W11, Ischemic Heart Conduction disorders
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
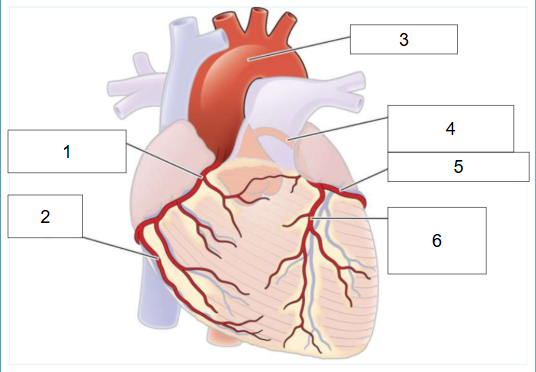
What is #1?
Right coronary artery
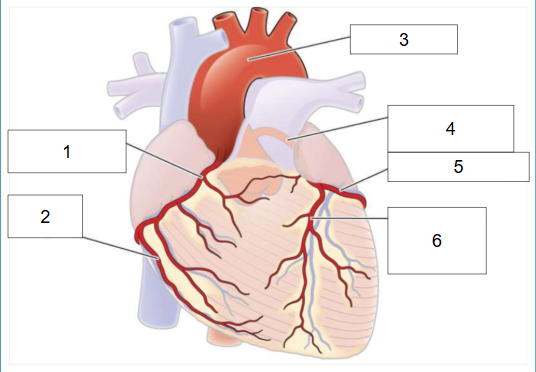
What is #2?
Posterior artery
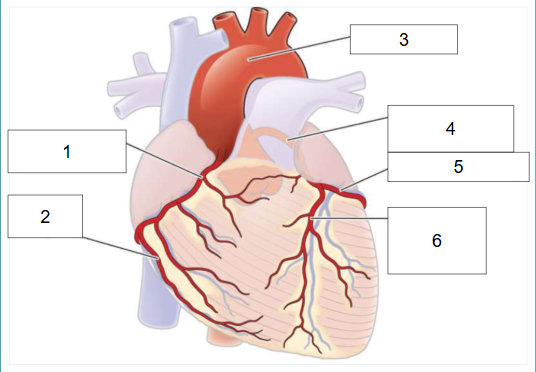
What is #3?
Aortic arch
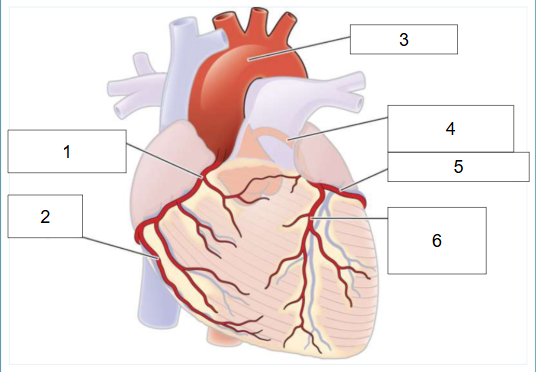
What is #4?
Left main coronary artery
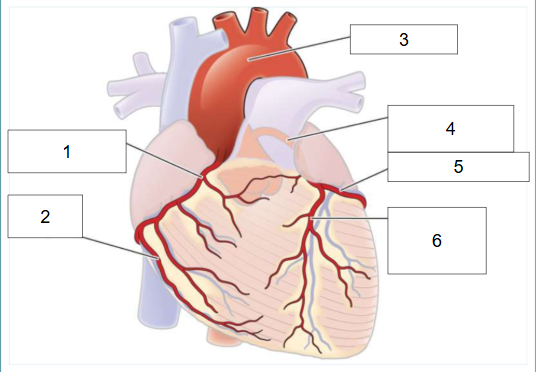
What is #5?
Circumflex artery
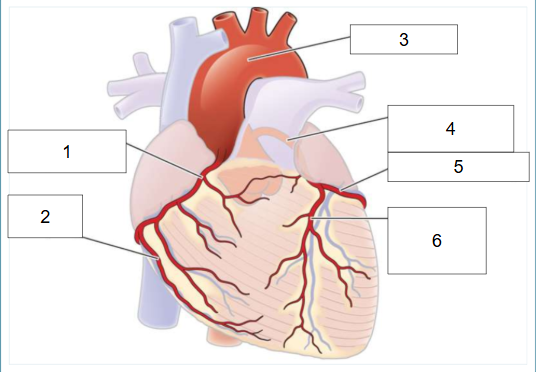
What is #6?
Left anterior descending artery
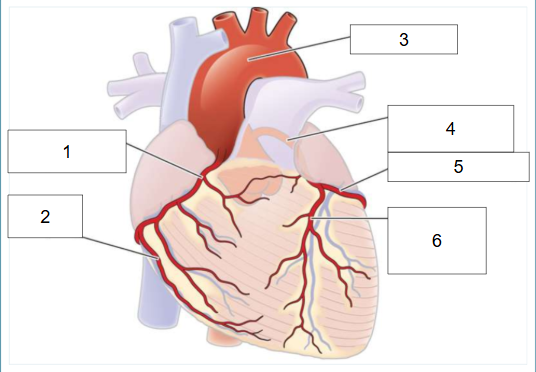
Why is the left anterior descending artery (#6) called the widowmaker?
Because a blockage here can can a massive, often fatal heart attack
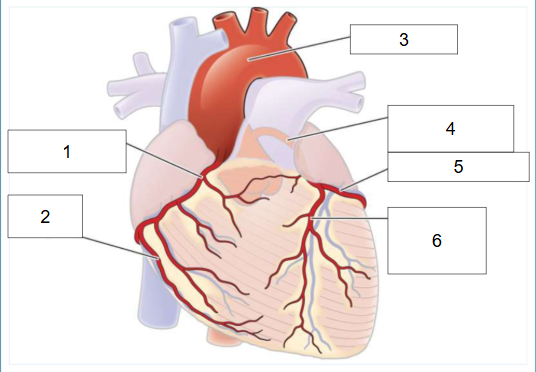
What are two parts that branch off of left main coronary artery (#4)?
Circumflex artery (#5), left anterior descending artery (#6)
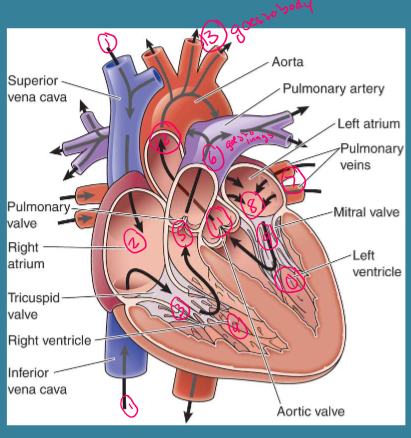
What is this?
Circulation, path of blood flow through heart
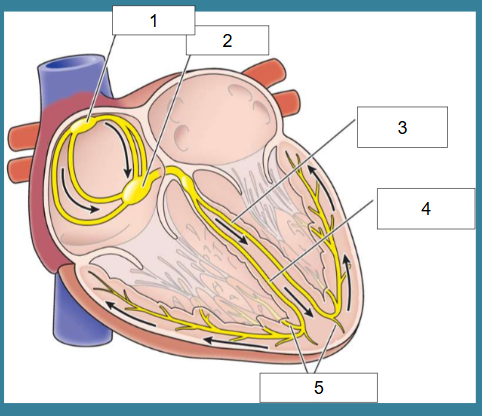
What is this?
Cardiac conduction
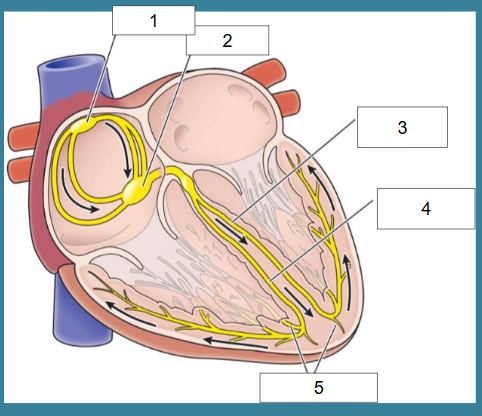
What is #1?
SA node
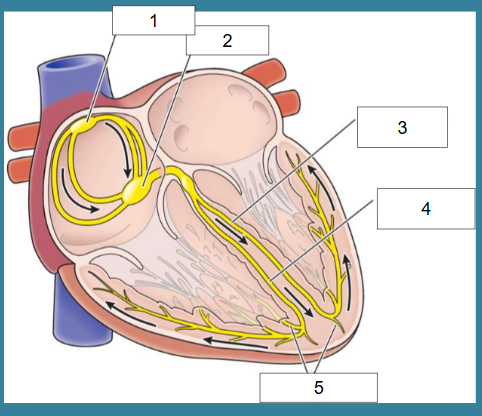
What is #2?
AV node
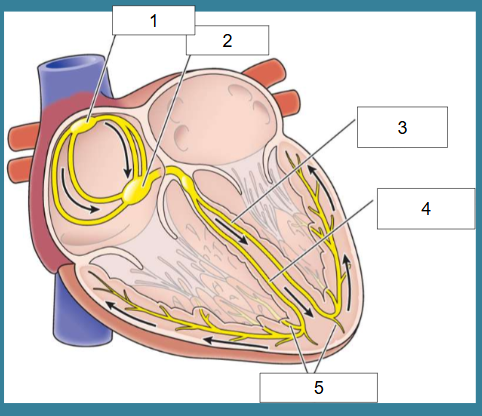
What is #3?
Left bundle of His
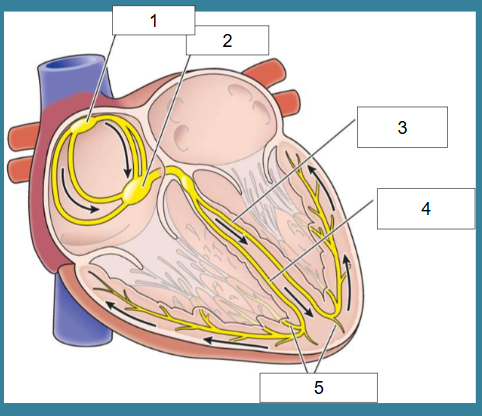
What is #4?
Right bundle of His
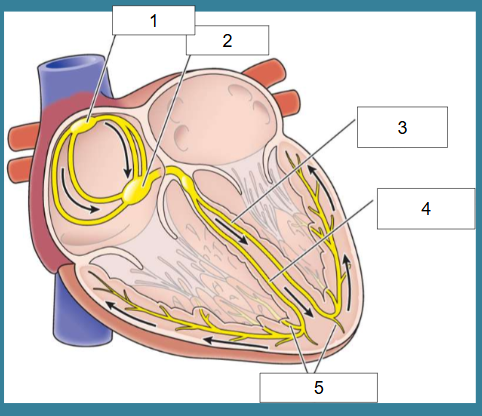
What is #5?
Purkinje fibers
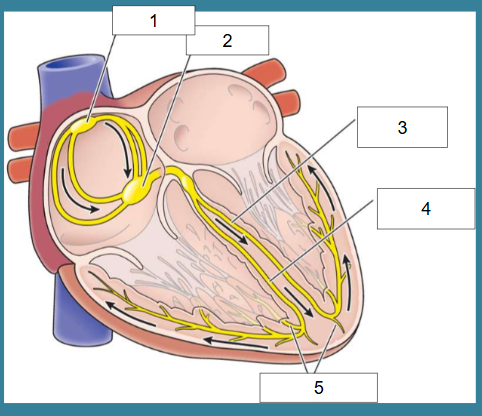
True/False: Electrical activity leads to contraction of heart which leads to pumping
True
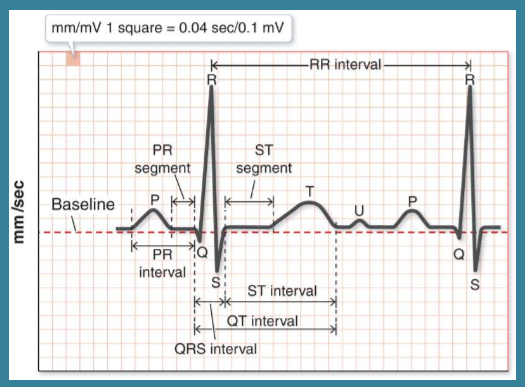
What is this?
Normal ECG Waveform
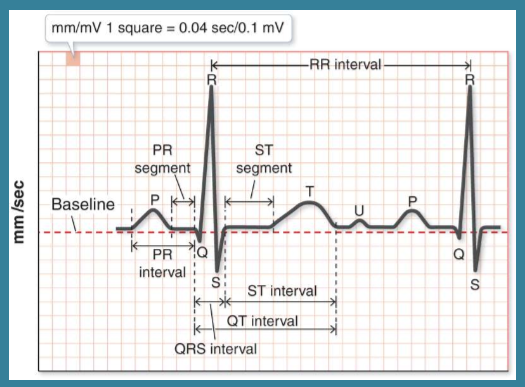
True/False: A nurse doesn’t need to know what a normal ECG looks like
False; study this!
What is angina pectoris?
Squeezing pain in chest
What are 3 types of angina pectoris?
Stable, prinzmetal (Variant), unstable
What is prinzmetal angina pectoris also called?
Variant angina
What is stable angina triggered by?
Triggered by exercise or stress
What are characteristics of stable angina?
Predictable pattern, relieved by rest or nitroglycerin
What relieves stable angina?
Rest of nitroglycerin
What is prinzmetal (variant) angina caused by?
Caused by coronary artery spasm and often occurs at rest, usually at night
When does prinzmetal (variant) angina often occur?
At rest, at night
What changes does prinzmetal (variant) angina produce on ECG?
Can produce transient ST-segment elevation on ECG
True/False: Stable angina can produce transient ST-segment elevation on ECG
False; prinzmetal (variant) angina can produce transient ST-segment elevation on ECG
True/False: Unstable angina is type of acute coronary syndrome
True
What is unstable angina also referred to as?
ACS (acute coronary syndrome)
What are characteristics of unstable angina?
Unpredictable, more severe, may last longer
When does unstable angina occur?
At rest or with minimal exertion
Why is unstable angina medical emergency?
There is a blockage so can progress to myocardial infarction
What is unstable angina usually caused by?
Usually caused by plaque rupture from atherosclerosis or thrombus formation (blockage)
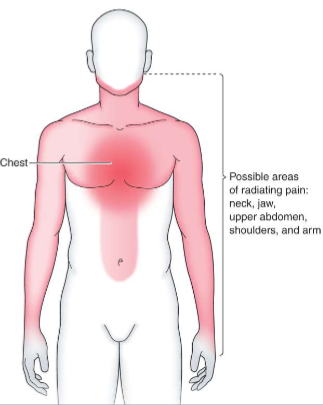
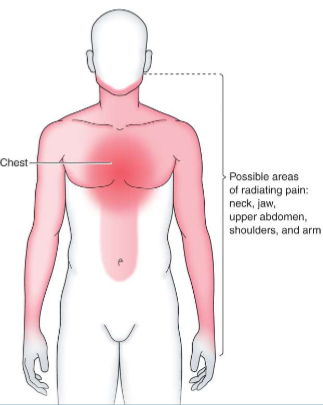
What is this?
Possible areas of angina and MI pain
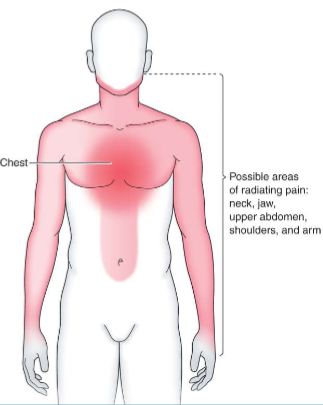
What are possible areas of angina and MI pain?
Both arms but mostly left-sided pain because of nerve shared on left side of heart, as well as neck, jaw, upper abdomen, shoulders
True/False: Most tests done for angina pectoris and MI pain and symptoms were performed on men, not women
True
What does infarct mean?
Tissue is dead (localized)
What does ischemia mean?
Blood flow, and thus oxygen, is not getting to that area, but tissues are not dead yet
What are 4 causes of myocardial ischemia?
Coronary thrombosis (blood clot in heart), atherosclerotic plaques, coronary artery vasospasm, anemia
What does coronary thrombosis mean?
Blood clot in heart
What percent does coronary thrombosis blockage have to be to cause inadequate blood flow?
50% to 75%
What happens in coronary artery vasospasm?
Blood flow is stopped
What happens in anemia?
There is not enough blood (hemoglobin) so oxygen delivery will be decreased
What is classic cardiac chest pain?
A crushing sensation felt on left side of chest radiating into left shoulder down inner aspect of left arm
True/False: Classic cardiac chest pain is a crushing sensation felt on right side of chest radiating into right shoulder down inner aspect of right arm
False; classic cardiac chest pain is a crushing sensation felt on left side of chest radiating into left shoulder down inner aspect of left arm (LEFT)
What are symptoms of retrosternal chest discomfort?
Pressure, choking, squeezing, or heaviness on chest
Where does retrosternal chest discomfort take place in body?
Behind sternum (in chest)
What are signs and symptoms of classic cardiac chest pain?
Dyspnea so SOB, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, feeling of impending doom
What is anginal equivalent?
Symptoms of myocardial ischemia other than classic angina
What populations experience anginal equivalent?
Women and elderly
What is most common symptom in women that appears before MI?
Fatigue is most common symptom and can appear weeks before MI
True/False: Fatigue is most common symptom and can appear weeks before MI in men
False; fatigue is most common symptom and can appear weeks before MI in women
What are symptoms of anginal equivalent?
Episodic dyspnea, dizziness, lightheadedness, and pain of jaw, epigastric region, or back in response to exertion or stress
How is Thallium stress test performed?
Patient goes on treadmill, or is given medications to get the heart going, after receiving thallium through IV
What does thallium highlight in Thallium stress test?
Highlights coronary artery blood flow and deficits of blood flow, and if there is a blockage because it won’t be able to highlight (which indicated blockage)
What is Thallium stress test used for?
Used to evaluate blood flow to the heart muscle, diagnose and monitor heart conditions like coronary artery disease, and assess heart damage after a heart attack
What are diagnostic tests for ischemic heart disease?
ECG, labs to determine MI or no MI, calcium-computed tomography (CT) scan, cardiac angiogram and cardiac catheterization
What is cardiac catheterization?
Opening up vessels and put stent in vessels to keep them open
What are labs used to determine MI or no MI?
Labs that look at cardiac enzymes like CPK, cardiac troponins (cTn), and chest x-ray
Why is chest x-ray done as a diagnostic test for ischemic heart disease?
To find out size of heart and see if it is enlarged (which indicates problem)
What happens to myocardial cells in acute MI?
Myocardial cells suffer irreversible damage
When an acute MI has happened and myocardial cells have suffered irreversible damage, what won’t go through cells anymore?
Electrical activity
When an acute MI has happened and myocardial cells have suffered irreversible damage, what is damage influenced by?
Location of occlusion in coronary artery, length of time that coronary artery has been occluded, heart’s availability of collateral circulation
True/False: Damage of acute MI is determined by location of occlusion in coronary artery, length of time that coronary artery has been occluded, heart’s availability of collateral circulation
True!
What are 3 things damage of acute MI is determined by?
Location of occlusion in coronary artery, length of time that coronary artery has been occluded, heart’s availability of collateral circulation
When acute MI occurs and heart gets damaged, how does heart’s availability of collateral circulation try to help heart?
Starts developing small micro arteries to get to damaged area, but could also be blocked with occlusion of main artery
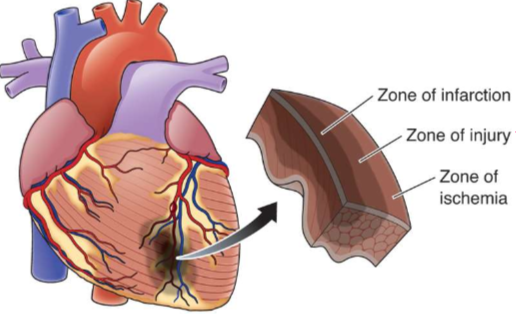
What is this?
Zones of injury
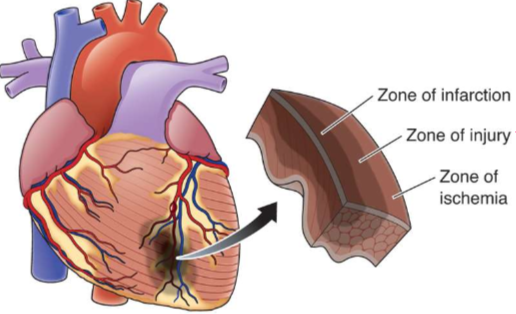
What is happening in zone of infarction?
Tissue is dead
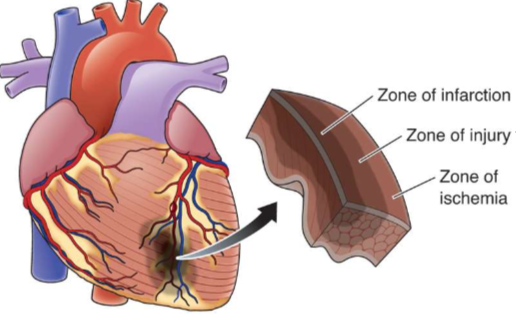
What is happening in zone of injury?
Tissue is not completely dead yet, so if oxygen is restored tissue can recover
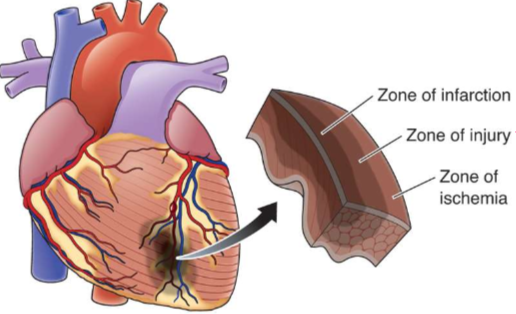
What is happening in zone of ischemia?
Electrical activity is unstable and can lead to dysrhythmia
What are signs and symptoms of myocardial infarction (MI)?
Diaphoresis (really sweaty), dyspnea, extreme anxiety, pain, pallor, weak pulses, Levine’s sign (fist to chest), nausea and vomiting
True/False: Diaphoresis (really sweaty), dyspnea, extreme anxiety, pain, pallor, weak pulses, Levine’s sign (fist to chest), nausea and vomiting are all signs of stroke
False; diaphoresis (really sweaty), dyspnea, extreme anxiety, pain, pallor, weak pulses, Levine’s sign (fist to chest), nausea and vomiting are all signs of myocardial infarction (MI)
What is serial CPK measurements?
Series of blood tests to measure CPK (creatine phosphokinase) enzyme in blood over period of time
What does serial CPK measurements detect?
CPK is an enzyme that is released into bloodstream when muscle or heart tissue is damaged
What are 3 cardiac markers (2 enzymes and 1 protein) that indicate extent of myocardial cell death?
CPK, CK-MB, troponin
How does CPK indicate extent of myocardial cell death?
It’s an enzyme found in muscle cells that gets released when muscle is injured (so higher levels means damage to heart)
How does CK-MB indicate extent of myocardial cell death?
CK-MB is specific type of CPK for heart (heart-specific isoenzyme) that gets released 4 to 6 hours after MI happens, and then it peaks at 8 to 10 hours and stays elevated for 2 to 3 days
True/False: CK-MB is specific type of CPK for heart (heart-specific isoenzyme) that gets released 4 to 6 hours after MI happens, and then it peaks at 8 to 10 hours and stays elevated for 2 to 3 days. Thus indicating extent of myocardial cell death
True
How does troponin (cTnI and cTnT) indicate extent of myocardial cell death?
Rises within 3 to 6 hours after MI, peaks 12 to 24 hours and stays elevated for 7 to 14 days
Why is troponin (cTnI and cTnT) thought to be gold standard for indication of myocardial injury?
Rises within 3 to 6 hours after MI, peaks 12 to 24 hours and stays elevated for 7 to 14 days

What is this?
Acute coronary syndrome
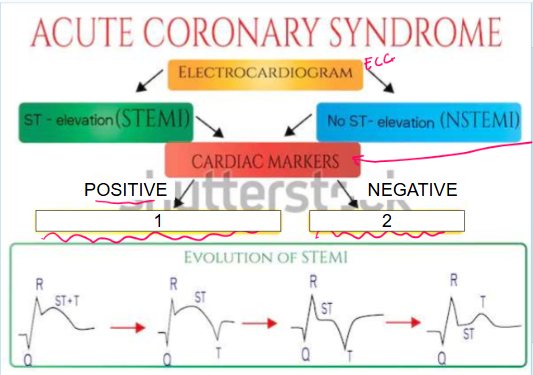
What are cardiac markers?
Troponin, CPK, CK-MB
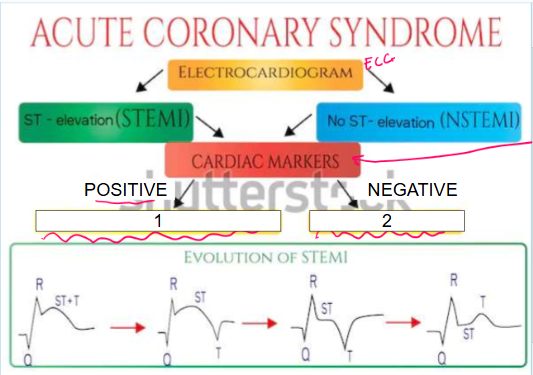
What does it mean if cardiac markers are positive (leading to #1)?
Patient is having MI so they must be sent to cath lab immediately as they only have 90 minutes
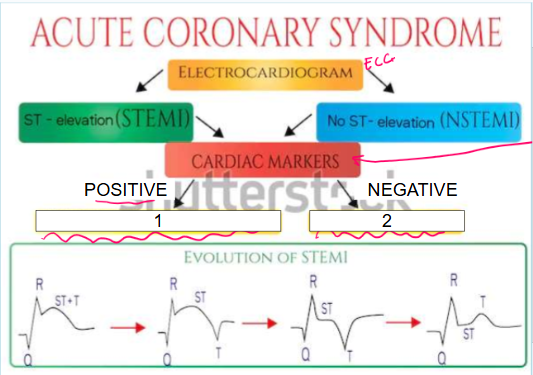
What is #1?
Cardiac markers like troponin, CPK, and CK-MB are positive which indicates patient is having ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION so they must be sent to cath lab immediately as they only have 90 minutes
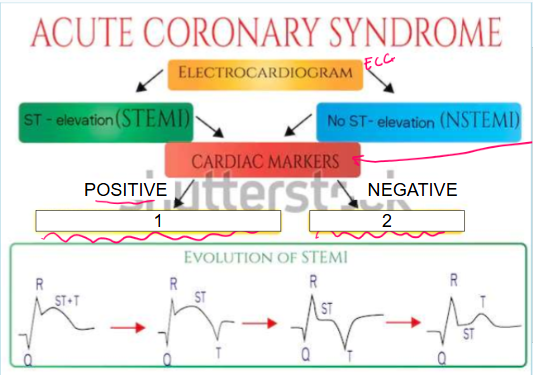
What does it mean if cardiac markers are negative (leading to #2)?
Patient is experiencing unstable angina
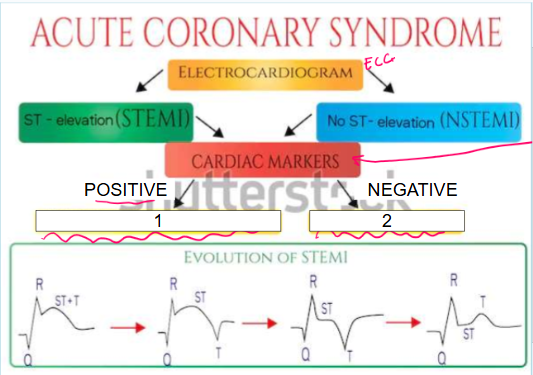
What is #2?
Cardiac markers are negative which indicates patient is experiencing UNSTABLE ANGINA
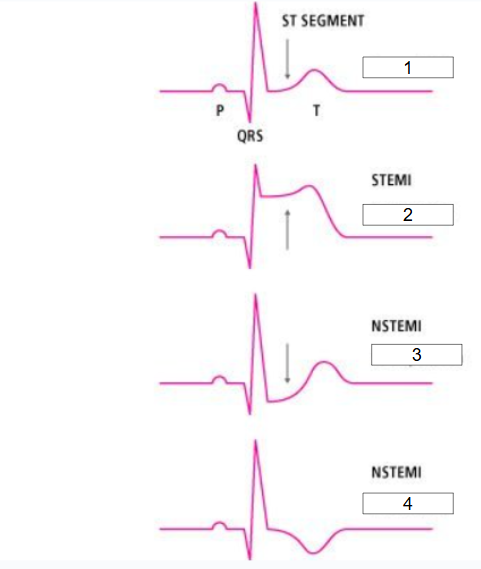
What is this?
STEMI vs. NSTEMI
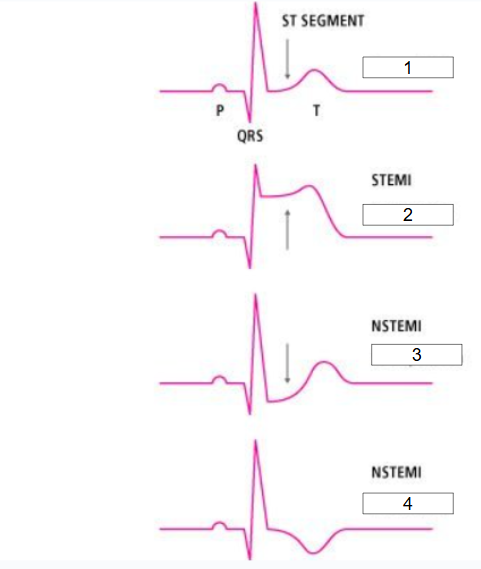
What is #1?
Normal ECG
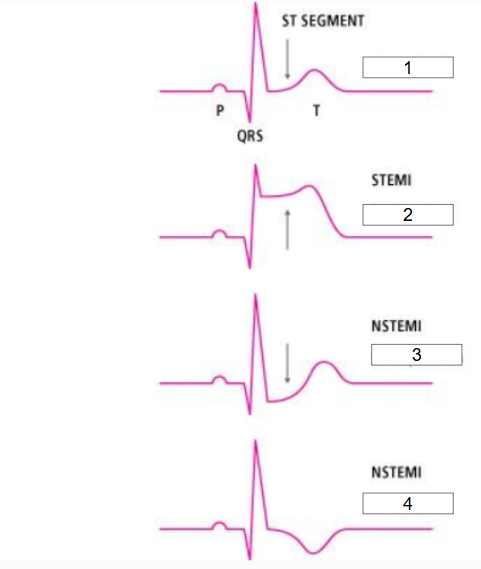
What is #2?
ST elevation
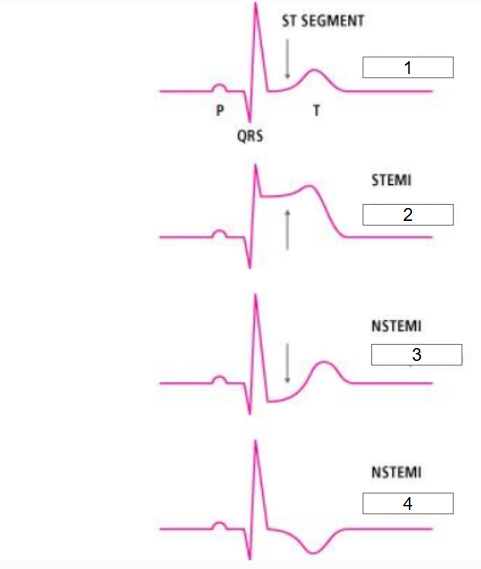
What is #3?
ST depression
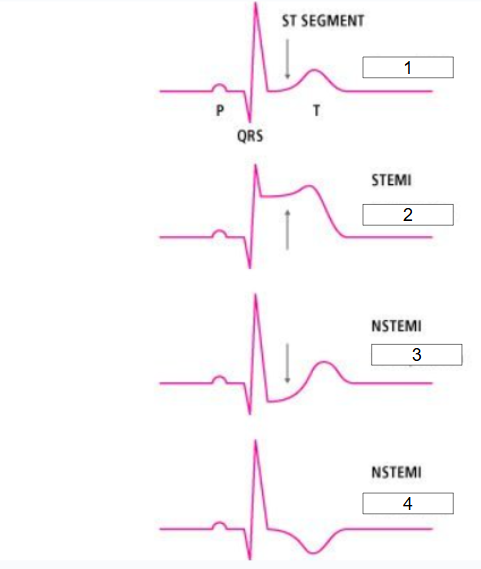
What is #4?
T inversion
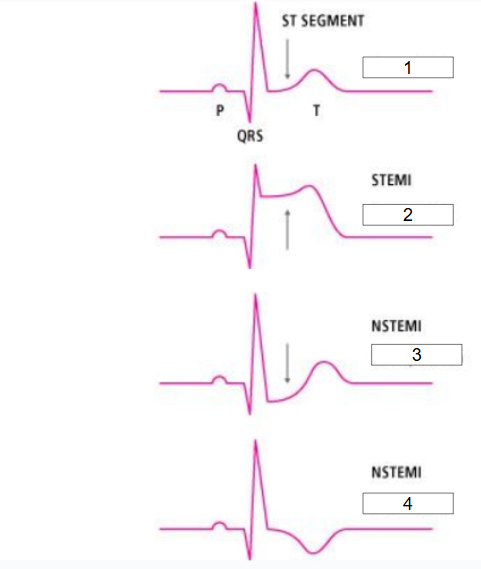
What should nurse do if #2, #3, or #4 are seen on ECG?
Immediately show ECG to doctor
What is treatment for MI and unstable angina?
Morphine, oxygen, nitroglycerin, aspirin
Why is morphine used as treatment for MI and unstable angina?
Actually new researchers are saying morphine is not useful
When is oxygen used as treatment for MI and unstable angina?
Only if SpO2 is less than 90% or patient is experiencing shortness of breath
True/False: Oxygen is given to every patient as treatment for MI and unstable angina
False; oxygen is not given routinely anymore as it is only used if SpO2 is less than 90% or patient is experiencing shortness of breath
Why is nitroglycerin used as treatment for MI and unstable angina?
For pain relief unless contraindicated (hypotension or sildenafil use)
When would nitroglycerin not be used as treatment for MI and unstable angina?
Unless it is contraindicated, like for those with hypotension or for those who use sildenafil (drug for erectile dysfunction)
How is aspirin used as treatment for MI and unstable angina?
Chewed immediately for antiplatelet effect