Membrane Learning objective
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
What is the structure of phospholipid?
Polar head (phosphate group) non-polar tails ( methyl) which are fatty acids
Which part of the phospholipid is hydrophilic?
Polar head (phosphate)
Which part of the phospholipid is hydrophobic?
the non polar fatty acid tails
What is the backbone of the phospholipid?
Glycerol molecule
Why is there a kink in the fatty acid tail?
unsaturated fat to prevent packing of phospholipids
Why is it important to prevent packing in phospholipids?
To allow fluidity in lipids
What prevents packing in cholesterol?
Bigger rings prevent packing of lipids resisting cell membrane becoming solid
where are lipids located?
Cell membrane
Lipids in the membrane contain mostly…
phospholipid and cholesterol
how do orient when in aq environment?
the polar end faces the aq environment
Why is the phospholipid bilayer important?
key to the origin of life
What is the amphipathic structure?
allowing cholesterol to tightly pack with phospholipid
What is in the lipid bi-layer?
protein
phospholipid
protein
Where are the proteins?
Imbedded in the membrane sticking out on the side
What are the proteins called in the membrane?
Transmembrane protein
What temperature are membranes fluid in?
cooler temperature becoming gel like
Membrane structure and dynamics describe the membrane as a…
fluid mosaic
Describing the membrane as a fluid mosaic that…
can make transmembrane proteins move laterally in the lipid bi-layer?
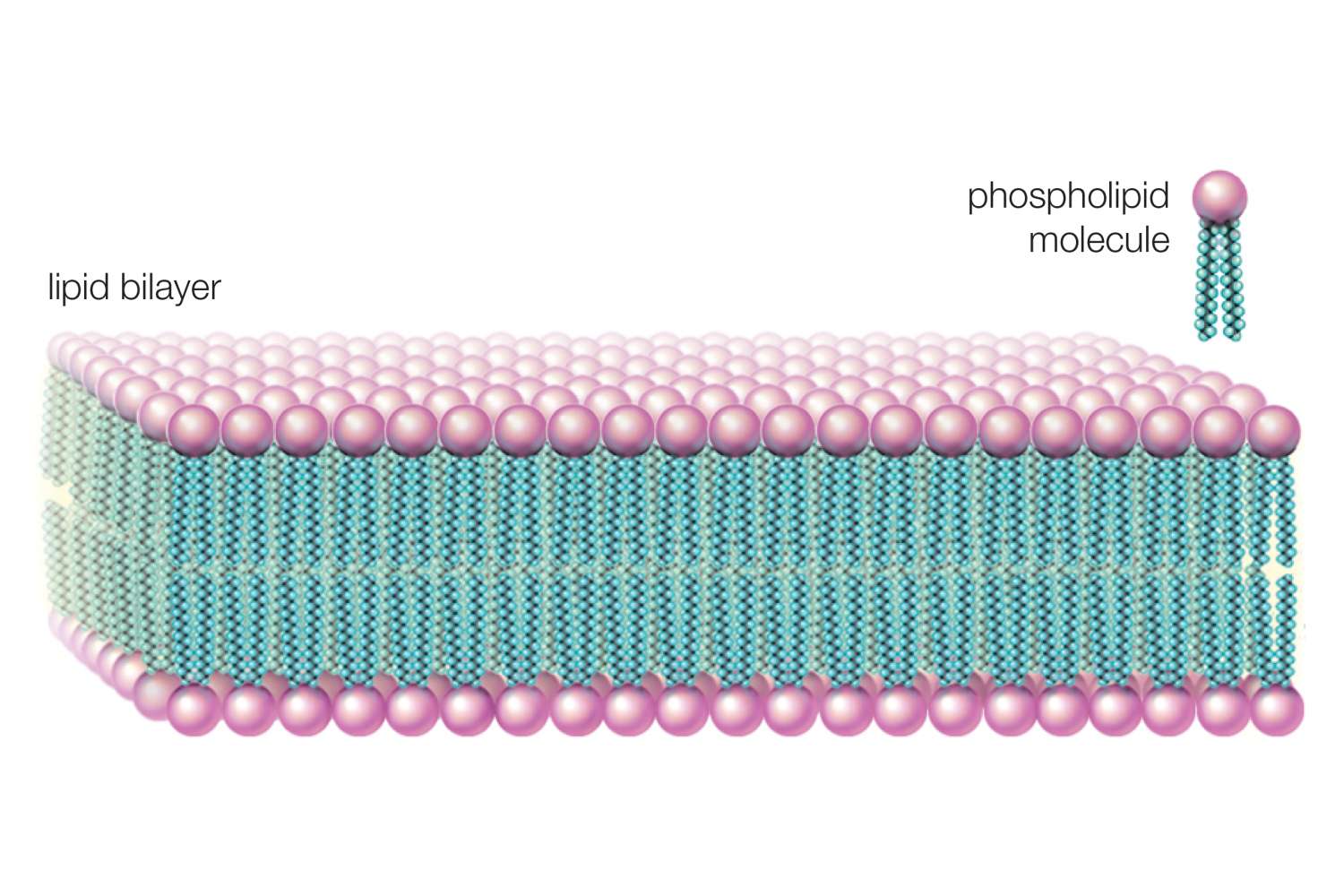
What lipid structure is this?
bi-layer sheet
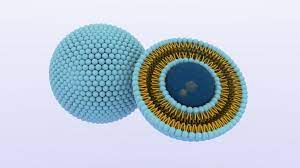
What lipid structure is this?
liposome (bi layer in a sphere that has aq in + out)

What lipid structure is this?
micelle (aq on the outside none on inside)
What do collection of lipids and proteins that make up a cellular membrane rely on…
On natural biophysical properties to form and function
what does natural biophysical properties mean?
Temperature to survive
What do cell membrane serve as…
Barriers and gatekeepers
What is semi-permeable?
some molecules can diffuse across the lipid bilayer but others cannot
True or false cell membranes are semi-permeable?
true
What cross through membranes rapidly?
Small hydrophobic molecules and gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide
What pass through membrane very slowly?
Small polar molecules, such as water and ethanol, can also pass through membranes
What do cell membranes restrict diffusion?
highly charged molecules, such as ions, and large molecules, such as sugars and amino acids
What are the purpose of transport proteins?
specific and selective for the molecules they move, and they often use energy to catalyze passage
How do membranes stay fluid?
Cholesterol hydrophilic end align with lipid hydrophilic head.
what is concentration gradient?
the process of particles, which are sometimes called solutes, moving through a solution from an area with a higher number of particles to an area with a lower number of particles.
The ability to maintain concentration gradients and sometimes move materials against them is…
vital to cell health and maintenance
These proteins transport some ____ against concentration gradient which require _____
Nutrients; additional energy
Due to membrane barriers and transport proteins
cells can accumulate nutrients in higher concentrations and get rid of waste products
What are the 4 types of protein?
tranporter
receptor
enzymes
anchor
how do the liposome structures form?
properties of the phospholipid and without action of enzymes. High concentration of phospholipids and the ph of solution is nuetral.
why is ph important?
Make sure head group is ionized
what is the bond between lipids?
Van der waals to move within the plane of the membrane between fatty acid tails.
Do saturated fatty acid tails have carbon-carbon double bonds?
no
Do unsaturated fatty acid tails have carbon-carbon double bonds?
yes
At high temperatures what do cholesterols do?
Decrease membrane fluidity (
At low temperatures what do cholesterols do?
Increase membrane fluidity prevention of phospholipid packing)
what do transporter membrane protein do?
Move ions or molecule across membrane
What do receptor membrane proteins do?
Allow cell to receive signals from environment (sometimes found in cytoplasm)
What do enzyme membrane proteins do?
causes the accelerate rate of chemical reaction.
What do anchors membrane proteins do?
attaches to other proteins maintain cell structure and shape
what are integral membranes?
forever attached can not be separated from membrane unless membrane is broken
what are peripheral membranes?
shortly connected with lipid bi-layer or integral membrane through weak non-covalent interactions
What are transmembrane proteins?
A protein spans the entire lipid bi-layer; most integral are transmembrane
What are the transmembrane proteins proteins composed of?
2 hydrophilic regions to aq and on hydrophobic in the hydrophobic interior of membrane
Peripheral membrane are associated with….
internal or external side of membrane
Peripheral membrane interact with…
polar heads a]of lipids or with integral membrane proteins by weak non-covalent interactions (hydrogen bonds)
Is it true that peripheral membrane proteins are forever connected membrane, playing a role in transmitting info received from external signals?
True
Are proteins free to move in the membrane?
true
What is the function of the contractile vacuole?
to help single-celled organisms maintain homeostasis in a hypotonic environment
A phospholipid molecule in a membrane can:
both spin (rotate around its vertical axis) and move side-to-side (lateral movement).