Mobility and Sexuality in Spinal Cord Injury
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
What is the definition of mobility?
The level to which one is able to have independent, purposeful movement of the body or of one or more extremities.
What does sexuality encompass?
Sexuality encompasses sex, gender identities and roles, sexual orientation, eroticism, pleasure, intimacy, and reproduction.
What is a major health problem affecting approximately 294,000 people in the U.S.?
Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
How many new cases of spinal cord injuries occur each year in the U.S.?
17,810 new cases.
What are the leading causes of spinal cord injuries?
Motor vehicle accidents (36.5%), violence (14.3%), falls (28.5%), and sports injuries (9.2%).
What percentage of spinal cord injuries occur in males?
Males account for 78% of SCIs.
What age group accounts for more than half of all new spinal cord injuries?
Young people ages 16-30.
What risk factors are associated with spinal cord injuries?
Alcohol and drug use, found in 25% of SCIs.
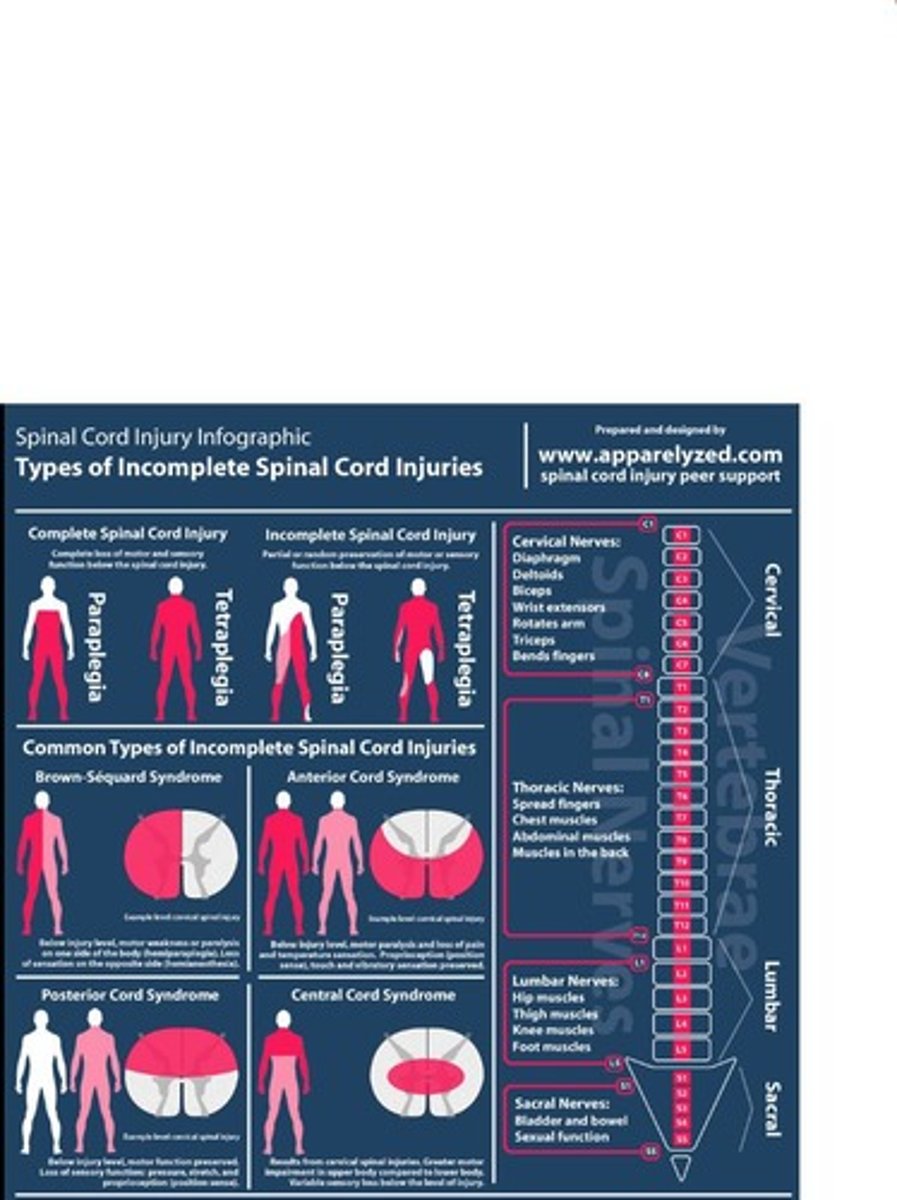
What are the two types of spinal cord injuries?
Complete and incomplete spinal cord injuries.
What characterizes a complete spinal cord injury?
Complete spinal cord injury involves complete transection, severing of the spinal cord.
What is a primary injury in the context of spinal cord injury?
The initial trauma, usually permanent.
What is a secondary injury in spinal cord injury?
Injury due to ischemia, hypoxia, or hemorrhage, often reversible/preventable.
What is Brown-Sequard Syndrome?
A type of incomplete spinal cord injury characterized by hemisection of the spinal cord.
What is anterior cord syndrome?
A condition involving damage to 2/3 of the anterior spinal artery.
What is central cord syndrome?
A condition where the center of the spinal cord is damaged.
What is spinal shock?
A form of neurogenic shock that occurs within an hour of spinal cord injury, characterized by areflexia and flaccid paralysis.
What are the symptoms of spinal shock?
Muscular flaccidity, lack of sensation and reflexes, loss of spinal reflexes, and bowel and bladder reflexes affected.
What is the duration of spinal shock?
It can last for up to 6 months.
What are the initial assessments for spinal cord injury?
Monitor respirations, assess lung sounds, monitor for changes in motor or sensory function, and assess for spinal shock.
What is the purpose of emergency care in spinal cord injury treatment?
To implement spinal precautions and immobilization.
What types of therapies are included in spinal cord injury treatment?
Respiratory therapy, pharmacological therapy, and surgical interventions.
What is the role of steroids in spinal cord injury treatment?
Steroids offer little benefit and are not used very often.
What diagnostic test is commonly used for spinal cord injuries?
CT scan.
What is the goal of surgery in spinal cord injury treatment?
To immobilize and stabilize the injury, preventing secondary injury or worsening the condition.
What is the primary goal of injury reduction?
To restore the injury to its normal position.
What is the purpose of early decompression in spinal injuries?
To stabilize the spine.
What does traction involve in the context of injury stabilization?
Using weights to align bones and put them in a neutral position.
What is halo traction used for?
To support the head and immobilize the spine, with fixation to the skull.
How often should neuro checks be performed for sensory and motor changes?
At least every shift and as needed (PRN).
What is autonomic dysreflexia and why is it considered an acute emergency?
It is a life-threatening condition that causes exaggerated autonomic responses to harmless stimuli, occurring in spinal cord injuries above T6.
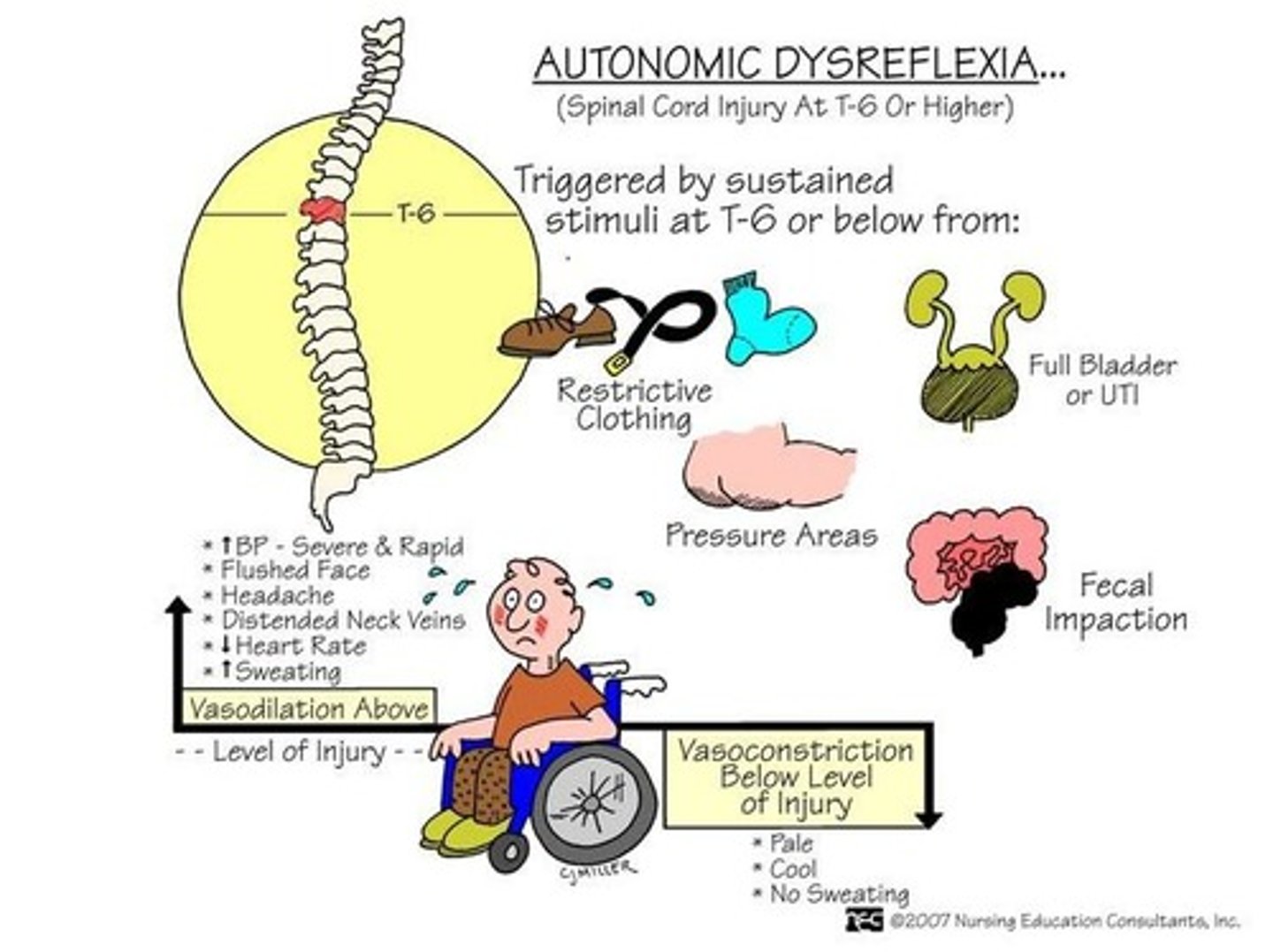
What are the most common causes of autonomic dysreflexia?
Distended bladder, distention or contraction of visceral organs, stimulation of the skin, and various physical stimuli.
List some symptoms of autonomic dysreflexia.
Severe headache, sudden increase in blood pressure, profuse diaphoresis, flushed face, cold clammy skin, goose bumps, restlessness, nausea, nasal congestion, and bradycardia.
What is the first intervention for a patient experiencing autonomic dysreflexia?
Place the patient in a seated position to lower blood pressure.
What should be done during a rapid assessment for autonomic dysreflexia?
Identify and eliminate the cause, such as emptying the bladder or examining for fecal mass.
What medications can be used to decrease blood pressure in autonomic dysreflexia?
Hydralazine, Nipride, and nitroglycerine.
What should be labeled on the chart of a patient at risk for autonomic dysreflexia?
Label as 'at risk for autonomic dysreflexia'.
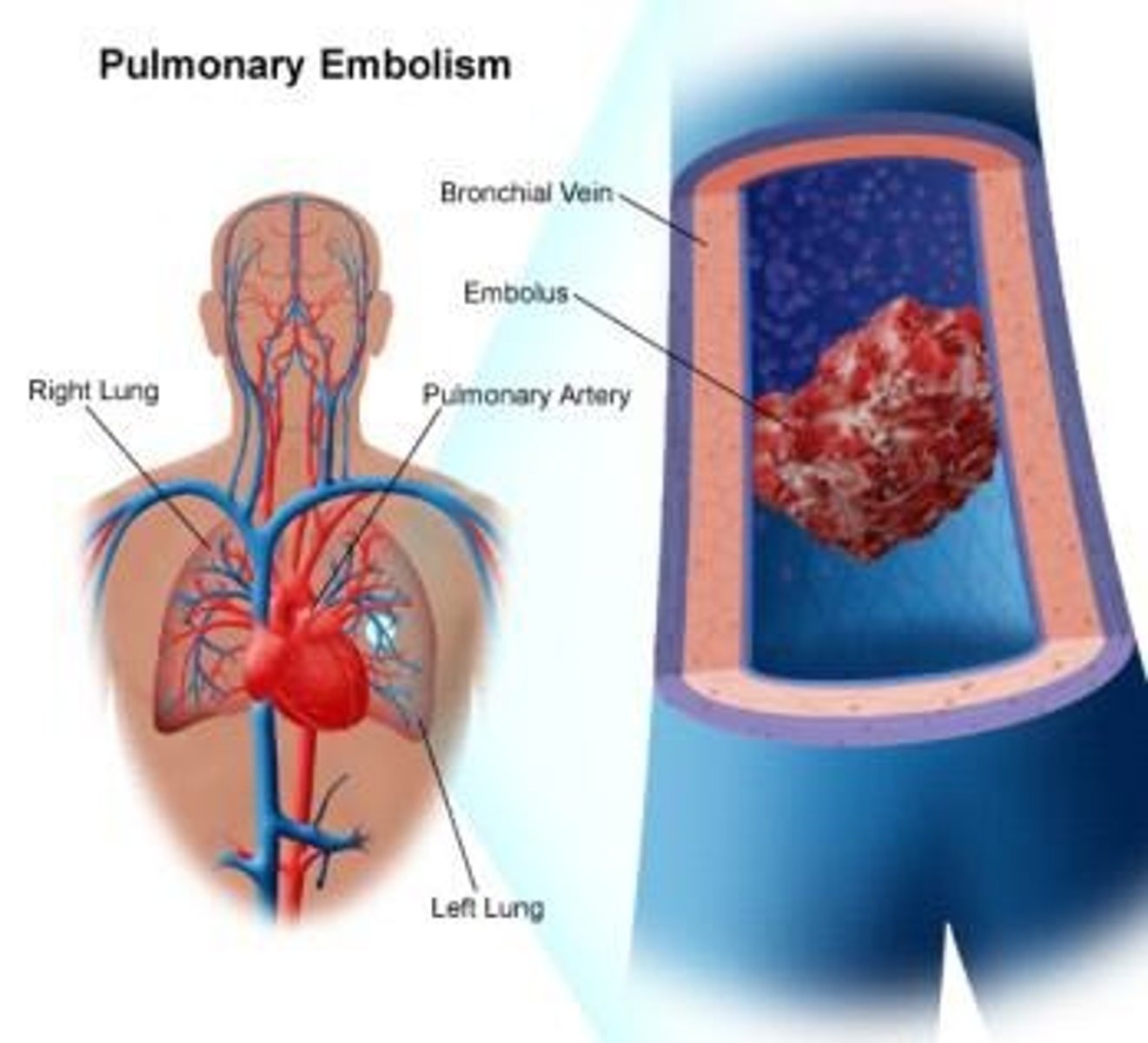
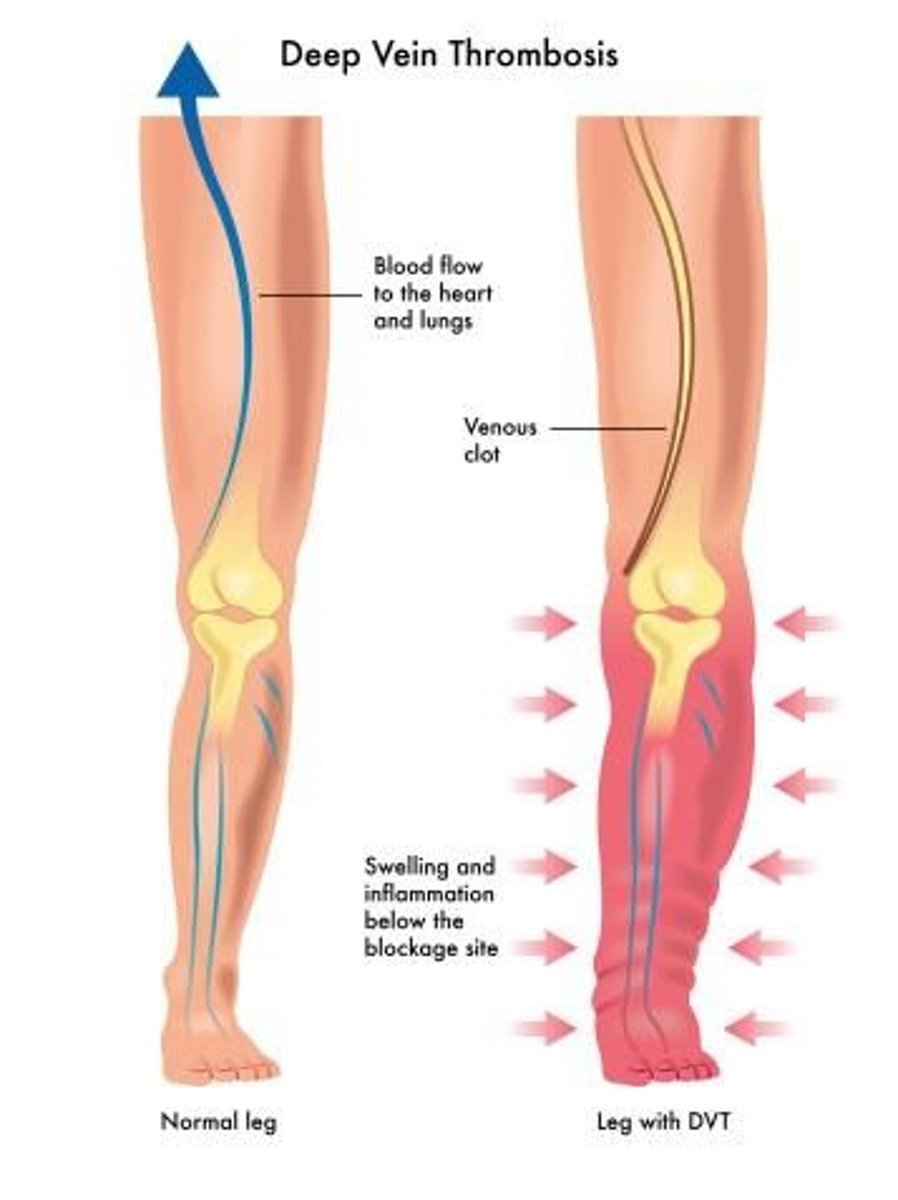
What are some complications from immobility?
Pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), skin breakdown, incontinence, infections, orthostatic hypotension, and contractures.
What should be avoided to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
Never rub calves or thighs.
What is a key prevention strategy for skin breakdown in immobilized patients?
Regularly check for pressure ulcers from sitting.
What is the recommended position change strategy for managing orthostatic hypotension?
Use slow position changes as blood pressure gradually returns to normal.
What are some strategies for improving mobility in patients with spinal injuries?
Maintain proper body alignment, monitor blood pressure with position changes, and perform passive range of motion (PROM) exercises.
What should be used when mobilizing a patient with a spinal injury?
A neck brace or collar, as prescribed.
How often should passive range of motion (PROM) exercises be performed?
Four times a day.
What should be done before turning a patient with a spinal injury?
Ensure the spine is stable and follow physician's indications.
What are some nursing interventions for maintaining skin integrity in immobile patients?
Strategies to compensate for sensory and perceptual alterations, hygiene and skin care related to traction devices.
What dietary considerations should be made for immobile patients?
A high-calorie, high-protein, high-fiber diet, along with a bowel program and use of stool softeners.
What are the two types of catheterization mentioned for immobile patients?
Indwelling catheterization and intermittent catheterization.
What are the potential effects of spinal cord injury (SCI) on men's reproductive health?
Changes in relationships, sexual activity, ability to biologically father children, and potential need to meet with a fertility specialist.
What are some reproductive health considerations for women with SCI?
Women can engage in sexual activity regardless of injury level, have the ability to become pregnant, and need contraceptives to prevent pregnancy.
What are the risks associated with pregnancy in women with SCI?
Increased risk for autonomic dysreflexia, changes in bowel function, bladder spasms, urinary tract infections, pressure sores, respiratory complications, muscle spasms, and swelling of the legs and feet.
What is the preferred method of delivery for pregnant women with SCI?
Vaginal delivery is preferred.
What are the clinical manifestations of fractures?
Pain or tenderness, swelling, bruising, shortening of limb, deformity, decreased range of motion, limb rotation, and crepitus.
What are the two classifications of fractures based on skin integrity?
Closed (simple) fractures do not break the skin, while open (compound) fractures do.
What initial nursing care should be provided for patients with fractures?
Assess ABCDE, vital signs, check urine for blood, stabilize the injured area, maintain proper alignment, elevate limb and apply ice, apply pressure for bleeding if needed, cover wounds with sterile dressing, and perform frequent CMS checks.
What are the goals of fracture management?
Realignment of bone ends and immobilization.
What is compartment syndrome?
A condition where increased pressure within a compartment compresses nerves and blood supply to muscles, leading to severe pain and potential loss of limb.
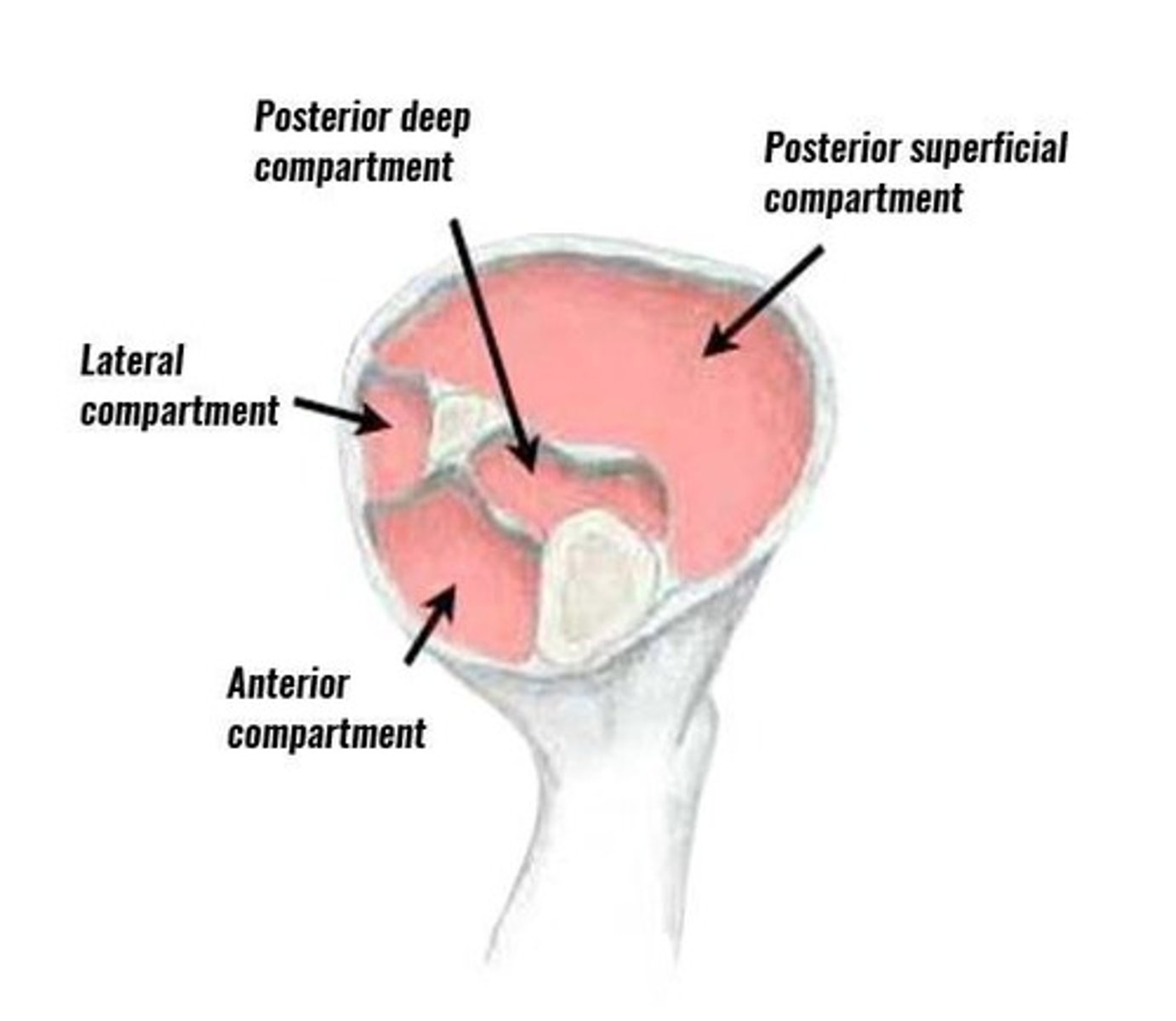
What are the six 'P's to assess for in compartment syndrome?
Pain, pallor, pulselessness, paresthesia, paralysis, and pressure.
What are common complications of fractures?
Hemorrhage, infection, neurovascular compromise, compartment syndrome, thromboembolic complications, and fat embolism syndrome.
What diagnostic tests are used for fractures?
X-ray examination, CT or MRI, CBC, and ESR.
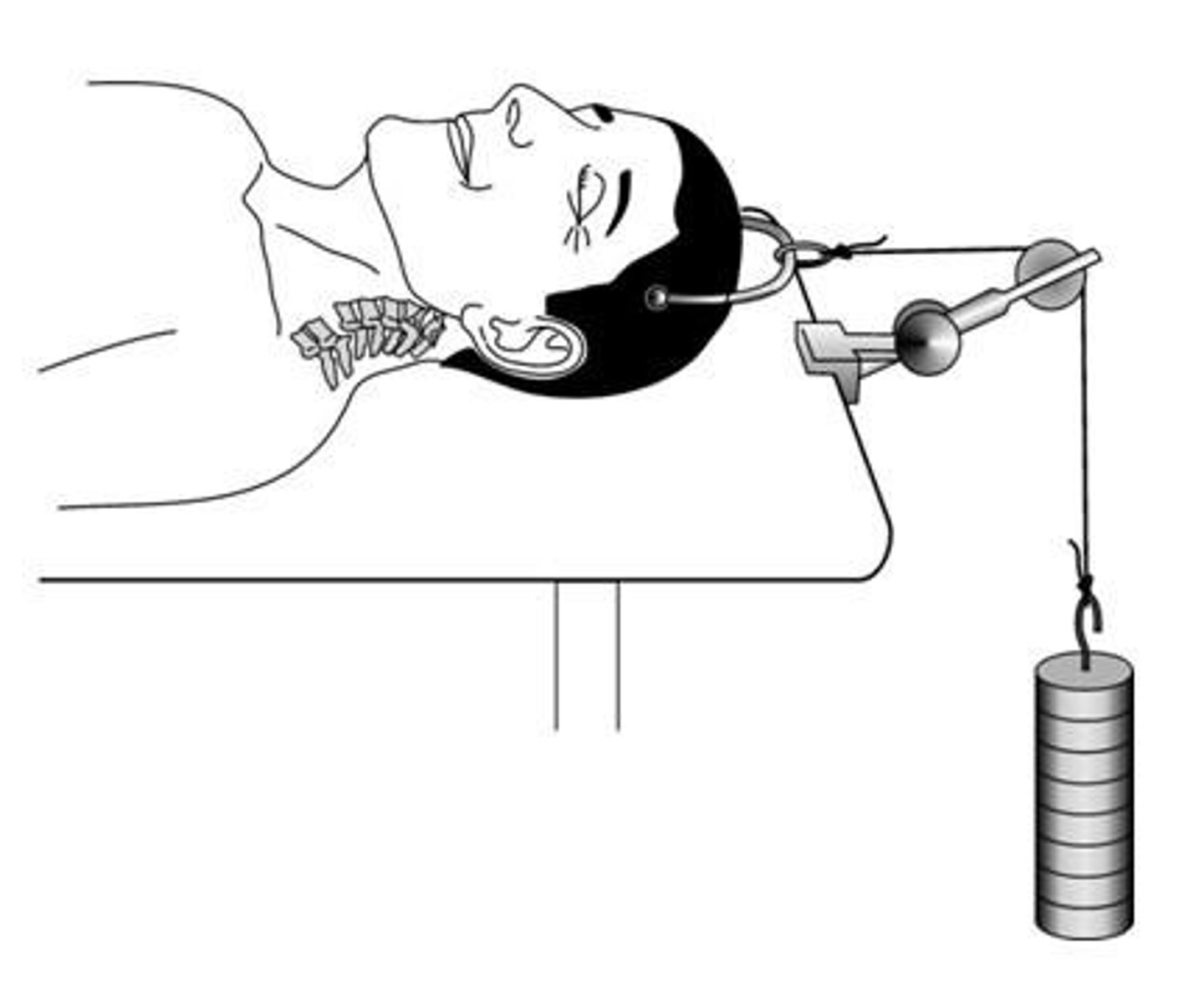
What is the purpose of traction in fracture management?
To immobilize the fracture and maintain proper alignment.
What is the difference between closed reduction and open reduction internal fixation (ORIF)?
Closed reduction involves manual realignment by a healthcare provider, while ORIF involves surgical intervention to stabilize the fracture.
What psychological considerations should be taken into account for patients with SCI?
Depression and the need for social worker involvement.
What is the significance of prenatal care for pregnant women with SCI?
Essential for monitoring and managing the increased risks associated with pregnancy.
What is the link for patient teaching regarding men's reproductive health after SCI?
for-men-after-a-spinal-cord-injury.
What is the link for patient teaching regarding women's reproductive health after SCI?
ftil d i j.
What are the signs to look for in patients with potential complications from fractures?
Signs of hemorrhage, infection, or neurovascular compromise.
What is the role of pain control in the management of fractures?
To alleviate discomfort and improve patient outcomes during recovery.