Structure 3.2 - functional groups, cis-trans isomerism, enantiomers, mass spectra, IR spectra, and H NMR spectra
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
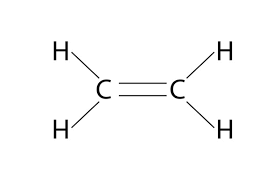
alkene
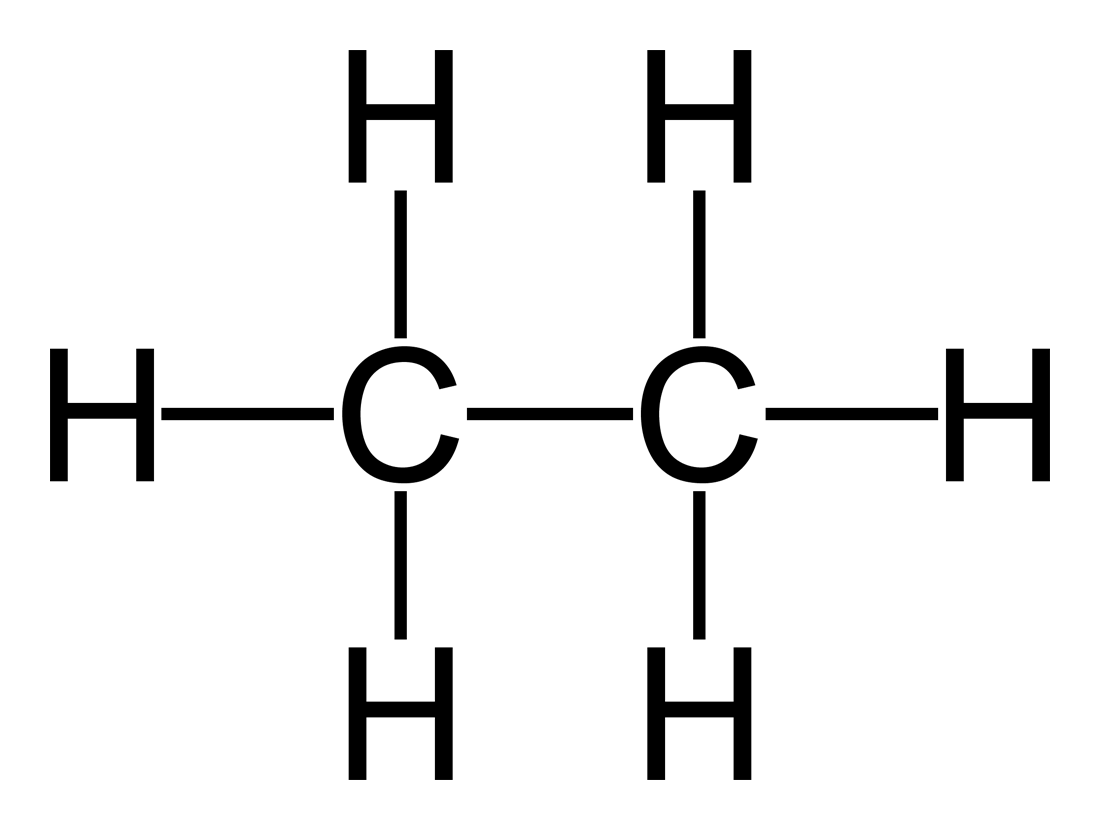
alkane
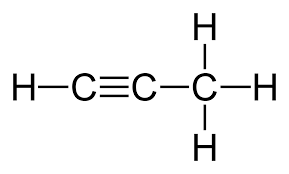
alkyne
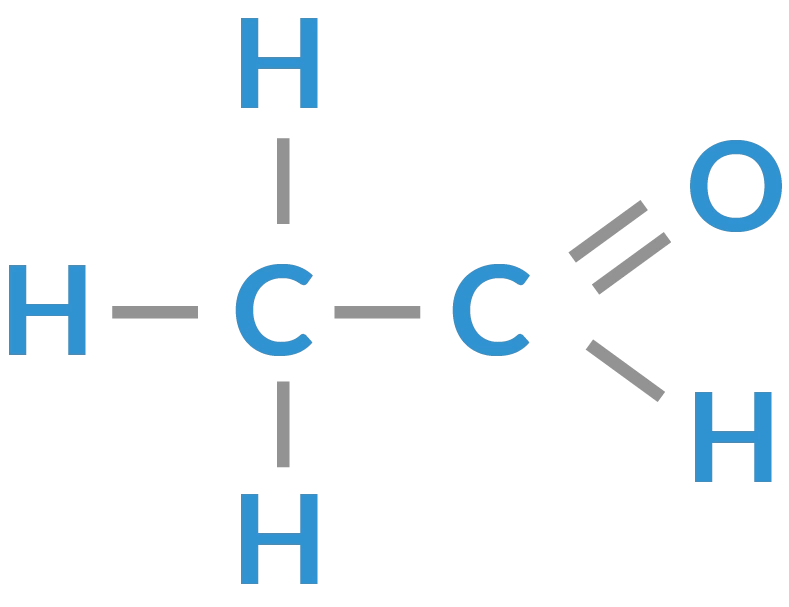
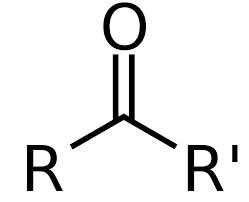
aldehyde
ketone
alcohol
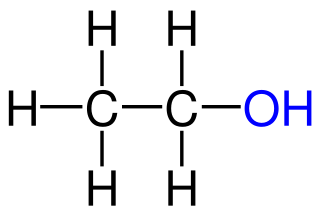
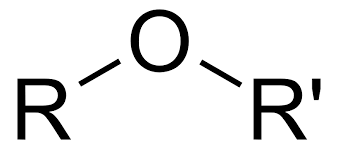
Ether
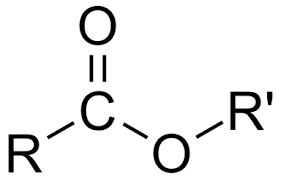
carboxylic acid
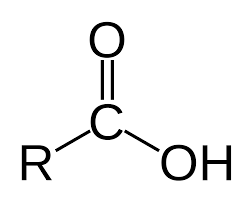
amine

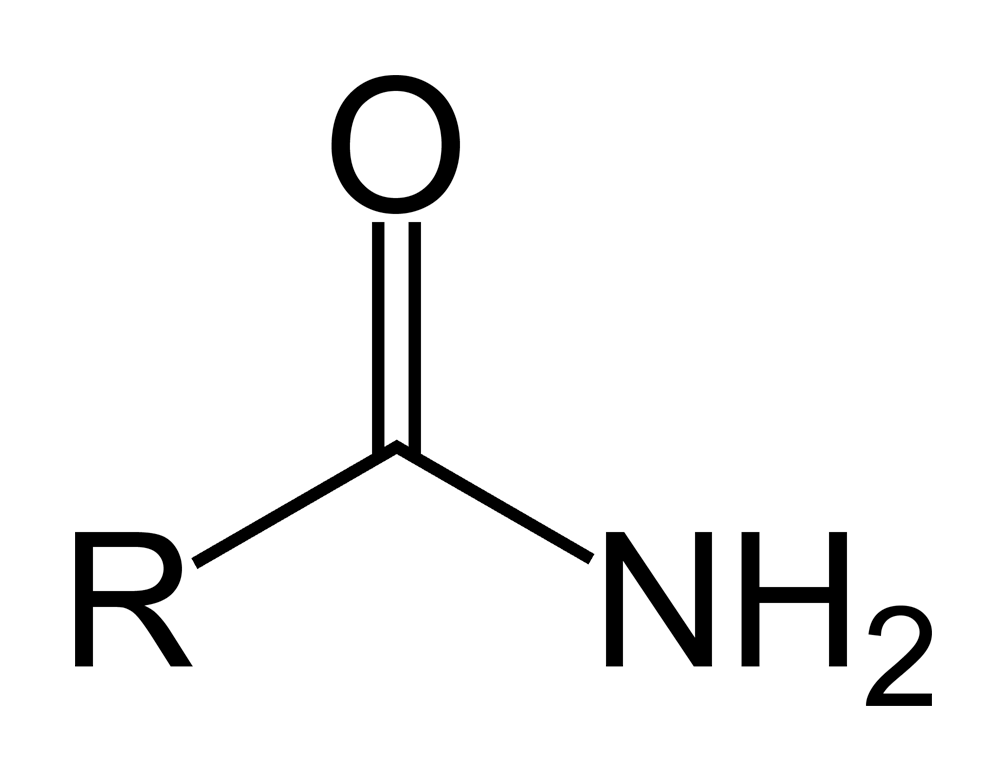
amide
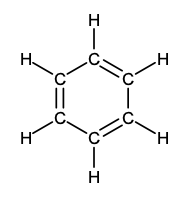
arene (phenyl)
Functional group
a group of atoms within a molecule that is responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of the molecule.
homologous series
a series of organic compounds of the same family that differ by a CH2 group.
characteristics of homologous series
similar chemical properties and show a gradation in physical properties
same general formula
same functional group
compounds that have hydrogen bonds
alcohols, amines, amides, carboxylic acids
compounds that have dipole-dipole
aldehydes, ketones, and esters
compounds that have LDFs
alkanes, alkenes, alkynes
cis-trans isomerism
When there is a restriction on the rotations that can occur around a bond because there is a double bond or there is a ring structure in a cyclic compound.
Cis isomer
An isomer that has the same groups on the same side of the carbon-carbon double bond.
Trans isomer
An isomer that has the same groups on opposite sides of the carbon-carbon double bond.
Chiral compound
A compound that has a carbon that is attached to four different functional groups.
Enantiomer
The two possible 3-D configurations of the chiral compounds which are mirror images and are non-superimposable.
Characteristics of enantiomers
rotate the plane of polarized light by the same amount but in different directions
they have the same physical properties
the same chemical properties
except in the case where they are reacting with other chiral compounds
Optically active
A term used to describe the observation that two enantiomers do indeed rotate light in different directions.
Racemix mixture
A mixture that contains equal amounts of two enantiomers.
IR spectroscopy
Used to determine the type of bond that is present in a molecule.
What happens when molecules absorb energy from the IR region?
The bonds between the atoms begin to vibrate (they stretch and bend).
What type of molecules have IR interactions
Polar molecules.
wavenumber
The frequency of IR radiation absorbed by a bond.
H NMR spectroscopy
Gives information on the different chemical environments of hydrogen atoms in a molecule (where they are located throughout the molecule).
chemical shift
The position of the NMR signals relative to the TMS standard position.