Chemistry - Unit 12: Experimental Techniques and Chemical Analysis
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
what apparatus is appropriate for measuring time?
stop-watches
what apparatus is appropriate for measuring temperature?
thermometer
what apparatus is appropriate for measuring mass?
balances
what apparatus is appropriate for measuring volume?
burettes (measuring volume of a liquid to the nearest 0.00cm3)
volumetric pipette (measuring a specific, fixed volume of a liquid)
measuring cylinder (measuring approximate volume of a liquid)
gas syringe (measuring volume of a gas)
state the advantages and disadvantages of stop-watches?
advantages - can measure time intervals to a high level of precision.
disadvantages - accuracy of stopwatch reading is dependent on the reaction time of the user so human error is introduced.
state the advantages and disadvantages of thermometers?
advantages - easy to use and cheap to acquire
disadvantages - limited temperature ranges, lower precision compared to a digital temperature probe and parallax error can occur
state the advantages and disadvantages of measuring balance?
advantages - speed readings to a high level of accuracy
disadvantages - sensitive to environmental factors such as air currents and fluctuations in temperature in the lab
state the advantages and disadvantages of burette?
advantages - wide range of burettes so a range of accurate volumes can be measured
disadvantages - meniscus reading error can occur if user does not view the measurement at eye level
state the advantages and disadvantages of volumetric pipettes?
advantages - can accurately measure a specified volume consistently
disadvantages - limited to measuring only one fixed volume
state the advantages and disadvantages of gas syringes?
advantages - can measure volumes of a gas to a high levwl of accuracy
disadvantages - gases in the closed system can become sensitive to environmental factors such as changes in temperature or pressure
how to comment on the advantages and disadvantages of an experimental method?
ask the following questions:
what are the advantages of the apparatus used?
how many repeats have been done? were the answers similar or different? the results are more precise if the repeat readings are closer
were there any controlled variables to ensure that the independent variable is the only factor causing a change?
what is a solvent?
a substance that dissolves a solute
what is a solute?
a substance that is dissolved in a solvent
what is a solution?
a mixture of one or more solutes dissolved in a solvent
what is a saturated solution?
a solution containing the maximum concentration of a solute dissolved in the solvent at a specified temperature
what is residue?
a substance that remains after evaporation, distillation, filtration or any similar process
describe an acid-base titration
use the pipette and pipette filler and place exactly 25 cm3 sodium hydroxide solution into the conical flask
place the conical flask on a white tile so the tip of the burette is inside the flask
add a few drops of a suitable indicator to the solution in the conical flask
perform a rough titration by taking the burette reading and running in the solution in 1 – 3 cm3 portions, while swirling the flask vigorously
quickly close the tap when the end-point is reached (sharp colour change) and record the volume, placing your eye level with the meniscus
now repeat the titration with a fresh batch of sodium hydroxide
as the rough end-point volume is approached, add the solution from the burette one drop at a time until the indicator just changes colour
record the volume to the nearest 0.05 cm3
repeat until you achieve two concordant results (two results that are within 0.1 cm3 of each other) to increase accuracy
what is the colour of litmus solution in acid, alkaline and neutral?
colour in acid: red
colour in alkaline: blue
colour in neutral: purple
what is the colour of red litmus paper in acid, alkaline and neutral?
colour in acid: stays red
colour in alkaline: turns blue
colour in neutral: no change
what is the colour of blue litmus paper in acid, alkaline and neutral?
colour in acid: turns red
colour in alkaline: stays blue
colour in neutral: no change
what is the colour of methyl orange in acid, alkaline and neutral?
colour in acid: red
colour in alkaline: yellow
colour in neutral: orange
what is the colour of phenolphthalein in acid, alkaline and neutral?
colour in acid: colourless
colour in alkaline: pink
colour in neutral: colourless
what is the colour of thymolphthalein in acid, alkaline and neutral?
colour in acid: colourless
colour in alkaline: blue
colour in neutral: colourless
describe how paper chromatography works
paper chromatography is used to separate substances that have different solubilities in a given solvent.
pencil line is drawn on chromatography paper and spots of the sample are placed on it. pencil is used for this as ink would run into the chromatogram along with the samples
the paper is then lowered into the solvent container, making sure that the pencil line sits above the level of the solvent so the samples don´t wash into the solvent container
the solvent travels up the paper by capillary action, taking some of the coloured substances with it
different substances have different solubilities so will travel at different rates, causing the substances to spread apart. those substances with higher solubility will travel further than the others
this will show the different components of the ink / dye
how can paper chromatography be used to identify unknown substances?
compare the chromatogram of the unknown substance with chromatograms of known substances.
if the chromatograms between the 2 substances are identical, they are the same substance
how can paper chromatography be used to identify whether a substance is pure or impure?
the chromatogram of a pure substance will only have one spot
the chromatogram of an impure substance will have multiple spots show up
describe the use of locating agents.
colourless mixtures of chemicals can be analysed if the ‘spots’ can be coloured by a chemical or light treatment.
state the equation for Rf
Rf = distance travelled by substance ÷ distance travelled by solvent
describe and explain how a mixture can be separated using a suitable solvent.
a solvent is a substance that dissolves a solute
the type of solvent must be carefully chosen depending on the type of solute that needs to be separated to ensure no other impurities or components dissolve in the solvent and only the desired substance is dissolved in the solvent.
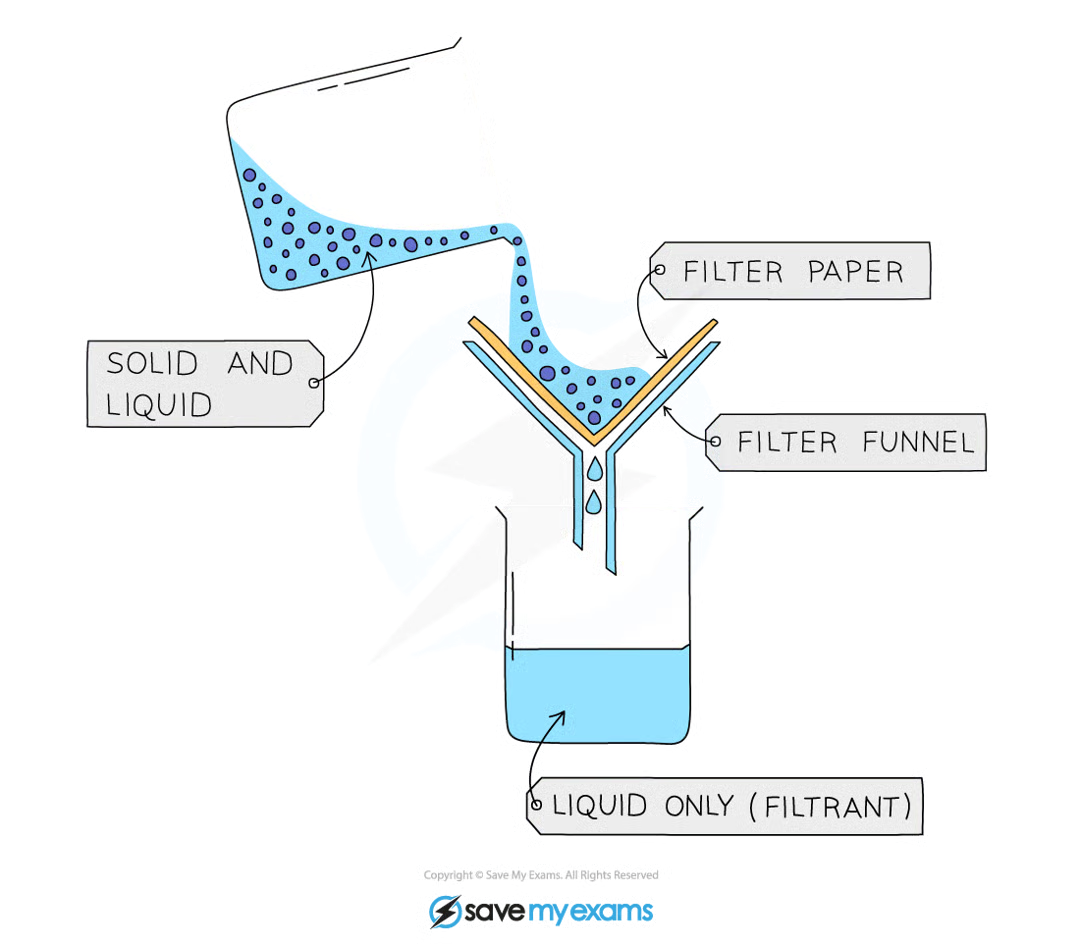
describe and explain how a mixture can be separated using filtration.
filtration separates an insoluble solute from a solution
filter paper is placed into a funnel, the small pores only allow liquids to pass through
the mixture is poured into a beaker through the funnel, leaving the solute behind
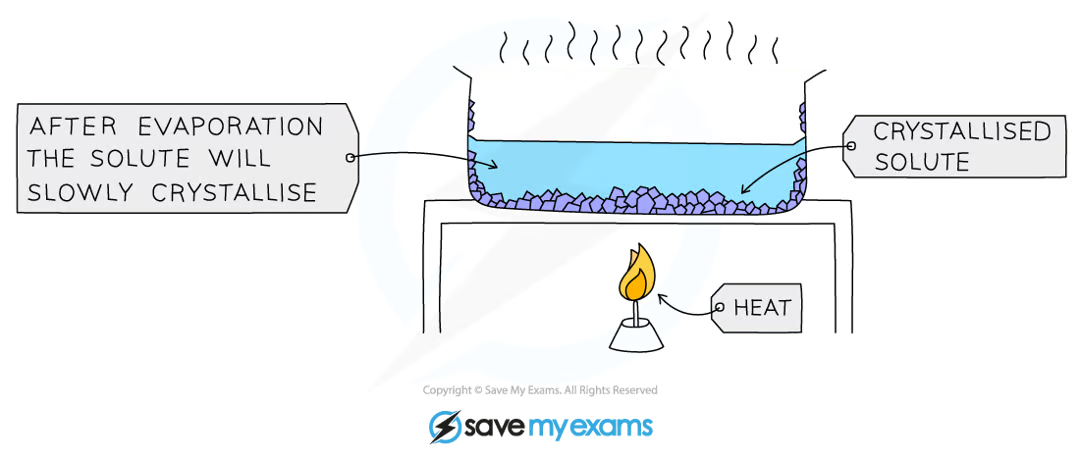
describe and explain how a mixture can be separated using crystallisation.
crystallisation separates a soluble solute from the solution it is dissolved in
heat the solution in an evaporating dish over a bunsen burner until boiling (specify that no more than half of the solution is boiled off before it is removed from the heat)
remove from the heat and allow the solution to cool and evaporate
the saturated solution will leave behind crystals as it cools
the crystals will grow and can be collected and allowed to dry
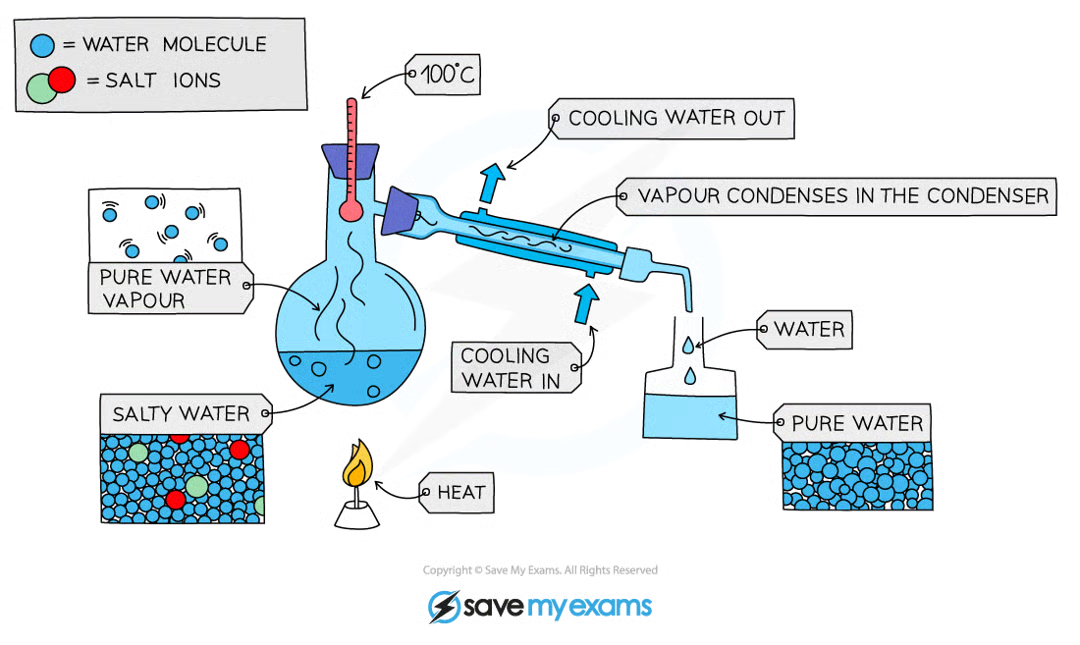
describe and explain how a mixture can be separated using simple distillation.
simple distillation separates a solvent from a solution
simple distillation works because the dissolved solute has a much higher boiling point than the water so the water will boil and evaporate first and the salt stays behind
the water vapour will cool and condense as it travels through the condenser, collecting in a separate flask
the remaining solution becomes more concentrated in solute as the amount of solvent in it decreases
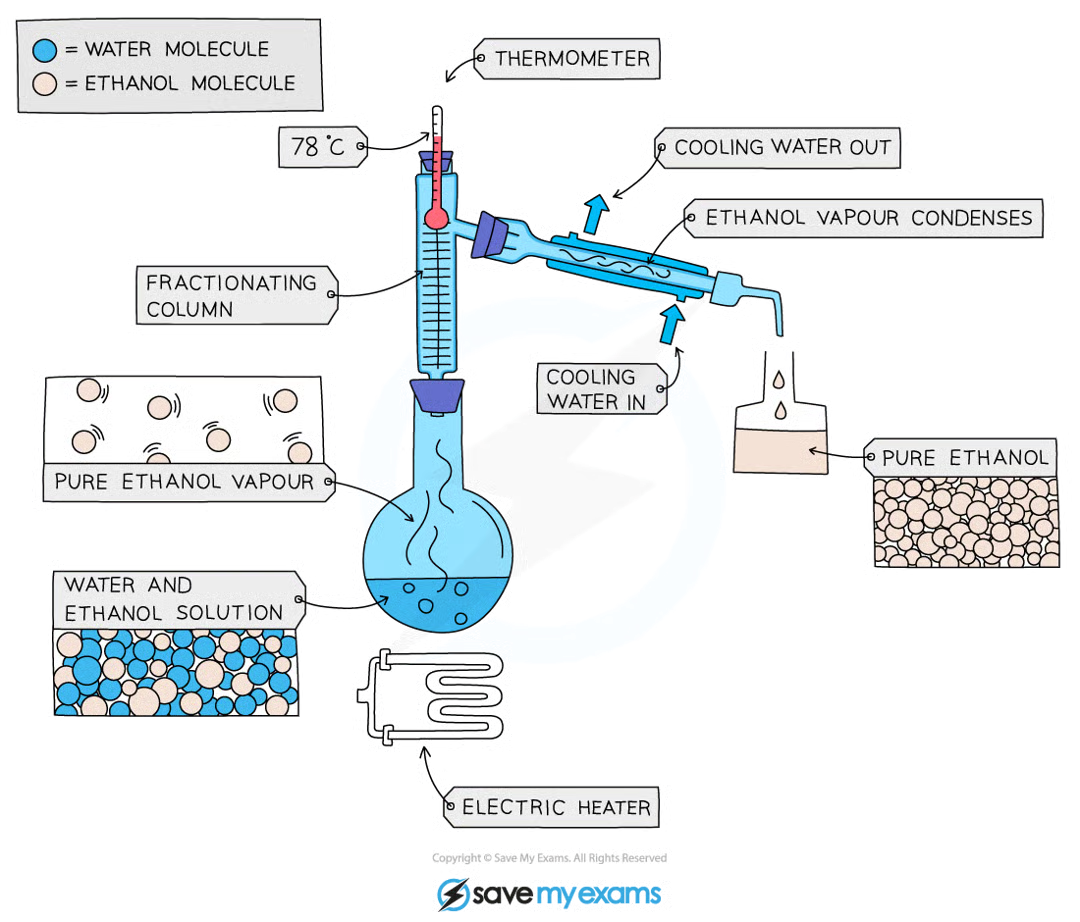
describe and explain how a mixture can be separated using fractional distillation.
fractional distillation separates a pure liquid from a mixture of liquids
fractional distillation works because the liquids have different boiling points
the mixture is heated to the boiling point of the liquid with the lowest boiling point, which will evaporate first, pass through the condenser and collect in its fraction. this process is repeated, until every component of the mixture has evaporated in its associated boiling point and separated into its individual fractions.
how to identify the purity of a substance using their melting and boiling point information
pure substances have a sharp, exact melting and boiling point whereas impure substances will melt/boil over a range of temperatures