Freshwater Ecology - Exam 2 COMPREHENSIVE
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
171 Terms
what is a lake?
a very slowly flowing or nonflowing open body of water in a depression and not in contact with the ocean
lentic
nonflowing (still water)
what percentage of lentic water do lakes make up?
20%
what continent has the highest number of lakes?
North America
what continent has the largest total lake surface area?
North America
what continent has the most volume of water stored in lakes?
Europe
what country has the highest surface area of lakes?
Canada
what country has the highest volume of lake water?
Russia
what freshwater lake has the largest volume of water?
Lake Baikal
lacustrine
habitat w deep, still water
littoral
region lying along a shore
what freshwater lake is the deepest?
Lake Baikal
what freshwater lake is the oldest?
Lake Baikal
what lake is the largest by surface area?
Lake Superior
benthic
bottom
pelagic
open waters
photic
penetrated by light
aphotic
absence of light
lotic
moving water
what is a bathymetric map?
a depth contour map
retention / residence time
the average amount of time a molecule of water stays in a body of water
how can you calculate retention time?
R = V/L (V=water volume, L=loss of water per time unit)
what does this equation assume?
R = V/L
inflow and outflow are equal
how can residence time impact pollution worries?
it’s worse to pollute a lake with higher residence time; it will take longer to get rid of the pollution
what is shoreline development (D_L)?
irregularity or degree of convolution of the shore
what is the equation for shoreline development?
D_L = L/(2*sqrt(piA_0)) (L=length of shore, A_0=surface area of lake)
how does reservoir depth vary?
deep near the dam and become shallower further out in the delta
how do reservoirs impact sediment deposition?
sediment is deposited in the reservoir’s delta and not reaching the ocean, therefore increasing erosion
what is the largest dam in the USA?
the Hoover Dam
what dam has the largest storage capacity?
the 3 Gorges Dam
epilimnion
uppermost layer of stratification
thermocline
middle layer of stratification, usually where the epilimnion and hypolimnion mix
hypolimnion
bottom layer of stratification
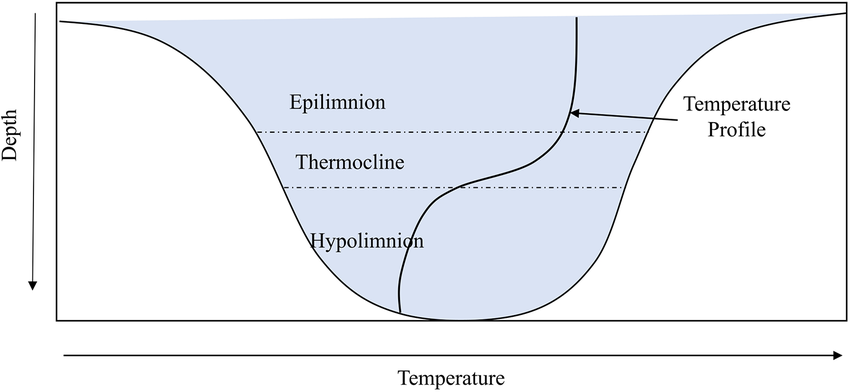
what season is this image displaying (referencing Northern lakes)?
summer
what is turnover?
occurs when layers of stratification in a lake become the same temperature and mix
TRUE OR FALSE: if winds are strong enough, stratification can be broken
false; not even a hurricane can break stratification of a lake
why haven’t lakes responded more drastically to climate change?
the high heat capacity of water
what impacts does climate change have on lake stratification changes?
shortening the duration of ice cover and shortening the length of time between fall and spring turnover
monomictic lake
one stratification and one mixing time per year
polymictic lake
mixes and stratifies many times per year
where are polymictic lakes found?
tropical regions
amictic / meromictic lake
never mixes
where can amictic / meromictic lakes be found?
some tropical regions, saline lakes tend to be amictic
what factors determine wave height?
strength and duration of the wind
length of the lake affected by the wind
geometry and materials on the shoreline
which shoreline will experience more erosion: steep shoreline or shallow shoreline?
steep
what is a fetch?
the area of lake being affected by wind
autotroph
self-feeding organism
heterotroph
other feeding organisms
where do autotrophs get carbon from?
CO2
where do heterotrophs get carbon from?
organic Carbon molecules
filterer
filters organic particles out of the water
collector
eats small organic particles from the benthos
shredder
break up large organic material (leaves) into small pieces to get organic material
scraper
remove biofilms from hard benthic surfaces
predator
eats other animals
archaea
single-celled organism with no nucleus or organelles
archaea are only numerically dominant in what type of system?
extreme systems, such as anaerobic water, hot springs, or hypersaline water
bacteria
single-celled organisms without organelles or a nucleus
TRUE OR FALSE: bacteria have a greater active biomass than any other group on Earth
true
phytoplankton
floats freely
periphyton
attached to aquatic vegetation, rocks, and other substrate
benthic algae
grows on bottom sediments
cyanobacteria
blue-green algal bacteria capable of nitrogen fixation and algal blooms
nitrogen fixation
transformation of N2 gas into N that can be used by organisms
heterocyst
a cyanobacterial cell that carries out nitrogen fixation
akinete
heat / drought resistant spore
TRUE OR FALSE: once cyanobacteria are dead, their toxins are no longer a threat
false
golden algae are mostly in what type of lake?
oligotrophic
facultative heterotroph
an organism capable of switching between autotrophy and heterotrophy
Xanthophyceae
yellow-green algae
what class are yellow-green algae?
xanthophyceae
what do xanthophyceae have that gives them their color?
carotenoids and chlorophylls
how many cilia do xanthophyceae have?
2 (1 hairy, 1 smooth)
frustule
the silica glass cell wall of a diatom
what type of algae are diatoms?
periphyton
how many cells does a single green algae organism have?
one to complex multicellular
what pigments do green algae contain?
chlorophyll a & b, carotenoids
how do green algae store nutrients?
as starch and cellulose
which algae is thought to be the lineage that led to higher plants?
green algae
what shape chloroplast does zygnema have?
star-shaped
what shape chloroplast does spirogyra have?
spiral-shaped
what green algae attaches to turtle shells?
basicladia
detritus
debris in water (leaves, wood, other waste)
what type of heterotroph are fungi mostly?
decomposers
which fungi species is causing amphibian species declines and extinctions?
Batrachochytum dendrobaditis
what is peat?
mostly dead sphagnum
where is sphagnum dominant?
peat bogs
are mosses vascular or nonvascular?
nonvascular
are liverworts vascular or nonvascular?
nonvascular
where are liverworts mostly found?
banks of streams, marshy ground, damp soil
macrophyte
aquatic plant
hydrophyte
aquatic plant
emergent plant
roots underwater but leaves and reproductive parts are out of the water
floating attached plant
floating leaves/flowers but anchored by roots
floating unattached plant
freely-floating plants not anchored
submersed plant
plant completely underwater
sedge
grasslike plant
Carek grayii
sedge that has a spike-ball flower that appears in May and persists through the summer
what is the gulf coast’s worst invasive plant?
water hyacinth
what type of macrophyte is a water hyacinth?
floating