Unit 2: Supply & Demand
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
demand
behaviour of buyers; various quantities of a good/service the consunmer is willing + able to buy @ different possible prices during a particular time period
ceteris paribus
“all others things than price that can affect how much the ocnsumer is willing & able to buy are constant + unchanging”
demand curve
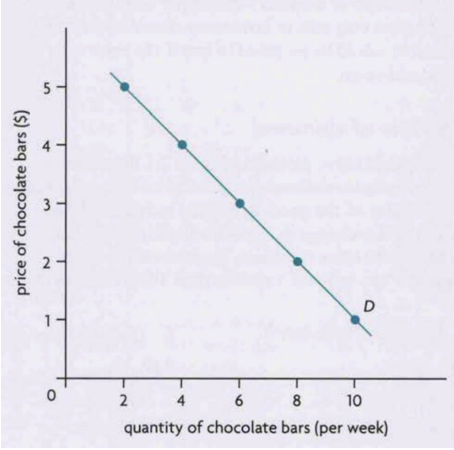
law of demand
law stating there’s a negative relationship b/w a good’s price & quanity demanded over a particular time period, ceteris paribus
market demand
total quantities in the market for good customers are willing + able to buy @ different prices
non-price determinants of demand (definintion)
variables besides price that can influence demand
NPDs of Demand (list)
normal good - when demand increases in response to an increase in consumer income
inferior good - when demand decreases in response to an increase in consumer income
substitute goods - 2 goods satisfying a similar need
complementary goods - two good tended to be used together
number of consumers - a lot = increase D; little = decrease D
preferences and tastes - good = increase D; bad = decrease D
supply
various quantities of a good/service a firm is willing + able to produce & supply to the market for sale at different possible prices, during a certain time period, ceteris paribus
supply curve
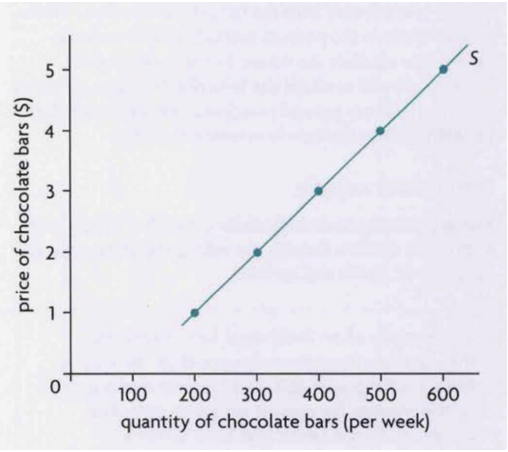
law of supply
positive relationship b/w the quantity of a good supplied over a particular time period and its price, ceteris paribus
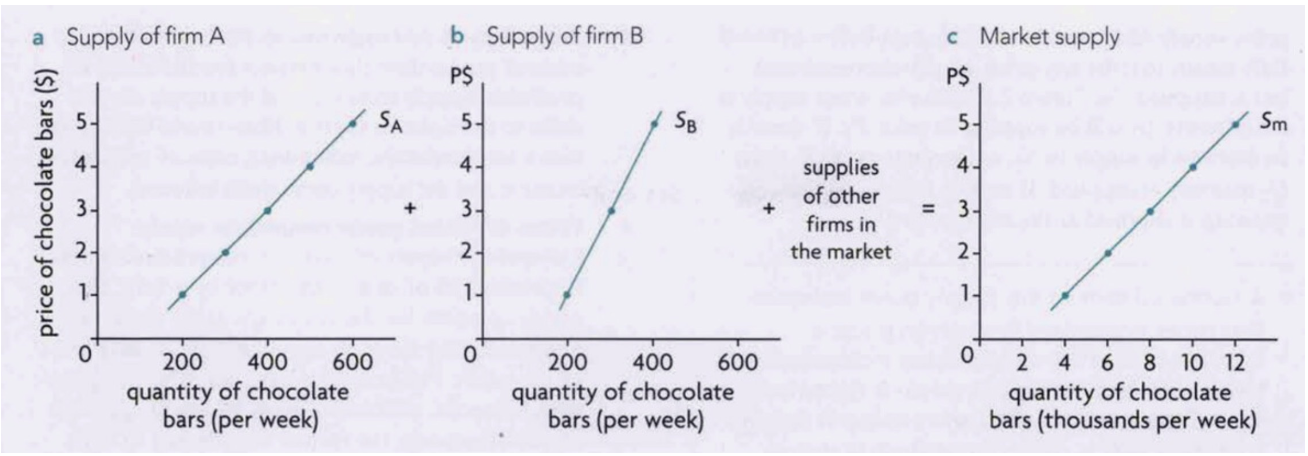
market supply
sum of all individual firms’ supplies for a good
vertical supply curve
graph explaining that as price increases, quantity can’t change
can happen due to fixed quantity b/c there’s no time to produce more (overselling tickets) or no possibility of producing more (vintage pieces)
non-price determinants of supply
factors besides price that can influence supply
NPDs of Supply (list)
cost of factors of production - LLCE determining the firms’ costs of production; LLCE increase = prod. decrease = ← shift; LLCE decrease = prod. increase = → shift
technology - new tech lowers costs of production = shift →
competitve supply - when 1 firm produces 2 goods who use same resources
joint supply -production of goods derived from 1 product
producer price expectations: expect rise = withhold supply = shift ←; expect fall = increase supply = shift →
subsidy - payments made to firm by government; subsidy increase = shift →; subsidy decrease = shift ←
# of firms - increase in # = shift →; decrease in # = shift ←
‘shocks’ -sudden unpredictable events (ie. oil spill)
excess supply/surplus
when there are more products than what’s demanded
excess demand /shortage
when there is more demand than what’s been produced
equilibrium
state of balance b/w different forces, such that there’s no tendency to change
market equilibirium
when the quantity demanded = quantity supplied
equilibrium price
price in market eq.
equilibrium quantity
quantity in market eq.
competitive market equilibrium
quantity demanded = quantity supplied, w/ no tendency for price change
price mechanism
prices determined by forces of supply & demand in competitive markets
invisible hand of the market
mechanism coordinating the buying + selling decisions of 100s+ decision-makers in an gov’t w/o central authority
consumer surplus
highest price consumers are willing to pay for a good minue the price they actually paid
producer surplus
price received by firms for selling their goods – lowest price willing to accept w/ production
community surplus
sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus
welfare
amount of consumer and producer surplus
welfare loss
when markets fail to achieve allocative efficiency = decrease in social surplus