History Exam 1
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Catalhoyuk
Turkey
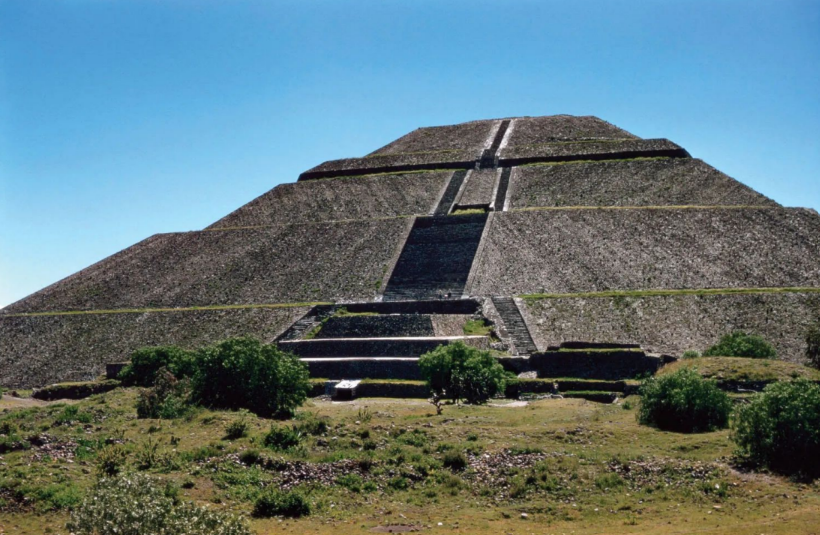

Pyramid of the Sun
Teotihuacan
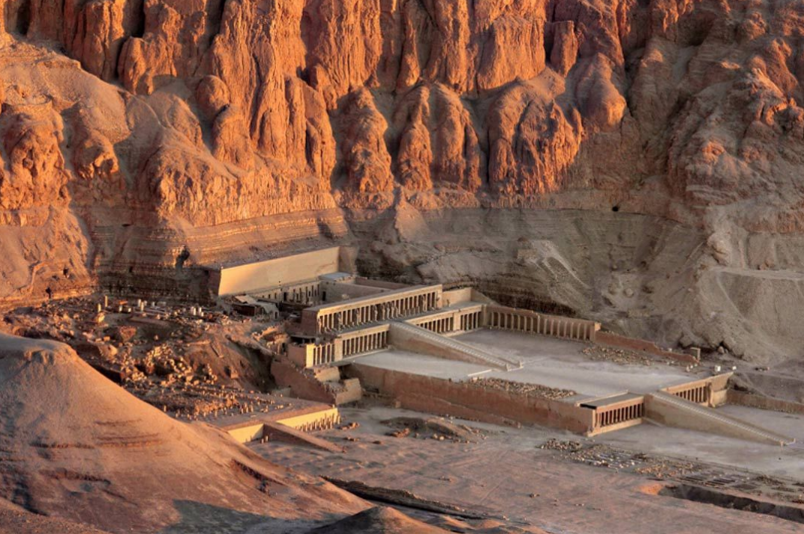

Funerary Temple of Hatshepsut
Deir-el- Bahari
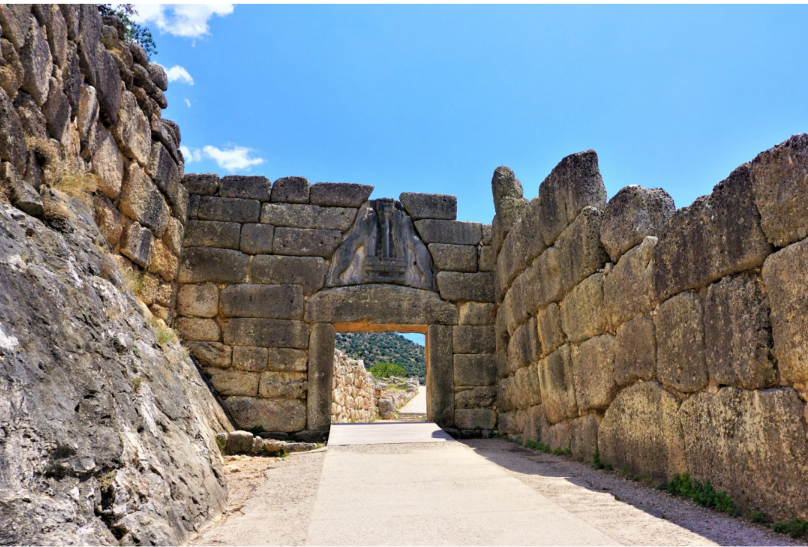

Lions Gate
Mycenae
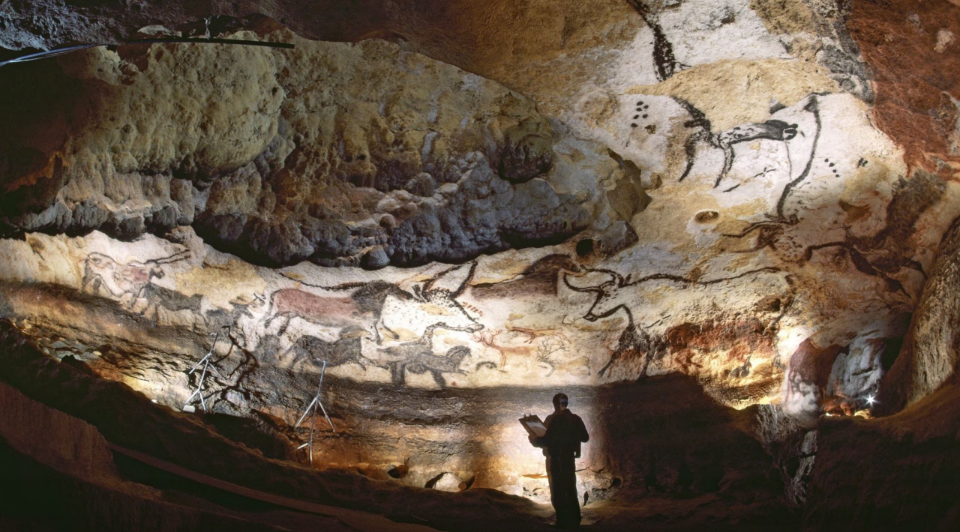

Lascaux
Lascaux, France
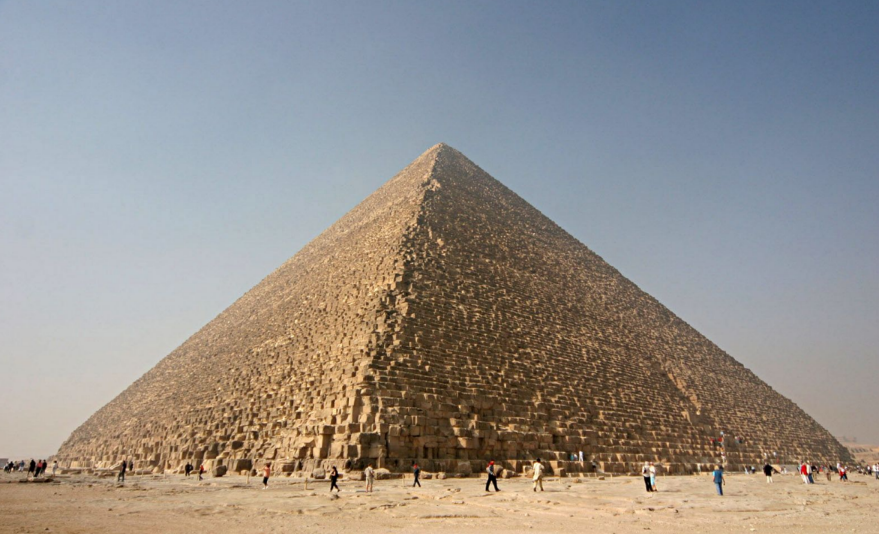

Pyramid of Cheops/Khufu
Giza
Hemiunu
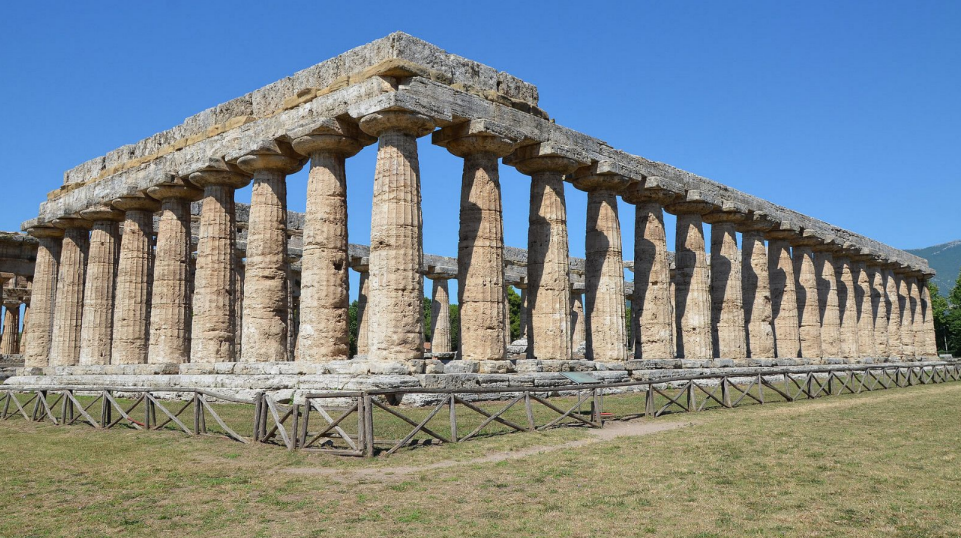

Basilica/ Temple of Hera I
Paestum
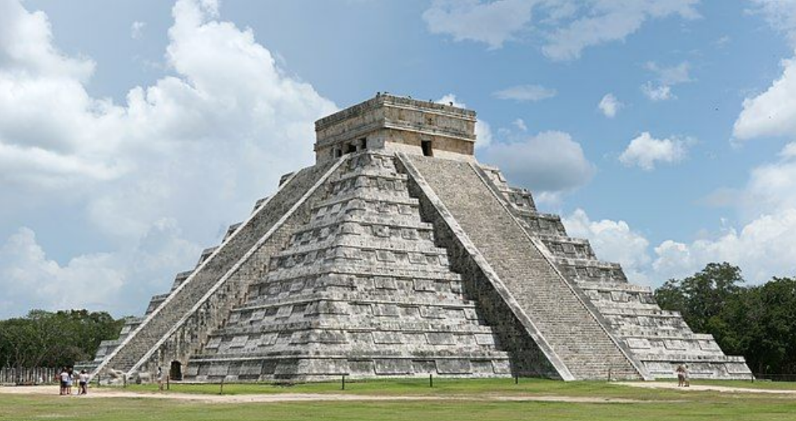

Castillo
Chichen Itza, Yucatan
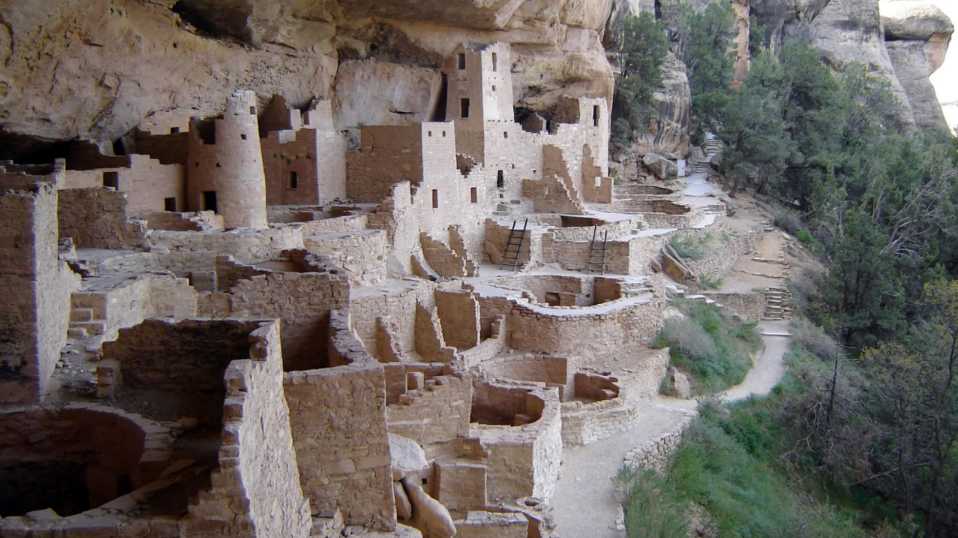

Cliff Palace/ Cliff House
Mesa Verde, AZ

Great Ziggurat
Ur

Minoan Palace
Knossos, Crete
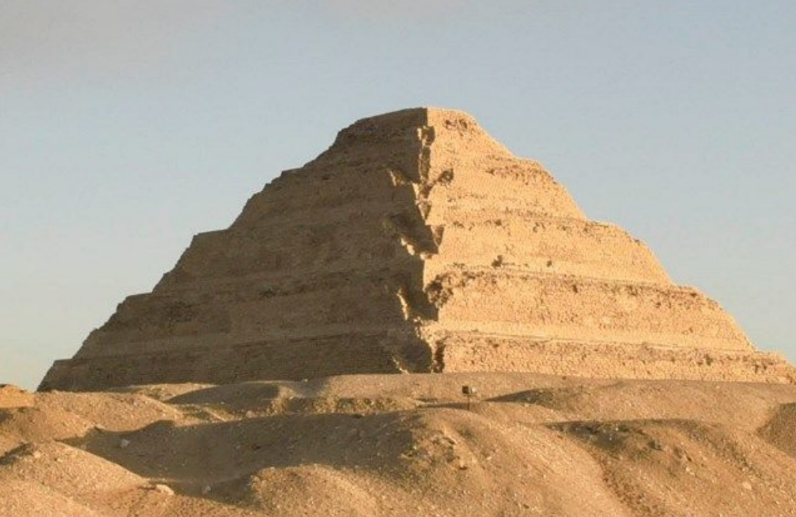

Stepped Pyramid of King Djoser
Saqqara
Imhotep
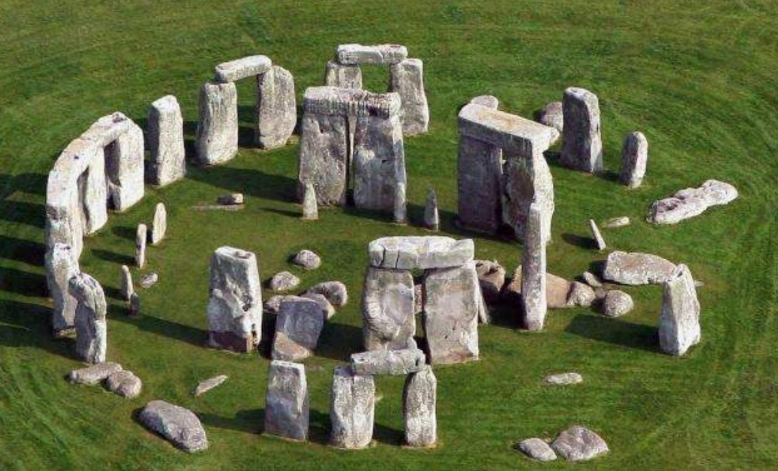

Stonehenge
Salisbury Plains
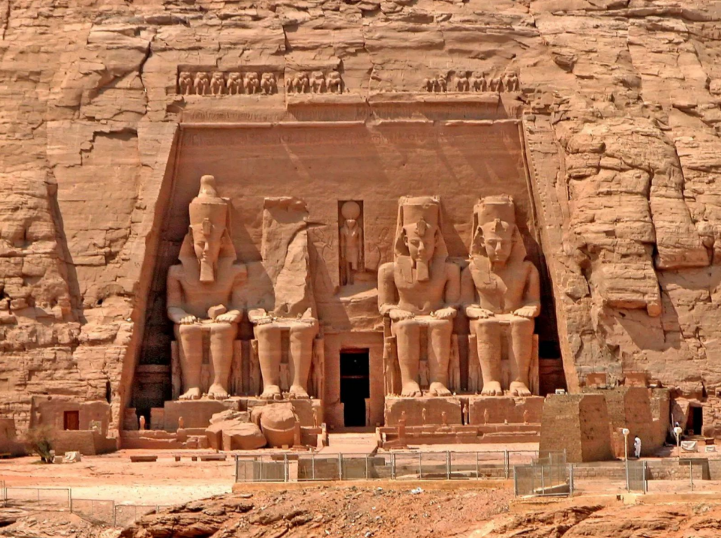

Temple of Ramses II
Abo Simbel
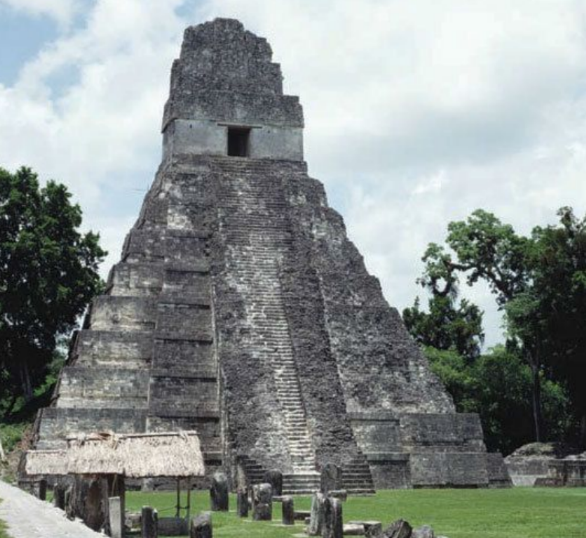

Temple of the Great Jaguar
Tikal
Which one is older, Funerary Temple of Hatshepsut or Pyramid of the Sun?
Funerary Temple of Hatshepsut
Which one is older, Great Ziggurat or Catalhoyuk?
Catalhoyuk
Which one is older, Stonehenge or Lascaux?
Lascaux
What order from oldest to earliest, Pyramid of Cheops, Castillo, and Pyramid of the Sun?
Pyramid of Cheops, Pyramid of the Sun, Castillo
What order from oldest to earliest, Minoan Palace, Temple of the Great Jaguar, and the Basilica?
Minoan Palace, Basilica, Temple of the Great Jaguar?
wigwam
a bark and mat carved structure, typically round or oblong in shape
ex. Ojibwe winter house
kiva
round ceremonial structure, usually round and partially underground
ex. Cliff Palace
Vigas
large beams
Post and Lintel construction
structural system that supports the weight through posts around openings and light support weight on top
ex. Lions gate
Trilithons
2 free standing megaliths supporting a lintel
Ziggurat
Mountain of God, temple tower in the form of stepping pyramid
Great Ziggurat
Megalith
large stone
Gobekli Tepe, Turkey
Mastaba
Egyptian flat-topped rectangular tomb w/ sloped sides, first burial grounds built by the Egyptians
Egyptian
Column
base, shaft, and capital
ex. Temple of Hera or Zeus
Hypostyle Hall
room w/ roof supported by many columns
ex. Minoan Palace
Peristyle
rows of columns surrounding a space or building
ex. Temple of Hera I
Clerestory Window
opening at a change in roof height that brings natural light into a space
Imhotep
first known architect, built the Stepped Pyramid of King Djoser, vizier, architect, and priest to King Djoser
ex. Egyptian
Corbel Vaulting
an opening formed by placing blocks in horizontal courses to each side of the space, with/ each level cantilevering outward from the one below
ex. Great Pyramids of Giza
Major Elements of an Egyptian Pyramid
Valley Temple, Causeway, Mortuary Temple, Pyramid
Obelisk
square tower topped by a Ben Ben
Megaron
palace form in Bronze Age Greece that consists of one main room (cella) and a front porch with columns (later developed into the basis structure of Greek Temples
ex. Mycenae
Cyclopean Masonry
stonework consisting of large boulders, named after the Cyclops of Homer
ex. Lions Gate
Cella
the inner area of an ancient temple
Entasis
a slight convex curve in the shaft of a column
ex. Temple of Apollo
Pediment
triangular element of a building located above the entablature and below the roof
triglyph
rectangular block with three vertical lines
metopes
rectangular elements that fills the space between triglyphs in a Doric Frieze
Fluting
set of vertical grooves around a column shaft in Doric Freize
ex. Temple of Hera II
Volutes
the spiral scroll element in Ionic capitals
ex. Temple of Artemis
Frieze
a broad horizontal band that forms part of the entablature
ex. Greek culture, Doric and Ionic Order
Dentils
small rectangular blocks resembling teeth, usually under the soffit of a cornice
Doric Refinements
concave bases, corner columns brought inwards, columns sloping inwards, entasis, corner columns slightly thicker
Form of Stonehenge
oriented in a way that is assumed to correlate with time
no ornament
circular
greystones, bluestones
Structure of Stonehenge
post and lintel
variety of materials (timber to stone)
tectonic
Stonehenge function and culture
ritual site
created by builders
rocks transferred from far away
Stonehenge physical
stands alone
rural
salisbury plains
dominates
Stonehenge historical
tourist site
many steps
culture monument
Pyramids of Cheops Form
large=power
triangular shape- references to the rays (Ra)
pyramid form
inner chambers and tunnels
Pyramid of Cheops Chambers and Tunnels
Ventilation shafts, kings chamber, queen chamber, grand galley, suberanian chamber
Pyramid of Cheops Structure
corbel vaulting, stereotomic, acts in compression, limestone
Pyramid of Cheops Function and Culture
tomb for pharaoh
protects ruler and treasure from outsiders
larger equals more power of pharaoh
hemiunu
pharaoh commissioned for himself
protects pharaoh as the soul (ka) travels to afterlife
shape refers to the sun god Ra
skilled laborers
worker camps
Pyramid of Cheops Physical
pyramid
Giza
one of three, largest of the three
west side of nile
Golden sandy color
pyramid complex (valley temple, causeway, mortuary temple, pyramid)
Pyramid of Cheops Historical
white limestone
finish worn away
raided
protected now, tourist site
Funerary Temple of Hatshepsut
stepped terraces
rectangular
partially within the cliff
large scale
hieroglyphs painted in interior
statues within
columns hypostyle
Funerary Temple of Hatshepsut Structure
stone
stereotomic and tectonic
acts in compression
Funerary Temple of Hatshepsut Function and Culture
Funerary Burial of Pharoah Hatshepsut
senmut architect
protects her legacy
legacy of stepson threatened
erased history
Funerary Temple of Hatshepsut Physical
Deir-el-Bahari
west side of the Nile
across the Temple of Amun Ra
located in Sacred Valley
Funerary Temple of Hatshepsut Historical
History erased
stepson took off face because of the threat of matriarchal legacy
tourist attraction
Temple of the Great Jaguar Form
stepped pyramid
9 steps
steep slope
corbel vaulting
likely plastered
temple on top
92 steps on each side, 365 days a year
Temple of the Great Jaguar Structure
limestone bricks
underneath is a rubble core
stereotomic
Temple of the Great Jaguar Function and Culture
religious ceremonies
only included for the gods
some sacrifices
funerary temple for the great jaguar
9 layers of the Mayan underworld
commissioned by emporer
Temple = mountains
ground= sea
other= trees
Temple of the Great Jaguar Physical
Tikal
did not stand alone
urban, part of a large plaza
across other temple
Temple of the Great Jaguar Historical
tourist site
abandoned
jungle took over
deforestation, people revolted
skeletons of children as evidence of malnutrition
1848 rediscovered
mapped out with radar imaging
Minoan Palace Form
plastered
paintings inside
no doors
no clear entrance inside
built like a maze
hypostyle columns
5 stories
complex floorplan
Minoan Palace Structure
tectonic and stereotomic
geometric
limestone
Minoan Palace Function and Culture
Theseus defeated minatour
athens defeated cretes
major power figure
no walls has no protection
strong navy to support no walls
palace for minoan government
symbol of Minoan power
Minoan Palace Physical
Crete
island location
stands alone
Minoan Palace Historical
fell into ruin
rebuilt
reconstructed in modern times
Greeks trying to make sense of their architecture
Discuss the advantages of an agricultural society over a nomadic one in the creation of permanent architecture.
agriculture can grow, more stabilised shelter, complex society, development of cities, increase in workforce, expanded workforce, more talents or skills, status developed, better health, better protection, dedicate spaces to more than shelter
Discuss why archaeologists now believe that structures like Pueblo Bonito in Chaco Canyon were designed to measure solar orientation.
summer solstice is in between, solar monumnet, carved sliver of sun on a spiral carving, every significant sun event has a marking
Describe the specific phases of development of Stonehenge over time, including main material, basic form, and other characteristics. Pre- Stonehenge
Wood
4 large Mesolithic holes from pine posts around 800 BC
3 with east-west alignment
Stage I Stonehenge
earth
earth circular mound (around 360’ in diameter) with ring of 56 holes
Stage II Stonehenge
Timber
new postholes suggest timber buildings in center of circle
cremated matter placed inside of earlier holes
Stage IIIi Stonehenge
Stone- Bluestone
double partial ring of about 6 feet high bluestones from South Wales
avenue to river added
Heel stone (sarsen) gray sandstone (possibly earlier or later)
Stage IIIii Stonehenge
Stone - Gray Sandstone
bluestones cleared away
post and lintel ring of 30 massive gray stone megaliths erected
a horseshoe arrangement of 5 20 feet high trilithons appear within circle
Stage IIIiii Stonehenge
Stone Rearrangements
bluestones reappear and rearranged inside horseshoe
two additional rings of holes dug outside of stone circle
Describe the basic function and form of a ziggurat.
temple tower in the form of a stepped pyramid, a temple that rose on one or more platforms to create a stepped profile, “house of the mountain” bound between heaven and earth, great height and mass alluded to the origin of the hill people who descended from the plains, represented the comfort of the earth, house of the gods, in Mesopotamia it embodies the mandate to influence the sky gods
Discuss the functional and formal differences between a Mesopotamia ziggurat and an Egyptian pyramid
ziggurat is a house for the gods while the pyramid is for the burial of a pharaoh
pyramids allow people in, ziggurats are only for the gods
both heights represent that figure’s strength
ziggurat has terraces, 3 stairways, rectangular, limestone, increased slope
Pyramid is triangular, mud brick, steps, decreased slope
Identify 4 major elements of a Pyramid Complex
Valley Temple (gathering or precision for the body), Causeway (moving towards death), Mortuary Temple (organs harvested and mummification), Pyramid
Discuss the basic evolution of Egyptian burial architecture from mastaba to pyramid
stacked to make them bigger, the slope smooths out and decreases over time, Djoser to Cheops
Discuss how mythology was used by later Greeks to explain the architectural remains of the Minoans and Mycenaeans, especially at Knossos. What is the basic story and how was it reflected at the site?
Discuss the functional and formal differences between Egyptian and the different types of Pre-Columbian pyramids. Be clear on dating
The pyramids are older, have a decreased slope, and steps of stones
Pre-Columbian pyramids are stepped pyramids, each level is pronounced
The pyramids are burial grounds while most Pre-Columbian pyramids are used for religious ceremonies.
Identify and define the basic elements of Greek Temple architecture
capital- top of the column
volutes- ioninc spiral
entasis- bulging of the colums
entablature- top of the columns beneath the pediment
pediment- triangular form underneath the roof
cella- inner room of the ancient temple
triglyphs and metopes
Identify the major refinements of a Doric temple
concave bases, corner columns brought inwards, entasis, corner columns slightly thicker, columns sloping slightly inwards
Discuss the basic development of the Doric and Ionic Greek temples.
Doric came first, compact, columns and forms, organic material, and stone
Ionic- capital changes, the volutes were formed, taller and more slender, more feminine, fluting became less rounded, arrived from another place
List and describe the subtle refinements of classical Greek temples as see in the design of the Parthenon.
elevated or exaggerated differences, column is brought more inwards, corner columns slightly thicker, corner columns sloping inwards, more emphasis