AMA: Intro to Materials Science and Engineering
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Stone Age
~ 2.6 million years ago – 3300 B.C.
Bronze Age
~ 3300 B.C. – 1200 B.C.
Iron Age
~ 1200 B.C – 600 B.C.
Modern & Advanced Materials
early 20th Century - Present
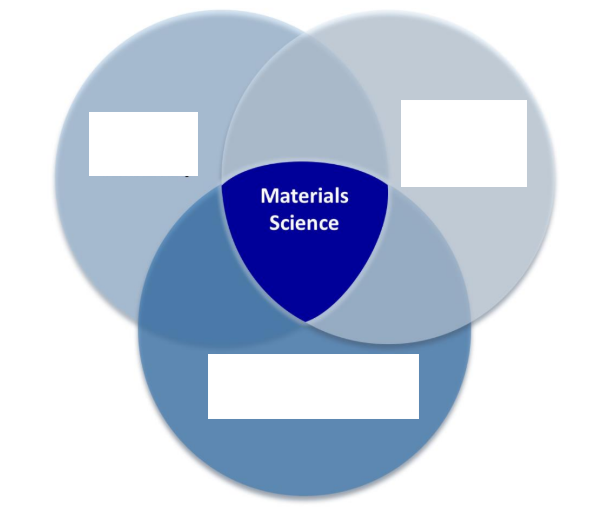
Materials Science
Investigates relationships that exist between the structures and properties of materials and develop and synthesize new materials
Material Chemistry, Material Physics, Materials and Process Engineering
Fill in the Blanks.
Materials Engineering
Design the structure of a material to produce a predetermined set of properties.
Materials Engineering
Create new products or systems using existing materials.
Materials Engineering
Develop techniques for processing materials.
Subatomic Level
Electronic structure of individual atoms that defines
interaction among atoms (interatomic bonding)
Atomic level
Arrangement of atoms in materials (for the same atoms can have different properties, e.g. two forms of carbon: graphite and diamond)
Microscopic Structure
Arrangement of small grains of material that can be identified by microscope.
Macroscopic Structure
Structural elements that may be viewed with the naked eye.
Physical Property
Properties that can be observed or measured without changing the composition of the material.
1.Density
2.Thermal
3.Electrical
4.Dimensional
5.Optical • Refractive index • Absorption • Transmission • Reflection • Scattering • Color
6.Magnetism
7.Permeability
8.Porosity
8 Physical Properties
Mechanical Property
Properties that involve a reaction to an applied load.
1.Hardness
2.Toughness
3.Elasticity
4.Plasticity
5.Ductility
6.Malleability
7.Brittleness
8.Tensile strength
9.Compressive strength
10.Shear strength
11.Fatigue strength
12.Impact resistance
13.Creep
14.Stiffness
15.Resilience
15 Mechanical Properties
Chemical Property
Properties that are discovered by observing chemical reactions.
1. Reactivity with acids
2. Reactivity with bases
3. Oxidation state
4. Corrosion resistance
5. Flammability
6. Toxicity
7. pH level
8. Heat of combustion
9. Electronegativity
10. Chemical stability
11. Radioactivity
12. Ability to tarnish
13. Enthalpy of formation
14. Solubility
15. Decomposition
15 Chemical Properties
Thermal Property
Properties of a material that is related to its ability to conduct heat.
1. Thermal conductivity
2. Specific heat capacity
3. Thermal expansion
4. Melting point
5. Boiling point
6. Thermal diffusivity
7. Heat of fusion
8. Heat of vaporization
9. Thermal emissivity
10. Glass transition temperature
11. Thermal shock resistance
11 Thermal Properties
Electrical Property
Properties of a material that is related to its ability to conduct electricity.
1.Electrical conductivity
2.Electrical resistivity
3.Dielectric constant
4.Dielectric strength
5.Permittivity
6.Electrical permeability
7.Power factor
8.Insulation resistance
9.Hall effect
10.Superconductivity
10 Electrical Properties
(Characterization) Structures, Properties, Processing, Performance
Materials Tetrahedron composed of?
Metal, Ceramic, Polymer, Composite
Classification of Materials Based on Types
Aerospace, Biomedical, Electronics, Energy Technology and Environmental, Magnetic, Optical, Structural, Smart Materials
Classification of Materials based on Functions
NATURAL Polymers (base on type)
DNA, Rubber, Cellulose, Wool: What kind of Material?
SYNTHETIC Polymers (base on type)
Nylon, Polyester, Teflon, Epoxy: What kind of Material?
Metals and Alloys (base on type)
What are these?

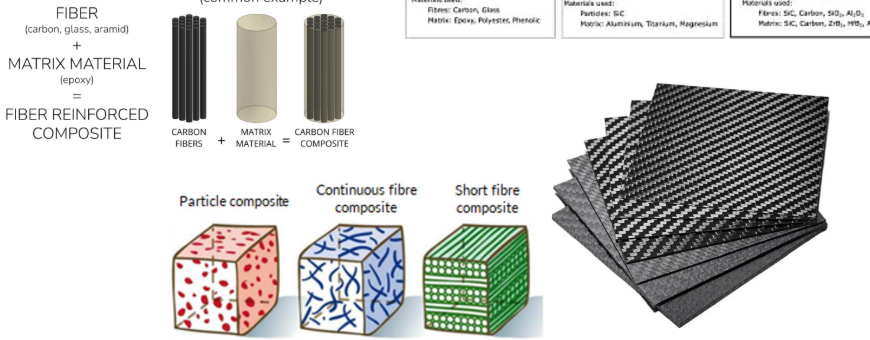
Composites (base on type)
These are?
Ceramics (base on type)
these are?

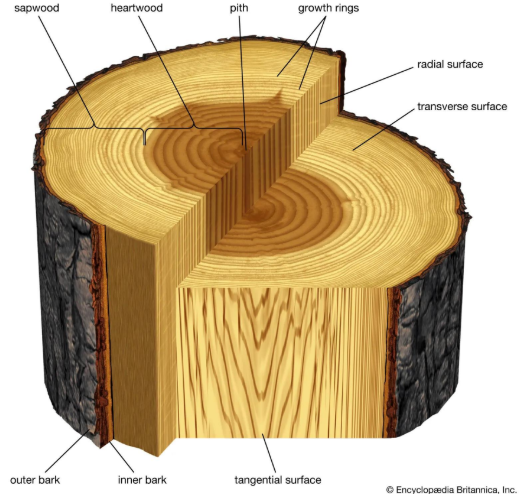
Strucrural Materials (base on Function)
these are?

Smart Materials (base on Function)
these are?
SUBATOMIC LEVEL STRUCTURE
What level of structure is this?
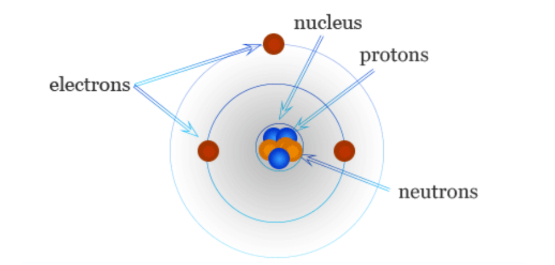
ATOMIC LEVEL STRUCTURE
What level of structure is this?
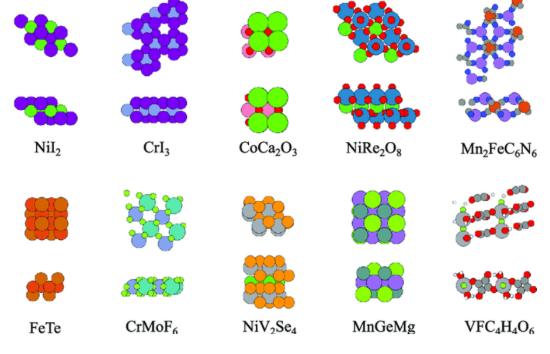
MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE
What level of structure is this?
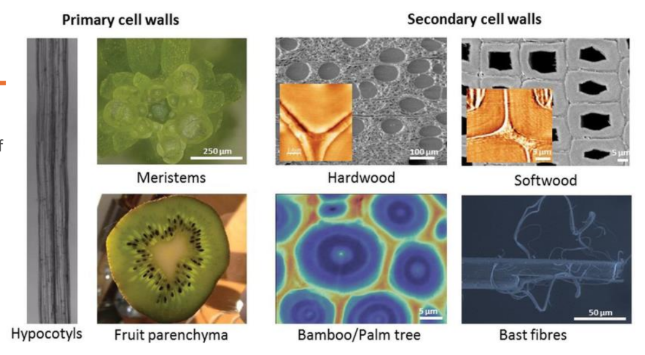
MACROSCOPIC STRUCTURE
What level of structure is this?