Chapter 4 - Muscles of the Hip
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
List the Muscles of the Posterior-Lateral Hip
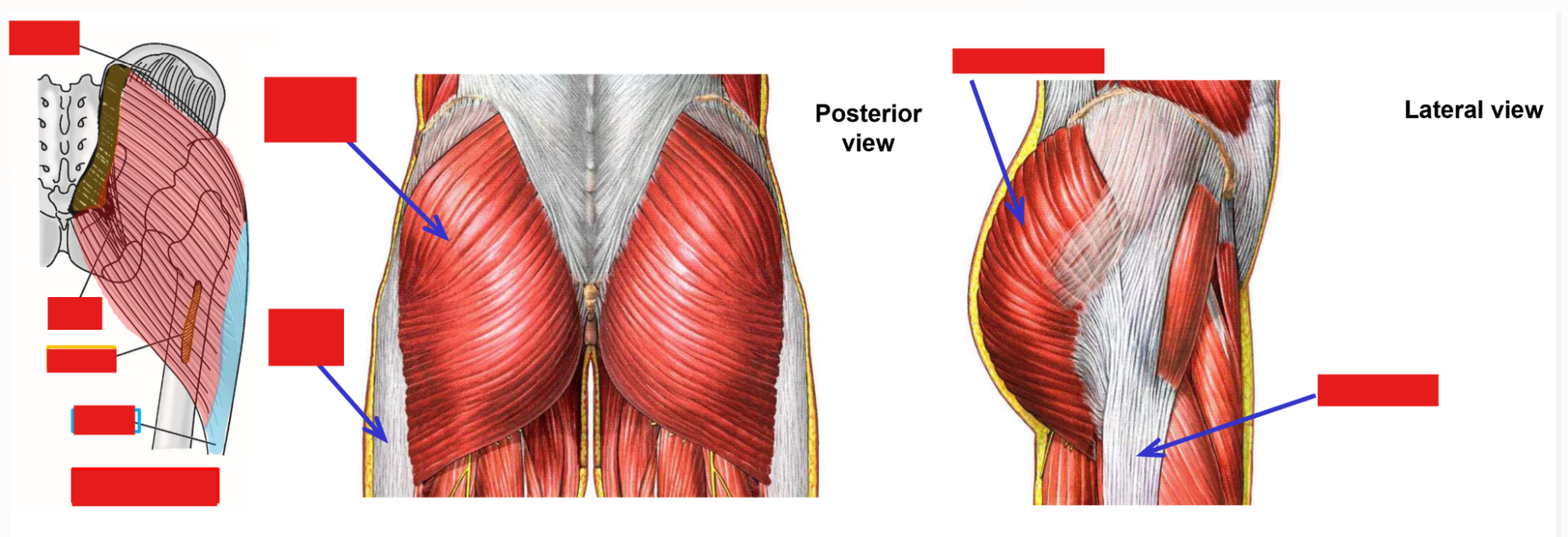
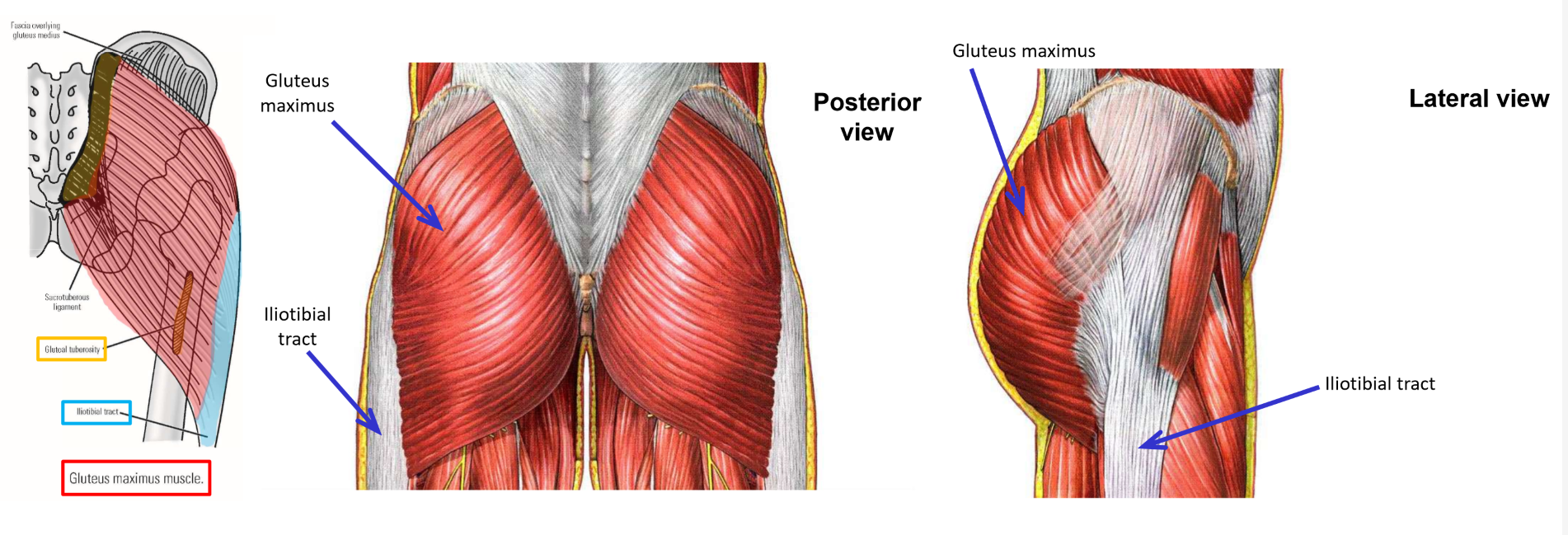
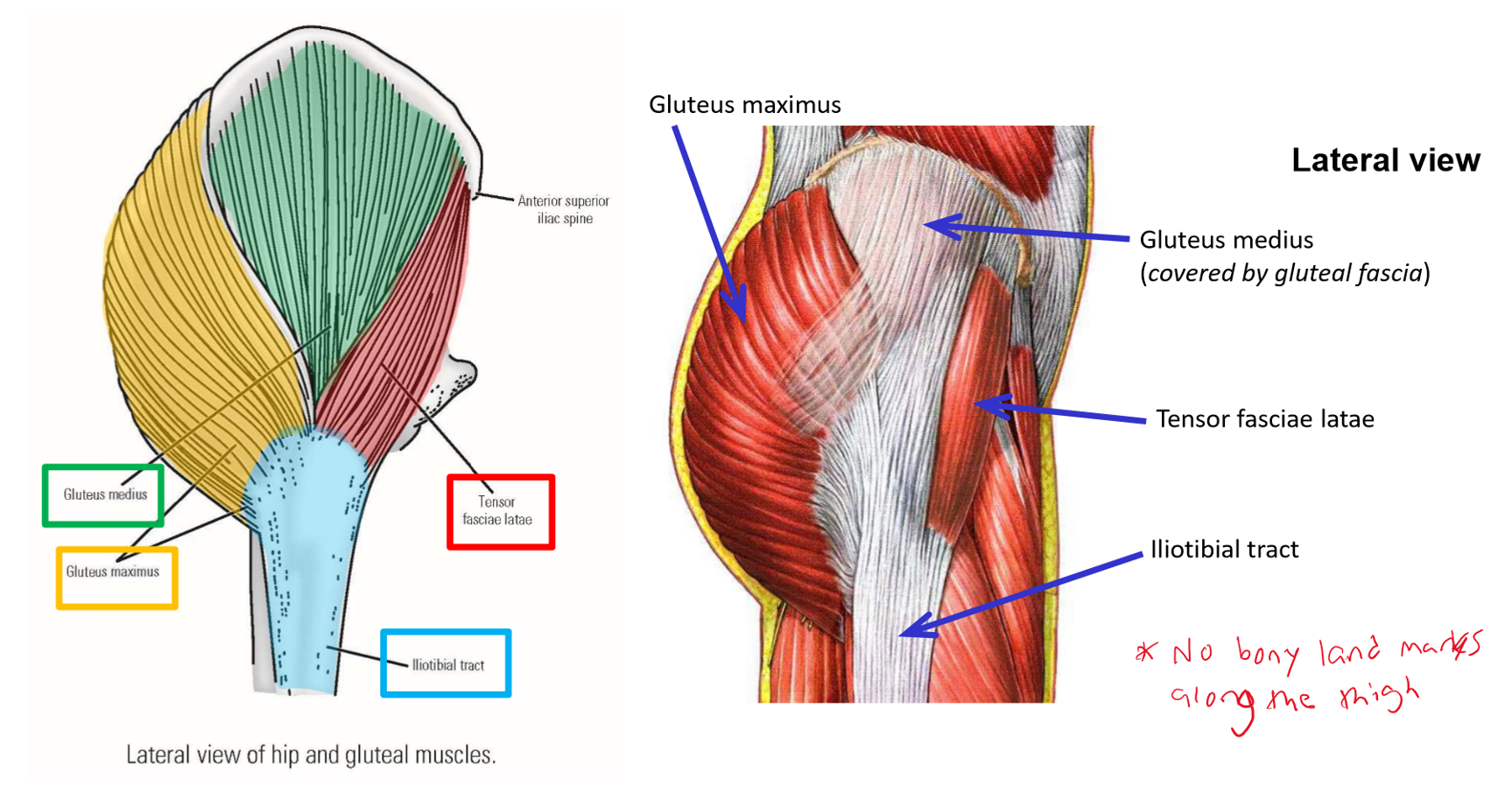
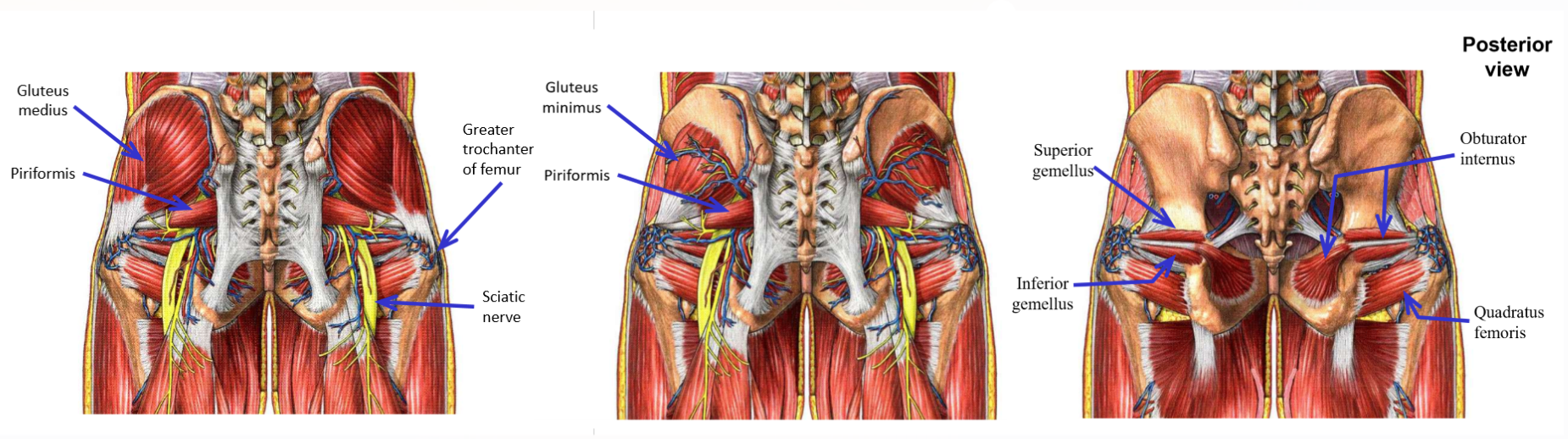
M. Gluteus maximus
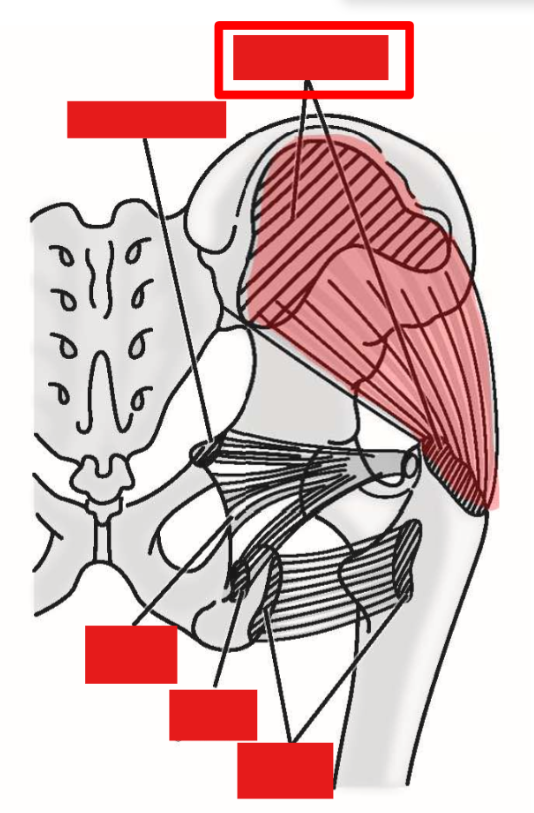
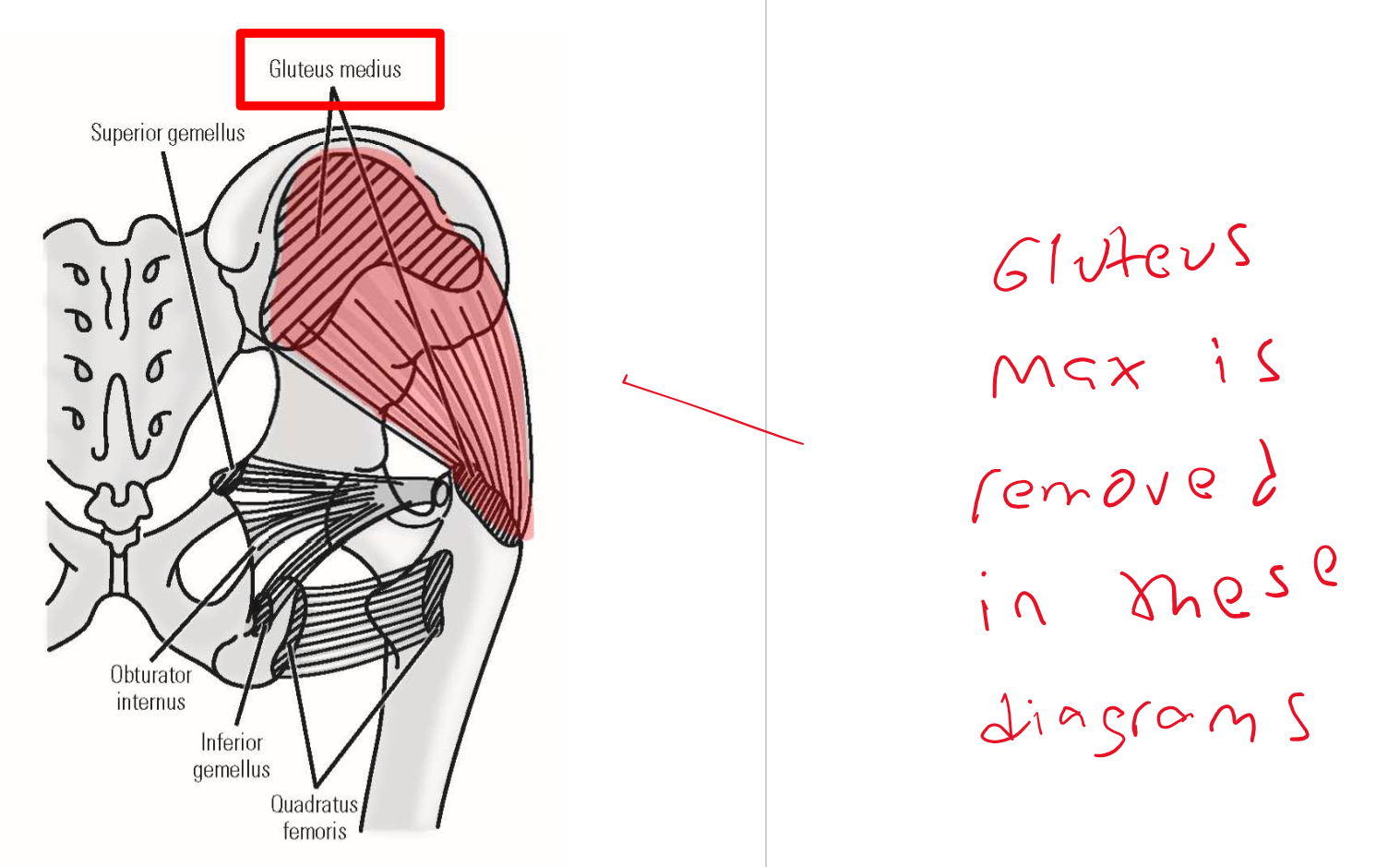
M. Gluteus medius
M. Gluteus minimus
Describe M. Gluteus maximus. Origin, Insertion, Action
Origin: posterior portion of iliac crest; posterior superior iliac spine; posterior sacrum
Insertion: 25% to gluteal tuberosity of femur; 75% into iliotibial tract of thigh fascia lata
Muscle acts directly on femur via gluteal tuberosity (roughened area)
Muscle acts indirectly on femur via iliotibial tract (attached to linea aspera of femur by lateral intermuscular septum)
Action: extension of thigh at hip joint
With foot planted and thigh flexed, gluteus maximus pushes body forward (running; climbing)
Progressive relaxation controls rate of thigh flexion during sitting
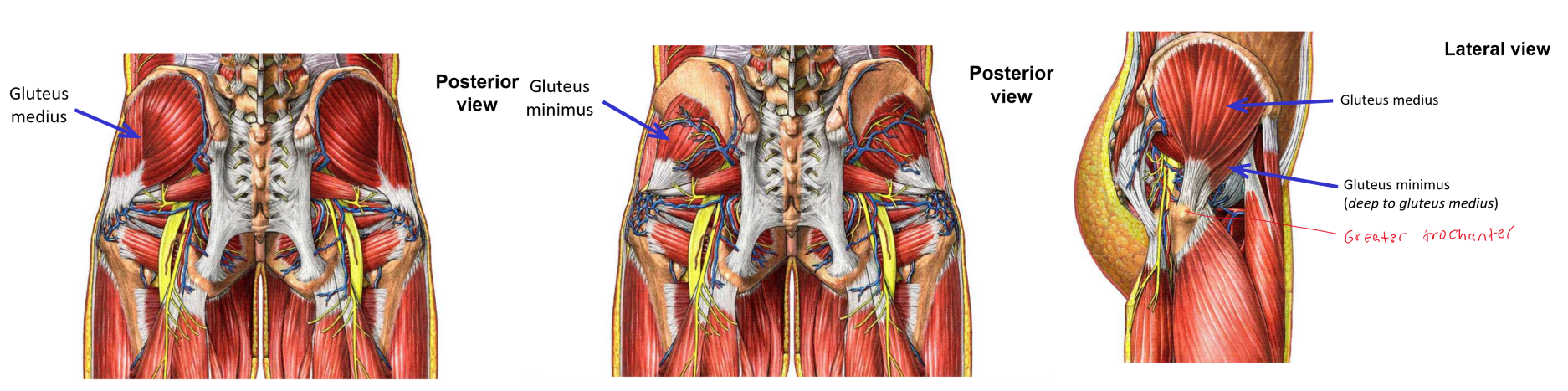
Describe M. Gluteus medius. Origin, Insertion, Action
Origin: lateral (external) surface of ilium portion of hipbone
Insertion: greater trochanter of femur
Action: abduction of thigh at hip joint
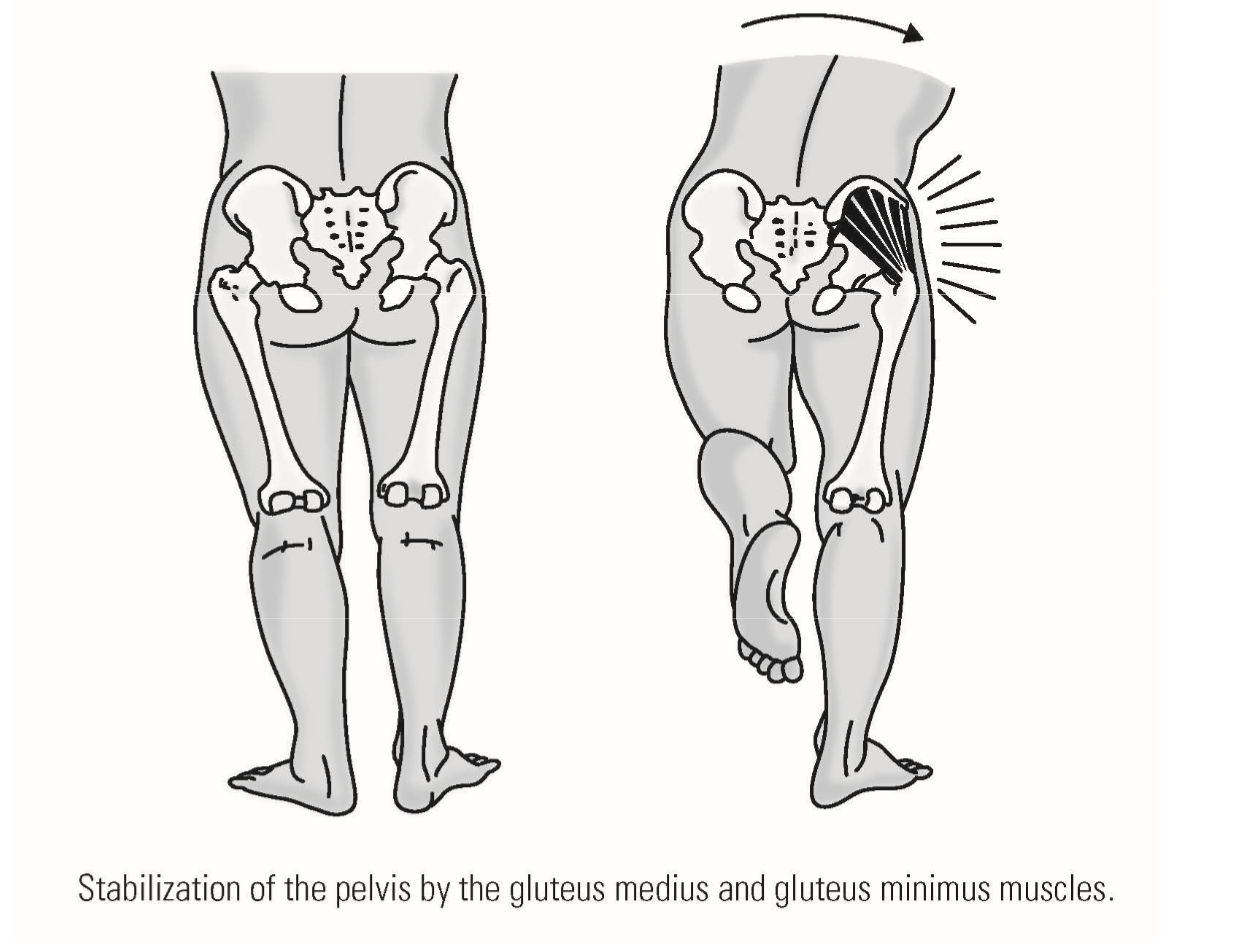
Action during walking: with one foot off the ground, these muscles contract on weight-bearing side to maintain horizontal position of the pelvis
—» Prevents drop of unsupported side of pelvis by pulling pelvis toward weight-bearing limb
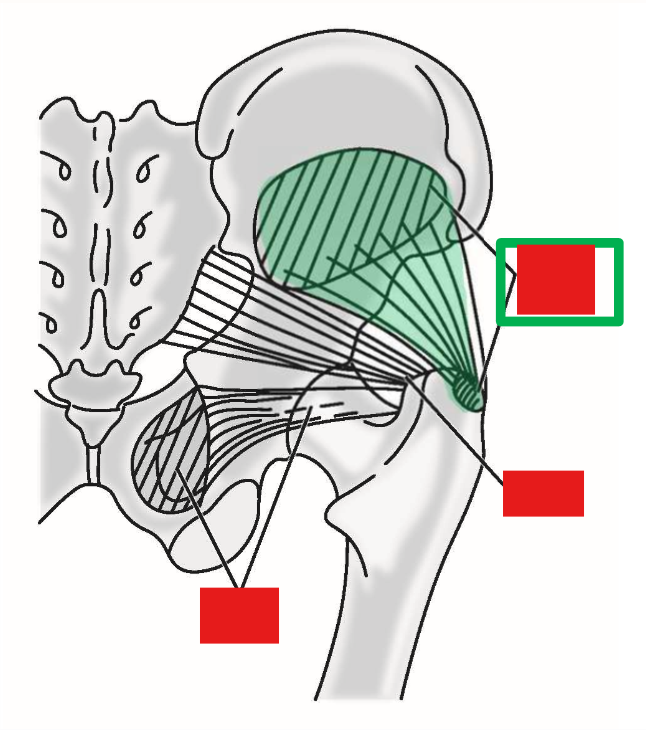
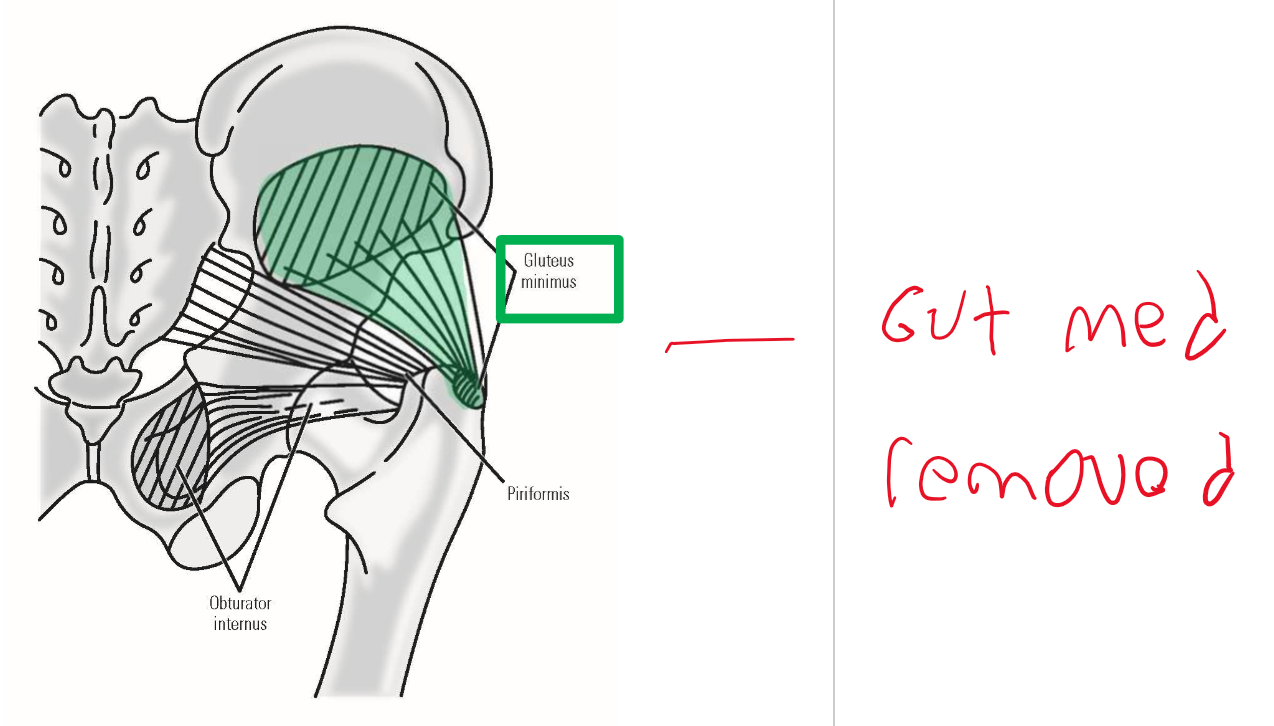
Describe M. Gluteus minimus. Origin, Insertion, Action
Origin: lateral (external) surface of ilium portion of hipbone (deep to m. gluteus medius)
Insertion: greater trochanter of femur
Action: abduction of thigh at hip joint
Action during walking: with one foot off the ground, these muscles contract on weight-bearing side to maintain horizontal position of the pelvis
—» Prevents drop of unsupported side of pelvis by pulling pelvis toward weight-bearing limb
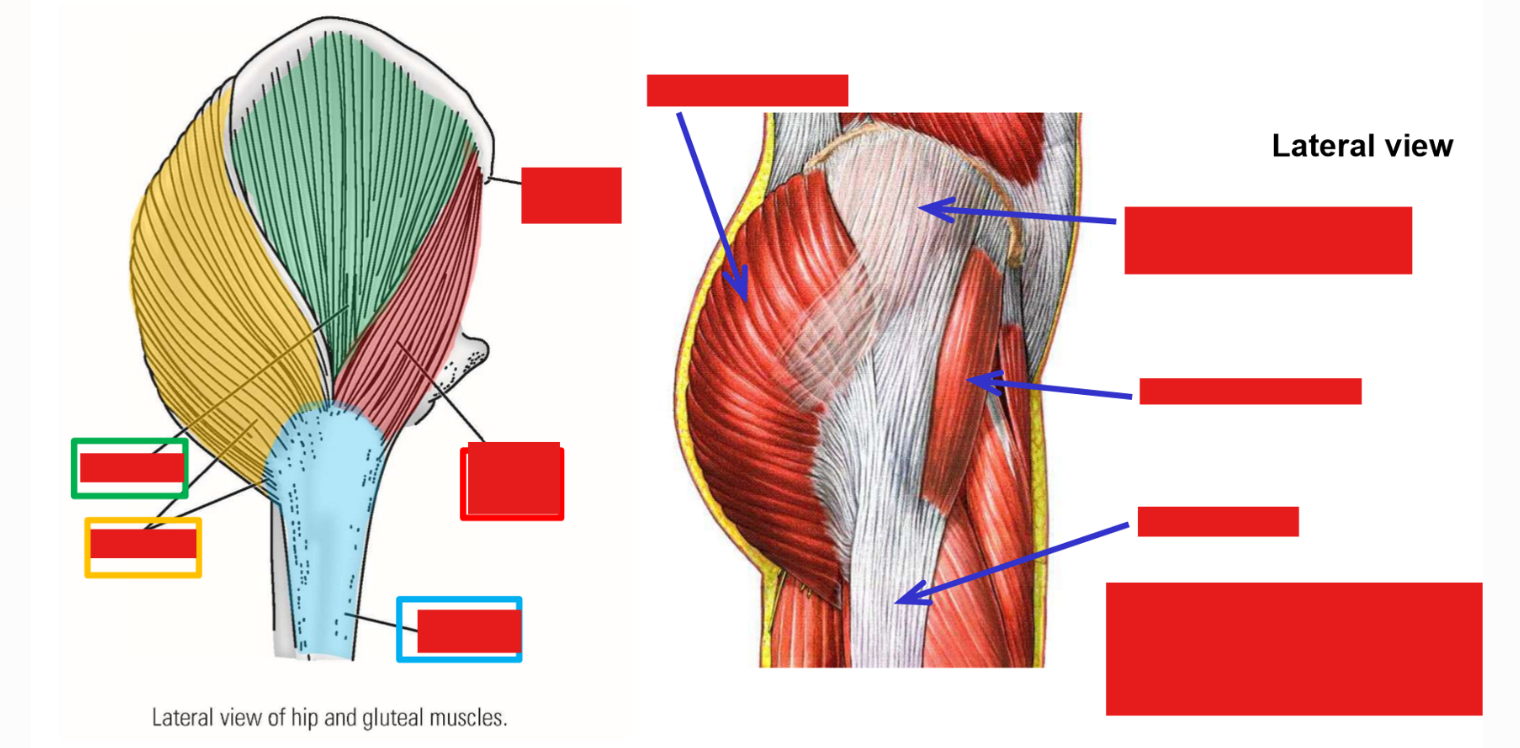
Describe M. Tensor fasciae latae. Origin, Insertion, Action
Origin: anterior superior iliac spine of hipbone
Insertion: iliotibial tract of fascia lata
Actions: abducts thigh at hip joint; extends leg at knee joint*
Attachment of iliotibial tract to tibia is anterior to axis of knee flexion-extension - pull by iliotibial tract thus produces extension of leg at knee joint
Slight contraction by tensor fasciae latae muscle serves to maintain extended knee during standing*
List the deep lateral rotator muscles
M. Piriformis
M. Obturator internus
Mm. Superior & Inferior gemelli
M. Quadratus femoris
M. Obturator externus
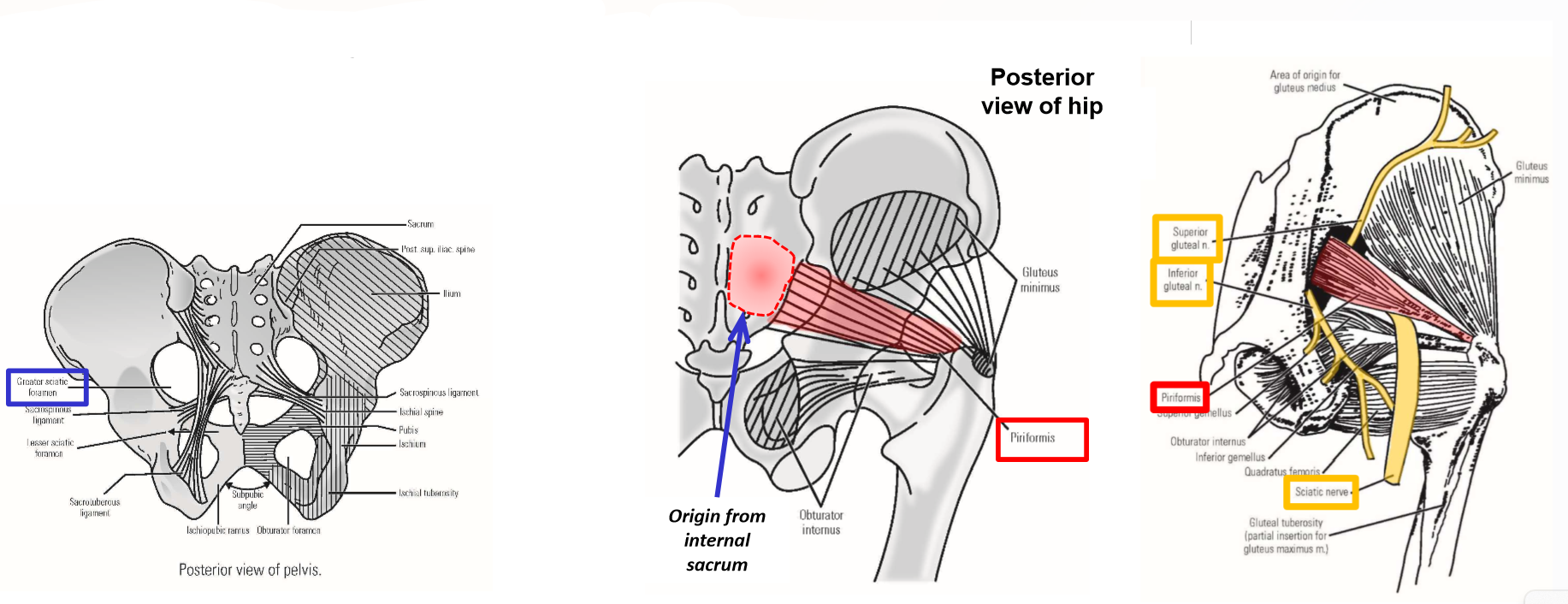
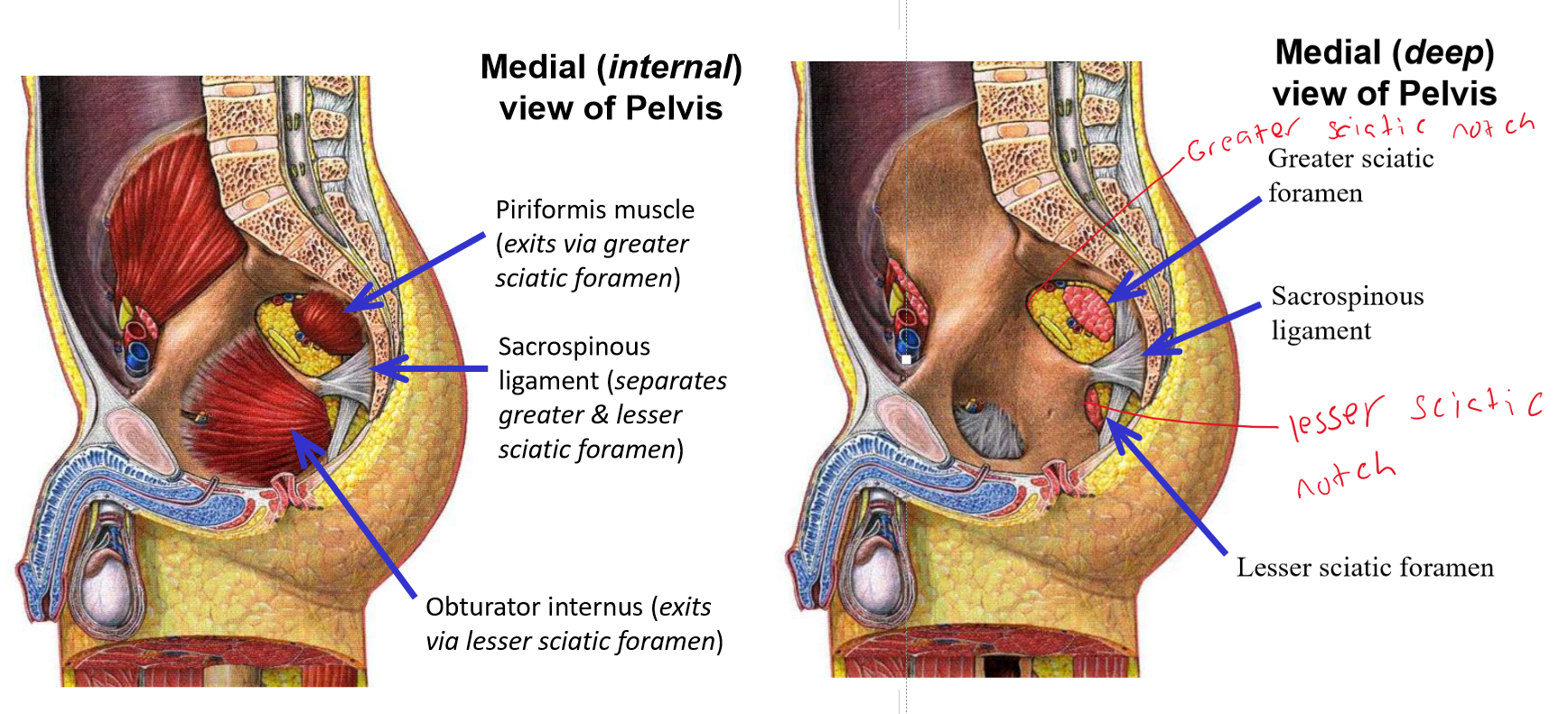
Describe M. Piriformis. Origin, Insertion, Action
Origin: anterior (internal) surface of sacrum
Exits pelvis via greater sciatic foramen
Insertion: greater trochanter of femur
Action: lateral rotation of thigh at hip joint
Piriformis muscle is a key landmark of the deep posterior hip region
Superior gluteal nerve & artery emerge at superior margin of piriformis
Inferior gluteal nerve & artery and sciatic nerve emerge at inferior margin of piriformis muscle
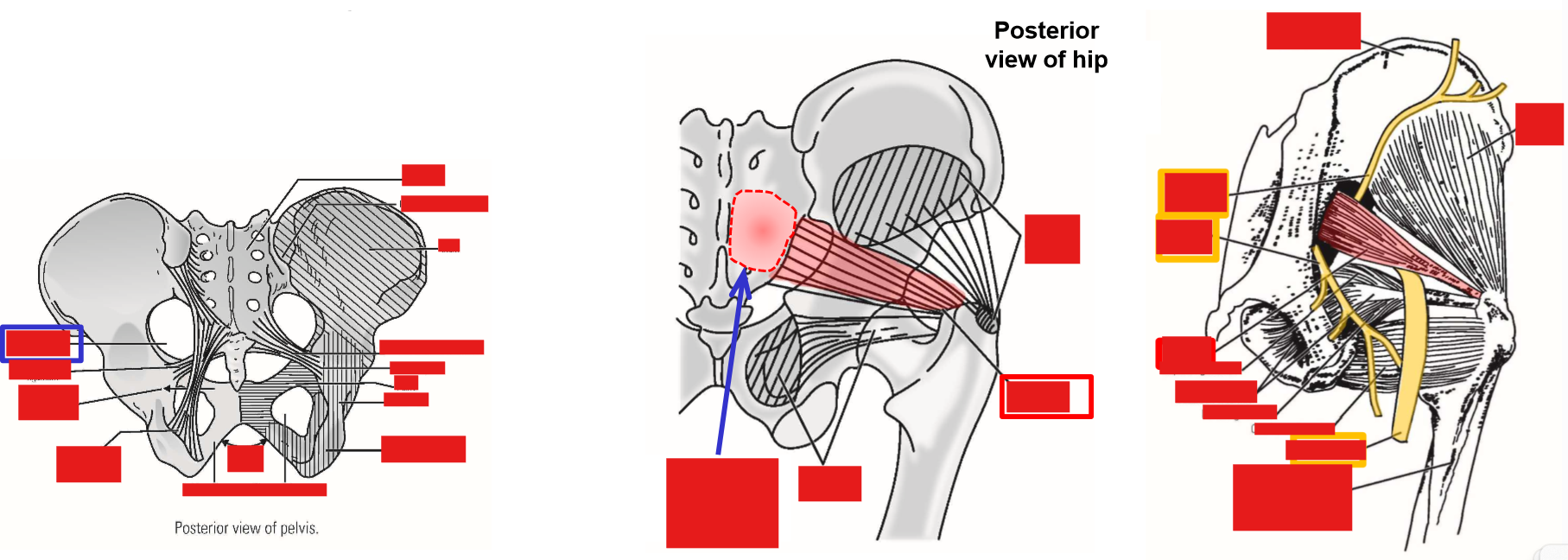
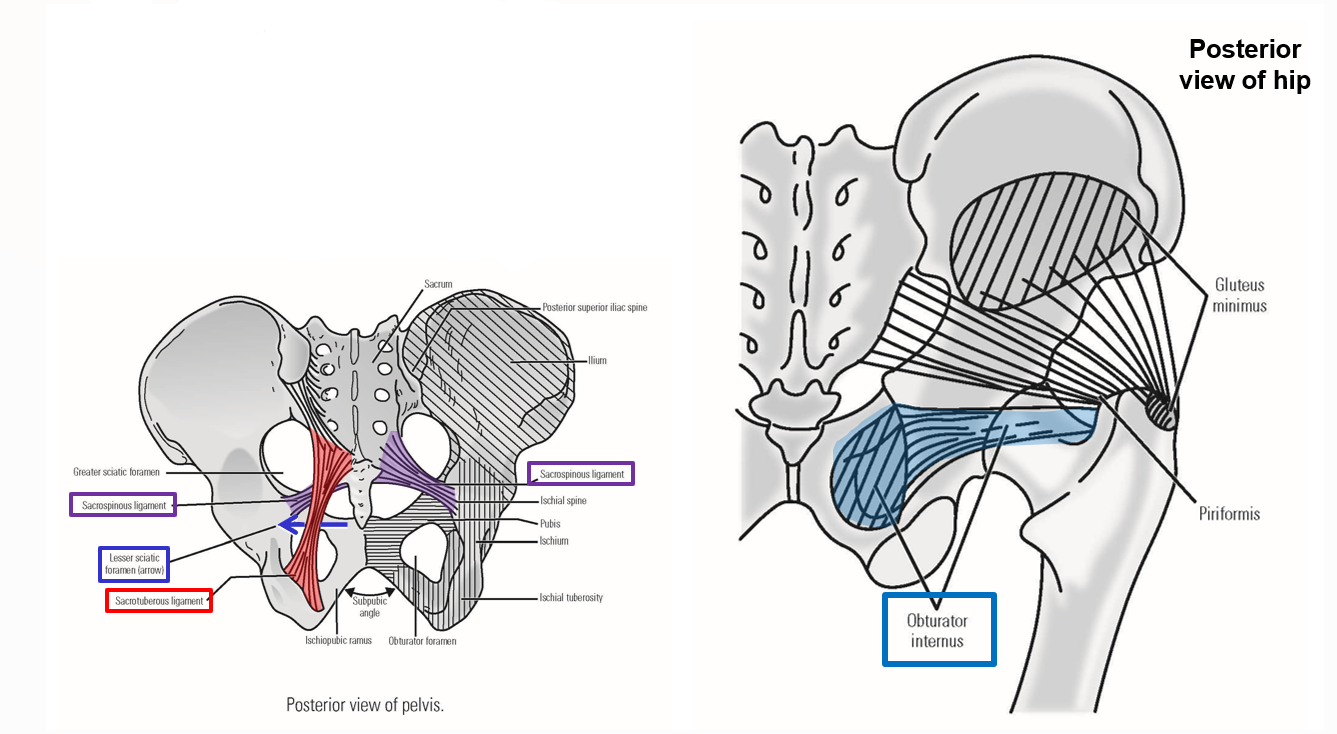
Describe M. Obturator internus. Origin, Insertion, Action
Origin: internal surface of obturator foramen
Exits pelvis via lesser sciatic foramen
Insertion: greater trochanter of femur
Action: lateral rotation of thigh at hip joint
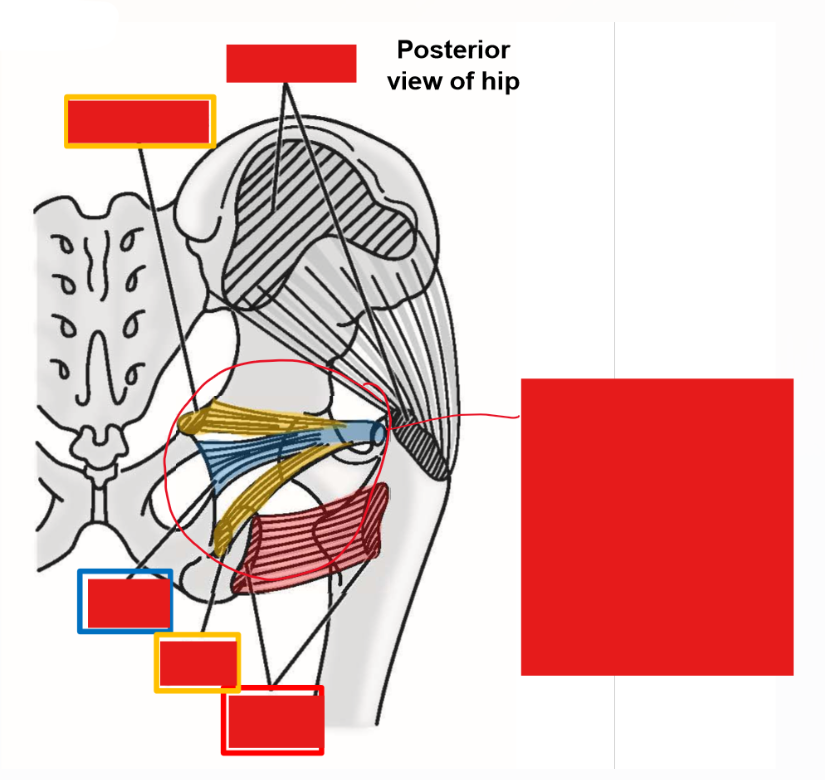
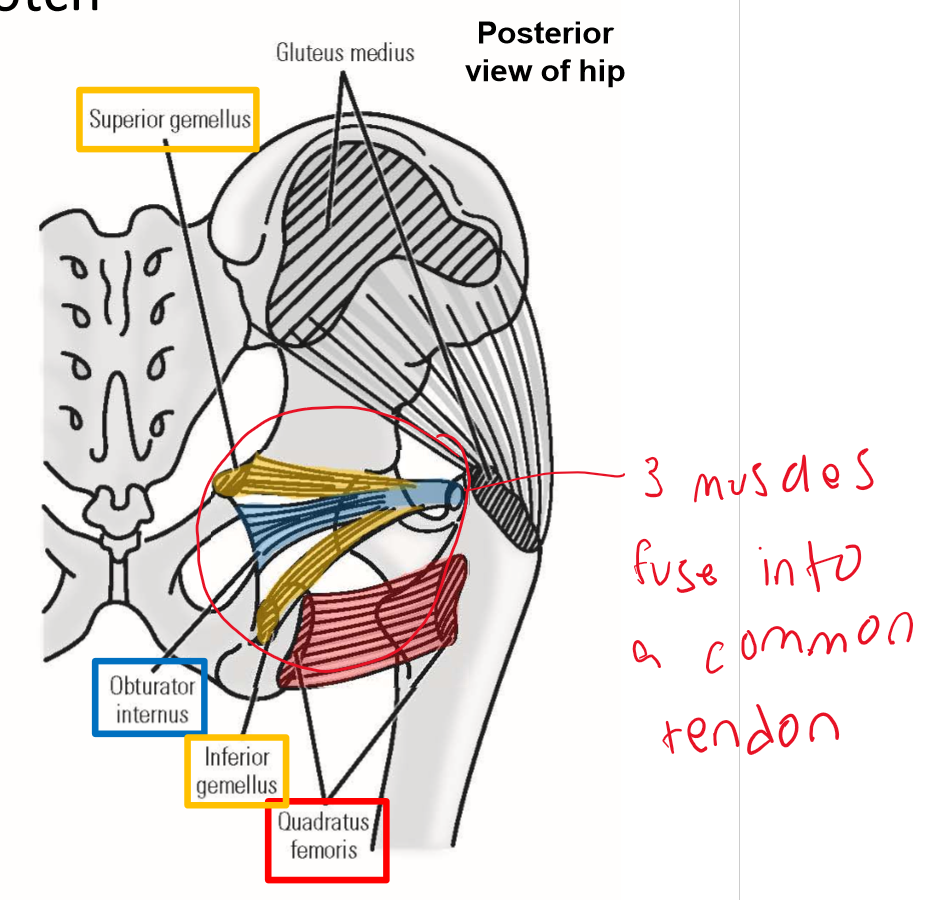
Describe Mm. Superior & Inferior gemelli. Origin, Insertion, Action
Origin: external surface of hipbone (ischium), just above or below lesser sciatic notch
Insertion: greater trochanter of femur
Gemelli muscle tendons fuse with tendon of obturator internus muscle just prior to insertion
Action: lateral rotation of thigh at hip joint
Describe M. Quadratus femoris. Origin, Insertion, Action
Origin: ischial tuberosity of hipbone
Insertion: greater trochanter of femur
Action: lateral rotation of thigh at hip joint
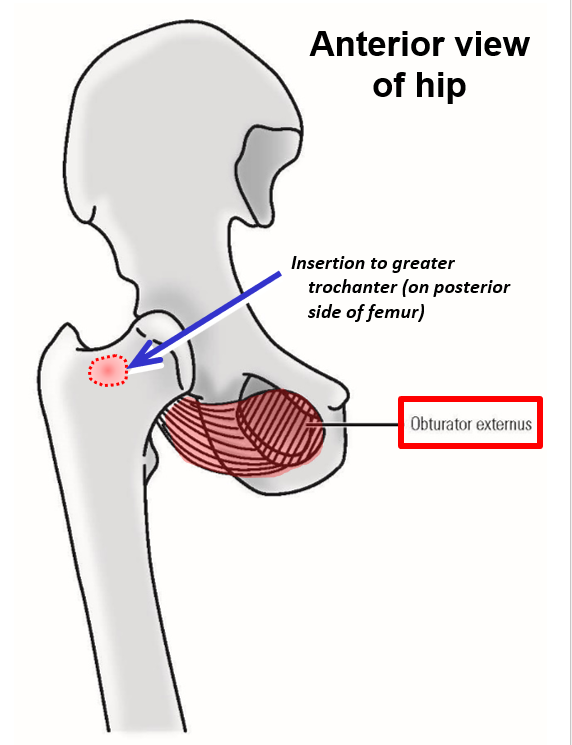
Describe M. Obturator externus. Origin, Insertion, Action
Origin - external surface of obturator foramen
Muscle origin is in deep, medial thigh - it then runs medial and posterior to the femur
Insertion - greater trochanter of femur (on posterior side of femur)
Action - lateral rotation of thigh at hip joint
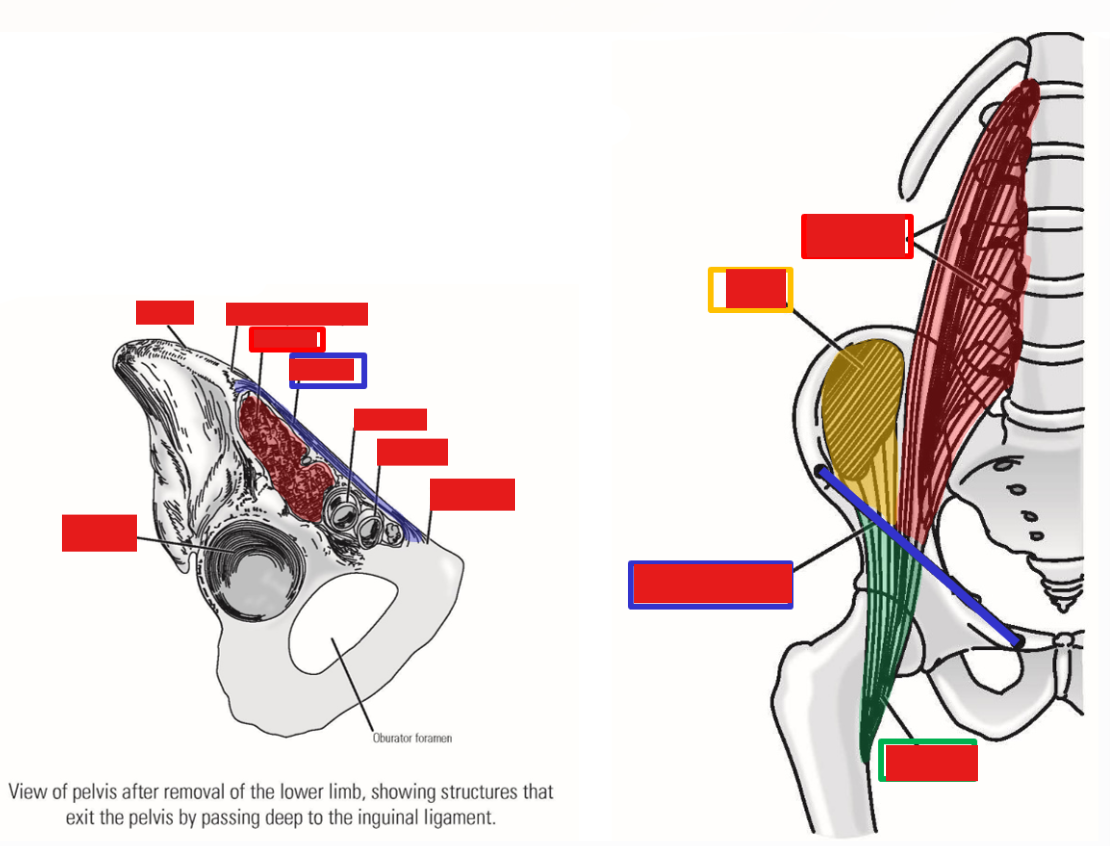
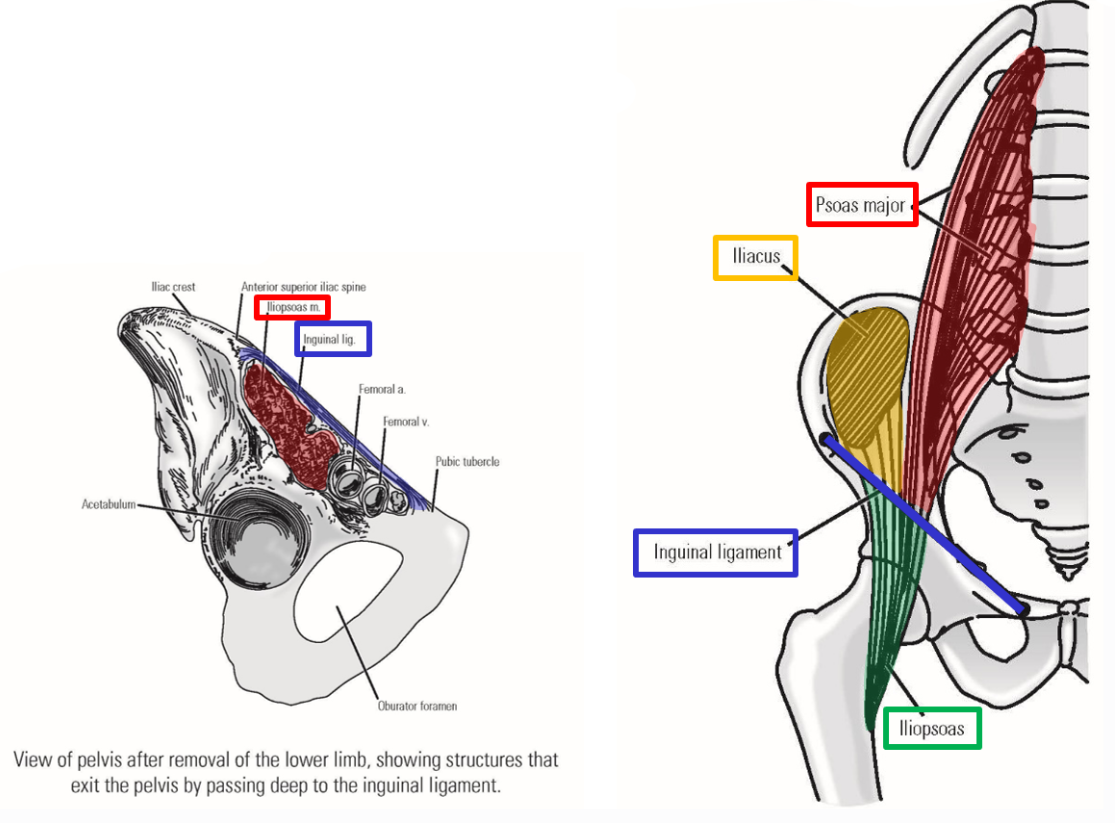
List the muscles of the anterior hip
M. Iliopsoas
M. Psoas major
M. Iliacus
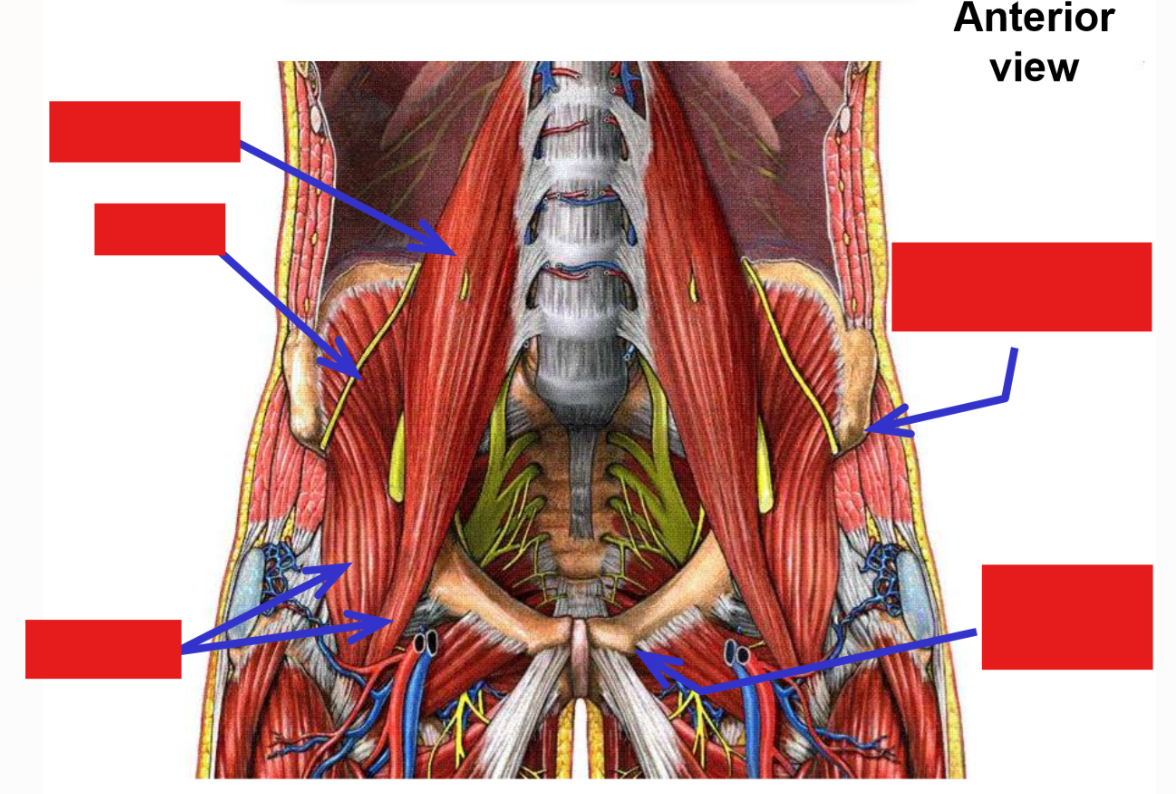
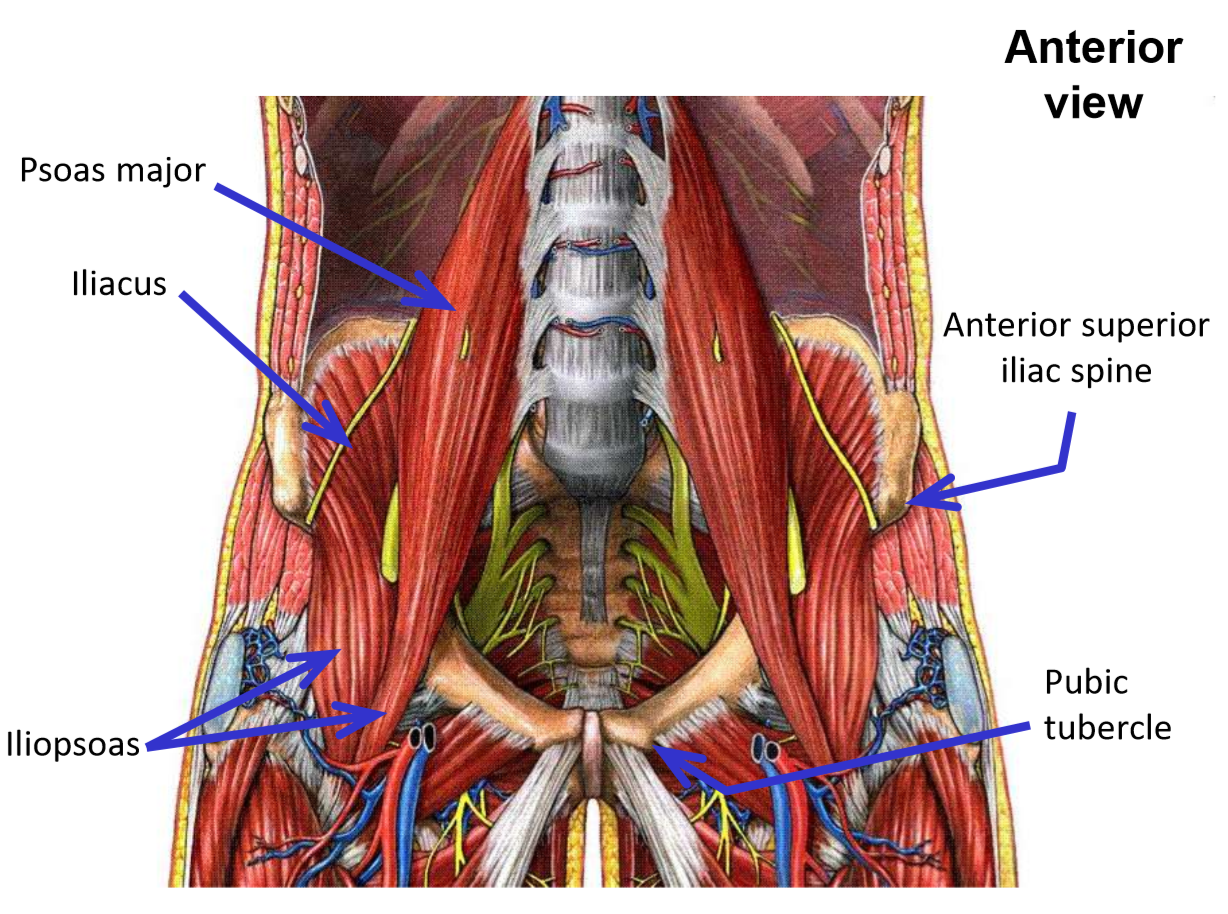
Describe M. Iliopsoas
formed by fusion of psoas major muscle and iliacus muscle
Describe M. Psoas major. Origin
Origin: lumbar vertebrae
Describe M. Iliacus. Origin, Insertion, Action
Origin: iliac fossa of hipbone
Both muscles descend along pelvic brim (psoas major is medial to iliacus), then pass under the inguinal ligament to enter the anterior thigh.
Iliacus and psoas major muscles fuse as they pass under inguinal ligament - name changes to become single M. iliopsoas
Insertion: lesser trochanter of femur (only muscle that attaches to lesser femur)
Action: flexion of thigh at hip joint