Comprehensive Guide to Integrated Pest Management (IPM) in Turfgrass
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is Integrated Pest Management (IPM)?
A science-based decision-making process that identifies and reduces risks from pests while coordinating pest biology, environmental information, and technology.

What are the main components of IPM?
Cultural practices, species/cultivar selection, proper irrigation/fertilization, mechanical control, natural enemies, and pesticides.
Why is IPM used?
To reduce costs, delay resistance to pesticides, minimize turfgrass injury, and provide health, social, and environmental benefits.
What is the goal of using pesticides in IPM?
To use them responsibly and only when necessary.
What is one successful example of IPM implementation?
Hørsholm Golf in Denmark, where IPM was introduced by the European Union since 2014.
What are the two approaches to implement IPM?
Preventative and reactive approaches.
What is a key best management practice in IPM?
Identify key pests and understand their life cycles to target the correct life stage.
What should be documented in an IPM plan?
Pest control efforts, including non-chemical methods and pesticide usage.
What are some management options in IPM?
Species/cultivar selection, cultural practices, pesticides, alternative control, and decision-supporting tools.
What is the importance of species/cultivar selection in IPM?
To choose resistant varieties, such as tall fescue resistant to brown patch.
What role do cultural practices play in IPM?
They include proper irrigation and fertilization to support healthy turfgrass.
What is the criteria for using pesticides in IPM?
Use only when necessary, prioritize playing surfaces, and choose less harmful active ingredients.
What are characteristics of less harmful active ingredients in pesticides?
Low impact on human health, low toxicity to non-target organisms, and lower potential for groundwater contamination.
What are alternative control methods in IPM?
Mechanical and biological controls.
What is the significance of naturalized areas in IPM?
They promote high diversity, which can help control pest populations naturally.
What should be monitored to assess pest problems in IPM?
Environmental conditions and turf conditions regularly.
What is a critical step after treatment in IPM?
Determine if corrective actions reduced pest populations and were economical.
What is the role of stakeholder collaboration in IPM?
To enhance the effectiveness of pest management strategies through shared knowledge and resources.
What is the purpose of mapping pest outbreak locations?
To identify patterns and susceptible areas for future target applications.
What should be established for key pests in an IPM plan?
Injury and treatment threshold levels.
How does IPM contribute to environmental sustainability?
By minimizing risks to people, property, resources, and the environment while managing pests.
What is the significance of monitoring pest populations?
To make informed decisions regarding damage assessment and control strategies.
What is the role of training personnel in IPM?
To ensure regular monitoring of pests through scouting or trapping.
What is a pest?
Any organism causing a measurable deterioration in the esthetic or functional value of turf.
What are the main types of pests in turf management?
Diseases, weeds, insects, nematodes, and large animals.
What are abiotic pests?
Pests caused by abiotic factors such as nutrient deficiencies and environmental factors.
What are biotic pests?
Pests caused by pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, algae, and fungi.
What are the symptoms of turfgrass diseases?
Leaf lesions, tip dieback, crown or stem damage, and root damage.
What signs indicate the presence of a fungus in turfgrass?
Mycelium or fruiting structures.
What is the disease triangle used for?
To diagnose diseases by examining symptoms, comparing with handbooks, and assessing management practices.
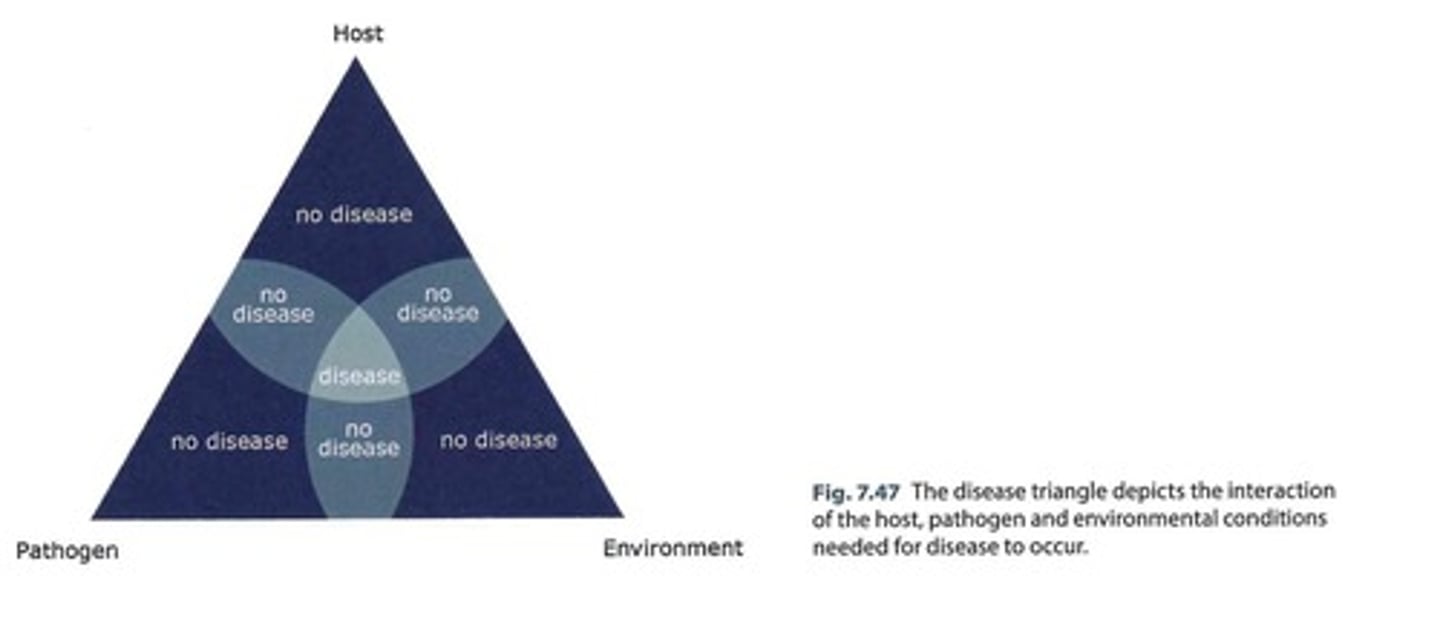
What are common abiotic disorders affecting turfgrass?
Soil moisture stress, air temperature extremes, compact or anaerobic soils, nutrition extremes, equipment damage, and herbicide injury.
What is St. Augustine decline?
A disease caused by the Panicum mosaic virus that weakens infected plants over time.
What are the structures of fungi important for turfgrass disease?
Mycelium, sclerotia, spores, and fruiting structures.
What is dollar spot?
A common turfgrass disease, particularly concerning for creeping bentgrass, that thrives in warm, wet weather.
What conditions favor the development of large patch disease?
Soil temperature dropping below 70°F in the fall.
What is fairy ring in turfgrass?
A condition caused by fungi that can damage turf by making soil hydrophobic or secreting toxins.

What are some common insect pests in turf management?
Billbugs, chinch bugs, fall armyworms, cutworms, sod webworms, white grubs, mole crickets, and fire ants.
What damage can nematodes cause to turfgrass?
They can feed on roots, crowns, and other parts of the plant, causing cell damage.
Name some large animals that can be pests in turf management.
Rodents, moles, dogs, Canada geese, and people.
What should be done when diagnosing turfgrass diseases?
Check Extension websites for publications and contact your County Agent.
How should samples for disease testing be collected?
From areas where the pathogen is active, typically at the edge of symptoms.
What is the role of chemical control in disease management?
To relieve stresses and manage diseases if needed.