Signal Circuits and Coding
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
microelectrode
A ______________ measures the voltage inside the cell.
defined as zero
A ground wire measures the voltage outside the cell (this value is ___________________)
amplifier
An _________ reports the difference to an oscilloscope or computer for display.
membrane potential (Vm)
The general term for the voltage difference across the plasma membrane is ______________________.
penetrates neuron
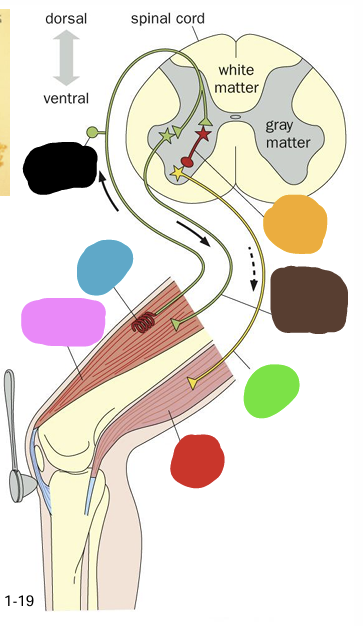
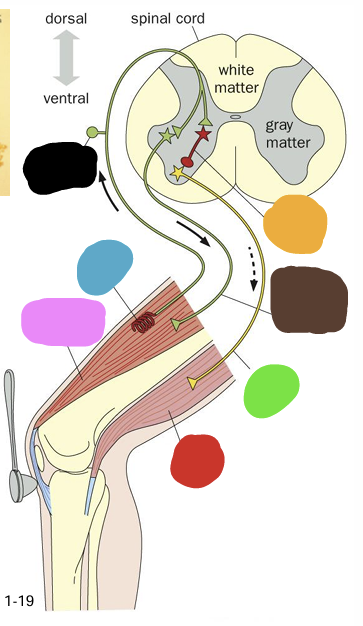
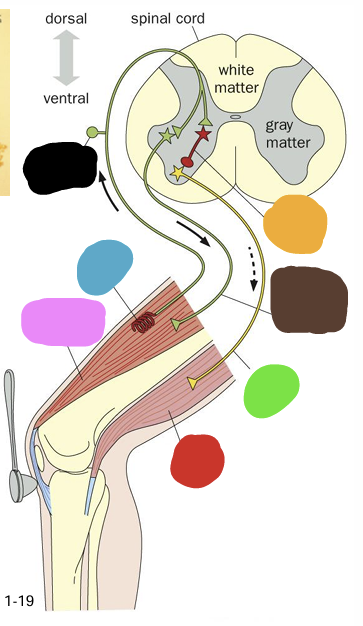
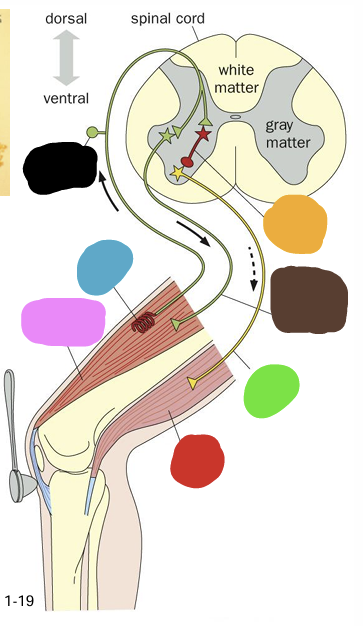
what does the blue box represent?
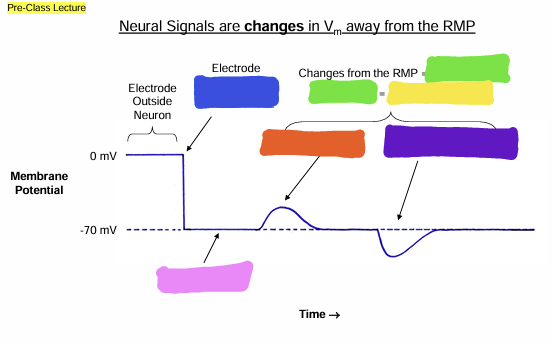
Signals
what does the green box represent?
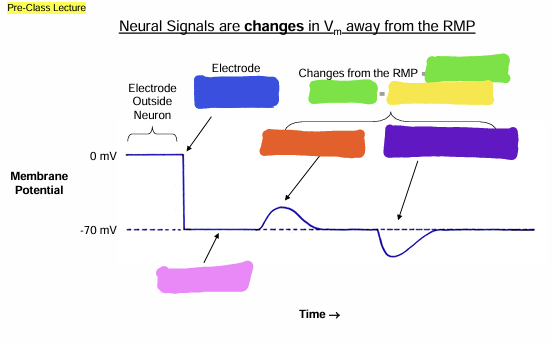
information
what does the yellow box represent?
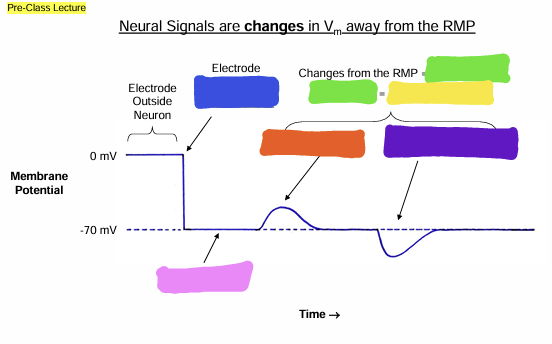
Depolarization
What does the orange box represent
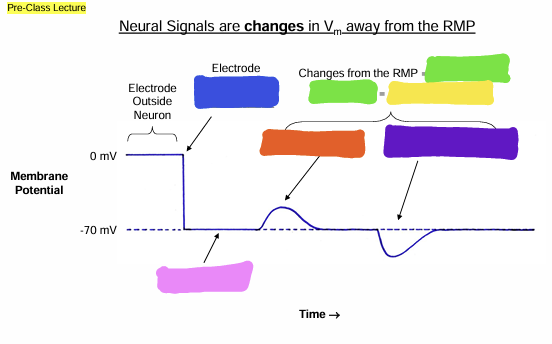
Hyperpolarization
what does the purple box represent?
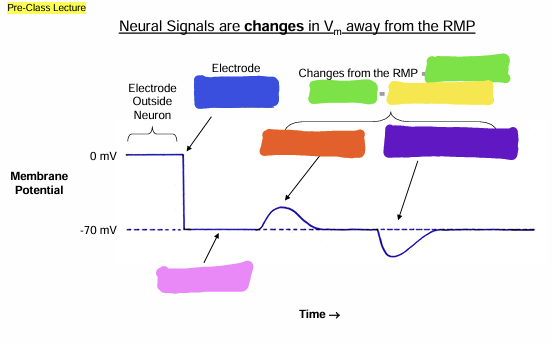
Resting Membrane Potential (RMP)
what does the pink box represent
Graded
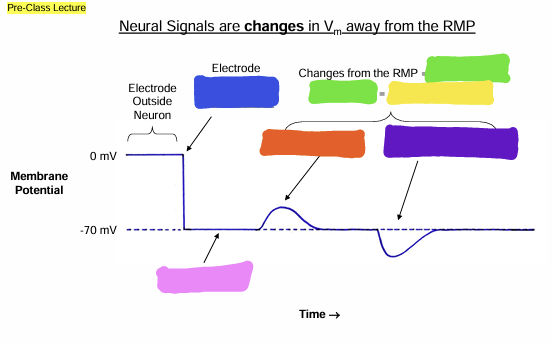
what does the pink question mark represent?
Action
what does the yellow question mark represent?
Graded Potential
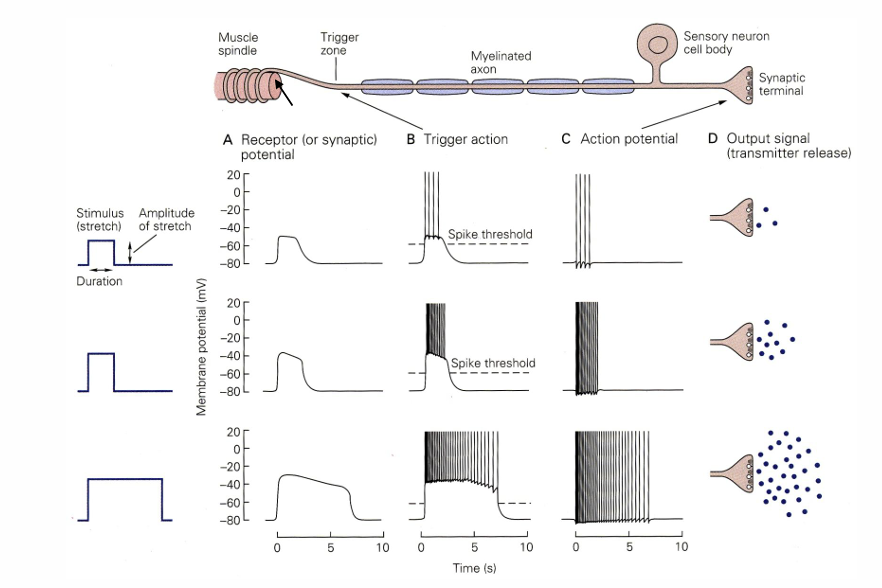
often small (less than 10mV change in Vm)
Hyperpolarization or Depolarization
Graded in amplitude
amplitude coding of stimulus intensity
Graded in Duration
code for stimulation with their duration
local - decay with distance from the site of initiation - dissipate within about 1mm
triggered by external energy or chemicals
Occur in:
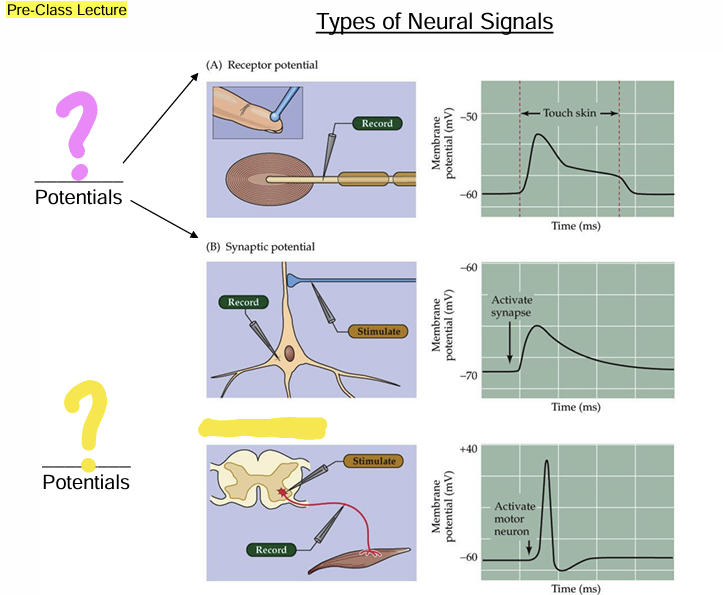
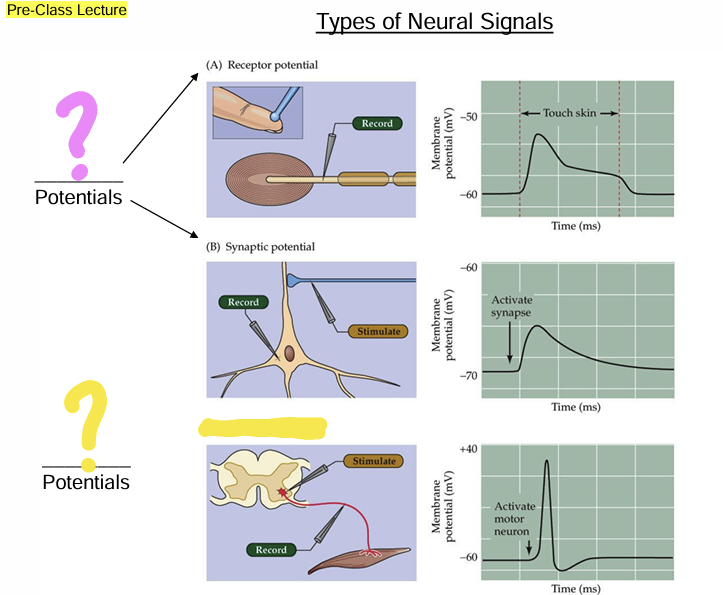
Sensory nerve endings - Receptor potential Transduced from external energy [light (vision), pressure (touch), vibration (hearing), or chemicals (smell and taste)]
Dendrites, soma, or axons - synaptic potential induced by a chemical neurotransmitter
Action Potentials (Impulses or spikes)
A large change in Vm
peak depolarization overshoots 0mV
Peak is depolarizing only
Fixed amplitude (all-or-none)
frequency coding of stimulus intensity
Fixed duration (1-3msec)
Code for stimulus duration with burst duration -how long was the cell firing?
Propagated (do not decay with distance) along the axon
Triggered by depolarizing graded potentials that cross a Vm threshold
Sodium-based spikes occur primarily in axons
Calcium-based spikes can occur in some dendrites
The amplitude of the stretch impacts the amount of Vm for the graded potential. The stimulus duration also increases the duration of the graded potential. As time goes on, the graded potential decays but if the graded potential exceeds the spike threshold at the trigger zone will allow for an action potential to be generated. An action potential signal does not decay over time and continues to propagate through out the rest of the cell.
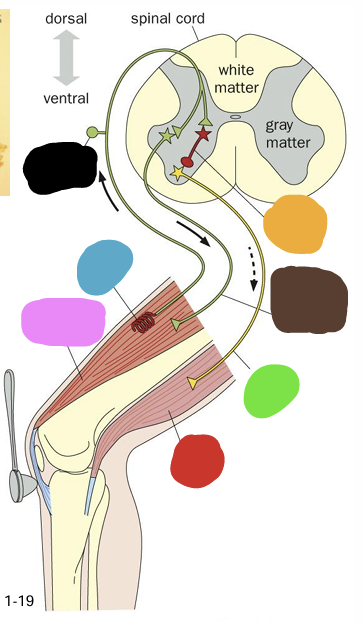
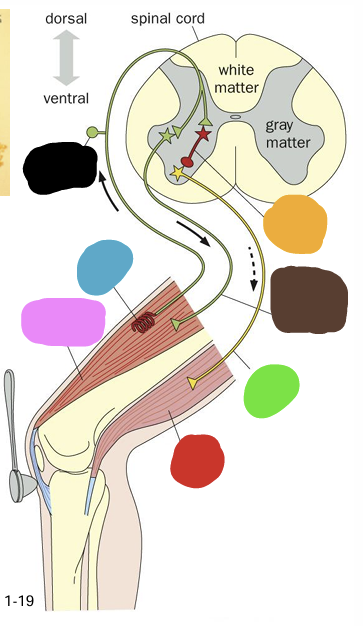
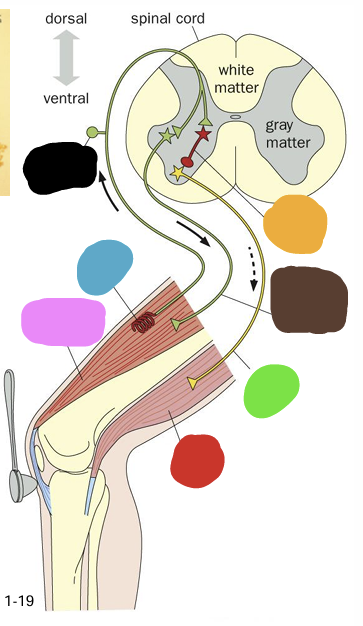
what is being shown in this image?
Dorsal Root
what is represented by the blue section
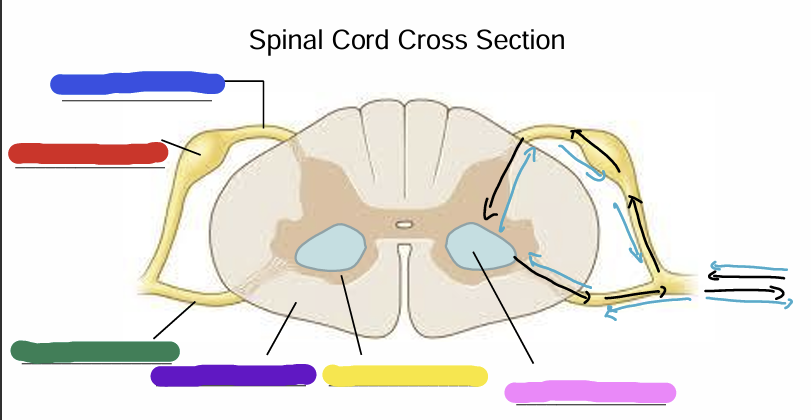
Dorsal Root Ganglion (Pseudounipolar)
What is represented by the red
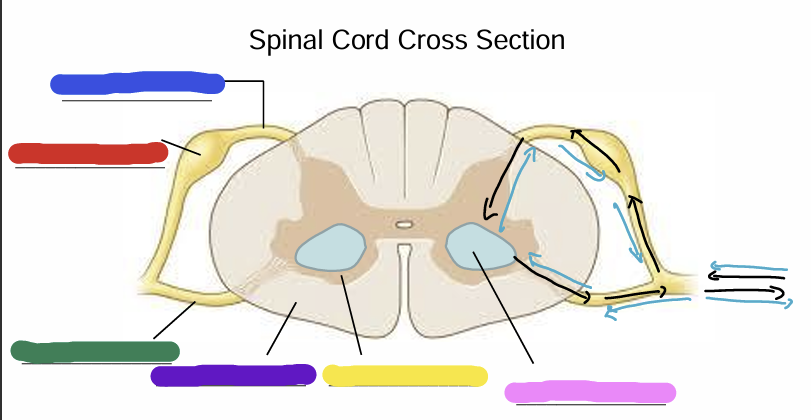
Ventral Root
what is represented by the green box
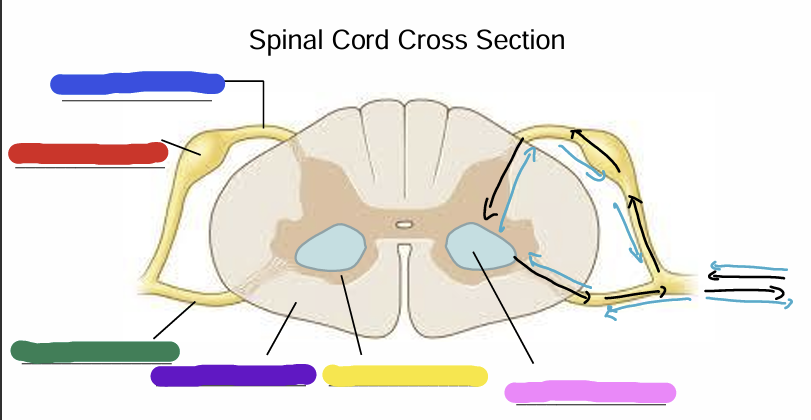
White Matter (axons - myelin is white)
what is represent by the purple
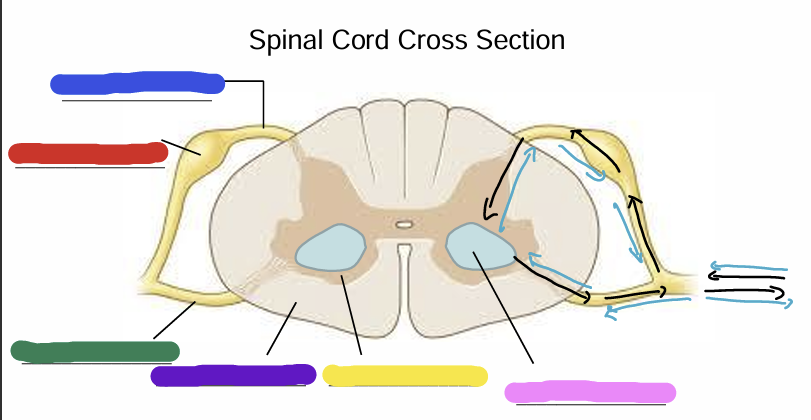
Gray matter
what is represented by the yellow
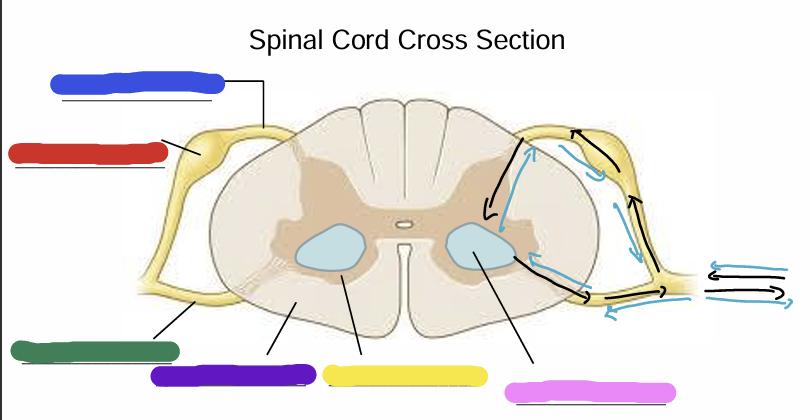
Cell bodies of alpha motor neurons
what does the pink box represent
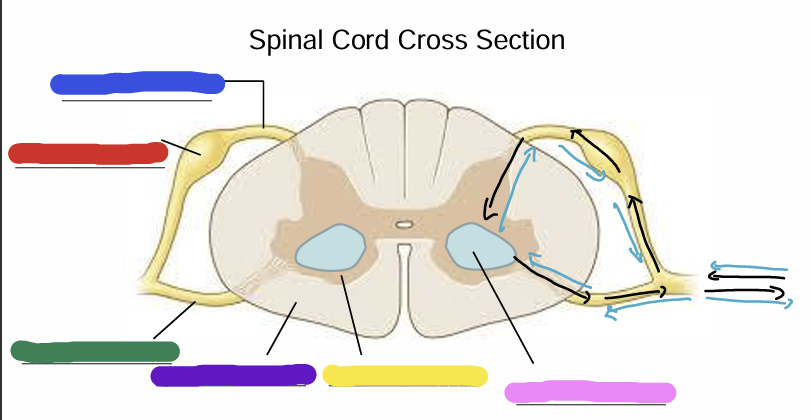
Black arrow
what is the correct flow of information? (blue arrow or black arrow)
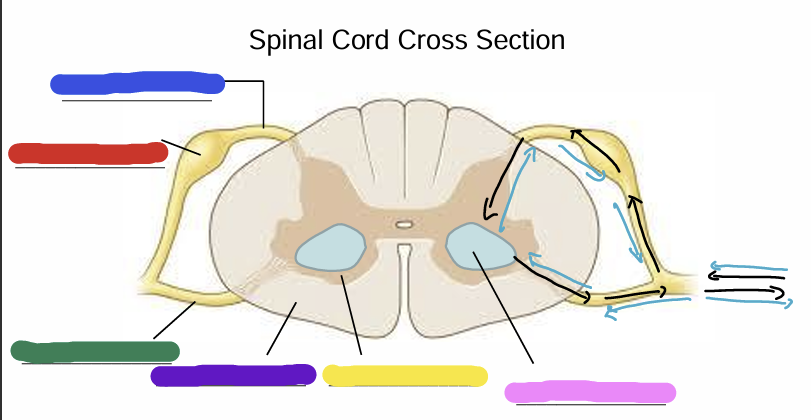
muscle spindle organ
• Connective tissue capsule
• Intrafusal muscle fibers
• Sensory neuron ending
sensory neuron
what is represented by the black box
muscle spindle
what is represented by the blue box
extensor muscle
what is represented by the pink box
Flexor muscle (hamstring)
what is represented by the red box
flexor motor neuron axon
what is in the green box
extensor motor neuron
what is represented by the brown box
Inhibitory neuron
what is represented by the orange box
Inhibitor motor neuron
Inhibition of this neuron is a result of hyperpolarization which leads to less activation since tonic firing is decreased, which leads to the muscle becoming more relaxed.
Stretch receptor
The stimulus generated by the muscle spindle acts as the ________________ (circuit element)
Neuromuscular synapses
The sensory motor neuron synapse sends another signal down the motor neuron which will be transferred to the ____________. This leads to the contraction of the extensor muscle.
Postural control
stabilize skeleton during walking
What is the normal function(s) of this reflex? (hit on the knee)
homeostatic
More generally, the circuit is a ______________ control system
set point - “desired” length of muscle
Stimulus - change in muscle length
motor output - effector
feedback - return to desired length
identical
All information in the nervous system is carried by two types of signals, graded potentials and action potentials. Moreover, all action potentials are essentially ______________
intrinsic properties
In a sensory pathway, the quality of the sensation encoded (e.g. light versus sound) by the signal is not based on the ______________________ of the signal (e.g. its size or shape).
source and/or destination
Interpreting the meaning of a given signal depends entirely on knowledge of the __________________________of that signal.
events in the external world
As scientists, we can only determine the function of individual nerve cells or different parts of the brain by correlating neural activity with ________________________
precise and orderly; separate and specialized
It also follows that:
The “brain” can only interpret signals in a similar fashion. Thus, the connections between neurons must be ___________________
2. The CNS possesses initially _______________________ pathways for different sensations and various other qualitatively distinct processes
What information is represented in any given part of a neuronal circuit?
How is that information encoded (e.g., in neuronal firing patterns)?
How is the information then decoded by downstream neurons?
What are the computations that transform input representations to output representations? We can think of this numerically, but also conceptually. Example: a primary role of the retina is to convert the absolute brightness (luminance) of objects to the amount of contrast between objects.
Understanding how the nervous system uses its signals to carry out its functions requires answering four basic questions:
unambiguous rate code
what kind of code is illustrated by the graph
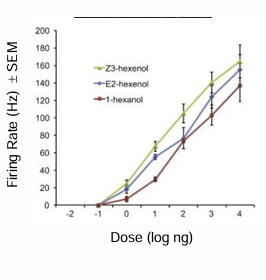
Coding for knee reflex
sensory representation: Change in length in muscle → computation: Reflex gain → motor representation: force require for contraction
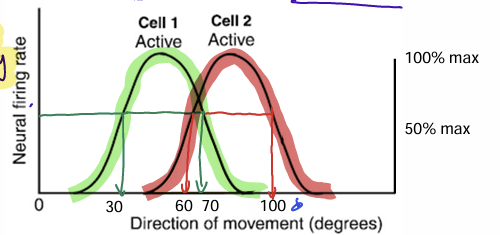
Coarse-Coding
each individual neuron is broadly tuned (rather imprecise), but the collective population of neurons can provide a very accurate and precise averaged response. Such coding is typically found in primary motor and sensory areas of the cerebral cortex
In order for both cells to be at 50% activity at once, the direction of movement must be in-between 60 and 70 degrees
what is the best conclusion that can be made from this graph?
Temporal Code
Average firing rate of the neuron during presentation of these two different stimuli is identical. Instead, what varies is when the cell tends to fire during stimulus presentation. Thus, precisely when the cell fires fires provides more information than its overall firing frequency.
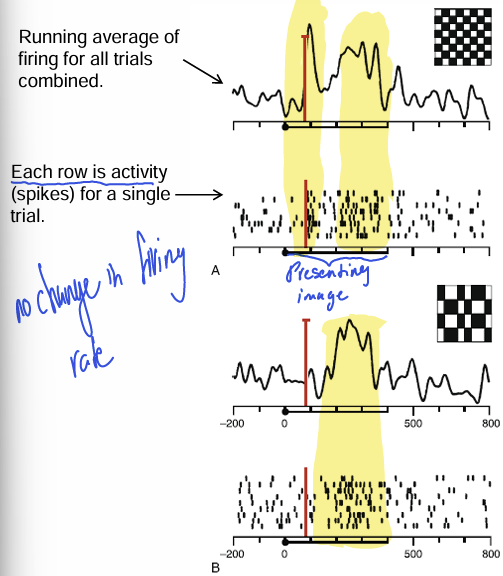
Control trials
Computation Study: expose rat to a grid-like visual pattern to map cell’s orientation selectivity and construct a response “tuning curve.”

Experimental trials
Computation Study: repeat experiment but simultaneously stimulate one of two types of cortical inhibitory interneurons (+PV or +SOM types)
Optogenetics
Stimulation was accomplished via ________________. The PV or SOM cell type expressed a protein called channelrhodopsin-2.
Channelrhodopsin-2
_________________ is a light activated cation channel from green algae. Entry of positive charges into the cell excites the neuron, causing it to fire action potentials.
Inhibition
Later, optical ____________of neurons was achieved. Most recently (2015), a rhodopsin like light-activated anion (chloride) channel was discovered in the protist G. theta
inhibitory synaptic input
When activated with blue light, the ChR2 channels open, causing depolarization that evokes action potentials in the inhibitory interneurons, thus activating ________________________ onto the pyramidal cell
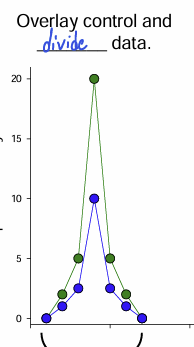
Division
Activation of +PV type interneurons causes _______________ (peak response is weaker). gain Thus, the response gain is smaller. On the other hand, the inhibitory input did not affect the cell’s selectivity for a given orientation.
Gain
(difference between peak and edges of tuning curve)
selectivity
(extremes of the tuning curve are unchanged – cell continues to respond to the same range of orientations).
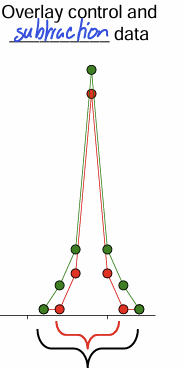
Subtraction
In contrast, stimulation of the +SOM type interneurons cause ______________. All responses, regardless of orientation, were weaker. This means that the response gain was unchanged. However, the downward shift caused the cell to cease responding to some orientations (at extremes) This means that the cell’s orientation preference has become more selectivity.
lower gain and similar selectivity
explain the results of obtained with the PV interneurons
similar gain and more selectivity.
explain the results obtained with the +SOM interneurons
detailed and sophisticated
New methods such as optogenetics are permitting researchers to ask ever more _______________________ questions about how the brain processes information.
subtypes; awake animal
Some of the key procedures employed in this study were:
1. Simultaneous activation of multiple neurons of a particular ____________.
2. Doing the above while recording the electrical responses of the target cell in the brain of an _______________ undergoing a sensory perception task.
The brain appears to have evolved separate types of interneurons to carry out different types of computations. Interestingly, the PV type interneurons synapse onto the pyramidal cell’s soma while the SOM type interneurons synapse onto the pyramidal cell’s dendrites. Thus, synapse location may be important in determining the type of computation that is performed on a target cell.
What does this study (computations) tell us about visual processing?