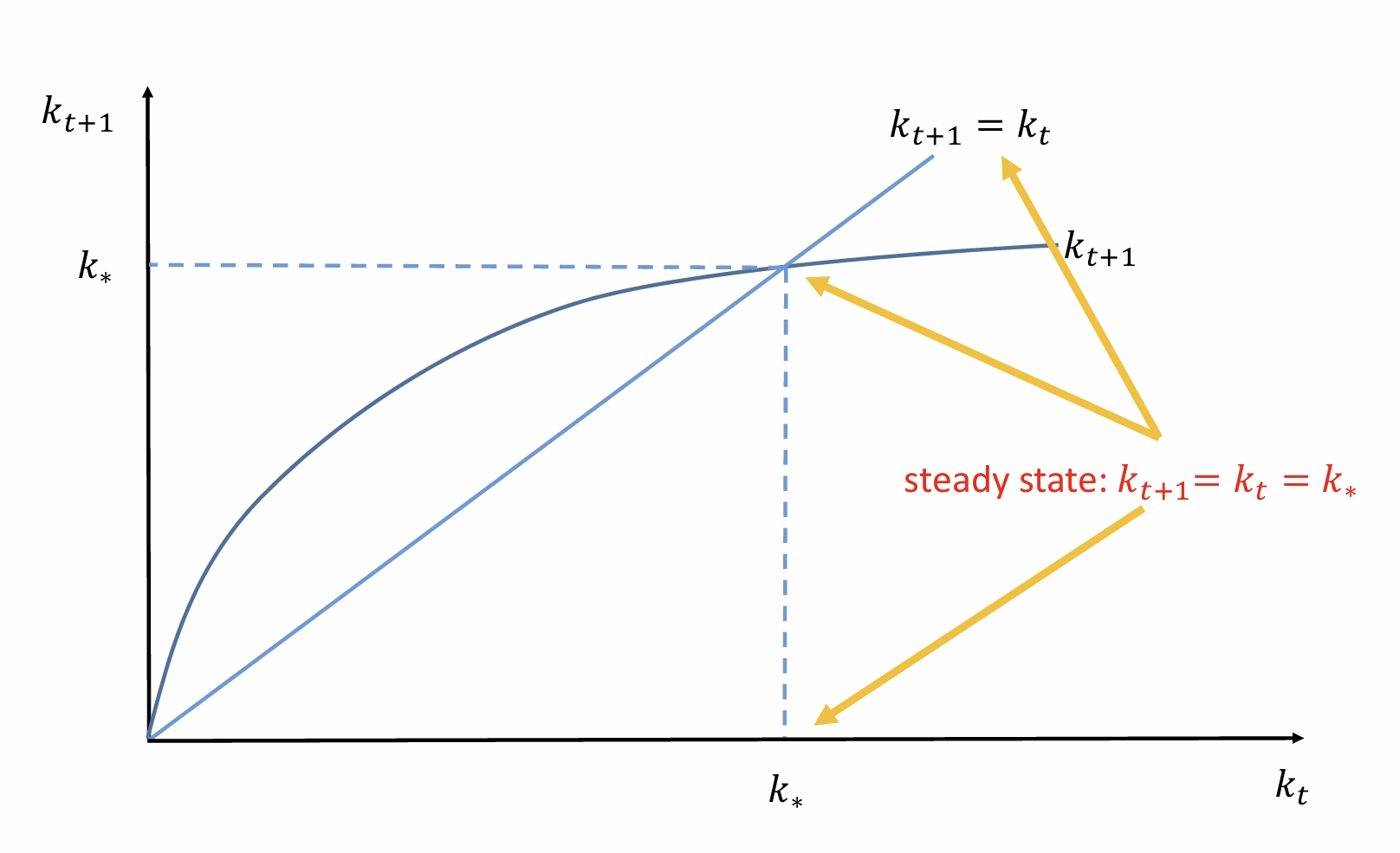
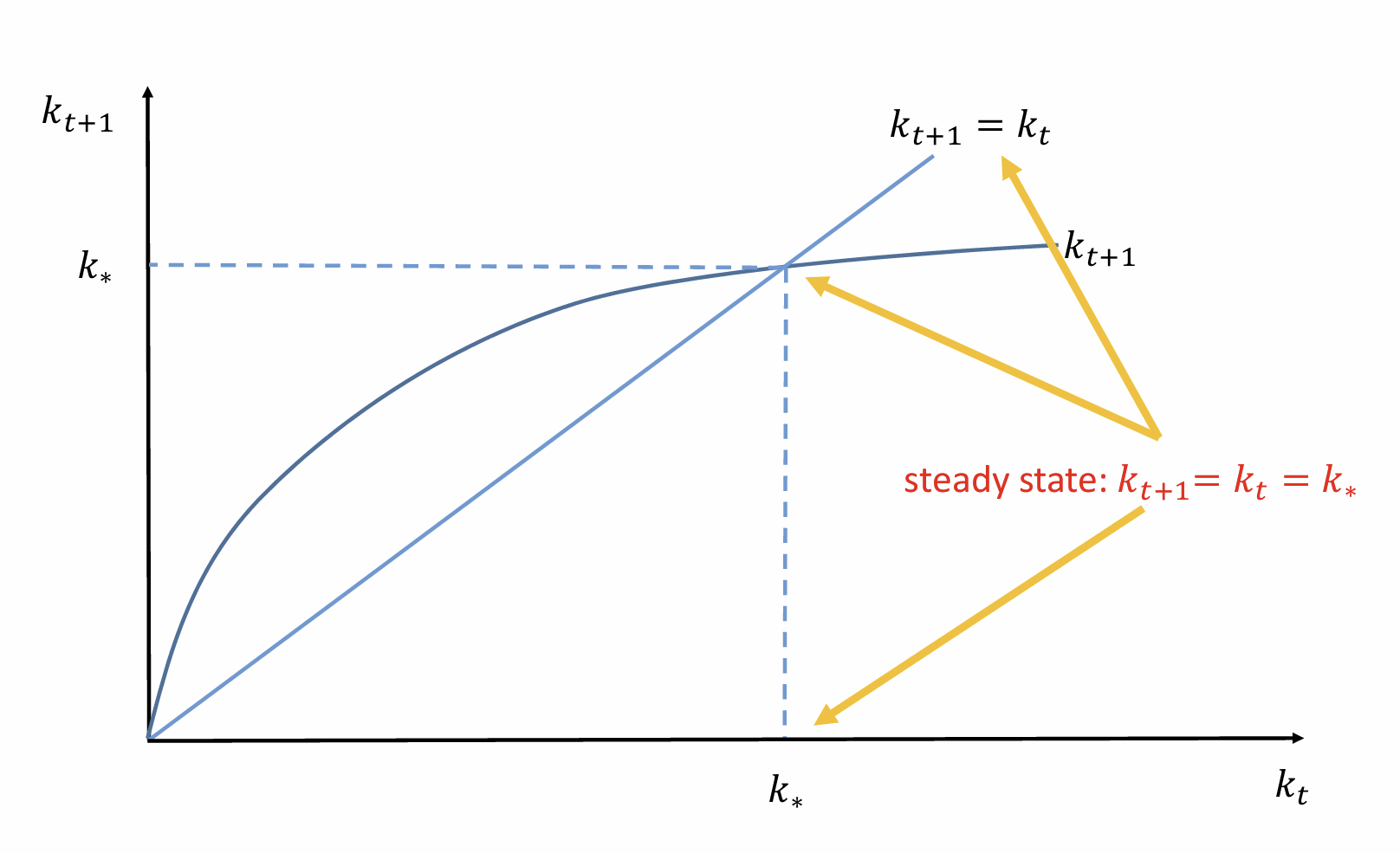
Show how capital evolves in each period to reach the steady state. What does it tell us about its stability?
Unique and globally stable steady state with a constant capital intensity due to diminishing marginal returns to capital