Genetics Ramaswami lecture 3
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
what is the name of the short DNA sequences which can be chemically synthesised?
oligonucleoties
are oligos usually single or double stranded?
single
how long are oligos usually?
21 to 29 bases
outline the 3 major steps of PCR (denaturation, annealing and extension)
denaturation by increasing the temp to 95C to separate the two DNA strands
annealing of primers by reducing the temp to 50-60C
extension of a new complementary dna sequence by dNTPs and Taq pol
amplification of the target DNA proceeds … in PCR
exponentially
what technique is used for rapid diagnosis of viruses which use reverse transcriptase?
rRT PCR
rRT PCR amplifies what?
cDNA produced by reverse transcriptase from viral mRNA
which enzyme is used to convert the viral RNA into cDNA which is then amplified with PCR and used during fluorescence based product detection to identify infections of SARS CoV 2?
reverse transcriptase
what genome does SARS CoV 2 (virus which causes covid 19) have?
+ssRNA
in real time fluorescence detection:
a fluorescent … or … binds only to the amplified target dsDNA
the PCR machine measures … after each cycle, so you see the amplification curve in real time
dye or probe
fluorescence
in quantification of real time fluorescence detection: the lower the number of cycles needed to reach a certain fluorescence threshold, the higher the levels of … in the sample
viral RNA
PCR is used in genotyping of alleles which show what kind of polymorphism?
length polymorphism
what does VNTRs stand for
variable number of tandem repeats
region of DNA where a sequence is repeated multiple times
tandem repeat
are tandem repeats found in the coding or noncoding DNA?
noncoding
are short tandem repeats (STR) classified as micro or minisatellites?
microsatellites
are variable number tandem repeats (VNTR) classified as micro or minisatellites?
minisatellites
any tandem repeat where copy number varies (VNTR/STR)
VNTR
a tandem repeat where te sequence repeated is short (ie 2-6 bases) - is a subtype of VNTR
STR
for PCR we have to design … and … primers for the gene of interest
forward and reverse
a major application of PCR
genotyping of alleles based on the allele specific length differences
what technique is used to separate different amplified target alleles based on their length
gel electrophoresis
what type of genotyping uses fluorescently labelled primers designed to amplify alleles of different sizes (which can also be separated on the same gel)?
multiplex
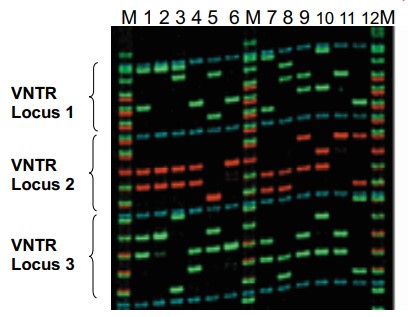
what type of genotyping produces this gel electrophoresis?
multiplex
multiplex genotyping allows alleles at many different … to be investigated at the same time
loci
areas of major applicationf of multiplex genotyping
… science
… testing
… genetics
… genetics
forensic science
paternity testing
population genetics
evolutionary genetics
what kind of nucleotides can terminate chain synthesis?
dideoxynucleoties
which is faster next generation sequencing or chain termination sequencing?
next generation
is it sanger or next generation sequencing where billions of strands of DNA are sequenced at once?
next generation
is it sanger or next generation sequencing where only one strand of DNA is sequenced at once?
sanger
the DNA analysis method where a long DNA strand is randomly broken into many small, overlapping fragments, each sequenced individually, and then reassembled by computers using the overlaps to reconstruct the original, full sequence
shotgun sequencing
the DNA/RNA sequencing technology that rapidly reads millions of genetic fragments in parallel
next generation sequencing
what are genomics?
the study of the entire set of DNA of an organism and its genes, exploring how they function, interact and influence traits
human genomics are useful to identify … which cause specific diseases, disease …, drug … and traits
answer with a list
mutations which cause specific diseases
disease resistance
drug sensitivity
traits
suggestive evidence for RNA being the intermediate between DNA and proteins
DNA is located in the nucleus
RNA is synthesised in the nucleus
RNA migrates to the cytoplasm where proteins are synthesised
in viral infection RNA synthesis precedes new viral particle formation
at which position does deoxyribose lack OH at?
2
what does UMP stand for?
uridine monophosphate
what does AMP stand for?
adenine monophosphate
what does CMP stand for?
cytidine monophosphate
what does GMP stand for?
guanosine monophosphate
name all four nucleotides in RNA
adenine, cytidine, guanosine and uridine monophosphate
which type of RNA represents <10% of RNA in a cell?
mRNA
does mRNA have a long or short half life?
short
what is the most abundant RNA in cells?
rRNA
which type of RNA represents >90% of RNA whithin a cell?
rRNA
rRNA represents a … and … component of ribosomes
structural and functional
which type of RNA is the smallest?
tRNA
which type of RNA is less than 100 bases long?
tRNA
do prokaryotes have one or multiple RNA polymerases?
one
what are the three RNA polymerases in eukaryotes?
RNAP I, RNAP II and RNAP III
which RNA does RNAP I make?
rRNA
which RNA does RNAP II make?
mRNA
which RNA does RNAP III make?
tRNA
does the template or nontemplate strand get transcribed?
template
is the coding strand the same as the template or nontemplate strand?
nontemplate
is it the template or nontemplate strand which has the same nucleotide sequence as the mRNA being produced except T → U
nontemplate
is it the template or nontemplate strand which is the antisense?
template
template = …
nontemplate (coding) = …
(sense/antisense)
template = antisense
nontemplate = sense
the DNA sequences which guide RNAP to the beginning of the gene to start transcription
promoters
the DNA sequences that specify the termination of transcription and release RNAP from the DNA
terminators
3 steps of transcription (just 3 words)
initiation
elongation
termination
what number denotes the transcription initiation site?
+1
is there a 0 position relative to the trascription initiation site of +1?
no
is the upstream sequence denoted by +/-?
+
is the downstream sequence denoted by +/-?
-
what is another name for the TATA box in prokaryotes?
pribnow box
how many bases upstream is the TATA/Pribnow box in prokaryotes?
-10bp
what is the other upstream box in prokaryotes?
-35bp box
prokaryotic promoters contain 2 highly conserved regions.
copy this cus its important
prokaryotic promoters contain 2 highly conserved regions
how long are prokaryotic promoters typically?
40bp
what is the consensus for the -35 box in prokaryotes?
TTGACA
what is the consensus for the TATA box in prokaryotes?
TATAAT
two types of regulatory proteins?
activators and repressors
what are the subunits of the core of the prokaryotic RNAP?
2 alpha, 1 beta, 1 beta’ and 1 omega
when you add the sigma subunit to the core of the RNAP it becomes a …enzyme
holoenzyme
what is the principle sigma subunit?
sigma 70
what is the heat hock sigma subunit?
sigma 32
what is the sigma subunit for nitrogen starvation?
sigma 60
which subunit recognises the promoter sequence?
sigma
which two things form the closed promoter complex? (DNA not yet unwound)?
RNA pol and the promoter
what happens for the closed promoter complex to form the open promoter complex?
RNA pol unwinds about 12bp of DNA
which subunit dissociates soon after transcription begins?
sigma
mRNA is produced in which direction?
5’ to 3’
does simple termination of transcription require a protein factor?
no
in simple termination of transcription what shape of structure does DNA formto cause RNAP to dissociate?
hairpin structure
in complex termination of transcription what protein is required to get RNAP to dissociate?
Rho
the rho factor is a … protein
helicase