ESS - End of Year Exams 10
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Photosynthesis
Autotrophs use light energy to create chemical energy. They do this by absorbing sunlight, along with carbon dioxide and water while producing glucose (an organic molecule) and oxygen as a biproduct
autotrophs
an organism which can produce its own energy via photosynthesis (aka producers)
heterotrophs
an organism that has to consume other organisms in order to gain more organic molecules
chlorophyll
chemical responsible for the green color of plants
Biosynthesis
chemical process by which organisms use the glucose produced to produce various products useful for life, such as protein, DNA, , starch, cellulose, etc
Heterotrophic Respiration
C(6)H(12)O(6) + 6O(2) —> 6CO(2) + 6H(2)O + ATP
Respiration
Respiration is the biochemical process in which the cells of an organism obtain energy by combining oxygen and glucose, resulting in the release of carbon dioxide, water, and ATP (the currency of energy in cells).
Stomata
pores/small holes found on leaves where air can go through and collect CO2
Organic molecules
complex molecules derived from living organisms built up by hydrocarbons
Pyramids of biomass
Pyramid showing the transfer of energy through the trophic levels
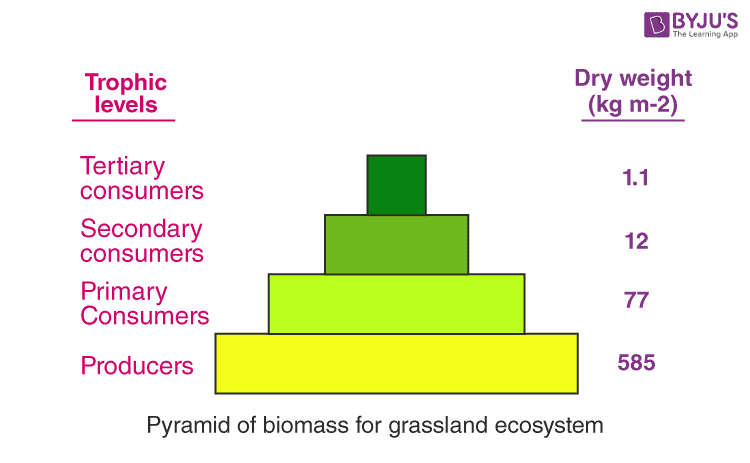
Trophic Levels
The different levels of organisms in the food chain - ranging from primary producer to apex predators
Reasons for loss of energy through the trophic levels (lose approx. 90% of energy per pyramid level)
biproducts
respiration (heat)
biosynthesis (heat)
uneaten material
hair, bones, skin
Excretion/feces
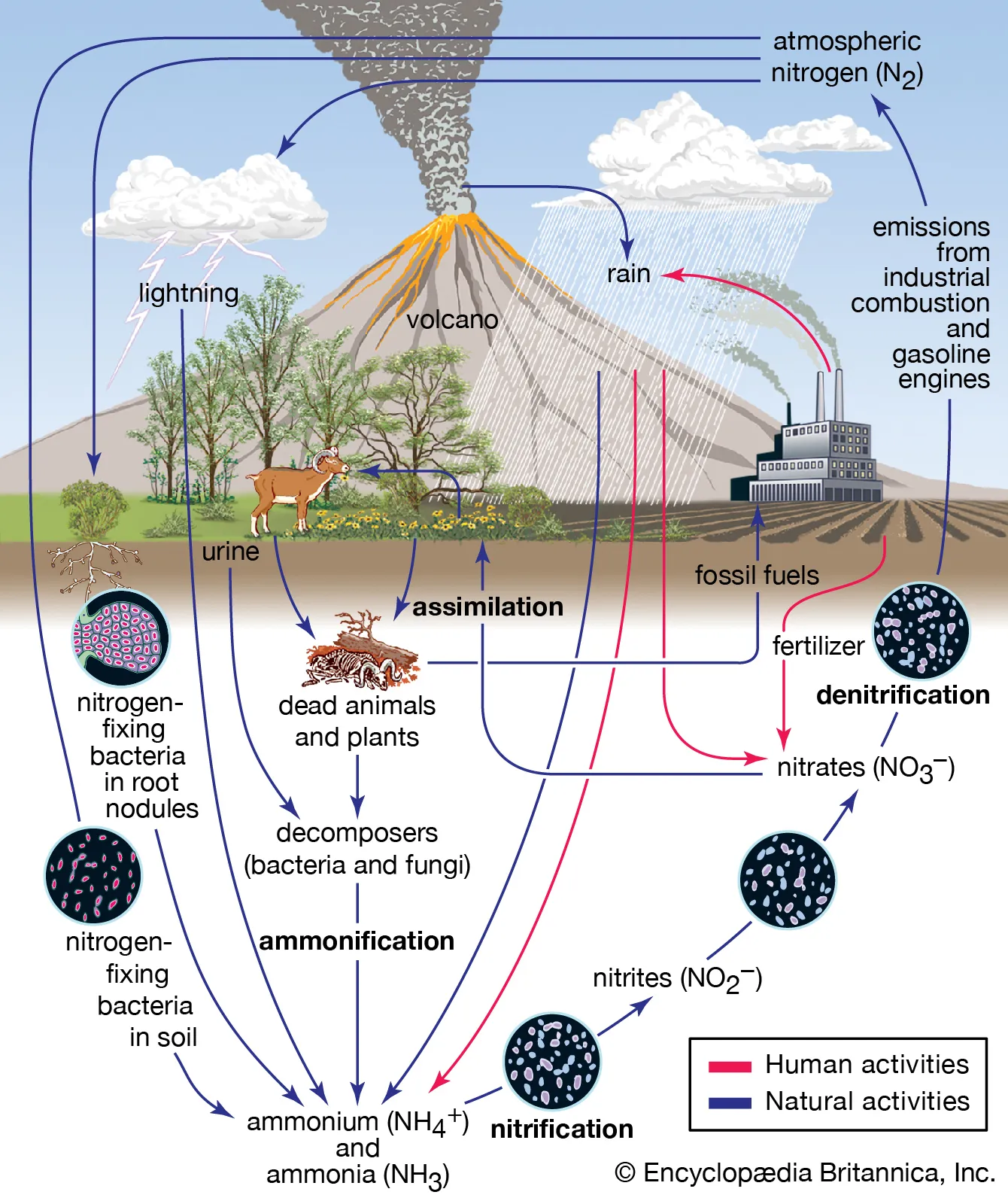
Nitrogen Cycle
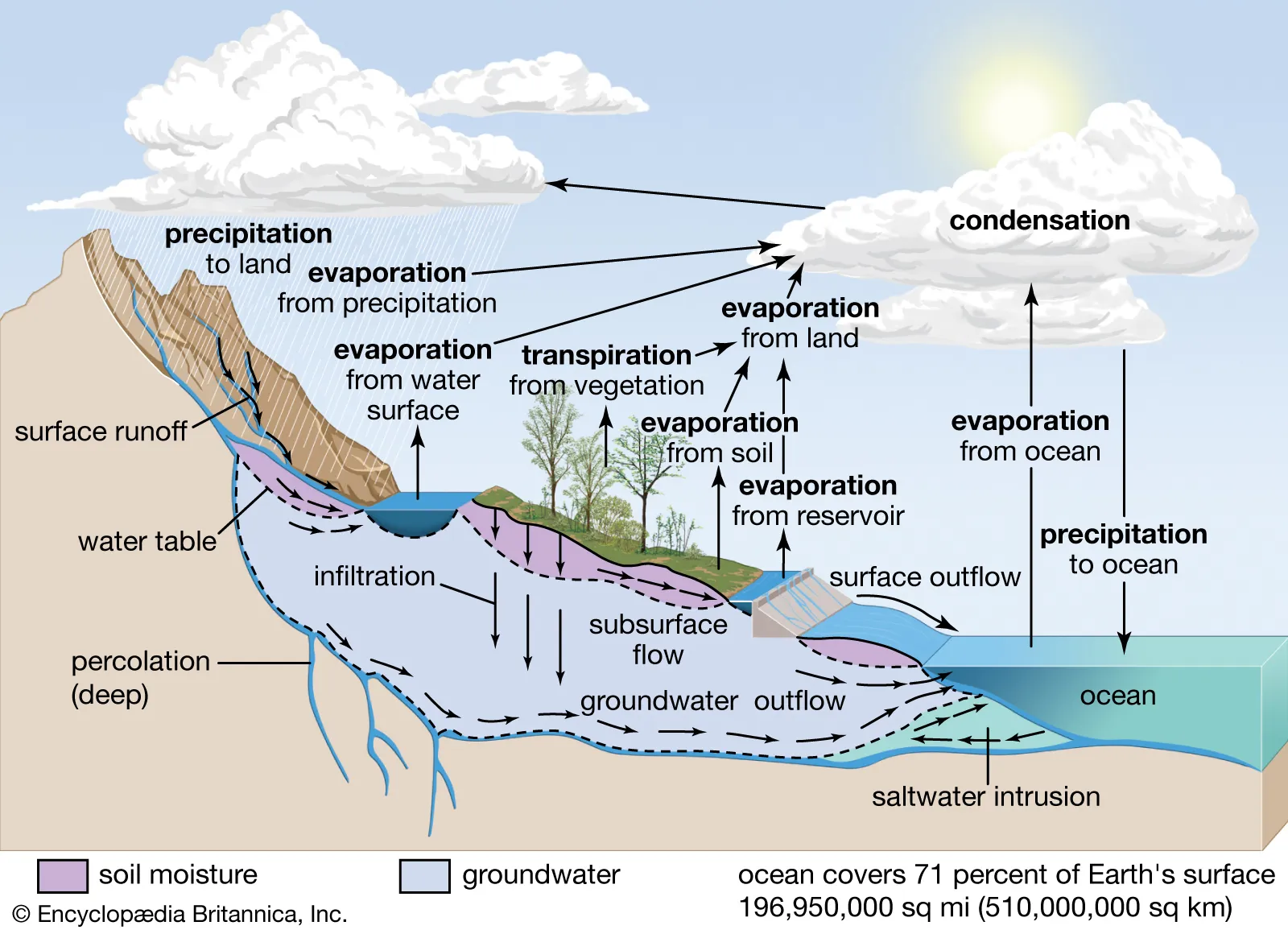
Water Cycle
Carbon Cycle

Abiotic factor
a nonliving condition or thing, as climate or habitat, that influences or affects an ecosystem
Biotic factor
A living things which has an effect on the ecosystem it inhabits
Limiting factor
anything that constrains a population's size and slows or stops it from growing
example of abiotic factor:
amount of sunlight an area gets
example of biotic factor:
amount of zooplankton in a bay
example of limiting factor:
Biotic: amount of mates in a particular area
Abiotic: altitude in an area