Ch 4 Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Three main shapes of bacteria
Bacillus (rod), Coccus (spheres), and Spirillus (spiral)
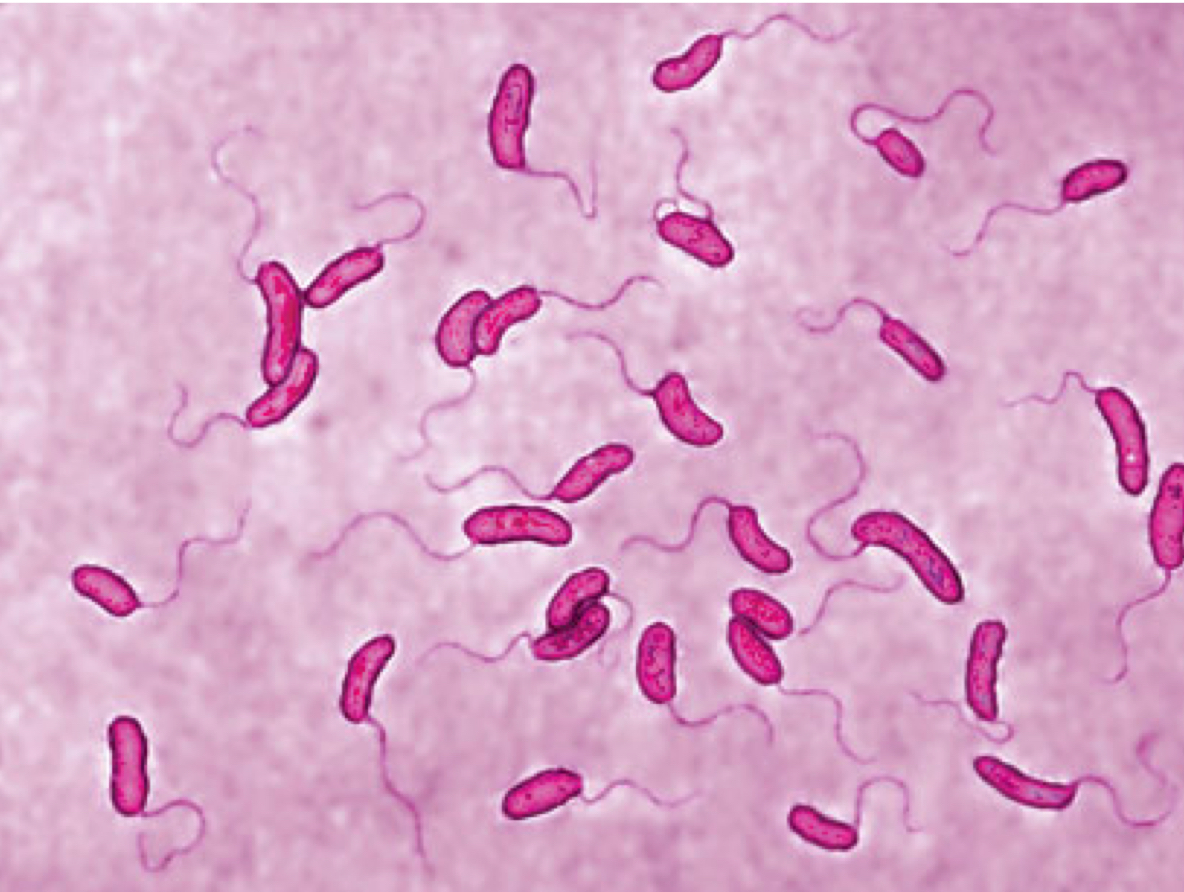
What shape is this?
The shape is Vibrio
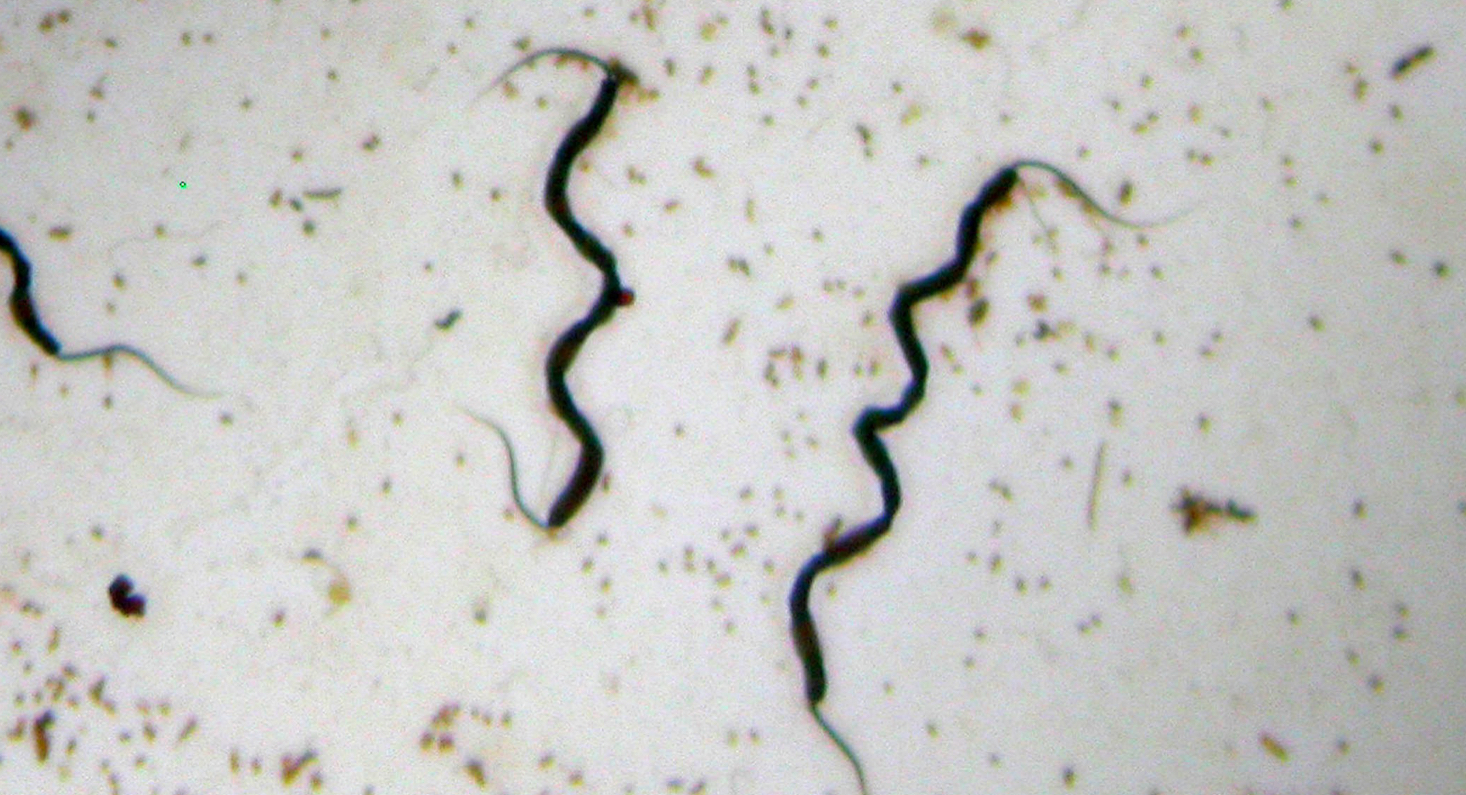
What shape Is this?
The shape is Spirillum
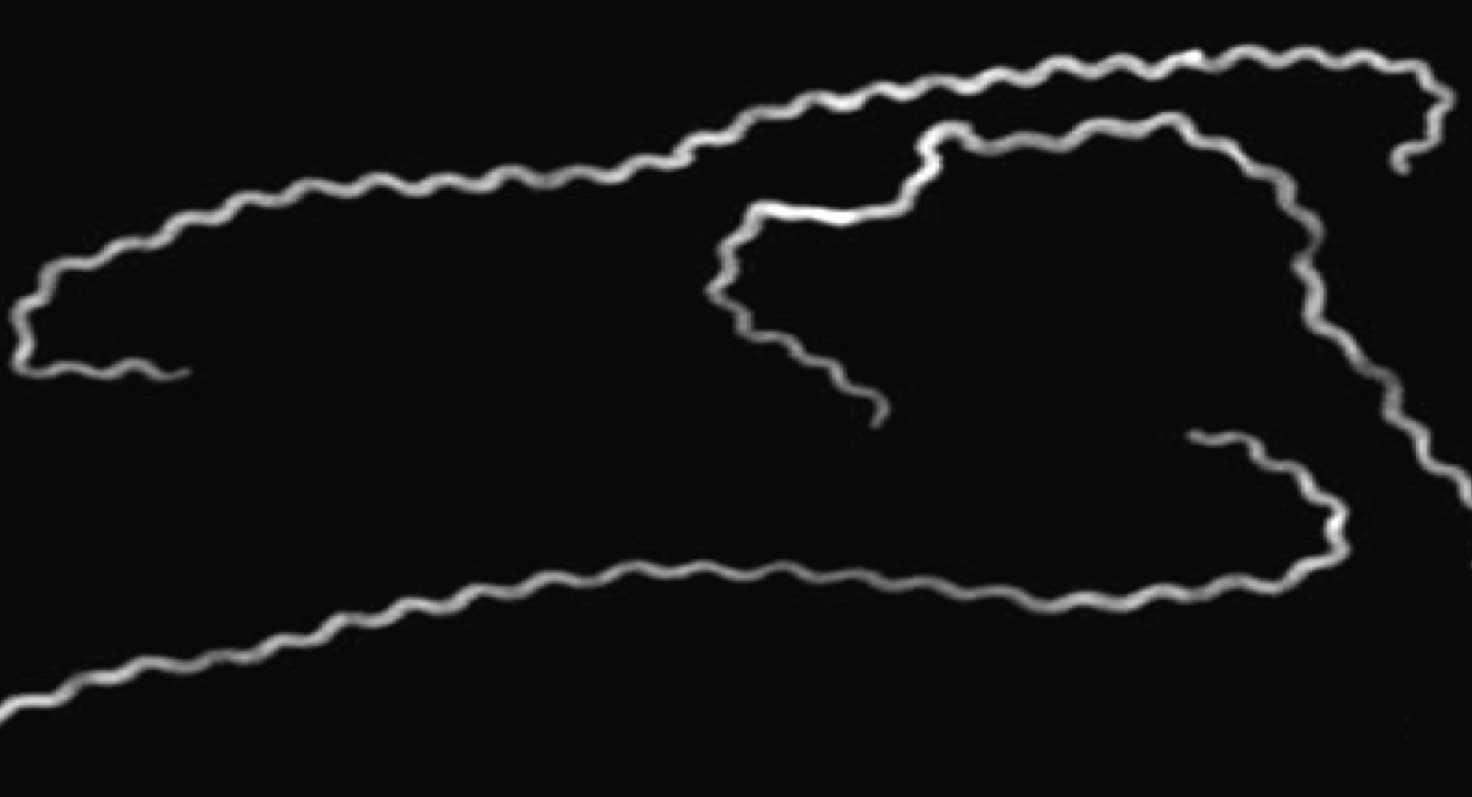

What shape is this?
The shape is Spirochete
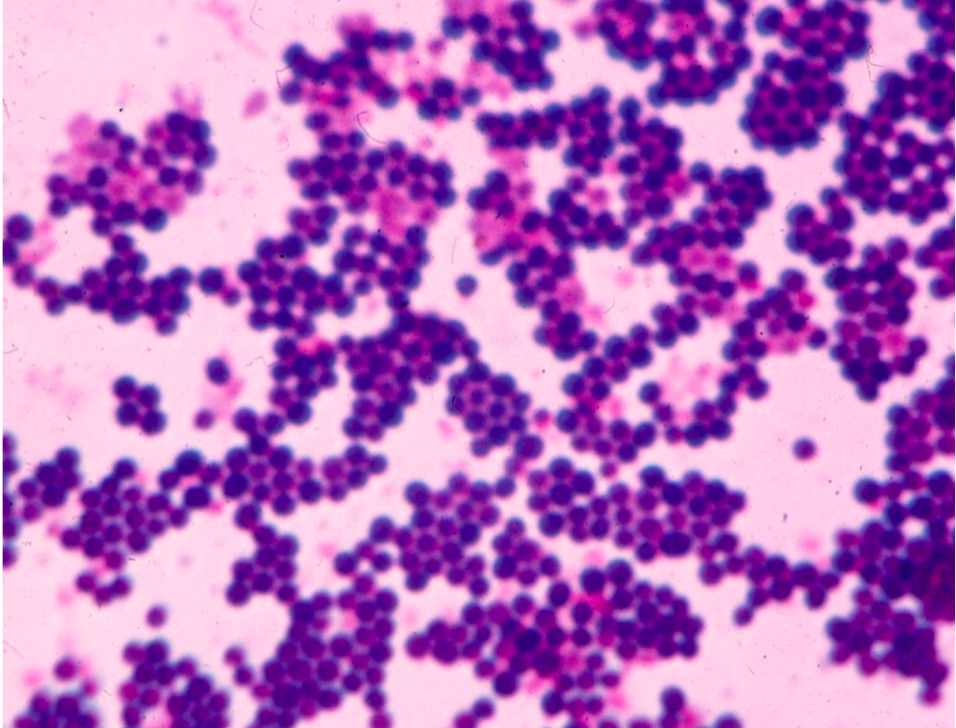
What shape and arrangement is this?
The shape and arrangement is Staphylococcus
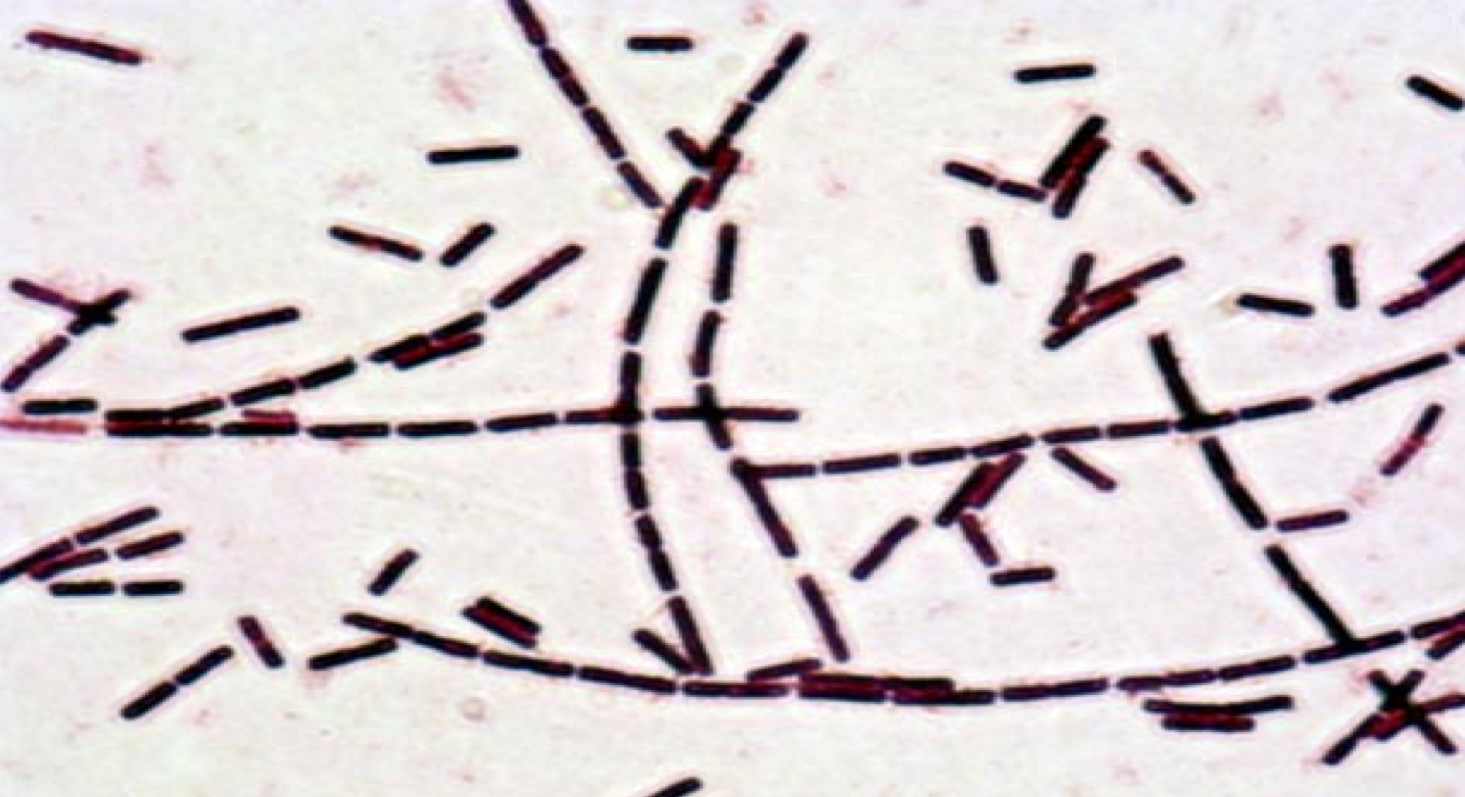
What shape and arrangement is this?
The shape and arrangement is Streptobacillus
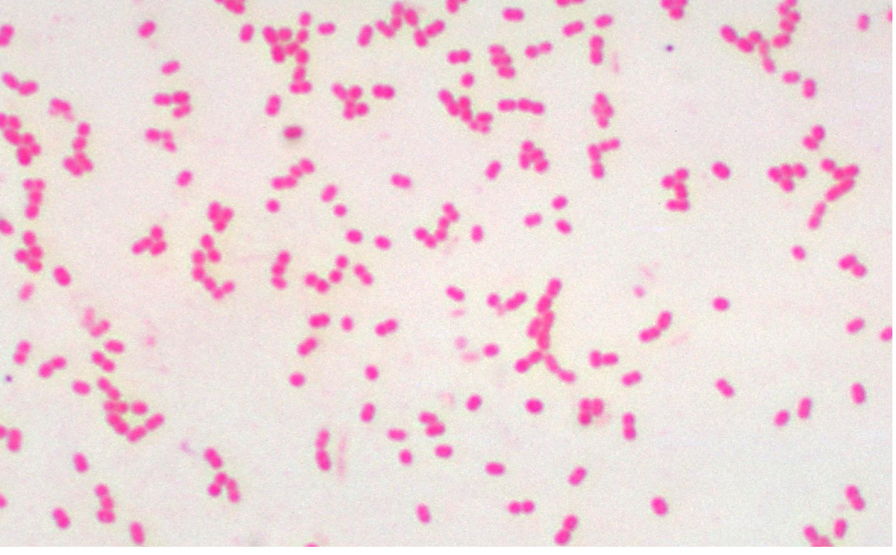
What shape is this?
The shape is Bacillus (singles)
Structures found in all bacteria
Cell membrane (cytoplasmic membrane), Cytoplasm, ribosomes, cytoskeleton, one (or a few) Chromosomes. In most → cell wall, glycocalyx
External structure of a bacterial cell
Appendages: Flagella, pili, frimbriae. Surface layers: S layer, glycocalyx, Capsule slime layer.
Cell envelope of a bacterial cell
(Outer membrane), Cell wall, Plasmic membrane
Internal of Bacterial cells
ribosomes, inclusions, nucleoid/chromosomes, endospore, plasmid,
Cytoplasmic membrane
Phospholipid Bilayer, fluid mosaic. Regulate the passage of materials in and out of the cell. Site for chemical reactions such as ATP synthesis and nutrient processing.
What can pass through a phospholipid bilayer?
Small and neutral (hydrophobic) Molecules
What is a bacterial cell wall made
Peptidoglycan
If the cell wall consists of a cell membrane and a thick layer of Peptidoglycan Then it is what?
Gram-positive cell wall
If the cell wall consists of a cell membrane, thin layer of Peptidoglycan, and outer membrane layer, what is it?
Gram negative cell wall
Peptidoglycan
Rigid mesh like structure and crucial for maintaining cell shape and providing structural support against osmotic pressure. Composed of sugar NAM & NAG strands cross-linked by short peptide chains
Gram-positive cell wall
Made of peptidoglycan (thick) with lipo/teichoic acids in it, And cytoplasmic membrane. More resistant to physical stress.
Gram-negative cell wall
Made of outer membrane with porin protein And lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in it, peptidoglycan (thin), And cytoplasmic membrane. More resistant to chemical stress than physical.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
Found an outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. O-antigen: highly varied among species, important for immune response. Core polysaccharide- connects lipid A to O-antigen. Function as signaling molecules & receptors. Lipid A- anchors into bacterial membrane, endotoxin → induces shock & fever
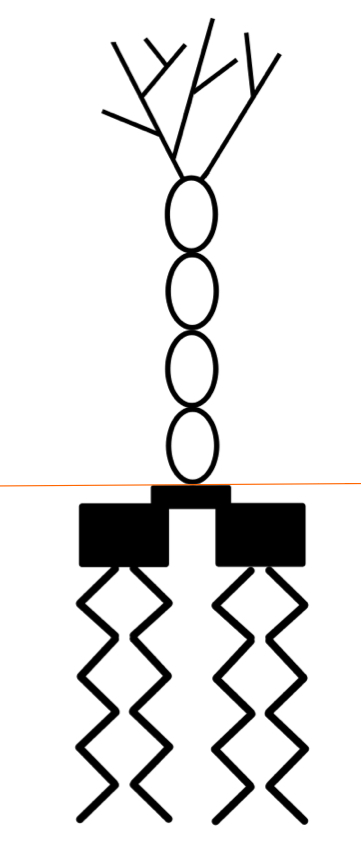
Lipoteichoic acid and teichoic acid
Found in the cell wall of gram-positive bacteria Making the cell negative. Lipo= anchored to lipid. Maintains cell structure, growth, prevents cell breakdown and provides antigenic specificity
What is the surface charge of gram-positive bacteria? Why?
Negative surface charge due to the teichoic and lipoteichoic acids
What is the surface charge of gram-negative bacteria? Why?
Negative surface charge due to the lipopolysaccharides
Functions of the bacterial cell wall
Determine shape, structural support → Resist, bursting or collapsing, due to changes in osmotic pressure
Effect of penicillin on the bacterial cell wall
Anabiotic That affects whether a cell is able to grow/live. Targets peptidoglycan layer, prevents the synthesis of peptide bridges that cross link the glycan chains of pepidoglycan
Lysozome
Natural antimicrobial agent breaking down bacterial cell walls. Primarily target gram positive bacteria, breaking down the Peptidoglycan layer of the cell wall.
What is the purpose of a gram stain?
A way that we are able to distinguish the different types cell walls a bacterial has
Crystal violet stain
Stains both gram positive and gram negative cells purple, because the dye combines with the peptidoglycan
Iodine
The mordant, When applied it forms large crystals with the dye that are not soluble in water
Alcohol in a gram stain
Dissolves the outer membrane of gram negative cells, and the crystal violet iodine is washed out of the thin peptidoglycan layer
Safranin
The counterstain, gram-negative bacteria are colorless after the alcohol wash, it turns the cells pink or red, providing a contrast color to the primary stain (crystal violet)
Mycoplasma
A bacteria with no cell wall, cytoplasmic membrane contains sterols (rigid lipids)
Mycobacterium
Contain mycolic acid (wax) in their cell wall, use acid fast staining
At the cell wall protects the bacterium, why do bacteria need a cell membrane?
The cell membrane regulates transport of substances and is a site of key metabolic processes while the cell wall provides structural support and protect protection
Gram type
Refers to the structural characteristics of the cell wall
Gram reaction
Refers to the observed color of the cells after the gram staining procedure
Morphology
Looks at external features: Shape, size, structure, and color. Helps identify in group organisms
cocci
Round, but not oval, elongated, or flatten on the one side

diplococci
spherical shapes in pairs

Streptococci
Spherical bacteria that remain attached in chain like patterns

Tetrads
Spherical bacteria that divide two planes and remain in groups of four

Sarcinae
Spherical bacteria that divide in three planes and remain attached in groups of eight

Staphylococci
Spherical bacteria that divide in multiple planes and form grape like clusters or broad sheets

Bacilli
Singular rod shaped bacteria, divide only across their short axis

Diplobacilli
Rod shaped bacteria that appear in pairs after division
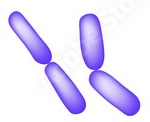
Streptobacilli
Rod shaped bacteria that occur in chains after division

Vibrio
Bacteria that look like curved rods, or comma shaped
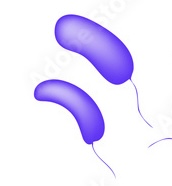
Spirilla / spirillum
Bacteria that have have a helical shape, like a cork shrew, and fairly rigid bodies. Use propeller like external appendages called flagella to move

Spirochete
Then, flexible, spiral shaped bacteria that move in a distinctive corkscrew motion. Move by means of axial filaments

Monomorphic
Maintain a single shape
pleomorphic
can have many shapes, not just one
Bacterial Glycocalyx
(Sugar coat) Substances that surround cells. Viscous (sticky) , Gelatinous polymer that is external to the cell wall and composed of polysaccharide, polypeptide, or both. Made inside the cell and secreted to the cell surface.
Capsule
If the glycocalyx is organized and is firmly attached to the cell wall. Protect pathogenic bacteria from phagocytosis (ingestion and digestion of microbe)
Extracellular polymeric substance (EPS)
Glycocalyx that helps cells in a biofilm attached to their target environment. Protect cells within, facilitates communication among them, and enables the cells to survive by attaching to various surfaces in their natural environment.
Flagella (Singular: Flagellum)
Long filamentous appendages that propel bacteria. Locomotion (rotate 360°)
Slime layer
If the glycocalyx Is unorganized and only loosely attached to the cell wall, Protects against dehydration
What are the three basic parts of flagellum?
Filament: Long outermost region, contains protein flagellin, arranged in several chains that intertwine and form a helix around a hollow core
Hook: Where filament is attached to
Basal body: Anchors the flagellum to the cell wall in plasma membrane
Monotrichous
A single flagellum at one end of cell
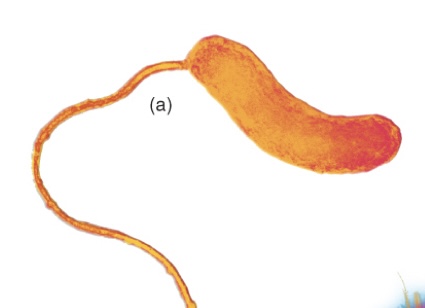
Lophotrichous
Tuft of flagella on one end of the cell
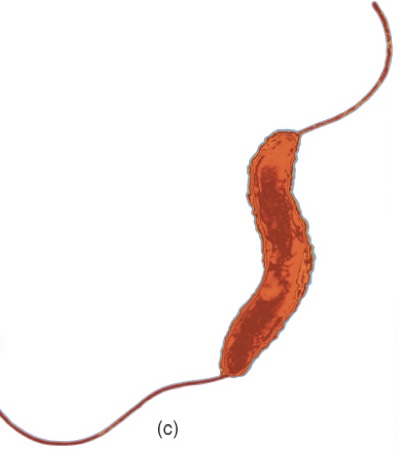
Amphitrichous
One or more flagella on both ends of the cell
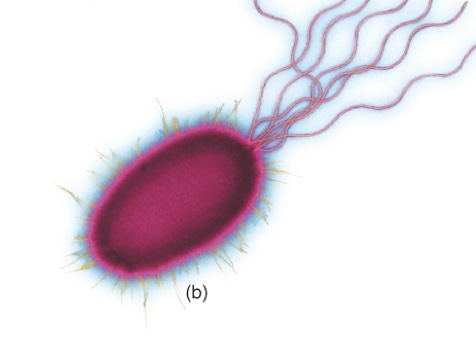
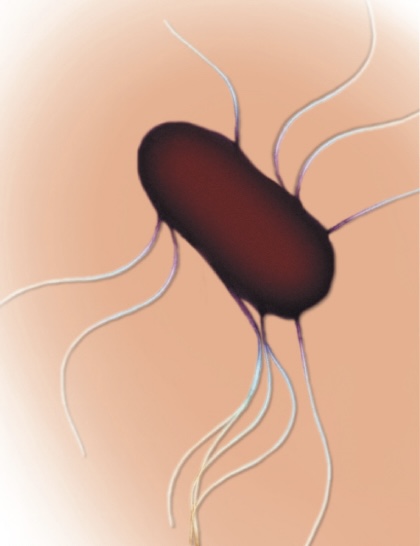
Peritrichous
Flagella distributed all over cell surface
Chemotaxis
Movement in response to chemical signals
Artichous
Bacteria that lack flagella, no projections
Motility
The ability of an organism to move by itself
Positive chemotaxis
Bacteria moving toward a stimulus
Negative chemotaxis
Bacteria moving away from stimulus
Axial filaments
Found on spirochetes , The rotation of filaments producing movement of the outer sheath that propels the spirochetes in a spiral motion (Corkscrew)
fimbriae
Short numerous bristle like fibers made of pilin. Help bacteria attach to each other or the surfaces. Involved in forming bio films.
Pilus
Compose of pilin, Long and few. Attachment of cell to cell to transfer DNA (Conjugation)
S Layer (the armor)
Single layers of thousands of copies of single protein linked together like a tiny chain mail, only made under hostile environment
What can pass through a cell membrane?
small, not charged, nonpolar molecules, Hydrophobic
What cannot pass through a cell membrane?
Large, charged molecules
Simple diffusion
Movement of molecules across the cell membrane without energy, molecules, move down their concentration gradient (High → low Concent.) No proteins required. Small not charged/Not polar molecules
Passive processes
Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, & osmosis
Facilitated diffusion
No energy required, moves down its concentration gradient, a transport protein is required To move across cell membrane(channel or carrier). Large, polar, or charged molecules
Active transport
Requires energy to remove molecules across cell membrane, solute going up concentration gradient [low] → [hi]. Transport protein.
Group translocation
Type of active transport In bacteria, the substance being transported is chemically modified as it Crosses the membrane. Modification traps, the molecule inside the cell.
Osmosis
Passive movement of water molecules across a Selectively permeable membrane, Low solute concentration → High solute concentration
Hypotonic solution
A lower solute concentration outside of the cell compared to inside. Water moves into the cell. Cells can swell and may burst (lysis)
Isotonic solution
Has the same solute concentration inside and outside the cell. Water moves in and out at equal rates.
Hypertonic solution
Higher solute concentration outside the cell compared to inside. Water moves out of the cell. Self shrinks (crenation)
Selective permeability
Certain molecules and ions are allowed to pass through the membrane, but others are stopped
Nucleoid
Dense area within the cell or the DNA aggregates
Plasmid
Extrachromosomal pieces of DNA, not essential to bacterial growth and metabolism. May carry genes for antibiotic resistance, tolerance to toxic metals, the production of toxins, and the synthesis of enzymes.
Ribosomes
Where protein synthesis takes place. Composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) And proteins
Inclusions
Mostly non-membrane bound granules, sometimes membrane-bound or protein encapsulated. Storage in times of excess.
Endospore
Dormant, tough, non-reproductive bodies. Resistant to heat, radiation, and disinfectant chemicals. Sporulation (production of endospores) Occurs due to nutrient depletion. Contain genetic material along with ribosomes and enzymes needed to return to vegetative stage.
Germination
An endospore returns to its vegetative state by this process. Triggered by high heat Or triggering molecules
Why are endospores important from a clinical viewpoint?
They are resistant to processes that normally kill vegetative cells in the food industry. So they are likely to survive underprocessing, and if conditions for gross occur, some species produce toxins and disease
Vegetative cell
A normal, actively growing, And Metabolizing bacterial cell