AP Psychology Ch.1 Test
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Evolutionary Perspective
Looks at how human behaviors helped our ancestors survive and reproduce
Natural Selection
Process where traits that enhance our survival and reproduction are passed on more frequently
Nature
The influence of genetic factors on the traits and behaviors
Nurture
The influence of environmental factors on traits and behaviors
Twin Studies
Research comparing the similarities between identical and fraternal twins to understand the influence of genetics v.s. environment
Adoption Studies
Studies that compare biologically related people, including those raised apart, to understand genetic influences
Family Studies
Research looking at behavioral traits in families to determine how much is genetic v.s. environmental
Heredity
The passing of traits from parents to offspring through genes
Genetic Predisposition
The likelihood of developing certain traits or disorders based on genetics
Eugenics
A controversial and unethical movement aimed at improving the genetic composition of humans through selective breeding
Cerebral Cortex
The outer layer of the brain, involved in complex mental processes such as thinking
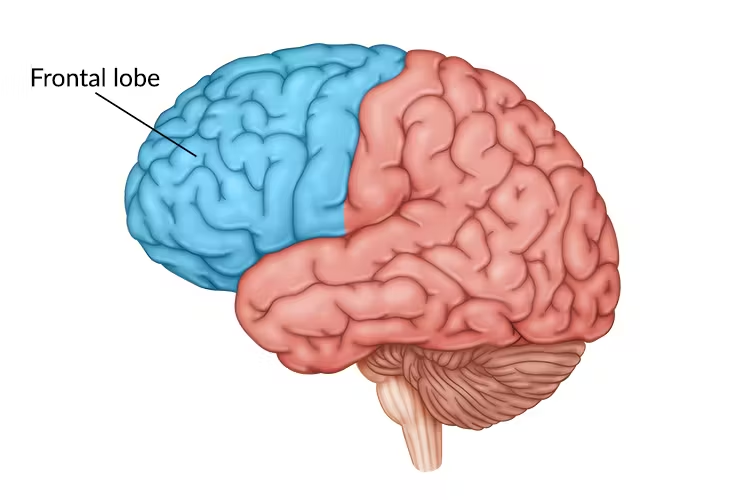
What is this lobe of the brain:
Frontal Lobe
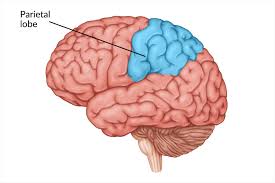
What is this lobe of the brain:
Parietal Lobe
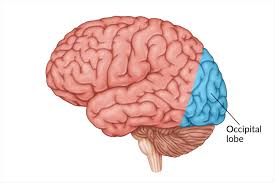
What is this lobe of the brain:
Occipital Lobe
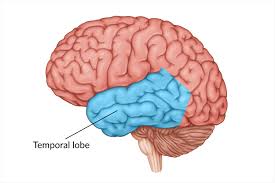
What is this lobe of the brain:
Temporal Lobe
Frontal Lobes
Involved in the decision-making, problem-solving, and controlling behavior
Parietal Lobe
Processes sensory information like touch and spatial awareness
Occipital Lobes
Responsible for vision
Temporal Lobes
Involved in hearing, memory, and, understanding
Prefrontal Cortex
Part of the frontal lobes involved in planning complex behaviors and expressing personality
Executive Functioning
Higher order processes including planning, organizing, and regulating behavior
Motor Cortex
Controls voluntary movements
Corpus Callosum
Thick band of nerve fibers that connects the two brain hemispheres
Brainstem
Supports basic life functions, including heart rate, breathing, and sleeping
Medulla
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions like heartbeat and breathing
Reticular Activating System
Regulates wakefulness and sleep-wake transitions
Cerebellum
Coordinates voluntary movements like posture, balance, and coordination
Limbic System
Involved in emotion, motivation, and memory
Reward Center
Brain areas that regulate the experience of pleasure
Thalamus
Relay motor and sensory signals to the cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus
Regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst, and other homeostatic systems
Pituitary Gland
The master gland of the endocrine system that regulates other glands
Hippocampus
Essential for learning and memory
Amygdala
Involved in emotion processing, particularly fear and aggression
Nervous System
The body’s communication network consisting of nerve cells
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Consists of the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
Autonomic Nervous System
Controls involuntary bodily functions
Sympathetic Nervous System
Activates the body’s resources during stress and emergencies
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Conserves energy and restores the body to a calm state
Somatic Nervous System
Controls voluntary movements
Neurons
Nerve cells that transmit information throughout the body
Glial Cells
Support cells in the nervous system
Motor Neurons
Carry signals from the spinal cord to muscles to produce movement
Sensory Neurons
Carry signals from body parts to the central nervous system
Interneurons
Connect sensory and motor neurons and carry impulses between them
Reflex Arc
The nerve pathway involved in a reflex action
Neural Transmission
The process by which neurons communicate with each other
Threshold
The level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
Action potential
A neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
All-or-Nothing Principle
The rule that neurons are either on or off
Depolarization
A decrease in the electrical charge across a cell membrane
Refractory Period
A period immediately following stimulation during which a nerve or muscle is unresponsive to further stimulation
Resting Potential
The state of the neuron when not firing a neural impulse
Reuptake
The absorption by a presynaptic nerve ending of a neurotransmitter that it has secreted
Consciousness
The awareness of internal and external stimuli
Circadian Rhythm
(Sleep/wake/cycle): The body’s natural 24-hour cycle, affecting sleep and wakefulness
Jet lag
Fatigue caused by travel across different time zones, disrupting the circadian rhythm
Shift Work
Employment with work hours scheduled at non-standard times
NREM Stage 1
The initial stage of sleep, characterized by light sleep and slow eye movement
Hypnagogic Sensations
Feelings of falling or hearing strange noises as one falls asleep during NREM Stage 1
NREM Stage 2
The second stage of sleep, where body temperature drops and heart rate slows
NREM Stage 3
The deepest and most restorative sleep stage; includes slow-wave sleep
REM Sleep
A sleep stage marked by rapid eye movement and dreaming brain waves are similar to wakefulness
REM Rebound
The tendency for REM sleep to increase following REM sleep deprivation
Activation-Synthesis (dreams)
A theory suggesting dreams are caused by the brain’s attempt to make sense of neural activity during sleep
Consolidation Theory
(Dreams):The theory that dreams help to cement memories and learning
Memory Consolidation
The process by which temporary memories are converted into a stable
Memory Consolidation