Week 4 - Pelvis, Acetabulum, and SI Joints
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering radiographic projections for pelvic fractures (inlet/outlet views), acetabular fractures (Judet views), and sacroiliac (SI) joints, including patient positioning, CR angulation, anatomical demonstration, and common positioning errors.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
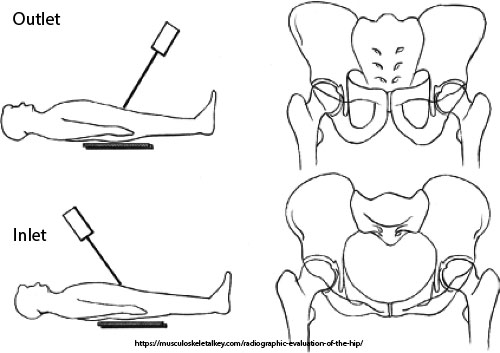
What do inlet and outlet views evaluate?
Pelvic fracture displacement and stability.
What displacement does inlet projection show?
Anterior/posterior displacement.
What displacement does outlet projection show?
Vertical displacement.
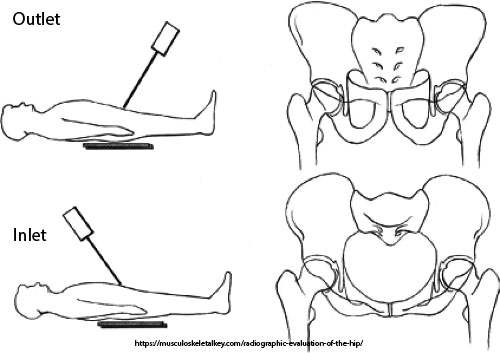
What is the CR angle for an inlet projection?
40° caudad.
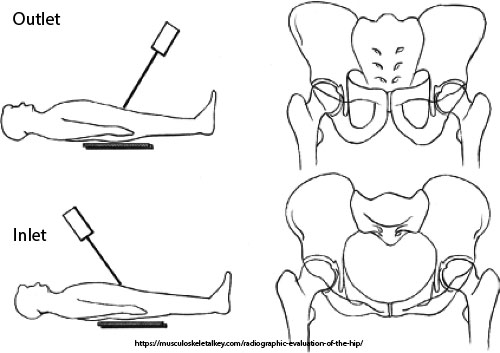
What is the CR angle for an outlet projection (male)?
20–35° cephalad.
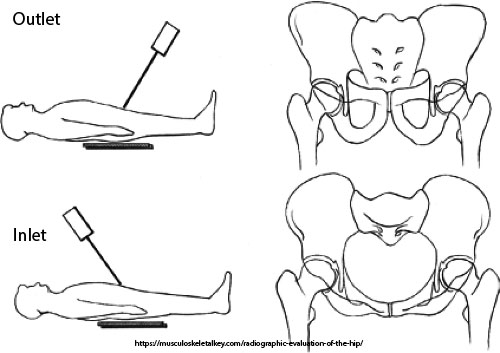
What is the CR angle for an outlet projection (female)?
30–45° cephalad.
What is the patient position for both inlet and outlet projections?
Supine, no rotation, legs extended.
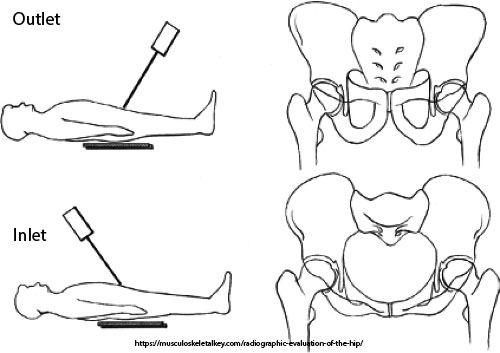
What anatomical structures does the inlet projection demonstrate?
Pelvic brim, anterior pelvis, acetabulum.
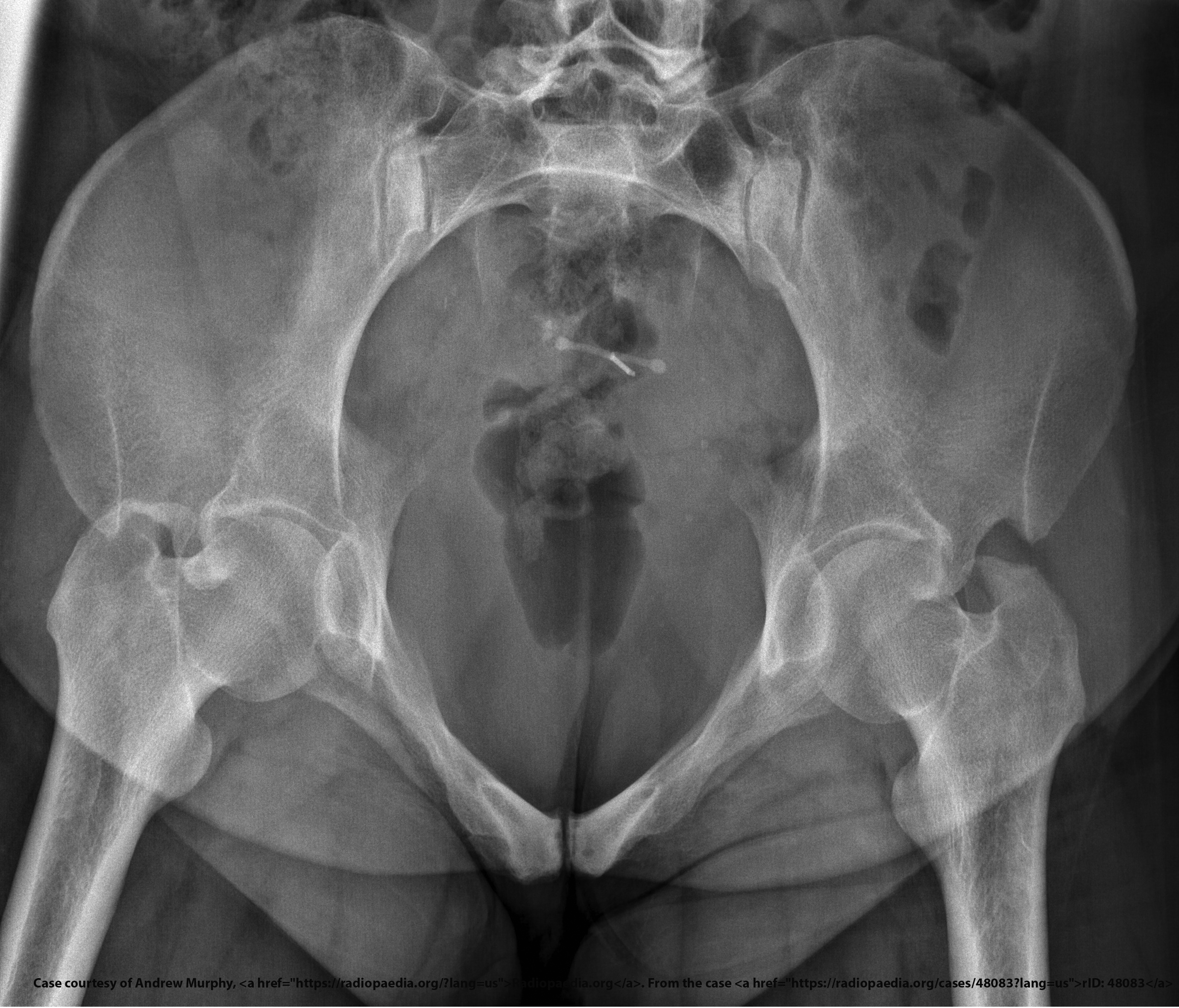
What anatomical structures does the outlet projection demonstrate?
Pubic and ischial bones, hip joints.
What error occurs with insufficient angulation in an outlet projection?
Pubic symphysis (PS) over distal sacrum/coccyx.
What error occurs with excessive angulation in an outlet projection?
Pubic symphysis (PS) over S2.
Which view superimposes pubic rami over the sacrum?
Outlet view.
Which sex requires a greater outlet CR angle?
Females.
Which view shows pubic rami without foreshortening?
Outlet view.
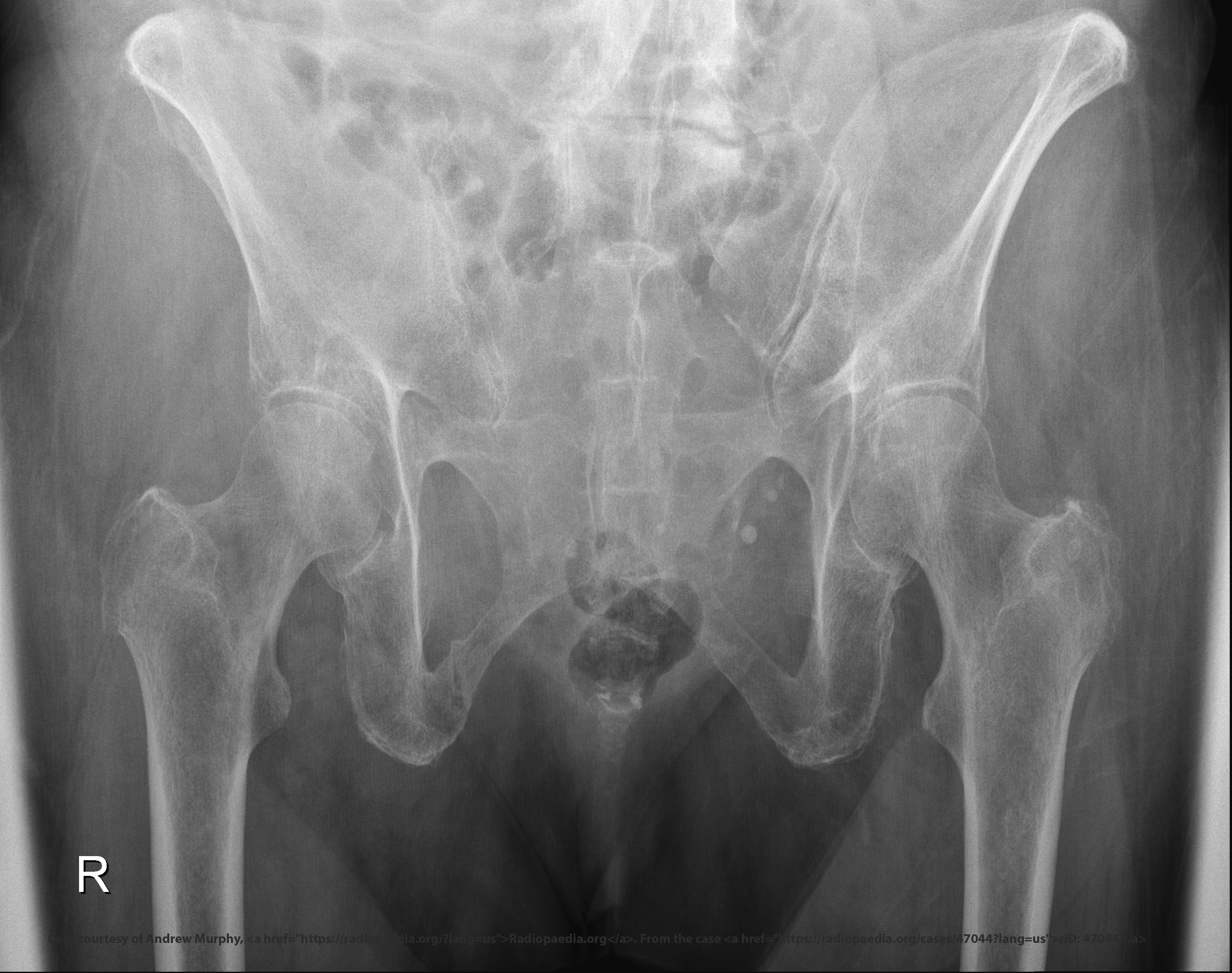
Why are both inlet and outlet views often ordered together?
Each reveals different fracture displacement.
Which projection helps assess anterior-posterior instability?
Inlet.
What are Judet views used for?
Evaluation of acetabular fractures.
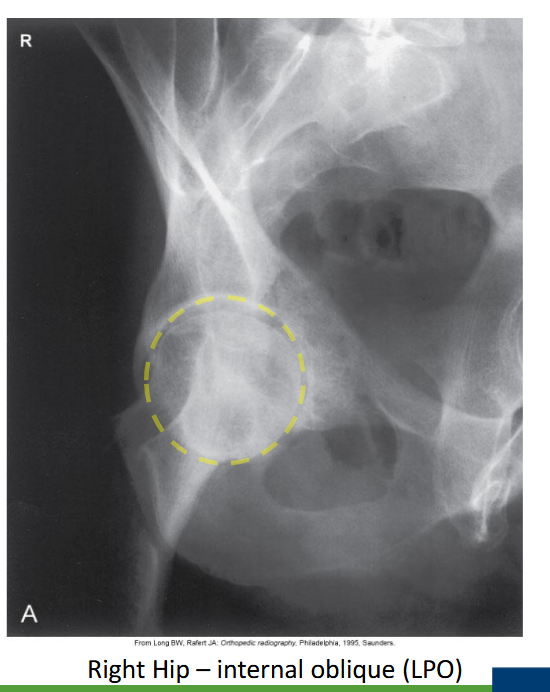
Which acetabular rim does the internal oblique Judet view show?
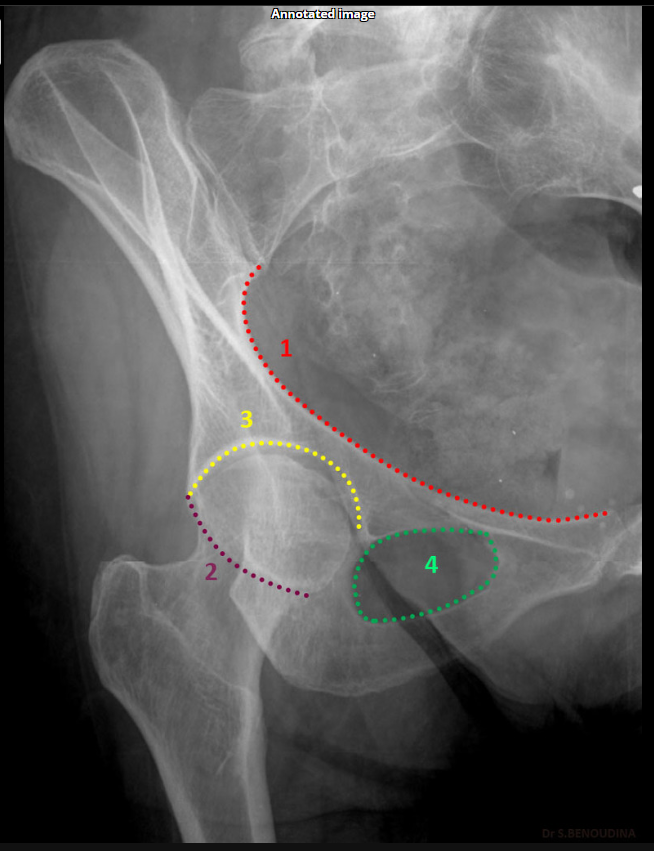
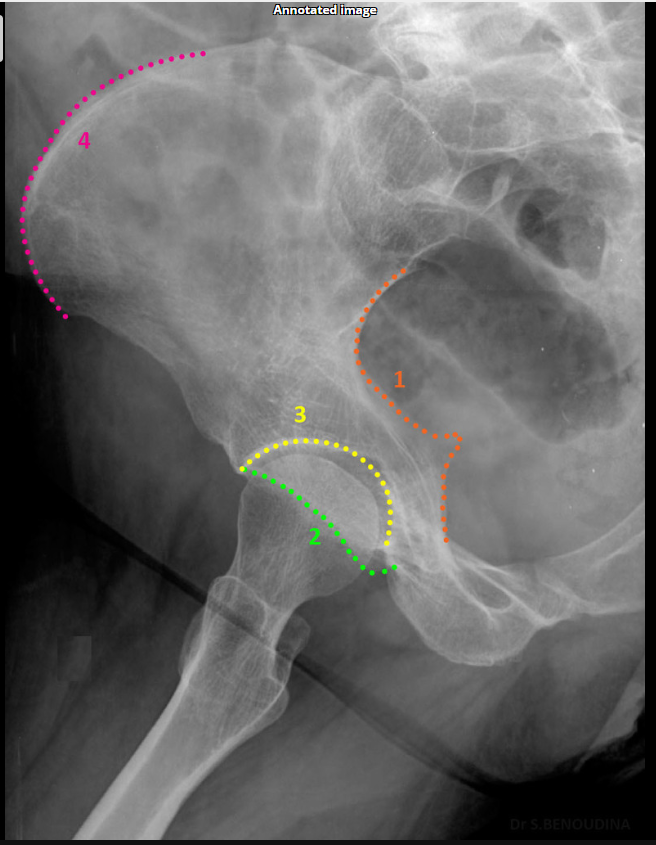
Posterior rim. (SHOWN #2 PURPLE)
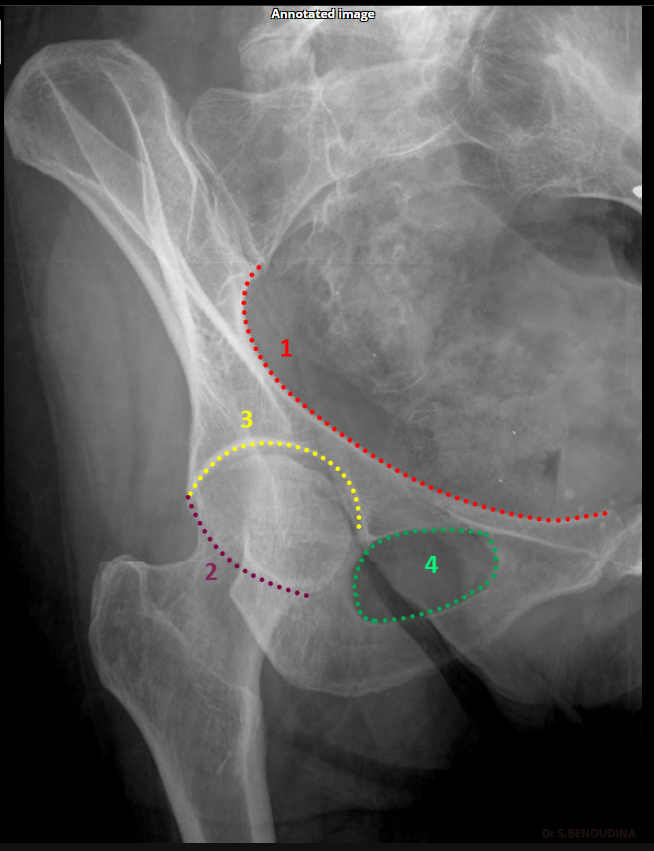
Which acetabular rim does the internal oblique Judet view show?
Anterior column. (SHOWN #1 RED)
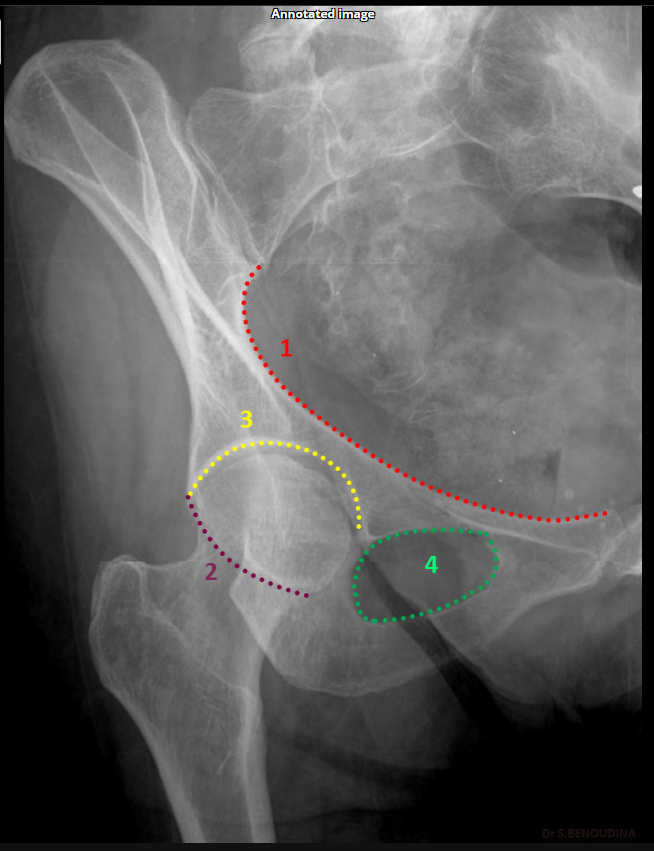
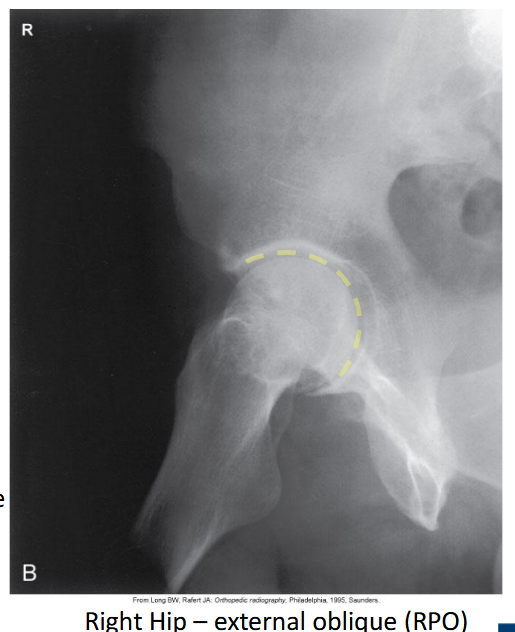
Which acetabular rim does the external oblique Judet view show?
Anterior rim. (SHOWN #2 GREEN)
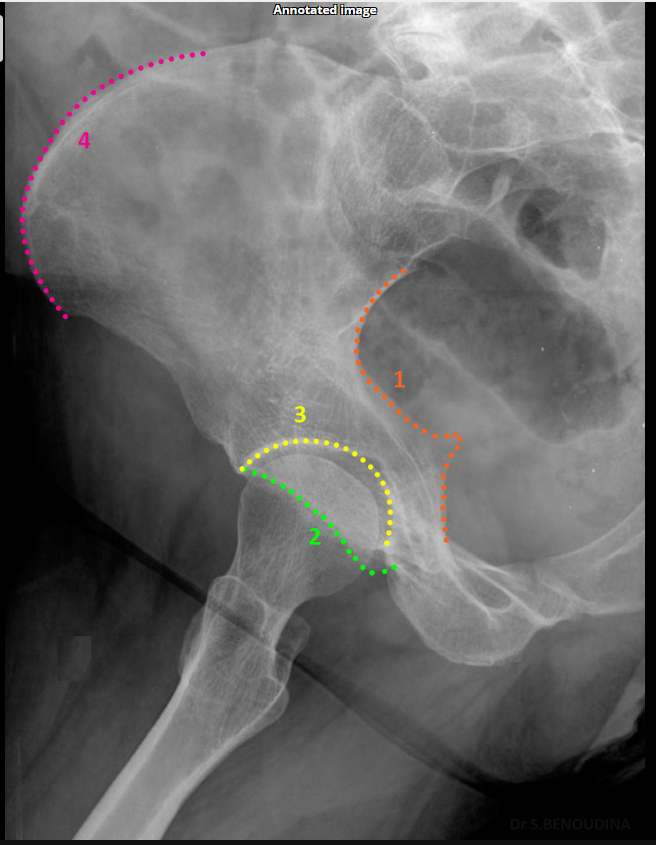
Which acetabular column does the external oblique Judet view show?
Posterior column.ilioschial(SHOWN #1 ORANGE)
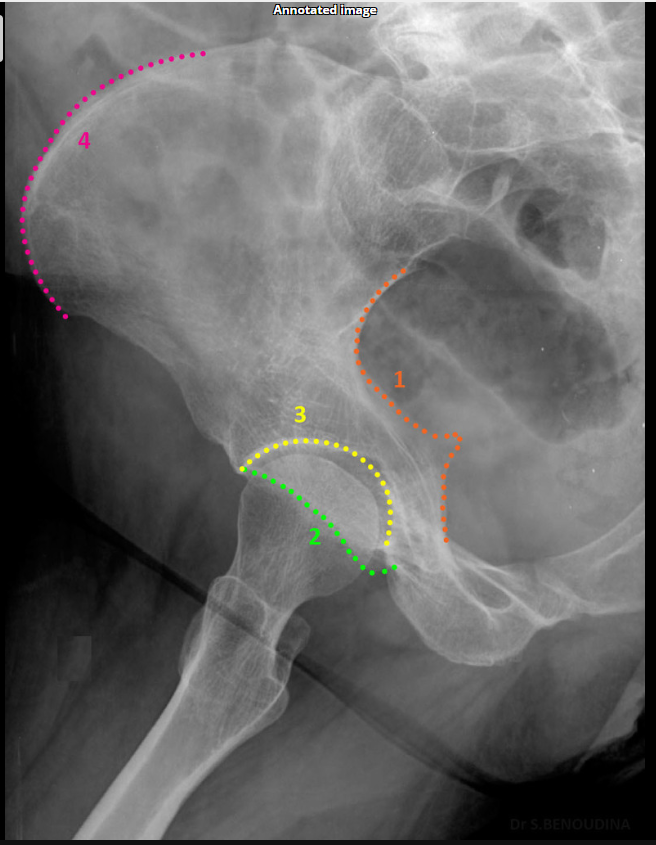
What is the degree of obliquity for Judet views?
45°.
What is the patient position for an internal oblique Judet view?
Affected side raised 45°.
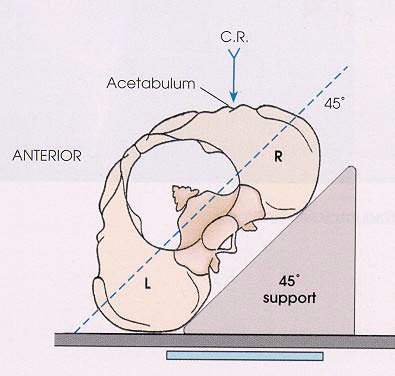
What is the patient position for an external oblique Judet view?
Affected side down 45°.
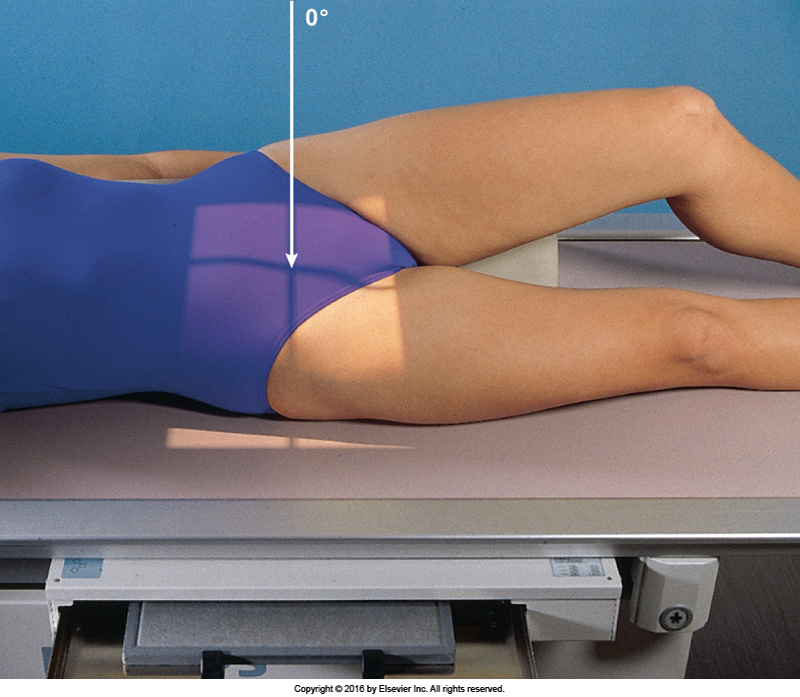
Where is the CR for a bilateral Judet view?
2.5 cm medial & inferior to the raised ASIS.
Where is the CR for a unilateral internal Judet view?
5 cm inferior to the raised ASIS.
Where is the CR for a unilateral external Judet view?
5 cm medial & inferior to the dependent ASIS.
Which oblique Judet view produces an 'O'-shaped acetabulum?
Internal oblique.
Which oblique Judet view produces a 'C'-shaped acetabulum?
External oblique.
What does the iliopubic line represent in Judet views?
Anterior column.(SHOWN #1 RED)
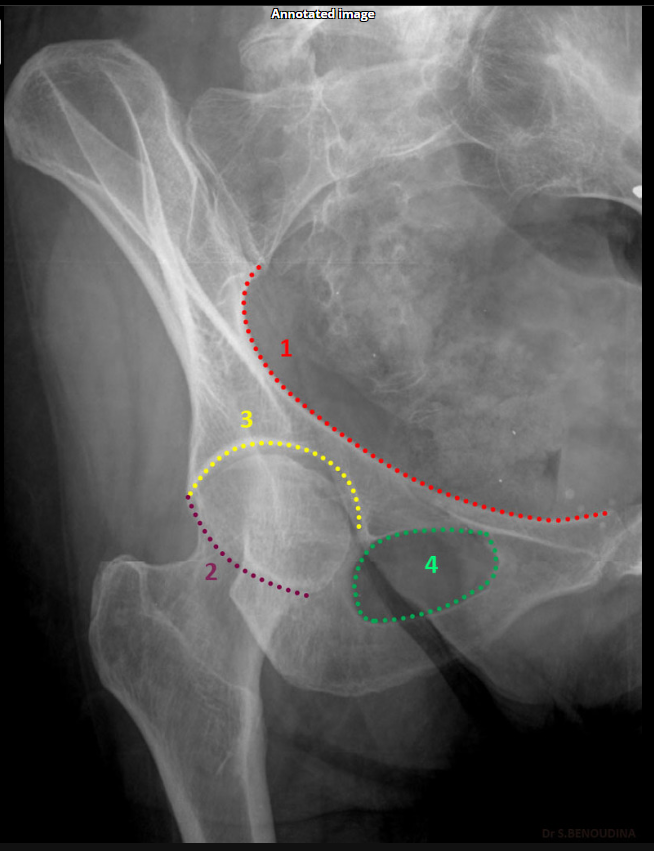
What does the ilioischial line represent in Judet views?
Posterior column.(SHOWN #1, ORANGE)
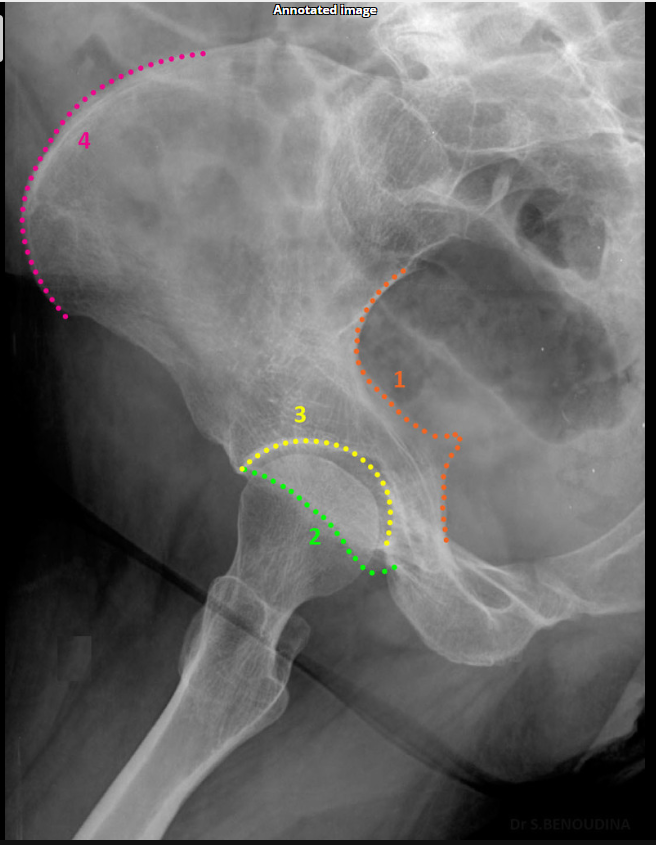
What does minimal overlap at the pubic symphysis indicate in Judet views?
Correct positioning.
Which Judet view shows the obturator foramen widest?
Internal oblique.
Which Judet view narrows the obturator foramen?
External oblique.
Why are Judet views performed in trauma cases?
To assess column involvement in acetabular fractures.
What is the CR angle for an AP axial SI joint projection (male)?
30° cephalad.
What is the CR angle for an AP axial SI joint projection (female)?
35° cephalad.
Where is the CR centered for an AP axial SI joint projection?
5–6 cm below the ASIS.
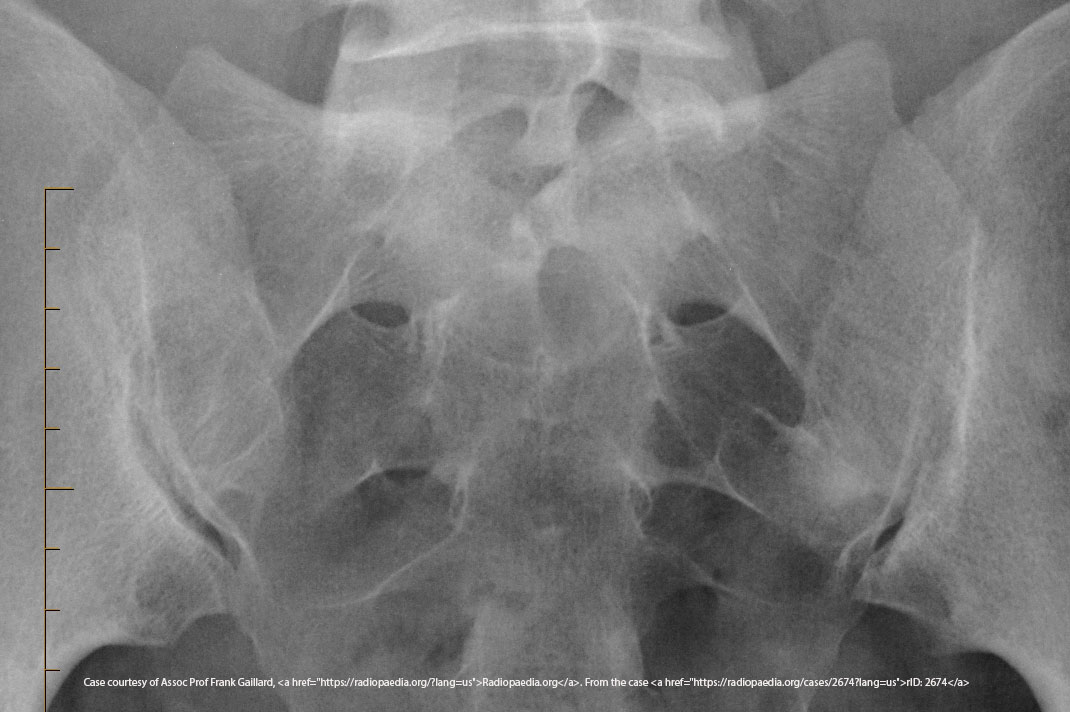
What is the CR angle for a PA axial SI joint projection?
35° caudad.
Where does the CR exit for a PA axial SI joint projection?
ASIS.
Which SI joint is shown in an AP oblique projection?
The joint of the raised side.
What is the degree of obliquity for oblique SI joint projections?
25–30° patient obliqued.
Where is the CR for oblique SI joint projections?
1" medial to the raised ASIS.
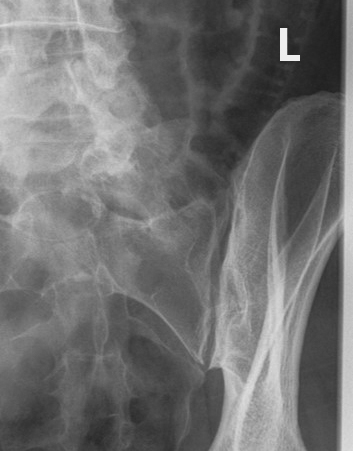
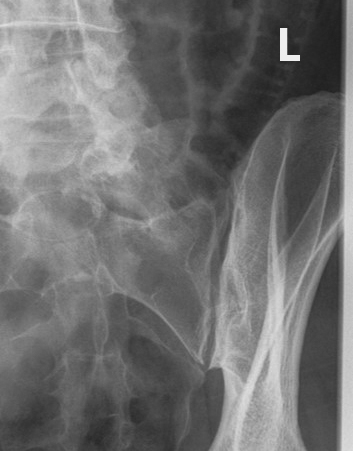
What does excess obliquity do in an oblique SI joint projection?
Closes the inferior joint space.
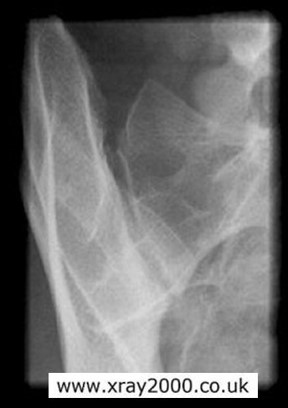
What does insufficient obliquity do in an oblique SI joint projection?
Closes the superior joint space.
What structures are shown in an oblique SI joint projection?
SI joint, sacral ala, ilium.
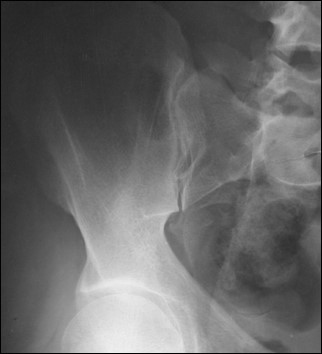
What does an elongated sacrum indicate in an axial SI joint projection?
Correct CR angle.
What indicates no rotation in an AP axial SI joint projection?
Symmetric SI joints.
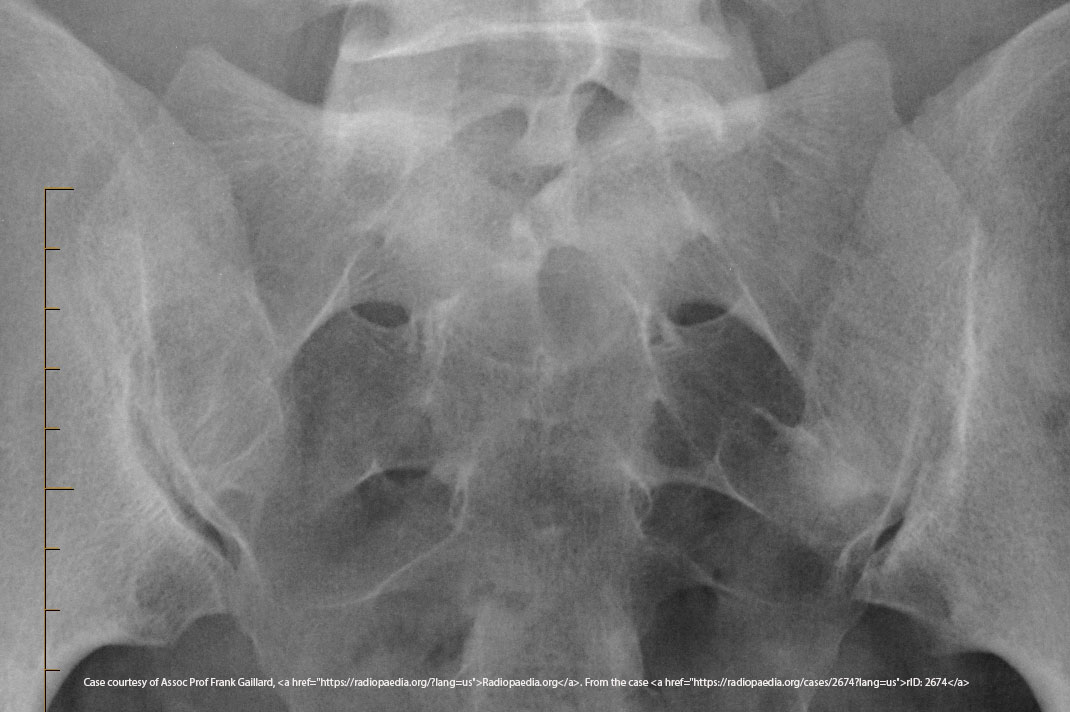
Which projection uses a cephalad CR angle for the SI joints?
AP axial.
Which projection uses a caudad CR angle for the SI joints?
PA axial.
What positioning error closes the SI joint space superiorly in an oblique projection?
Insufficient obliquity.
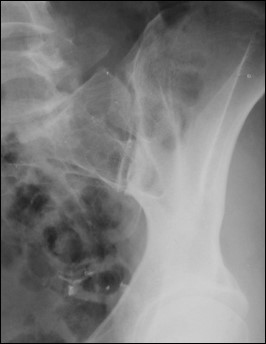
What positioning error closes the SI joint space inferiorly in an oblique projection?
Excess obliquity.