Lecture 12 - Attraction and Love
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Define the need to belong.
The motivation to bond with others that provide ongoing, positive interactions.
What promotes friendship and attraction?
close proximity
interactions
Why does proximity and interaction promote attraction and friendship?
This is due to the mere exposure effect, which is the tendency for people tend to develop a preference for things simply because they are familiar with them.
What makes the mere exposure effect stronger?
It is even stronger when we are not consciously aware of its presence.
What is a study that illustrates the effects of the mere exposure effect.
In a class a woman started attending everyday and sat in the same spot wearing a trash bag with two eye holes. She showed up every single day to class. Likeness of the woman increased over time, because whenever she was not there, the students always asked for her.
How does physical attractiveness affect dating?
This is due to the matching phenomenon, which is the tendency for people to choose partners who are a good match for them in terms of attractiveness.
It is also due to the physical attractiveness stereotype where people assume that good looking people possess socially desirable traits as well.
What are the gender differences between what people find attractive?
Men seem to find women with smaller noses more attractive. However, it varies for women as it depends on their menstrual phase.
Why does attractiveness influence our first impressions of people?
This is because when we see attractive people the physical attractiveness stereotype arises. Hence, we become much more sensitive to the good things they do because we are expecting them to do good things. Thus, improving our first impressions of the person since we are looking our for their good qualities.
However, if someone is unattractive, then we become much more focused on the bad things that they do, rather than the good things they do , because we are expecting such.
What quality in women is universally seen as attractive?
Plump women are universally seen as attractive as they are perceived to have more resources to effectively care for children—this plays into evolutionary psychology.
What quality in people is universally seen as attractive?
People who have average faces and average sized things (i.e., average nose, forehead, lips) and people who are symmetrical.
How do social comparisons affect how we perceive attractiveness?
When we have very beautiful and attractive people to compare ourselves and peers to, the bar at which we find people to be attractive increases.
Therefore, making others who you deem attractive on their own, seem less attractive when you compare them with other people.
Explain the evolutionary perspective on what people find attractive?
People find people who are adaptive as more attractive because they are seen as more biologically capable.
Women with more youthful characteristics are seen as more attractive because they seem more fertile
Men who are bigger and stronger tend to be seen as more attractive because they are perceived to be able to protect better
Why does dissimilarity breed dislike?
This is due to the false consensus bias, where we assume that everyone shares the same views as us. Therefore, when people get to know them better and realise that they are so different, it promotes disliking.
Why do opposites attract, and to what extent?
Opposites attract because the differences complete the gaps of what is missing in the other people. However, if people are very different in their values and beliefs, this can oftentimes cause more issues than benefits.
Why do we like others who like us?
If someone acts like they like us, and we attribute their positive behaviour towards us as genuine, then we will be more attracted to them, compared to if we perceive their feelings to have an ulterior motive
when others like us it can boost our self-esteem, making us like them because they make us feel good about ourselves
when others initially don’t like someone but then switch to liking them, we tend to like those people back because the relationship feels more genuine and authentic
What is the reward theory of attraction?
This is the idea that people are attracted to those who provide positive experiences and are drawn to relationships where the benefits outweigh the costs.
Explain the triangular theory of love.
According to this theory, there are 7 types of love:
Intimacy (liking)
friends, non-physical intimacy
Romantic love (intimacy + passion)
dating
Companionate love (intimacy + commitment)
bff, older couple
Passion (infatuation)
one night stand
Fatuous love (passion + commitment)
surface level relationship, regular one night stand
Commitment (empty love)
arranged marriage
Consummate love (intimacy + passion + commitment)
marriage
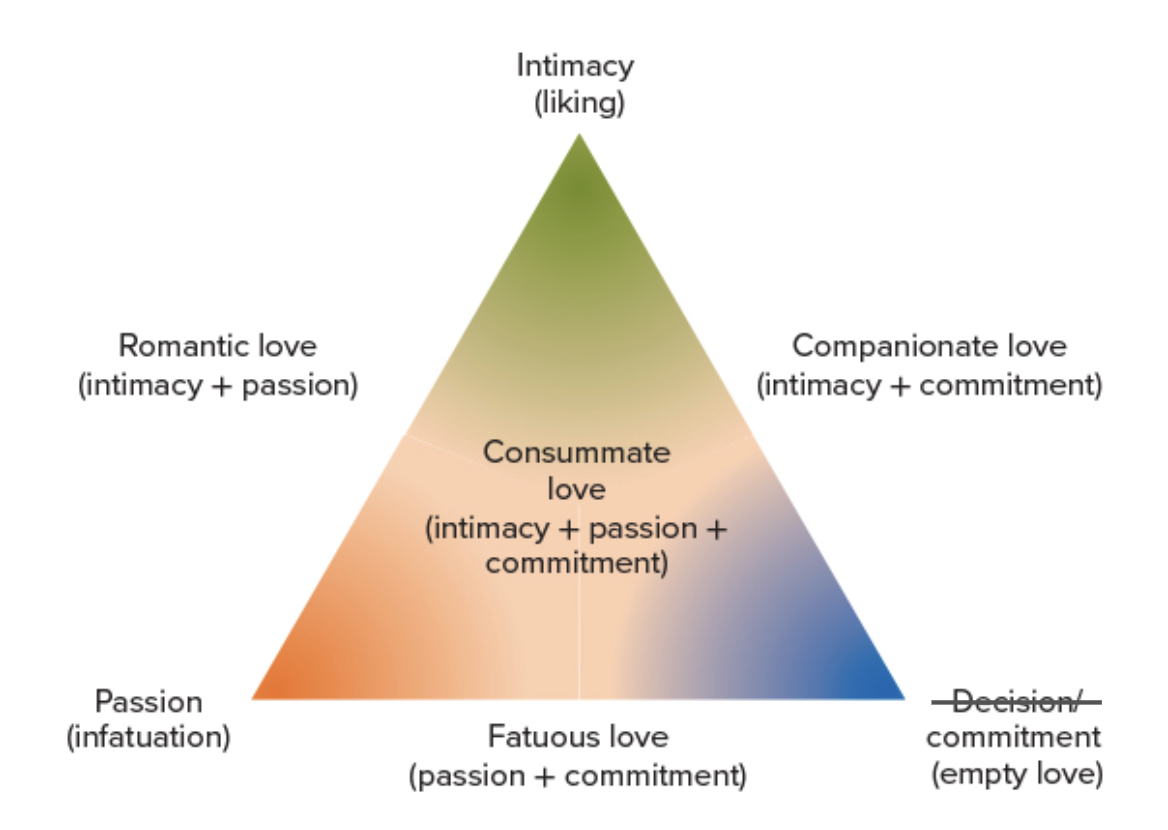
Define passionate love.
A state of intense longing for union with another.
What is the two-factor theory of emotion?
This is the idea emotions are caused by the combination of two factors: physiological arousal and cognitive interpretation of that arousal.
What is a study that illustrates the two-factor theory of emotion?
Male participants were either put on the Capilano Suspension Bridge or an elevated structure in a lab to physiologically arouse the men.
An attractive young woman approached the individual men on the bridge, asking them to help her fill out a class questionnaire. Then, she scribbled her name and phone number and invited him to call if he wanted to hear more about the project.
Most of those on the bridge accepted the phone number, and half who did so called.
However, men approached by the woman in the lab or by a male interviewer rarely called.
Therefore, highlighting how physical arousal intensified people’s romantic responses.
How is love perceived differently in different cultures?
In most cultures, love is seen as a component of marriage.
However, in some other cultures, love is thought to follow after marriage (i.e., in arranged marriages love is expected to grow over time).
Between men and women, who falls in love faster and why?
Men actually fall in love and out of love faster. This is because, from an evolutionary psychology perspective, women need to be more cautious than men because if they fall in love they could get pregnant and would have to face greater physical and emotional consequences than men.
Define companionate love.
The affection we feel for those with whom our lives are deeply intertwined.
ie. might see this with your grandparents where they are very close and committed but they sleep in separate beds because perhaps the passion has died out.
What is a study about romantic love and the time when passion runs out?
Those who married for love reported diminishing feelings of love after a five-year newlywed period. This is because passion faded at that time, which triggered a period of disillusionment as their love was highly intertwined with passion, so it being gone made couples feel like love was fading too.
By contrast, those in arranged marriages reported more love after five years because they were more focused on the practical aspects of being together, rather than just the emotion. Hence, making them less vulnerable to disillusionment.

What influences our close relationships? Why?
Our attachment styles and feelings of equity influence our relationships with people.
This is because, our attachment styles dictate how we feel about getting close to others and how we behave in our relationships.
Moreover, our feelings on equity in a relationship can either make us feel more secure in the relationship, or more lost. This is because, if we feel that we are putting more into the relationship than our partner, we feel this lack of equity and become dissatisfied. Therefore, hindering our relationship with the person.
What are the 3 different types of attachment styles?
secure attachment (attachment that is rooted in trust and shown through intimacy)
anxious attachment (attachment has anxiety and ambivalence in relationships)
avoidant attachment (attachment that feels discomfort or resistance to getting close to others)
Define equity.
A condition in which the outcomes people receive from a relationship are proportional to what they contribute to it.
Define self-disclosure.
The act of revealing intimate aspects of oneself to others.
Define the disclosure reciprocity effect.
The tendency for people to reciprocate self-disclosure with a similar level of intimacy.
When do people usually stay married? Why?
When they marry after 20. This is because when you get older you have a better understanding of who you are and have more life experience to know what you want/how to act with others.
When they both grew up in a stable, two-parent home because they had models to see how marriages can work. Also, you might feel pressure not to divorce due to how your family has been structured.
When they dated for a long time before marriage because then they can really get to know each other before committing forever.
How are people who have not grown up in a stable home still be able to have healthy marriages?
People who have not grown up in a stable home can still have healthy marriages because as long as they have a healthy view on marriage, they don’t have to follow in their parents’ footsteps.
Explain the detachment process.
There are 4 responses that people have to relationship distress within the detachment process.
Loyalty - this is where people will wait for their partner to improve, while not doing anything to help them improve
Neglect - this is where people will ignore the partner and not do anything to help them improve
Voice - this is where people will actively seek to improve the relationship
Exit - this is where people will end the relationship
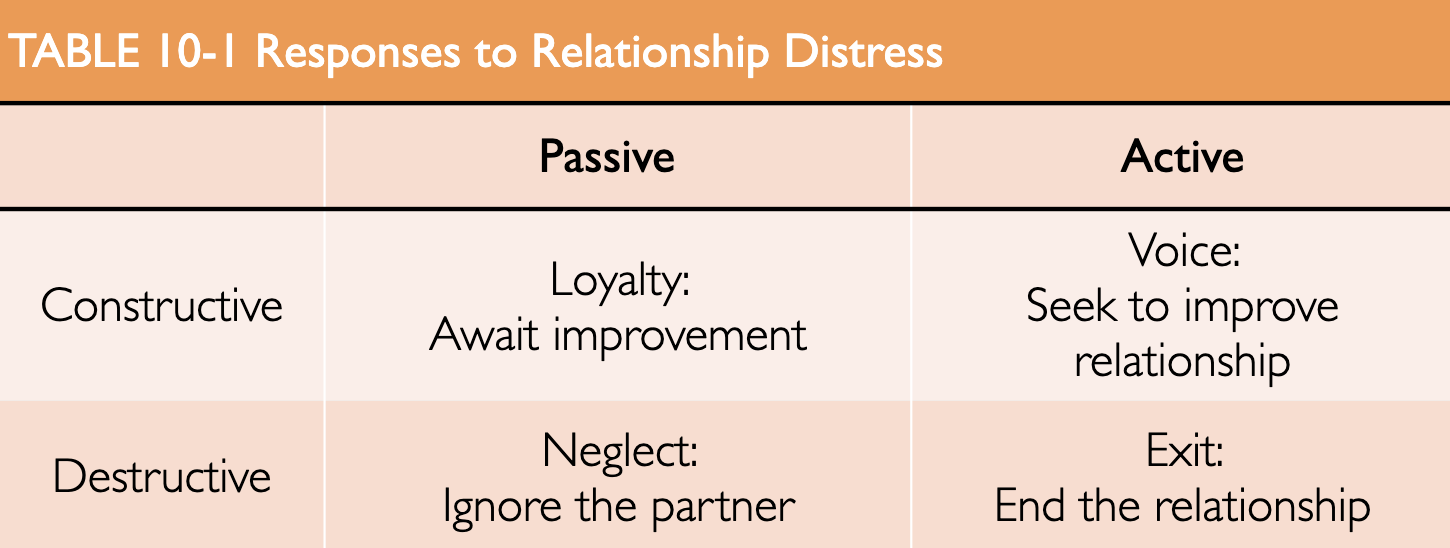
When do people usually exit in the detachment process?
People usually exit in the detachment process when there are other attractive people available.