CEM 141 MSU Final Exam
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Yes because it can be tested and answered though observations and experiments
Consider the question: Is there an attractive force between a pencil and the earth?
Is this a scientific question? [Yes or No]
Because
III. It can be tested and answered through observations and experiments
IV. The answer is already known and we find it online
V. There is no way to design an experiment to answer this question.
Atoms are mostly empty space
Atoms are in constant motion
Which of the following properties ascribed to atoms by the Greeks do we still consider valid?
I. Atoms are mostly empty space
II. The size and shape of the atoms determine a material's properties
III. Atoms are indivisible
IV. Atoms are in constant motion
The cathode ray tube experiment
The beam of particles emitted from the cathode bent toward the positively charged plate.
Electrons are negatively charged. Which experiment provided evidence to support this claim? What is the specific evidence used to support this claim?
Experiment:
I. The gold foil experiment
II. The cathode ray tube experiment
Evidence:
III. Most of the positively charged alpha particles shot at a thin gold foil passed straight through.
IV. A small fraction of the positively charged alpha particles shot at a thin gold foil were deflected.
V. The beam of particles emitted from the cathode bent toward the positively charged plate.
VI. The beam of particles emitted from the cathode behaved the same no matter what type of metal the cathode was made of.
All of the above
Which of the following contain(s) atoms?
a. Heat
b. Light
c. Energy
d. Dust
e. All of the above
III because the alpha particles go straight through the atom because it is mostly empty space.
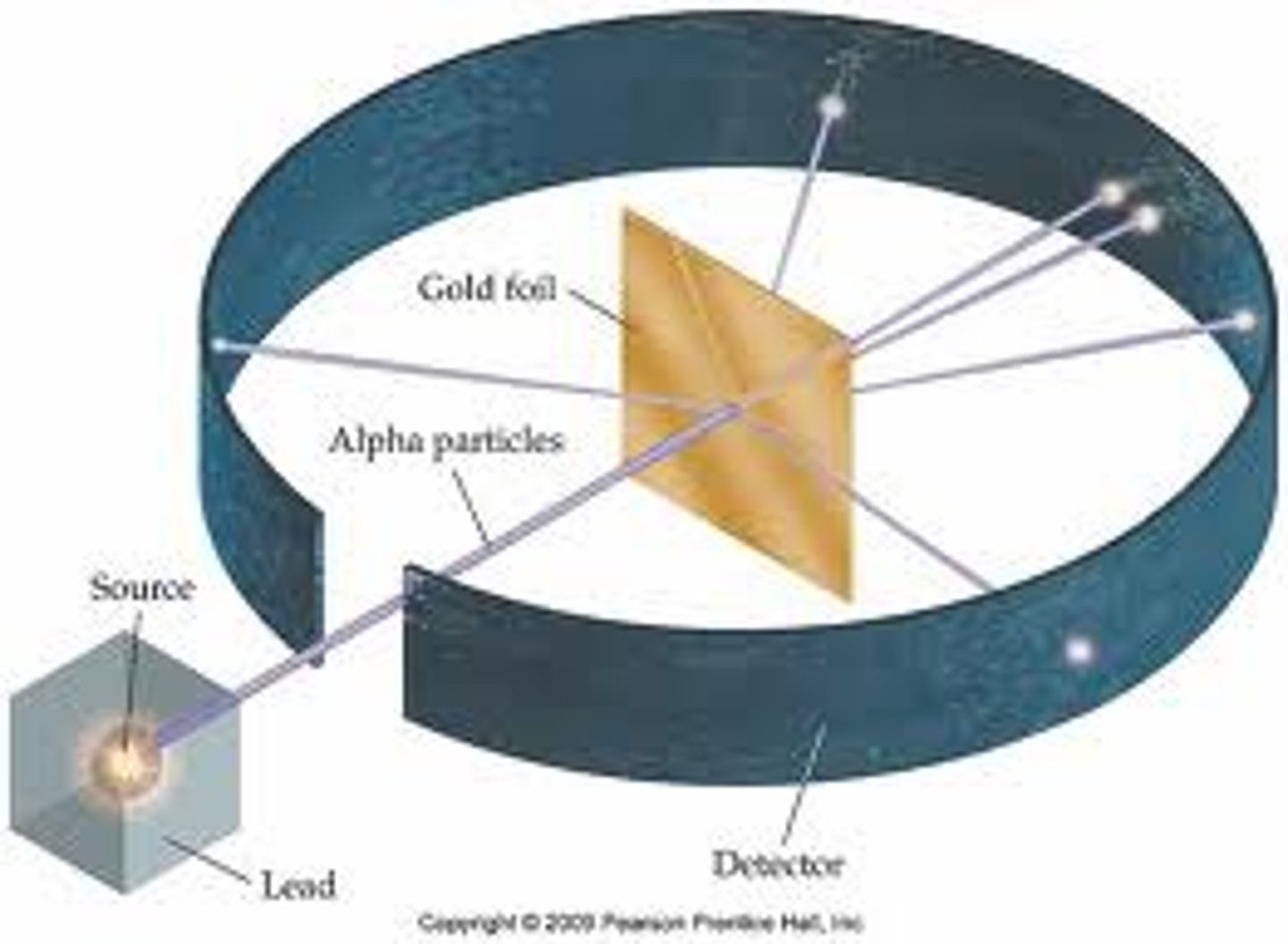
The diagram below shows alpha particles being fired at a piece of gold foil. Where will the majority of the alpha particles be detected (point I, II, or III) and why?
IV. Alpha particles bounce off the nuclei within the gold atoms because the nuclei are much more massive than the alpha particles.
V. The alpha particles are repelled when they come close to the nuclei because both are charged.
VI. The alpha particles go straight through the atom because it is mostly empty space.
All atoms are indivisible and indestructable
Thomson's cathode ray tube experiment proved FALSE what part of Dalton's atomic theory?
a. All atoms are indivisible and indestructible
b. All atoms of a given element are identical
c. All matter is made of atoms.
d. Compounds are formed from the combination of two or more elements.
e. Chemical reactions are rearranging of atoms
The electrostatic force would become stronger
How would the strength of the electrostatic force change if the distance between the two charged objects decreased?
a. The electrostatic force would become stronger
b. The electrostatic force would become weaker
c. The electrostatic force would become stronger or weaker depending on whether the force is attractive or repulsive.
d. It is impossible to say from the information given.
True because an element is made up of one type of atom. Nitrogen is an element that exists as diatomic molecules.
Consider the following statement: "A nitrogen molecule is made up of the same type of atoms." Is this statement true or false and why?
I. True
II. False
III. An element is made up of one type of atom. Nitrogen is an element that exists as diatomic molecules.
IV. Nitrogen is a compound that exists as diatomic molecules. Compounds are made of different types of atoms.
V. Nitrogen is an element and therefore must exist as separate atoms and not molecules.
Because the repulsive force between the overlapping electron clouds is dominant
Why does the potential energy increase as two xenon atoms move extremely close together?
a. Because the kinetic energy decreases as the atoms slow down.
b. Because the electrostatic attractive force from the instantaneous dipoles is dominant.
c. Because the repulsive force between the overlapping electron clouds is dominant.
d. Because there is more potential energy than kinetic energy when the atoms are close together.
The partial positive end of one atom's instantaneous dipole attracts the partial negative end of the neighboring atom's induced dipole.
Which statement best describes the forces that exist between helium atoms in the solid state?
a. The electron cloud on one helium atom is attracted to the electron cloud on the other atom.
b. The nucleus of one helium atom is repelled by the nucleus of the neighboring atom.
c. The helium atoms share electrons, forming a bond.
d. The partial positive end of one atom's instantaneous dipole attracts the partial negative end of the neighboring atom's induced dipole.
e. Both atoms have mass, so they are attracted to each other by gravitational forces.
Energy is released
A molecule is formed
When a covalent bond is formed between two nitrogen atoms:
I. Energy is absorbed
II. Energy is released
III. A molecule is formed
IV. The nitrogen changes from the gaseous to the liquid state.
Weaker because neon has a smaller electron cloud, therefore there will be a smaller separation of charge resulting in a weaker force.
The London dispersion force between two neon atoms compared to the London dispersion force between two argon atoms where both systems are the most stable is:
I. The same
II. Stronger
III. Weaker
Because:
IV. They are both noble gasses
V. Neon has a smaller electron cloud, therefore there will be a smaller separation of charge resulting in a weaker force.
VI. Neon has a smaller electron cloud, therefore there will be a larger separation of charge resulting in a stronger force.
True because there are LDFs in both the solid state and the liquid state, but more in a solid state
Is the following statement true or false?
When chlorine freezes, LDFs are formed.
This statement is:
I. True
II. False
Because:
III. When a substance freezes, covalent bonds are formed
IV. There are LDFs in both the solid state and the liquid state, but more in the solid state.
V. There are LDFs in the solid state, but not in the liquid state
F2 because the LDFs between fluorine molecules are stronger, requiring more energy to overcome.
Which do you predict to have a higher boiling point, fluorine (F2) or neon (Ne) and why?
a. Ne because the smaller atoms are packed more tightly together and harder to break apart.
b. Ne because the LDFs between neon atoms are stronger, requiring more energy to overcome.
c. F2 because the covalent bonds between fluorine atoms are stronger, requiring more energy to overcome
d. F2 because the LDFs between fluorine molecules are stronger, requiring more energy to overcome.
3.011x10^24 H atoms
How many hydrogen atoms are there in one mole of CH2Cl2?
5
Ammonia reacts with oxygen to produce nitric oxide in water. Balance the equation using small, whole number coefficients:
______ NH3 + ______ O2 --> ______ NO + ______ H2O
What is the coefficient for oxygen (O2)?
84%
Hydrogen reacts with oxygen to produce water according to the following equation:
2 H2 + O2 --> 2 H2O
You start a reaction with 53 grams of H2 and excess O2 and you end up producing 400 grams of H2O. What is the percent yield of this reaction?
When light shines through on a double slit, a pattern of bright and dark lines appear. Waves of light interfere constructively when they arrive in-phase and destructively when they arrive out-of-phase.
Select the evidence and reasoning that supports the claim that light is a wave.
Evidence:
I. When light shines on a piece of metal, electrons are ejected.
II. When light shines through a double slit, a pattern of bright and dark lines appear
III. When light shines on a sample of atoms, some of the light is absorbed.
Reasoning:
IV: Different waves of light are absorbed by the electrons in atoms depending on which element is present.
V. Waves of light interfere constructively when they arrive in-phase and destructively when they arrive out-of-phase.
VI. Waves of light transfer their energy to electrons, overcoming the electrostatic attraction with the nucleus.
The absorbtion lines for hydrogen would appear at exactly the same wavelengths because the energies of the photons emitted and absorbed by hydrogen are the same.
Hydrogen produces emission lines (colored lines on the spectrum) with the following wavelengths: 410 nm, 434 nm, and 656 nm. Where would you expect to see the absorbtion lines (dark lines) for hydrogen on its absorbtion spectrum and why?
a. The absorbtion lines for hydrogen would appear at exactly the same wavelengths because the energies of the photons emitted and absorbed by hydrogen are the same.
b. The absorbtion lines for hydrogen would appear at shorter wavelengths than the emission lines because the energies of the photons absorbed are higher than the energies of the photons emitted by hydrogen.
c. The absorbtion lines for hydrogen would appear at longer wavelengths than the emission lines because the energies of the photons absorbed are lower than the energies of the photons emitted by hydrogen.
d. The absorbtion lines for hydrogen would be red-shifted because of the doppler effect.
When light shines on metal, there is a threshold frequency, below which no electrons are ejected from a metal.
What is the evidence that supports the claim that light is a particle?
a. When light shines through a double slit, the light produces an interference pattern.
b. Increasing the amplitude makes light appear brighter
c. When light shines on metal, there is a threshold frequency, below which no electrons are ejected from a metal.
d. Electrons produce an interference pattern.
e. Electrons absorb certain photons of light to move to higher energy levels. The electrons can emit the photon to move back to the lower energy level.
1x10^4 m
An MRI machine operates at a frequency of 30 kilohertz (kHz), what wavelength radiation does this correspond to?
a. 1x10^10 m
b. 1x10^7 m
c. 1x10^5 m
d. 1x10^4 m
The wavelength of the electron is similar in size to the atom and affects its properties, whereas the wavelength of the macroscopic object is much smaller than the object and does not affect its properties.
Why must we consider the wave properties of an electron, but not the wave properties of macroscopic objects (such as humans)?
a. Only very small pieces of matter (such as electrons) are waves, whereas macroscopic objects are not.
b. We can calculate the wavelength of an electron but cannot calculate the wavelength for a macroscopic object using the de Broglie equation.
c. The wavelength of the electron is similar in size to the atom and affects its properties, whereas the wavelength of the macroscopic object is much smaller than the object and does not affect its properties.
d. We cannot tell if electrons are waves or particles because they are too small to see. Since we can see macroscopic objects, we can confirm they are not waves.
The valence electrons have different energies
The valence electrons are in different size orbitals
Write the electron configuration for fluorine (F) and the electron configuration for chlorine (Cl). What is different about the valence electrons in these two atoms?
I. There are different numbers of valence electrons
II. The valence electrons have different energies
III. The valence electrons are in different types of orbitals (s, p, d, f).
IV. The valence electrons are in different size orbitals.
1s2,2s2,2p6,3s1
What is the electron configuration of Mg+?
a. 1s2,2s2,2p6,3s2
b. 1s2,2s2,2p6,3s1
c. 1s2,2s2,2p6
d. 1s2,2s2,2p5
e. 1s2,2s2,2p6,3s2,3p3
f. 1s2,2s2,2p6,3s2,3p4
Cl- is larger because fewer protons are attracting the same number of electrons as in K+
Consider K+ and Cl-. Which do you predict is larger and why?
a. K+ is larger because potassium (K) is farther to the left and further down the table than chlorine (Cl).
b. K+ is larger because it contains more electrons so there are more electron-electron repulsions
c. K+ and Cl- are the same size because they both contain the same number of electrons so there is the same amount of electron-electron repulsion.
d. Cl- is larger because anions are always larger than cations.
e. Cl- is larger because fewer protons are attracting the same number of electrons as in K+
Decreases because the relative attraction between the protons and the outer electrons increases
Atomic radius _______________ from left to right across a row on the periodic table.
I. Increases
II. Decreases
Because:
III. The number of electrons increases
IV. The mass increases
V. The relative attraction between the protons and the outer electrons increases.
46 core and 7 valence
How many core and valence electrons does one atom of Iodine (I) have?
a. 36 core and 17 valence
b. 7 core and 36 valence
c. 36 core and 7 valence
d. 46 core and 7 valence
Part of the mass of the reactants is converted into energy
Nuclear reactions can release large amounts of energy because:
a. Covalent bonds form during a nuclear reaction so energy is released.
b. Part of the mass of the reactants is converted into energy.
c. Collisions between the reactants transfer energy into the surroundings.
d. The strong nuclear force squeezes energy out of the nuclei.
We cannot predict the state of matter because we don't know about the bonding/interactions present within C.
At room temperature, substance A is a solid and substance B is a gas. A and B react according to the following equation:
A +3B --> C
At room temperature, what state of matter do you predict for substance C?
a. Solid, because C is heavier than A or B
b. Gas, because C is three parts B (which is a gas) and one part A (which is a solid).
c. Liquid, because C will be intermediate between a solid and a gas.
d. We cannot predict the state of matter because we don't know about the bonding/interactions present within C.
In graphite, there are unhybridized p-orbitals that extend over the entire sheet forming a delocalized pi bonding network where electrons are free to move.
Carbon can exist in many forms known as allotropes. Two such allotropes are diamond and graphite. Unlike diamond, graphite conducts electricity. This is because:
a. In graphite, there are hybrid orbitals used for bonding that contain electrons.
b. In diamond, all of the electrons are in sigma bonds, which allows conductivity of electricity.
c. In graphite, there are unhybridized p-orbitals that extend over the entire sheet forming a delocalized pi bonding network where electrons are free to move.
d. In diamond, the bonding electrons have enough energy and can therefore conduct electricity.
When the nuclei move relative to one another, the valence electrons act as glue holding them together.
What is the best explanation for why metals are ductile?
a. Valence electrons carry charge anywhere within molecular orbitals that can span the metal.
b. Photons are absorbed and re-emitted
c. Metallic bonds involve delocalized electrons whereas covalent bonds involve localized electrons.
d. When the nuclei move relative to one another, the valence electrons act as the glue holding them together.
Cl2 because when this substance boils, LDFs are overcome and the strength of LDFs depends on the size of the electron cloud
Which do you predict has the higher boiling point and why?
I. Cl2
II. Ar
Because:
III. When this substance boils, covalent bonds are overcome
IV. When this substance boils, LDFs are overcome
V. Covalent bonds are stronger than LDFs
VI. The strength of the LDFs depends on the size of the electron cloud
There are covalent bonds between boron and nitrogen atoms which exist in a 3D network.
Boron nitride is the second hardest substance known (next to diamond). It has a very high melting point but does not conduct electricity. What types of bonding do you think is present in boron nitride?
a. There is covalent bonding within two-dimensional layers of alternating boron and nitrogen molecules, with London dispersion forces between the layers.
b. There is covalent bonding within boron nitride molecules (BN), and LDFs between the molecules.
c. There is a three dimensional network of metallic bonds between boron and nitrogen atoms.
d. There are covalent bonds between boron and nitrogen atoms which exist in 3D network.
e. It is not possible to predict the type of bonding from a consideration of bulk properties.
2 lone pair
Draw the Lewis structure for sulfur dichloride, SCl2. How many lone pair of electrons are on the sulfur atom?
a. 0 lone pair
b. 1 lone pair
c. 2 lone pairs
d. 3 lone pairs
e. 4 lone pairs
London dispersion forces
Draw the Lewis structure for a nitrogen molecule, N2. When nitrogen melts, what interaction(s) are overcome?
a. London dispersion forces
b. London dispersion forces and covalent bonds
c. London dispersion forces and hydrogen bonds
d. London dispersion forces, hydrogen bonds, and covalent bonds
e. Covalent bonds