2.1.3-add three neuron types
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
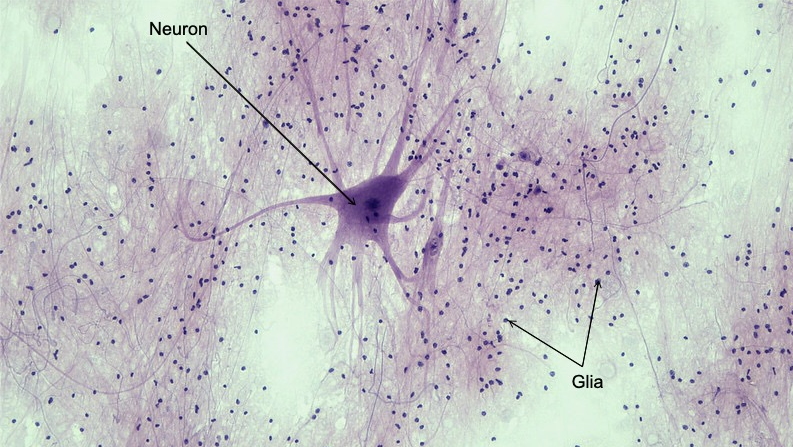
What are the cells of the PNS and CNS broadly grouped into what two categories.
They are neurons and glial cells.
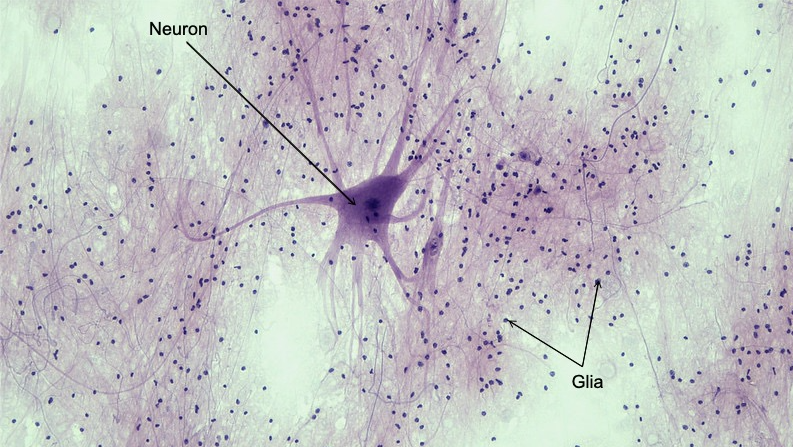
What are neurons?
Neurons are specialized cells that transmit nerve impulses, enabling communication within the nervous system.
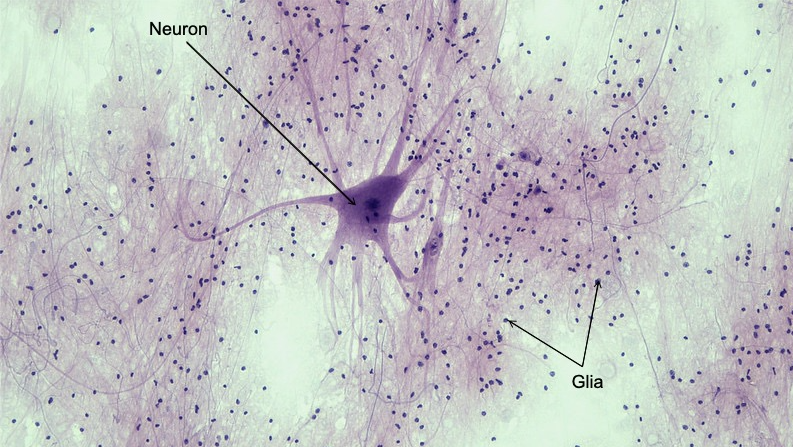
What are glial cells?
Glial cells are non-neuronal cells in the nervous system that provide support, nourishment, and protection for neurons, playing crucial roles in maintaining homeostasis.
Together what are neurons and glial cells responsible for?
Together, neurons and glial cells are responsible for the proper functioning of the nervous system, including signal transmission and support of neuronal health.
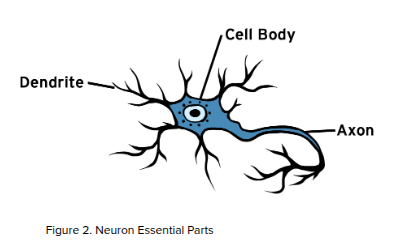
What are the three essential parts of a neuron?
The three essential parts of a neuron are the cell body, dendrites, and axon. These components work together to process and transmit information.
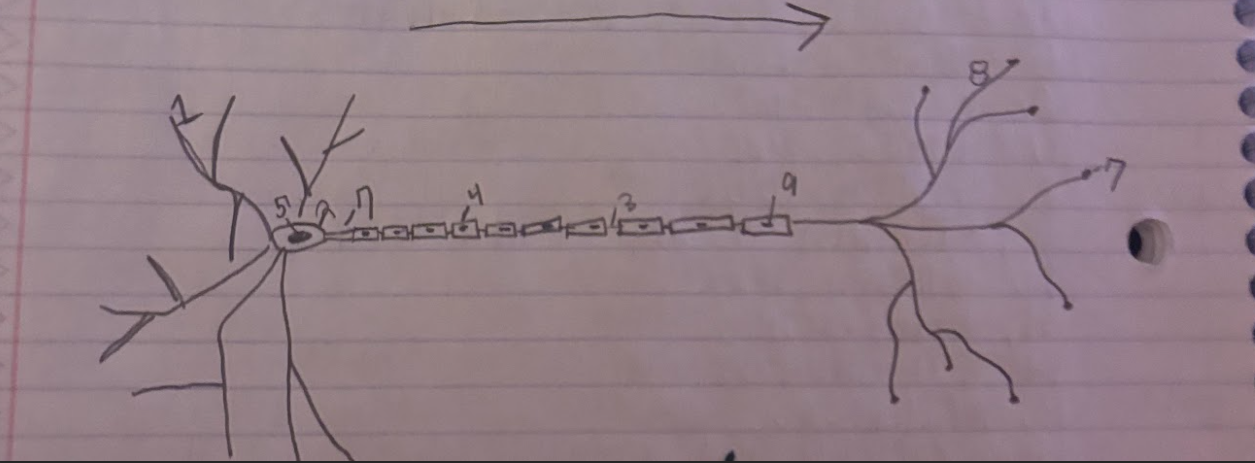
Structure of the Neuron:Schwann
Glial cells that form and produce the myelin sheath.-9
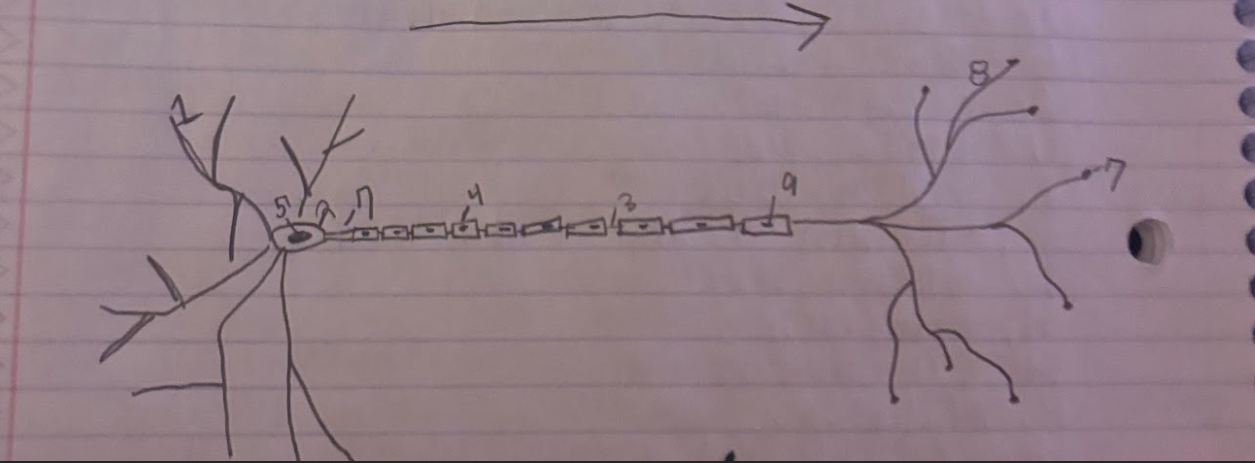
Structure of the Neuron:Dendrite
A part of neuron cells that receive signals and send information towards the Soma.-1
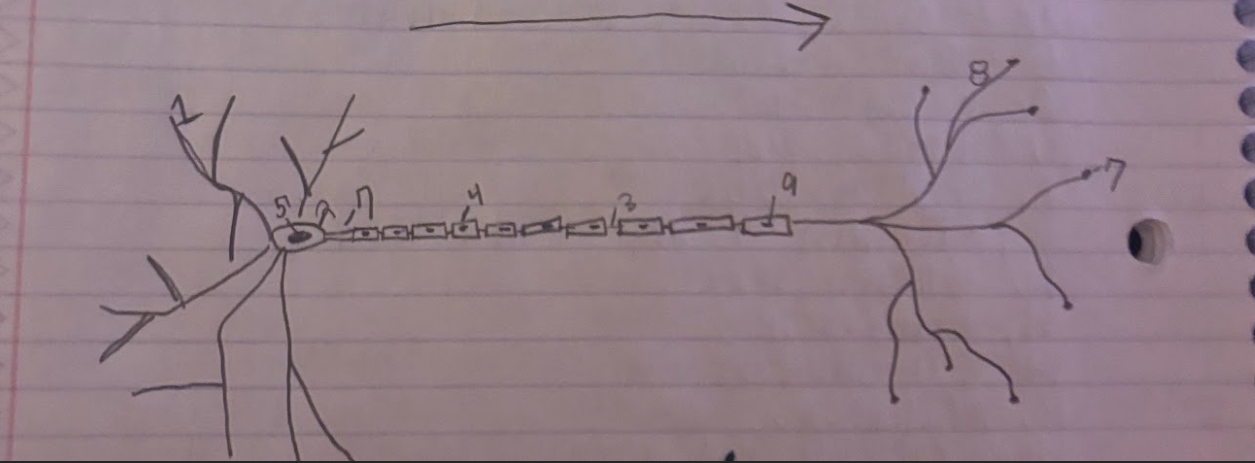
Structure of the Neuron:Soma
The cell body of a neuron, which contains the nucleus and organelles. It integrates incoming signals and communicates with the axon.-2
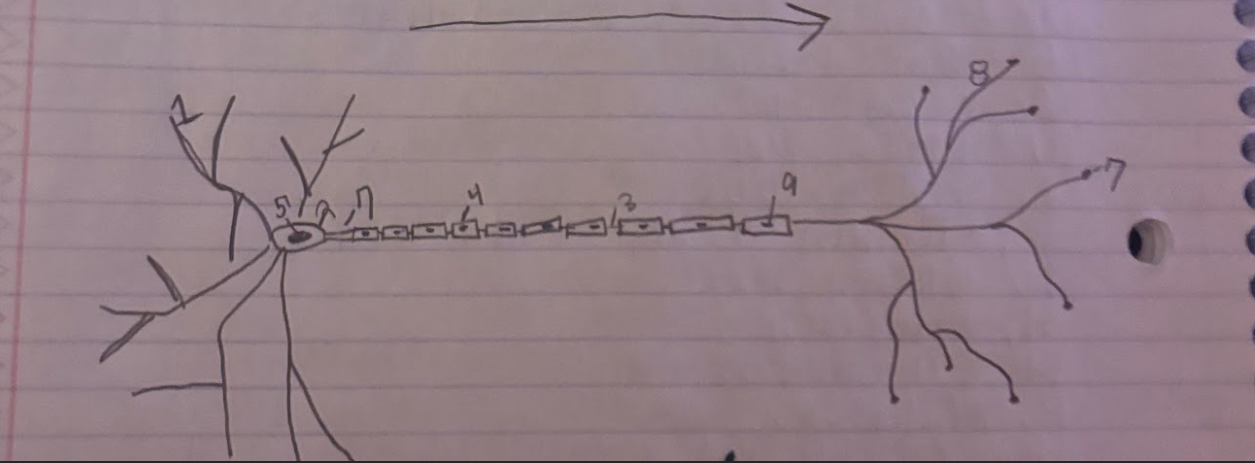
Structure of the Neuron:Node of Ranvier
A small gap in the myelin sheath of a neuron where ion exchange occurs, facilitating rapid conduction of electrical impulses.-3
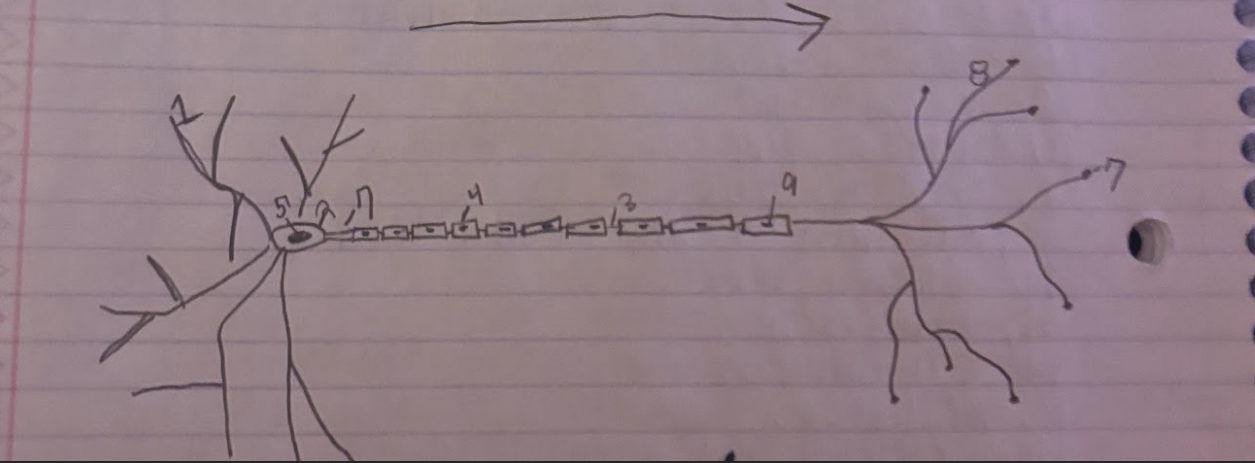
Structure of the Neuron:Normal Myelin sheath
A protective insulating layer that surrounds the axon of a neuron, enhancing the speed of electrical signal transmission.-4
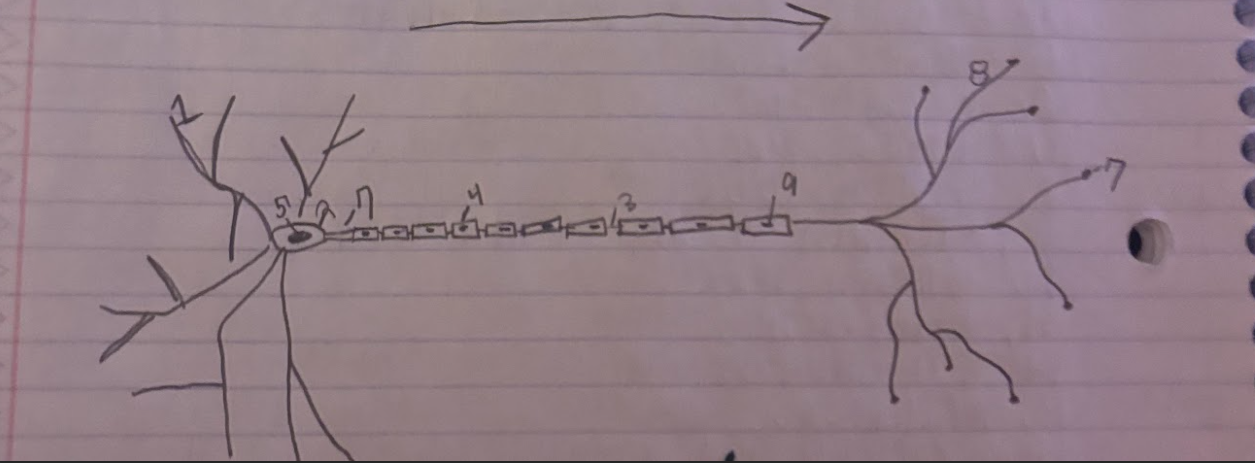
Structure of the Neuron:Nucleus
The membrane-bound organelle within the soma of a neuron that contains the genetic material (DNA) and regulates cellular activities.-5
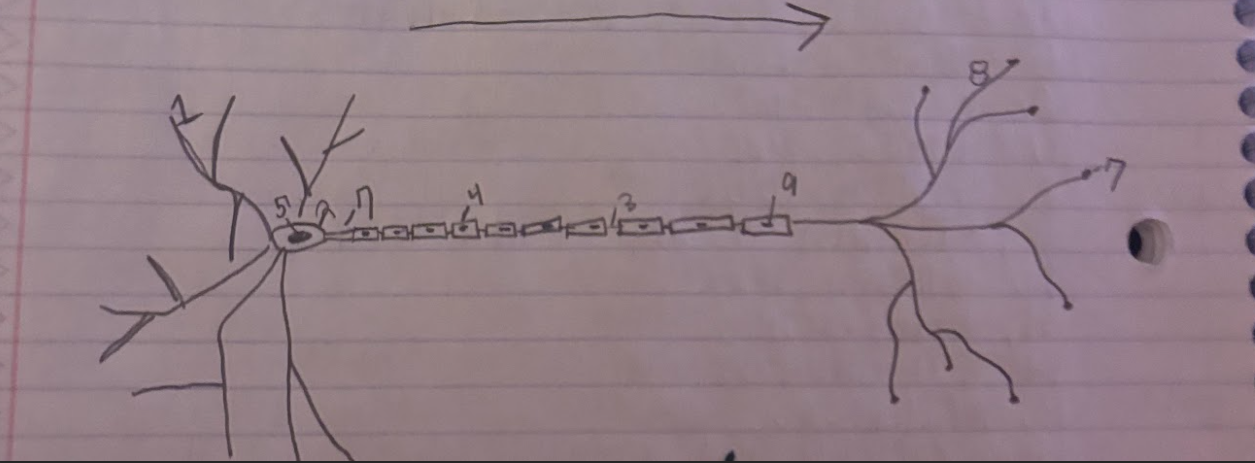
Structure of the Neuron:Axon Terminal
The endpoint of an axon where neurotransmitters are released to communicate with other neurons or target cells.-6
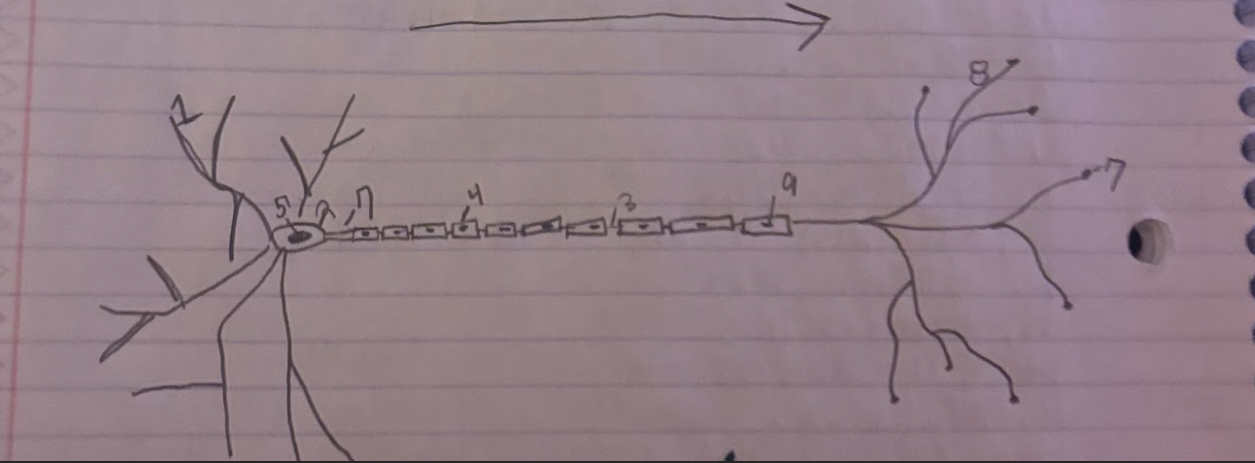
Structure of the Neuron:Axon
The long, slender projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses away from the soma toward other neurons or target cells.-7
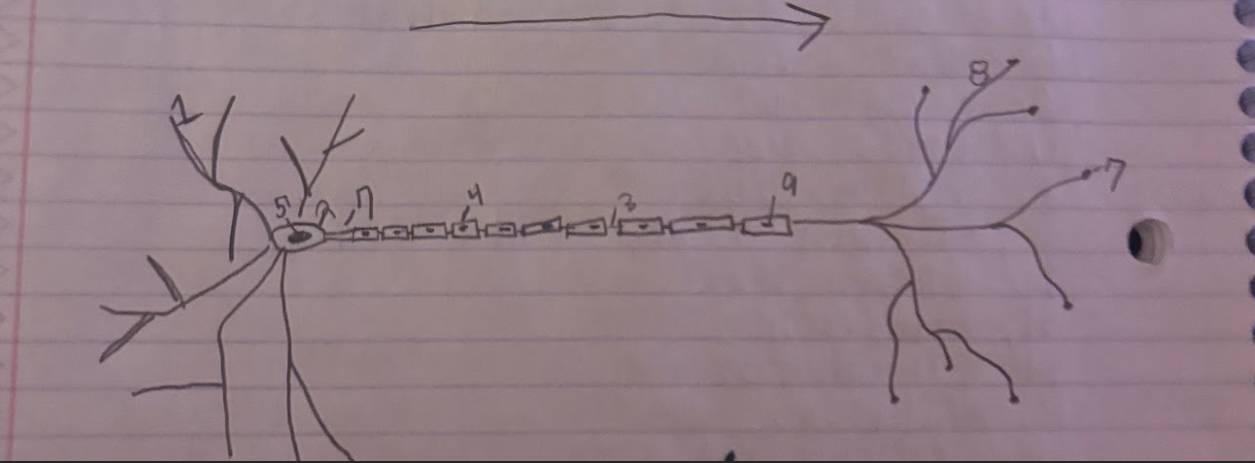
Structure of the Neuron:Synapse
The junction between two neurons or between a neuron and another cell, where neurotransmission occurs, allowing for communication between cells.-8
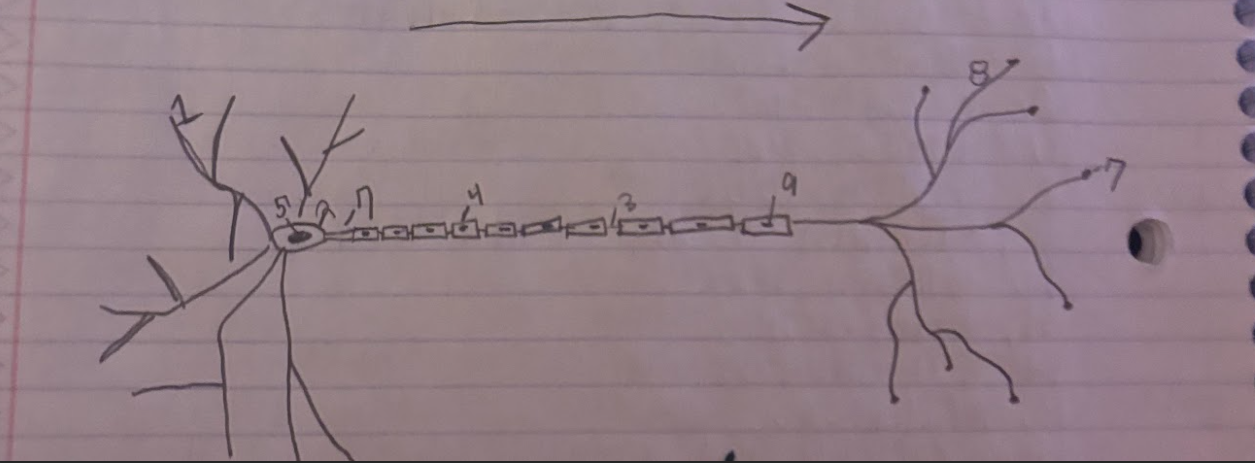
What is the direction of information through a neuron?
Information flows from the dendrites to the soma and then down the axon to the axon terminals.
What do glial cells do and what differentiates them from neurons?
Glial cells support and protect neurons, provide insulation, and maintain homeostasis, differentiating from neurons as they do not conduct electrical impulses.
What are the glial cells in the PNS?
The glial cells in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) include Schwann cells, which produce the myelin sheath, and satellite cells, which provide support and nutrition to neurons.
What are the glial cells in the CNS?
The glial cells in the central nervous system (CNS) include astrocytes, which support and nourish neurons; oligodendrocytes, which produce myelin; and microglia, which act as immune cells.Astrocytes maintain the chemical environment and contribute to the blood-brain barrier for protection.
When glial cells do not function properly what problems can occur?
When glial cells do not function properly, it can lead to various neurological disorders, including multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, and other neurodegenerative conditions, as they play crucial roles in maintaining neuronal health and support.
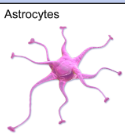
What do astrocytes do and in what nervous system are they in?
Astrocytes are glial cells in the central nervous system (CNS) that support and nourish neurons, maintain the chemical environment, and contribute to the blood-brain barrier for protection.
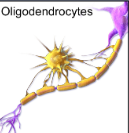
What do oligodendrocytes do and in what nervous system are they in?
Oligodendrocytes are glial cells in the central nervous system (CNS) that produce myelin, which insulates axons to enhance the speed of electrical signals between neurons.
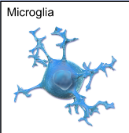
What do microglial cells do and in what nervous system are they in?
Microglial cells are glial cells in the central nervous system (CNS) that act as the main immune defense, responding to injury and infection by removing debris and pathogens.
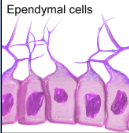
What do Ependymal cells do and in what nervous system are they in?
Ependymal cells are glial cells in the central nervous system (CNS) that line the ventricles of the brain and produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which cushions and protects the brain and spinal cord.
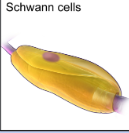
What do schwann cells do and in what nervous system are they in?
Schwann cells are glial cells in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) that form myelin sheaths around peripheral neurons, aiding in the faster transmission of nerve impulses.
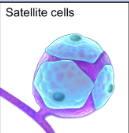
What do satellite cells do and in what nervous system are they in?
Satellite cells are glial cells in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) that provide support and nutrition to neuronal cell bodies, as well as regulate the microenvironment around them.
What are the differences between neuron and glial cell types? How do they work together in the nervous system?
Neuron types include sensory, motor, and interneurons, while glial cells consist of astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and Schwann cells. Neurons transmit signals and communicate information, while glial cells support, nourish, and protect neurons, ensuring proper functioning of the nervous system.
Neuron Form-multipolar location
CNS and efferent(motor) PNS. afferent is sensory.
Neuron Form-multipolar abundance
Most common neuron type in the human body. Makes up 99% of neurons.

Neuron Form-Multipolar Microscopy
nonsmooth polygonal shapes with many spine-like projections emerging from it. The nucleus is visible.
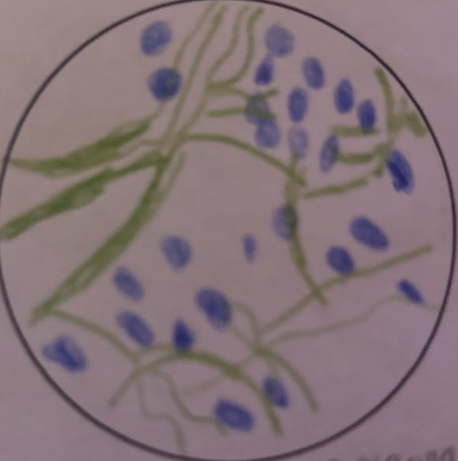
Neuron Form-bipolar location
Primarily located in sensory organs such as the retina, olfactory epithelium, and inner ear.
Neuron Form-bipolar abundance
Less common than multipolar neurons, mainly found in specialized sensory locations.Relatively rare.

Neuron Form-bipolar microscopy
The cell body is compact with dendrite extending from one side to receive sensory input and another axon extends the opposite to transmit a signal.
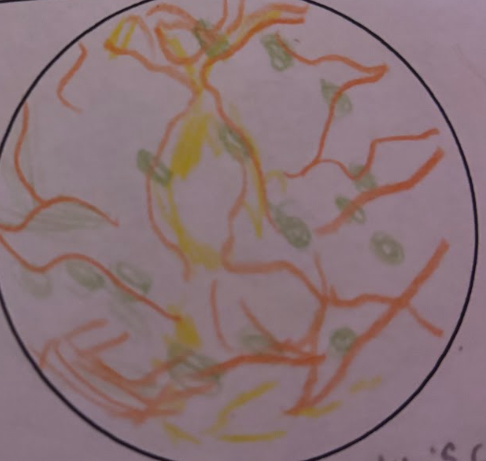
Neuron Form-Pseudounipolar location
Primarily found in sensory neurons, particularly in the dorsal root ganglia of spinal nerves.
Neuron Form-Pseudounipolar Abundance
More common than bipolar neurons, commonly found in afferent(sensory) PNS.
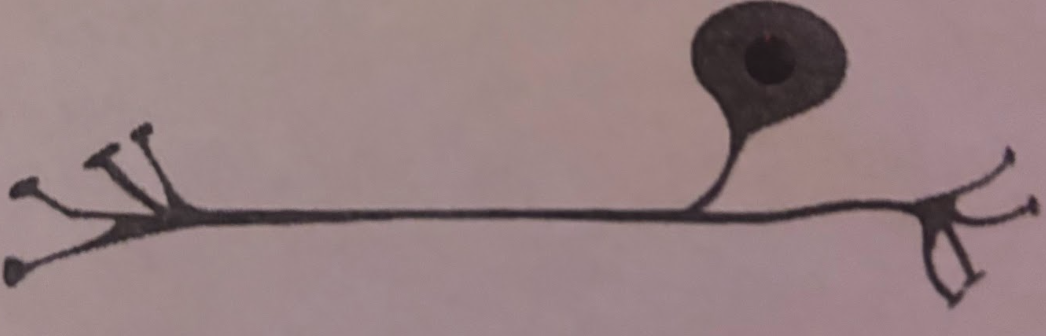
Neuron Form-Pseudounipolar microscopy
Characterized by a single process that bifurcates into two branches, one acting as a dendrite and the other as an axon. This structure allows for efficient transmission of sensory information.

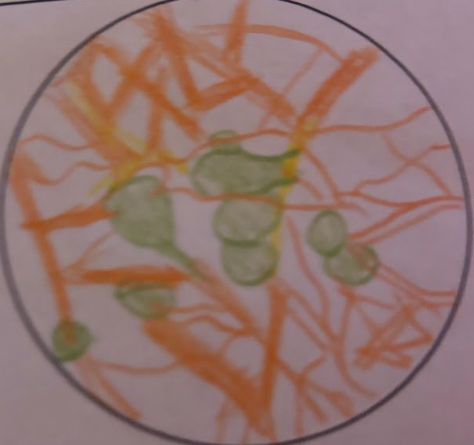
Neuron Form-unipolar location
Afferent(sensory) division of the PNS
Neuron Form-unipolar abundance
Common in invertebrates but rare in vertebrates.

Neuron Form-unipolar microscopy
Single process emerging from the cell body. Then it divides into branches and the body has a spherical shape.
What is the difference between afferent and efferent?
Afferent neurons carry sensory information from the body to the central nervous system, while efferent neurons transmit motor commands from the central nervous system to the body, facilitating actions and responses.
Describe one way in which neurons are similar to other cells in the body and one way in which they are different.
Neurons share similarities with other body cells, such as having a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and organelles. However, they are unique in their ability to transmit electrical signals and communicate through synapses.They have special extensions called dendrites and an axon. Dendrites receive signals from other neurons, while the axon sends signals away from the cell body to transmit information.
Explain how different types of neurons work together to sense, process, and respond to stimuli.
There are three main types of neurons:sensory,Interneurons, and motor neurons. Sensory neurons detect stimuli and transmit information to interneurons, which process the information and relay it to motor neurons that execute a response.
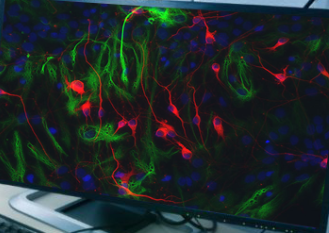
What type of cell is this?
Hypothalamus neuron
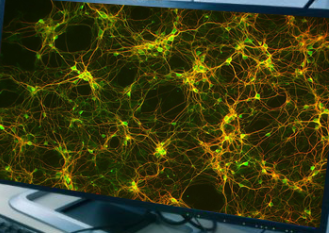
What type of cell is this?
Neonatal Retinal cells,bipolar

What type of cell is this?
CD1 Cortex neurons,multipolar

What type of cell is this?
Normal astrocytes
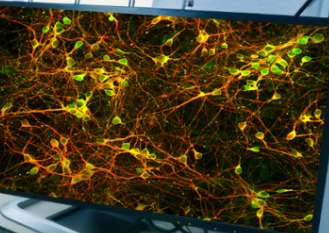
What type of cell is this?
Brain cortex neurons
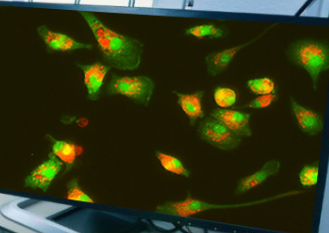
What type of cell is this?
Brain microglia
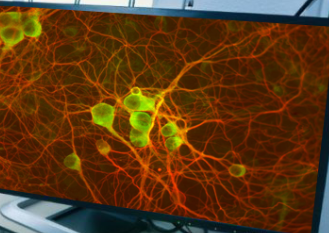
What type of cell is this?
Cerebellar cells,unipolar