Biological Molecules
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
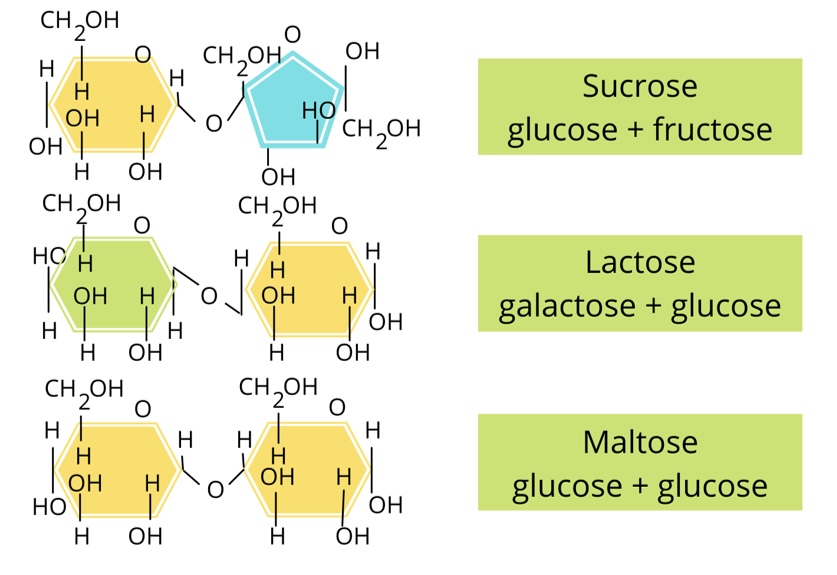
What kinds of bonds occur in carbohydrates
Glycosidic bonds between hydroxyl and hydrogen
What is an isomer
A compound with the same chemical formula but a different arrangement of atoms
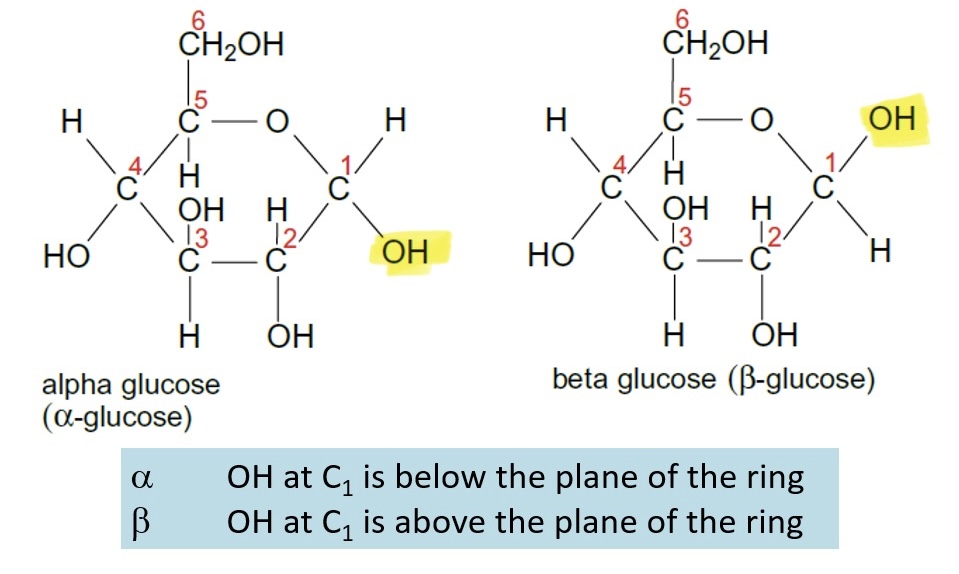
What are glucose's isomers - add a structural difference
Alpha-glucose: OH at C1 is below the plane of the ring
Beta-glucose: OH at C1 is above the plane of the ring
Whats the difference between a hexose, triose and pentose monosaccharide
Hexose - contains 6 carbon atoms
Pentose - contains 5 carbon atoms
Triose - contains 3 carbon atoms
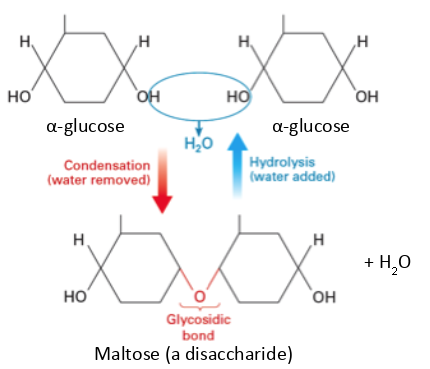
How is a disaccharide formed?
two monosaccharides join together
condensation reaction takes place
glycosidic bond is formed
water is released
How is glucose adapted for its role
small and soluble so can dissolve and be transported easily
low reactivity
How is a polysaccharide formed?
two monosaccharides join where a condensation reaction takes place
A glycosidic bond is formed
A molecule of water is released each time
Many more condensation reactions take place until a long chain is produced
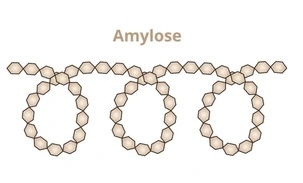
Describe the structure of amylose (starch)
long chain of a-glucose
has 1,4-alpha glycosidic bonds
coiled/helical shape
compact, allows large amount packed in small space
unbranched
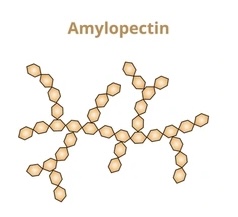
Describe the structure of amylopectin (starch)
long chains of a-glucose
1,4-alpha glycosidic bonds
branches formed by 1,6-alpha glycosidic bonds
coiled shape
more compact, allows large amount packed in small space
What is the advantage of having branches?
many accessible ends
allows rapid release of glucose
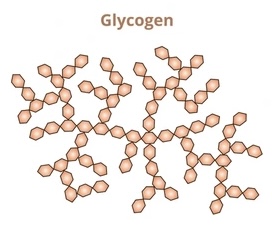
Describe the structure of glycogen
long chains of a-glucose
1,4-alpha glycosidic bonds
HIGHLY branched - VERY compact
branches formed by 1,6-alpha glycosidic bonds
accessible ends
smaller chains than amylopectin → less coiled
Describe the structure of cellulose
long, straight chains of beta-glucose molecules
b-glucose joined by 1,4 glycosidic links
unbranched
molecules invert alternatively by 180° (prevent coiling)
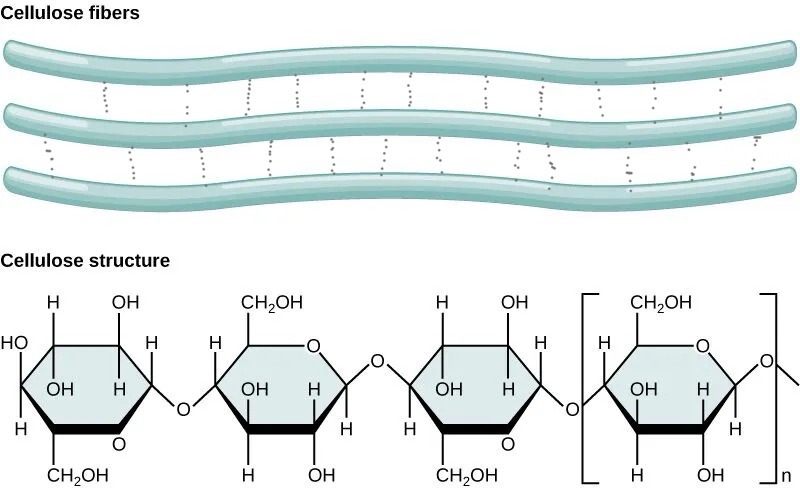
What are cellulose microfibrils?
parallel cellulose chains that become cross linked by
hydrogen bonds in between chains which provides strength (cross links)
Why are polysaccharides good sources of energy? (a-glucose for last)
compact - more energy stored in small space
can hold glucose in large chains - doesnt diffuse out of cell
can be (un)branched
insoluble in water - no impact on water potential of a cell
easily hydrolysed to a-glucose when energy is needed
What are the properties of water?
Polar
High SHC
High latent heat of evaporation
Cohesive
Ice has low density
Good solvent
Explain waters polarity
shared negative H electrons are pulled towards O atom
so other ends of H atoms have slight positive charge
unshared E-s on O atom give a slight negative charge
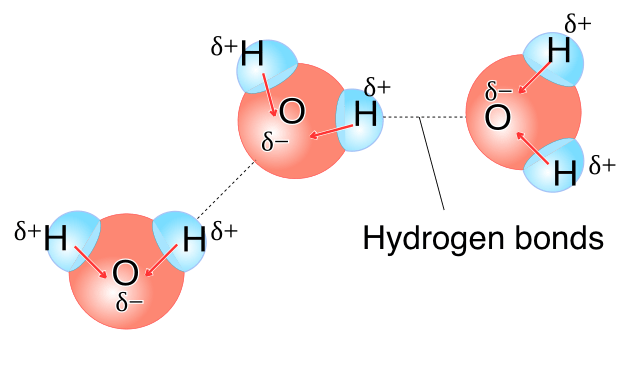
How are water molecules held together
delta negative O atoms attract the delta positive H atoms of other water molecules
this attraction = hydrogen bonding
Why is a high SHC good for water?
• water doesn’t experience rapid temperature changes
• living organisms have a stable temperature - for optimal enzyme reactions
Why is a high LH of evaporation good for water
good cooling property for mammals
eg when sweat evaporates, it cools surface of skin
Why is cohesion good for water
water molecules stick together as they’re polar so there’s a great attraction
helps water flow → useful to transport substances
provides surface tension
How is the structure of ice different to liquid water?
water molecules held further apart as each molecule forms 4 hydrogen bonds
this forms a lattice shape
Why is low density good for ice
ice forms insulating layer over water
ice on top provides habitat
animals underneath dont freeze and can still move
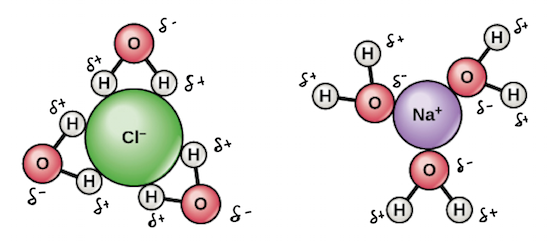
What is the benefit of water being a good solvent for living organisms
ions can dissolve in water
can be transported up the xylem in plants
the plant can absorb mineral ions for growth and survival
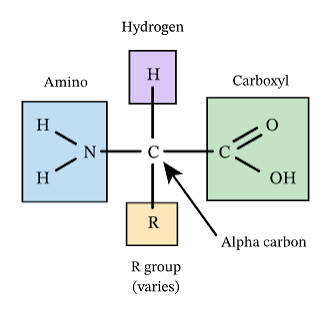
What is the structure of an amino acid
has amine group
has carboxyl group
has variable ‘R’ group
has hydrogen
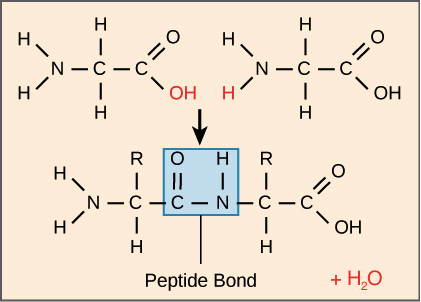
What bonds occur in proteins
Peptide bonds between amine and carboxyl
What is meant by primary protein structure
sequence of amino acids
determined by order of nucleotides in DNA
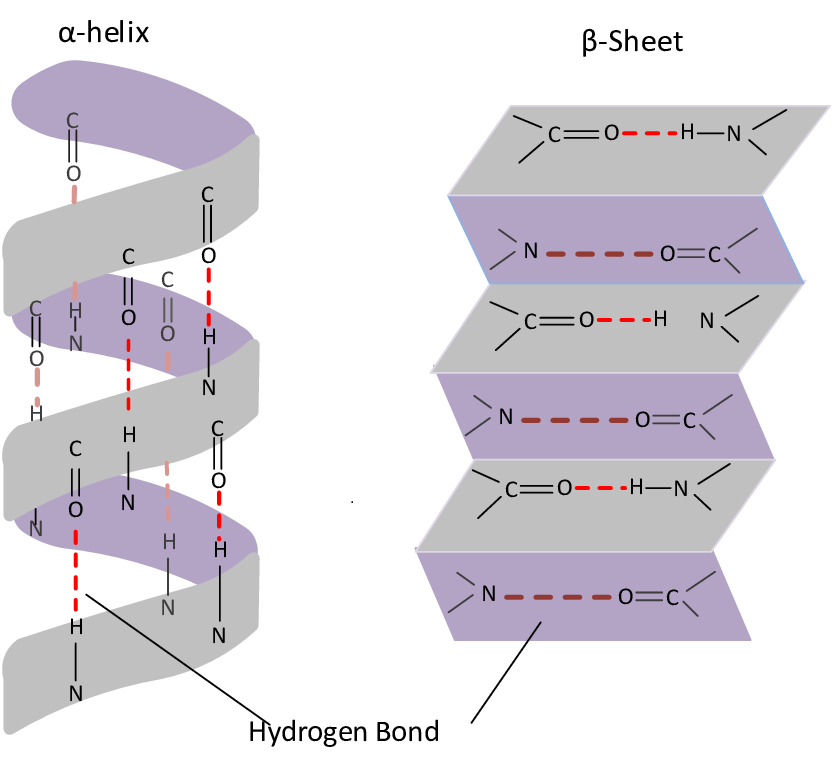
What is meant by secondary protein structure
initial folding of amino acids
folds into alpha-helix or / and beta-pleated sheet
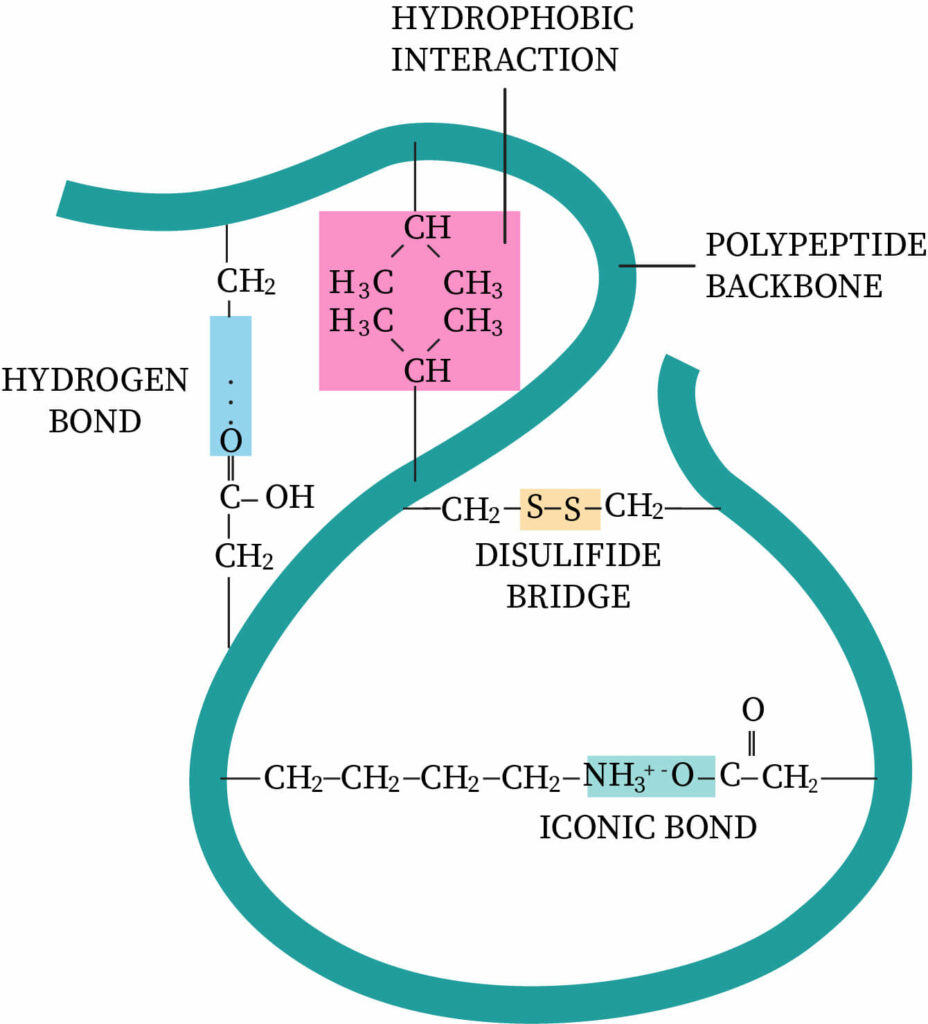
What is meant by tertiary structure
further folding of proteins to give it a 3D shape
gains a function - structure determined by the R group
disulfide bridges, hydrogen + ionic bonding, hydrophobic&phillic interactions
What is meant by quaternary structure
clustering of several polypeptide chains to give a final specific shape
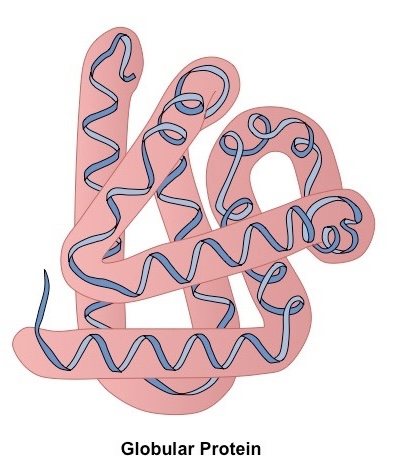
Describe structure of a globular protein
spherical
has specific shapes
soluble
external hydrophilic R group
irregular arrangement of amino acids
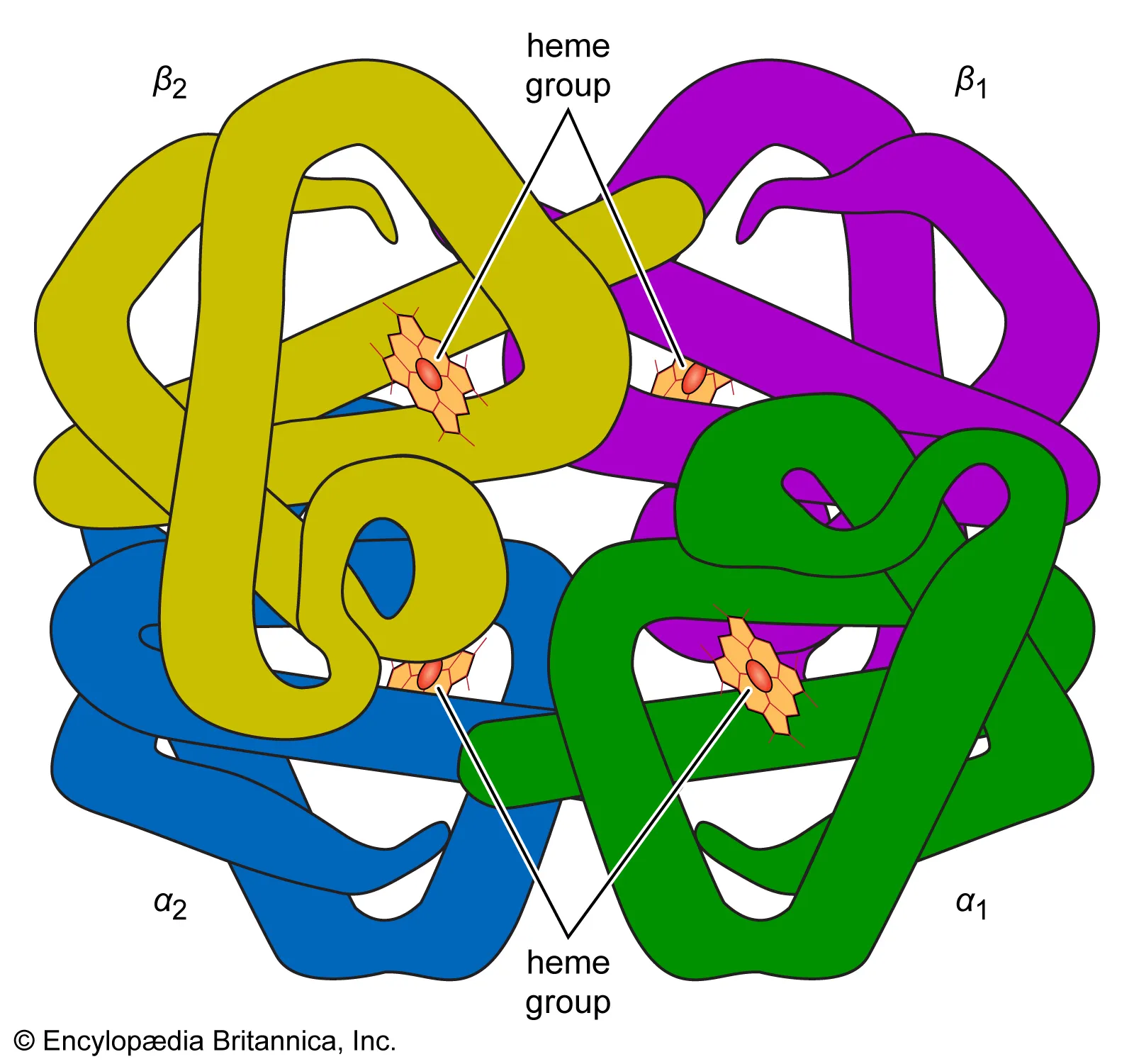
Describe structure of haemoglobin
spherical globular protein
specific shape
made up of 4 polypeptides (2X alpha 2X beta)
functional; transports O2
cofactor; prosthetic group HAEM Fe2+
has external hydrophillic R group

Describe the structure of a fibrous protein
form fibres; linear
regular and repetitive structure of amino acids
structural
insoluble
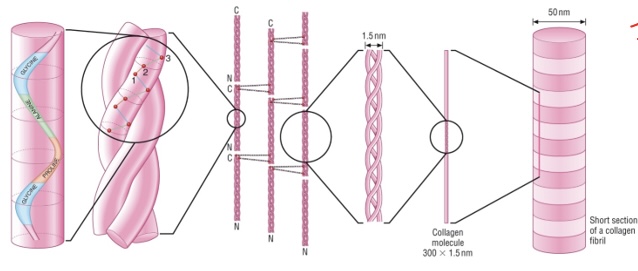
Describe the structure of collagen
forms fibrils→ fibrous protein
structural; provides support
repeating structure of Gly-Pro-Ala
3 polypeptides → coiled
chains are cross linked by hydrogen bonding
peptide bonds between AAs
insoluble - external hydrophobic R group
What is a beta pleated sheet?
secondary protein structure which has hydrogen bonds between R groups
sheet folds over itself
What is an alpha helix?
secondary protein structure that has a coiled shape
hydrogen bonds between R groups
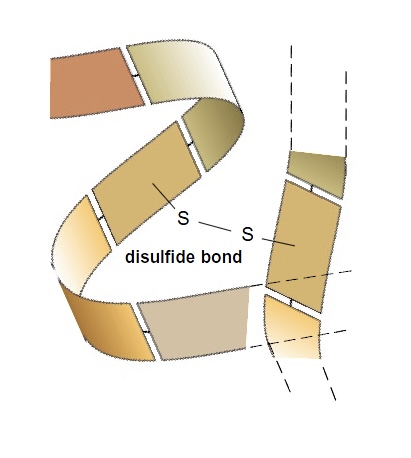
What is a disulfide bond
bond between 2 sulfur atoms
aa has S atom on its R group
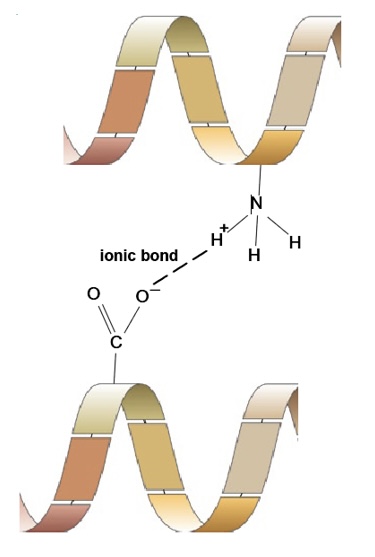
What is an ionic bond
forms between an R group with full -charge and one with full +charge
bond can be broken by a change in pH
What bonds occur in lipids? HYDROPHOBIC!
ester bonds between hydrogen and hydroxyl
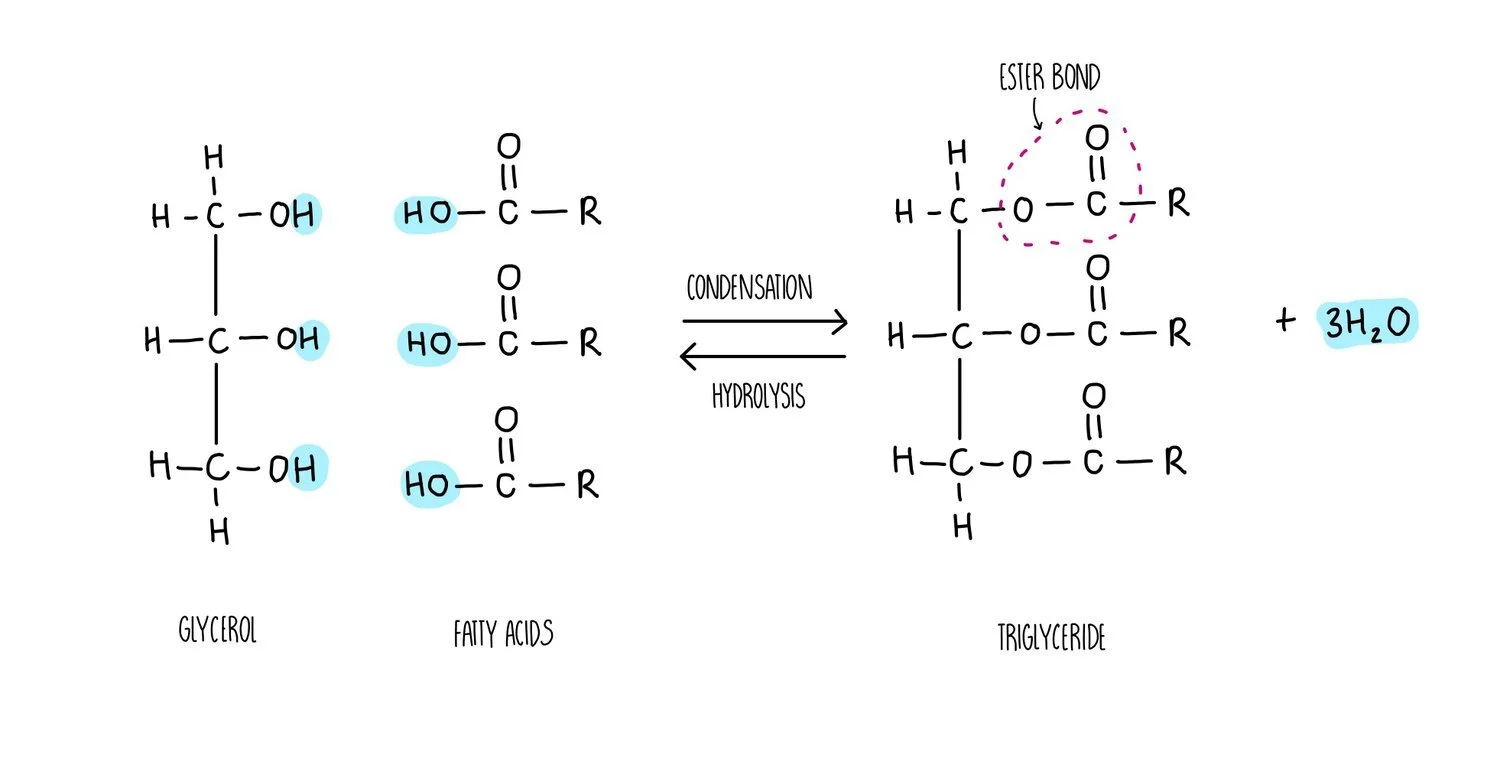
What is the structure of a lipid
has glycerol
has fatty acids - not identical so there are no monomers
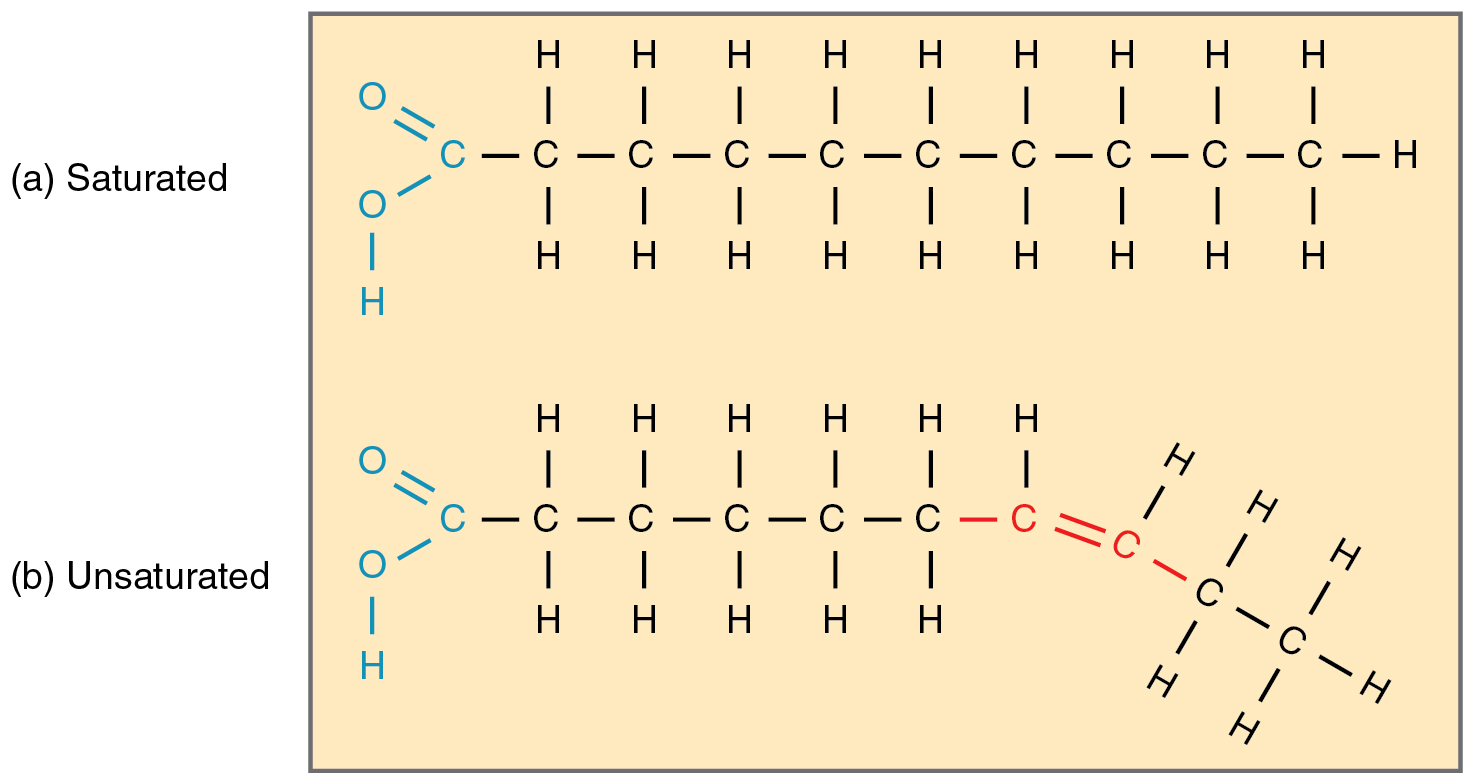
What is the structure of fatty acids?
long hydrocarbon tails
saturated FAC: no double carbon bond, saturated with H atoms, long straight chains
unsaturated FAC: double carbon bond, less H atoms, kinked chain
What are unsaturated fatty acids?
oils
liquid at room temp
What are saturated fatty acids
animal fats
solid at room temp
What is the structure of a triglyceride and how is it made
1 glycerol + THREE fatty acids
condensation reaction where X3 H2O lost
3 ester bonds formed
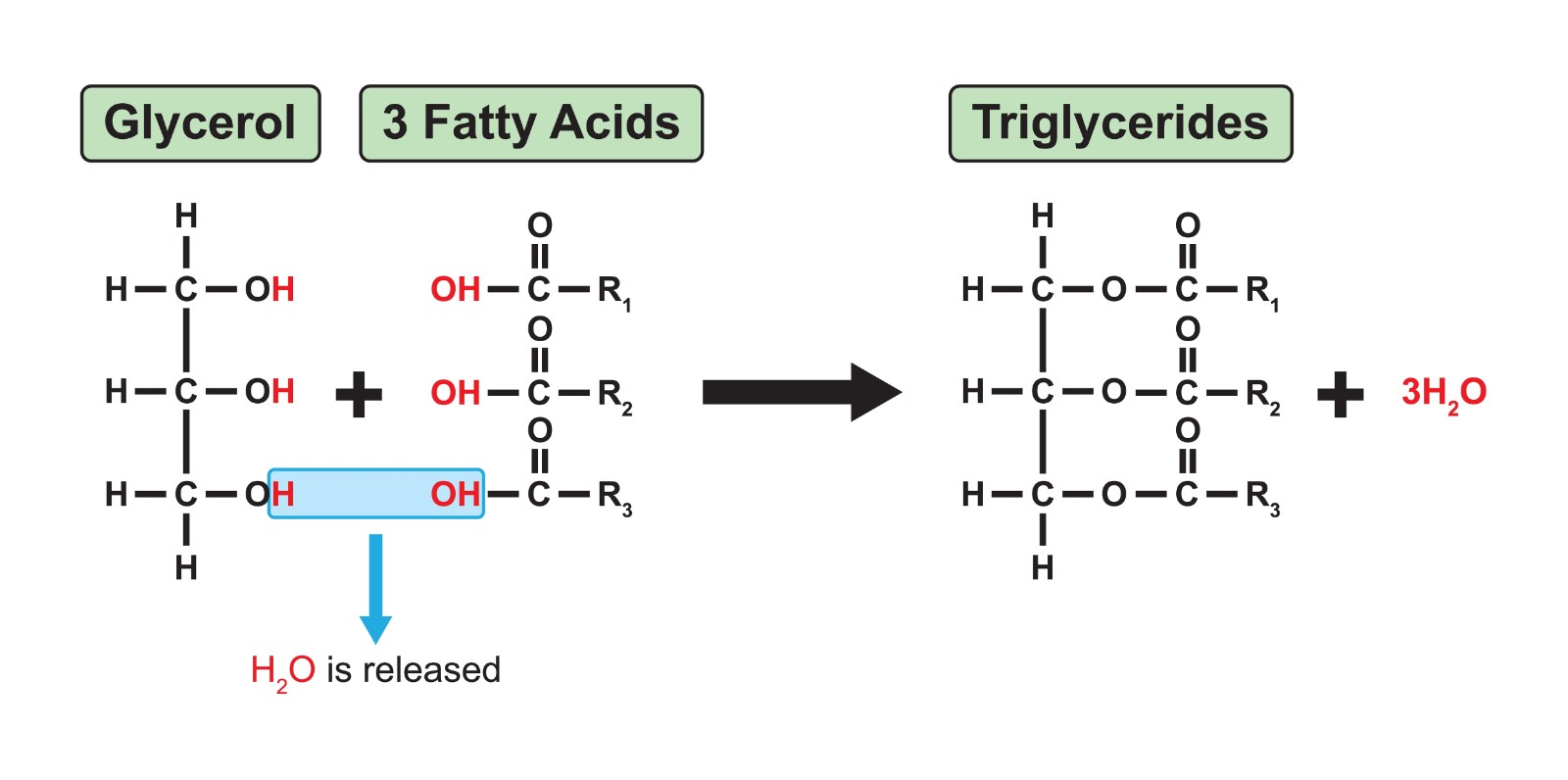
What is the function of triglycerides?
energy storage
insulation
provide buoyancy for aquatic animals
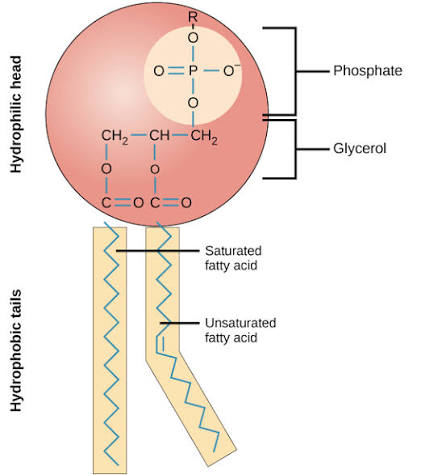
What is the structure of a phospholipid?
has glycerol
has 2 fatty acid tails which are hydrophobic; nonpolar
its third fatty acid replaced by phosphate head; hydrophillic
2 ester bonds
Whats the difference between phospholipid and triglyceride
phospholipid has a phosphate head which replaces the 3rd fatty acid
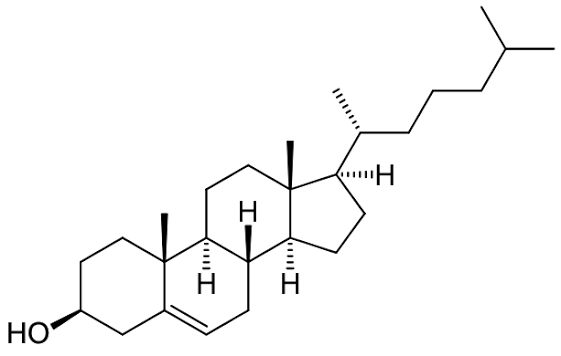
What is the sructure of cholestrol - STEROL
lipid not made from glycerol & fatty acids
has 4 carbon rings
small hydrophobic molecule
sits between hydrophobic tails in bilayer
What are the functions of cholestrol
regulates fluidity in the membrane
making vitamin D
steroid hormone
Describe the similarities of haemoglobin and collagen
more than one polypeptide chain
have quaternary structure
aa chains with peptide bonds
disulfide, ionic, hydrogen bonds
Role of H+ ions
affects pH - acidic
important in photosynthesis and respiration reactions
Role of Ca2+ ions
transmission of nerve impulses
bone and enamel structure
Role of Na+ ions
generating nerve impulses
regulating water potential
Role of K+ ions
allow reabsorption of water in kidneys
opening of the stomata
Role of NH4+ ions
absorbed by soil in plants as a source of nitrogen
deamination of proteins
Role of NO3- ions
absorbed by plants as a source of nitrogen
used for growth and repair in plants
Role of HCO3- ions
transport CO2 in blood
acts as a buffer to maintain pH
Role of Cl- ions
maintain pH balance
acts as cofactor for amylase
Role of PO4 3-
component of cell membrane - phospholipids
component of ATP and nucleic acids
Role of OH- ions
affects pH of substances - alkali
Which chemical elements make up the biological molecules?
carbs & lipids: C, H, O
proteins: C, H, O, N, S
nucleic acids: C, H, O, P
What is a conjugated protein
globular protein with a prosthetic group
such as Fe2+
attached by covalent bonds