Required Practical 4 - Investigate how pH changes when a weak acid reacts with a strong base and when a strong acid reacts with a weak base
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Why do you need to calibrate ph meters?
Calibrate meter first by measuring known pH of a buffer solution. This is necessary because pH meters can lose accuracy on storage. Most pH probes are calibrated by putting probe in a set buffer (often pH 4) and pressing a calibration button/setting for that pH. Sometimes this is repeated with a second buffer at a different pH
Describe the method to construct a pH curve.
1. Transfer 25cm3 of acid to a conical flask with a volumetric pipette
2. Measure initial pH of the acid with a pH meter
3. Add alkali in small amounts (2cm3) noting the volume added
4. Stir mixture to equalise the pH
5. Measure and record the pH to 1 d.p.
6. Repeat steps 3-5 but when approaching endpoint add in smaller volumes of alkali
7. Add until alkali in excess
How can you improve accuracy of this experiment?
Can also improve accuracy by maintaining constant temperature
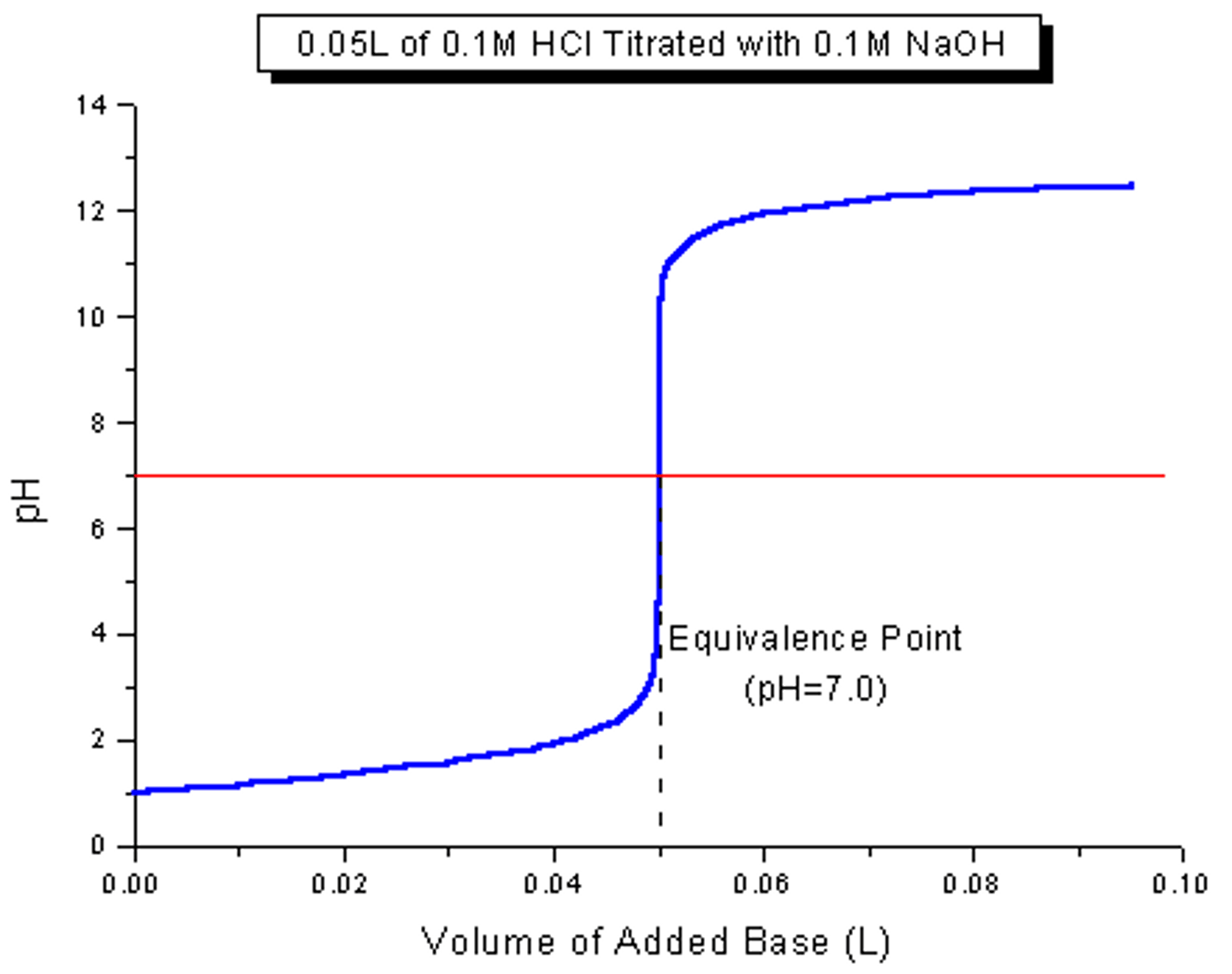
How does the graph for strong acid-strong base look like?
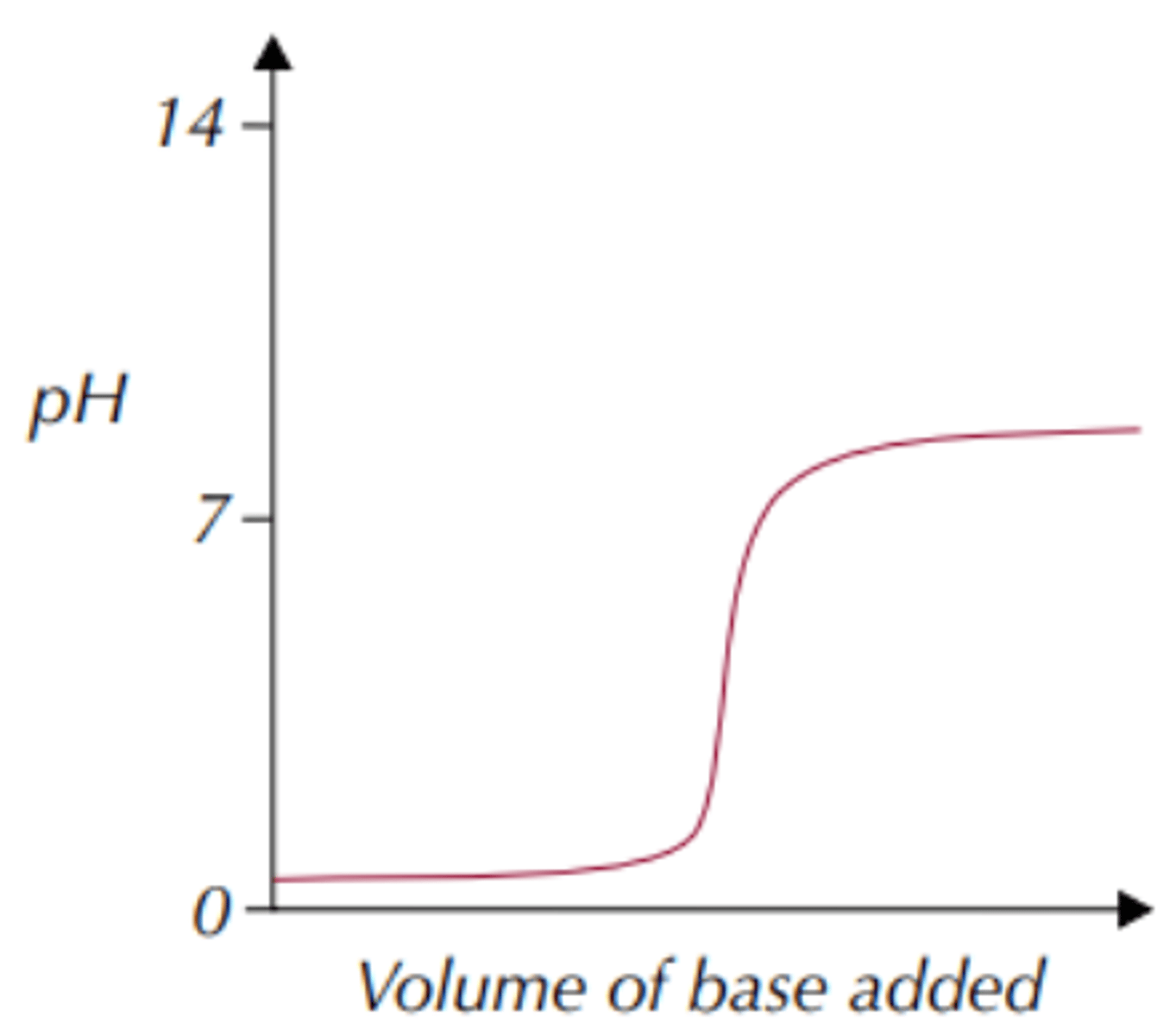
How does the graph for weak acid-strong base look like?
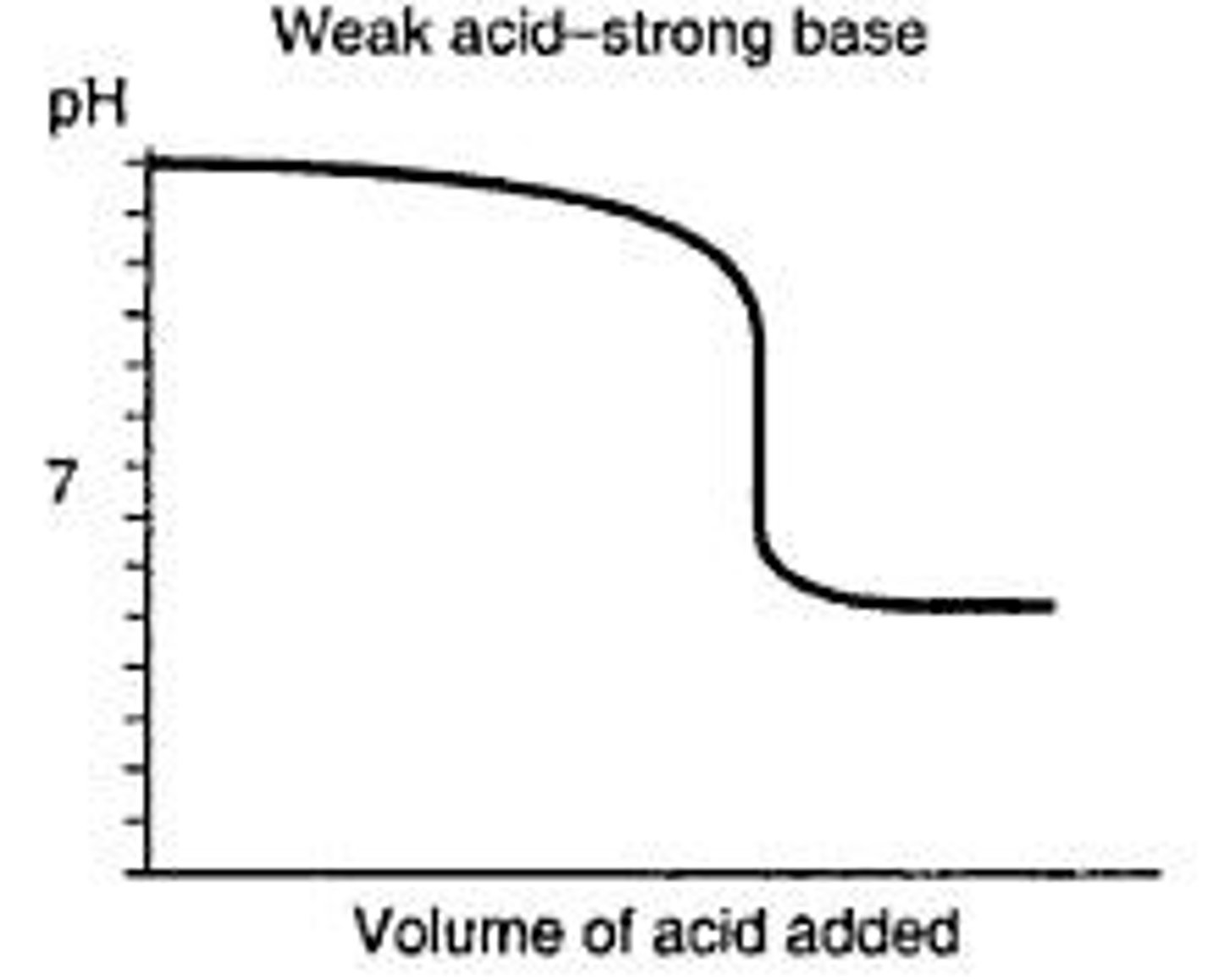
How does the graph for strong acid-weak base look like?
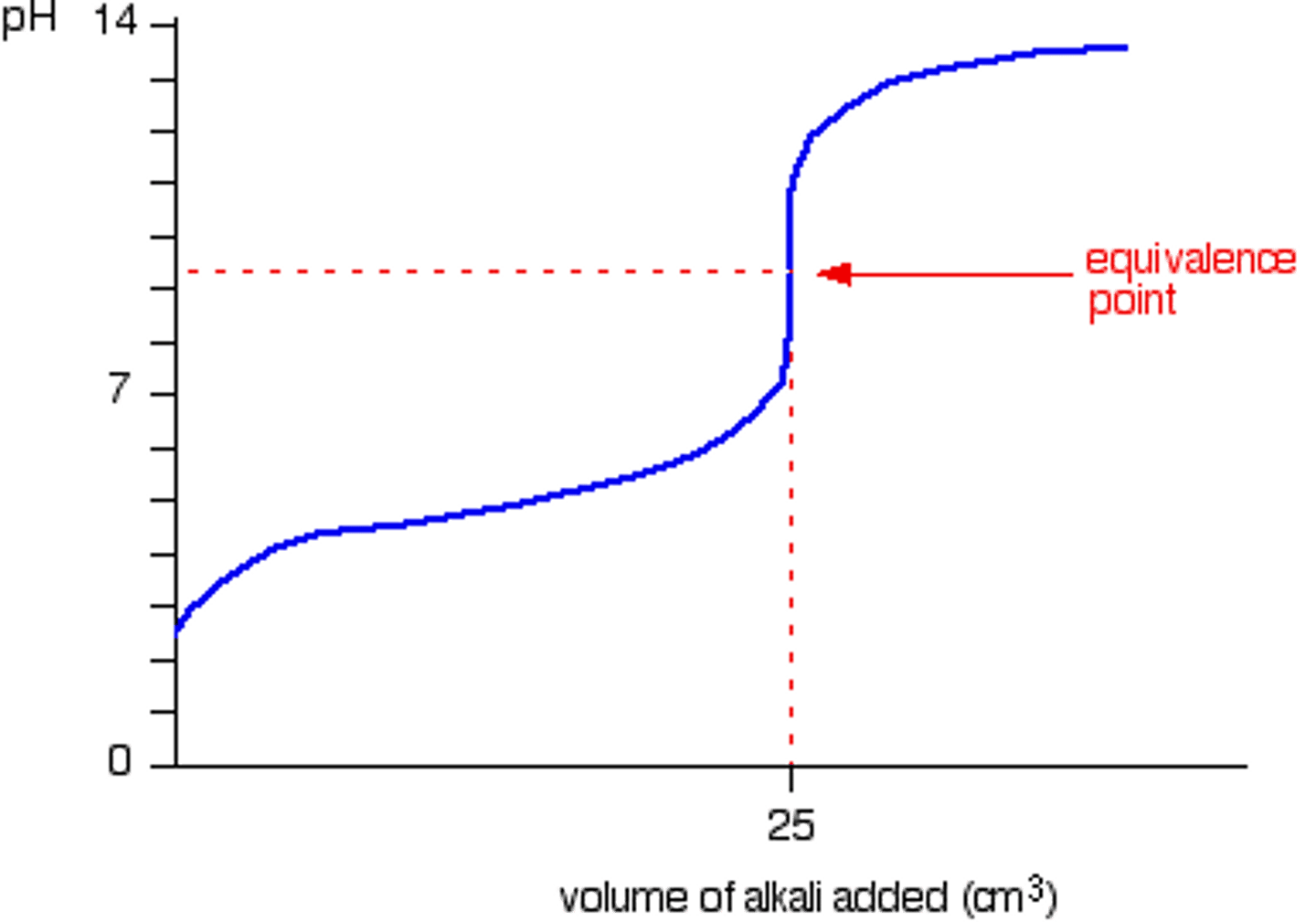
How does the graph for weak acid-weak base look like?
How do you find the half neutralisation volume?
At ½ the neutralisation volume the [HA] = [A-] So Ka= [H+] andp Ka= pH. If we know the Ka we can then work out the pH at ½ V or vice versa. If a pH curve is plotted then the pH of a weak acid at half neutralisation (½ V) will equal the pKa