APES Vocab
1/136
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
Biotic
Living components of an ecosystem.
Abiotic
Non-living physical and chemical elements of an ecosystem.
10% Rule
Only about 10% of the energy at one trophic level is transferred to the next.
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)
The total amount of solar energy captured by producers via photosynthesis.
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
GPP minus the energy used by producers for respiration; the energy available to consumers.
Photosynthesis
Converts solar energy into chemical energy.
Cellular Respiration
Releases energy from food.
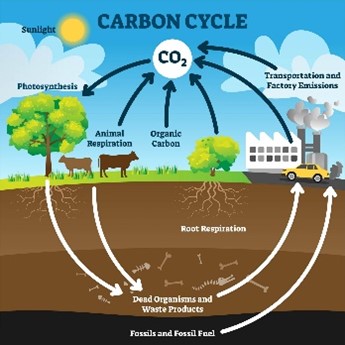
Carbon Cycle
The movement of carbon among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere.
Nitrogen Cycle
The series of processes by which nitrogen and its compounds are interconverted in the environment.
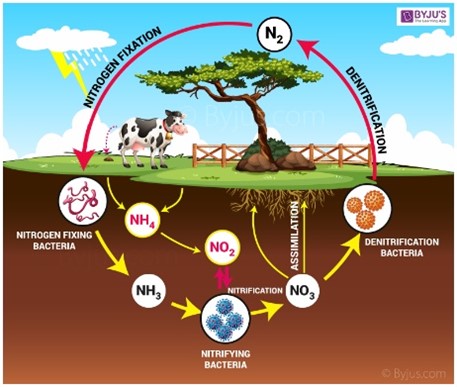
Nitrogen Fixation
Atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) is converted into ammonia (NH₃) by bacteria or through lightning.
Nitrification
Ammonia is oxidized to nitrites (NO₂⁻) and then to nitrates (NO₃⁻), which plants can absorb.
Assimilation
Plants take up nitrates and incorporate them into organic molecules.
Ammonification
Decomposers convert organic nitrogen back into ammonia.
Denitrification
Nitrates are reduced back to nitrogen gas, returning it to the atmosphere.
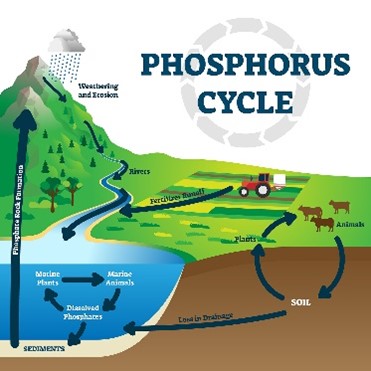
Phosphorus Cycle
The movement of phosphorus through the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere.
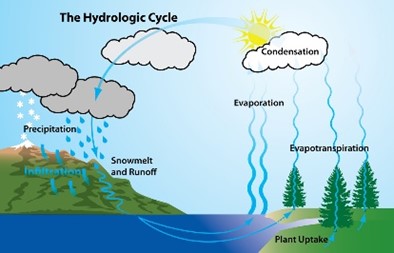
Hydrologic Cycle
The continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
Limiting Nutrient
A nutrient required for the growth of an organism but available in a lower quantity than other nutrients.
Biomes
Large ecological areas on the Earth's surface, with flora and fauna adapting to their environment.
Tundra
Cold, low plants (mosses).
Taiga
Cold, coniferous trees (spruce).
Temperate Forest
Four seasons, deciduous trees (oak).
Grassland
Moderate rain, grasses.
Desert
Dry, cacti.
Tropical Rainforest
Warm, wet, dense trees.
Savanna
Warm, seasonal rain, grass & widely scattered trees.
Chaparral
Dry summers, wet winters, shrubs.
Island Biogeography
Larger islands and closer are more diverse and higher immigration/lower extinction. Smaller, further islands have less biodiversity since there are less resources
Ecological succession (primary / secondary)
The gradual change in living communities that follows a disturbance. Primary begins on bare rock; secondary follows a disturbance in an existing community.
Overshoot / Die-off
When a population exceeds the carrying capacity of its environment, leading to a sharp decline (die-off) due to limited resources.
r-selected
reproduce quickly with many offspring
K-selected
reproduce slowly with fewer offspring and more parental care.
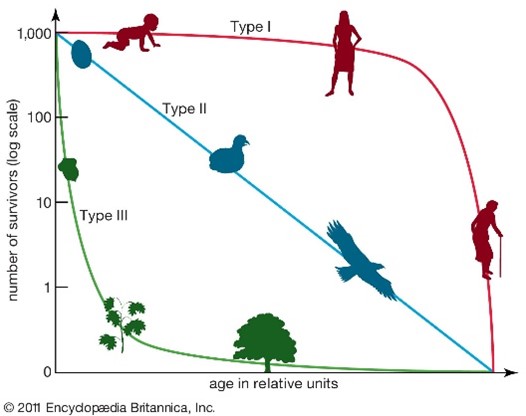
Survivorship curves (Type I, II, III)
Graphs showing the likelihood of survival at different ages: Type I (most survive to old age), II (constant death rate), III (high death rate early).
Total fertility rate (TFR)
The average number of children a woman will have in her lifetime.
Infant mortality rate
The number of infant deaths (under age 1) per 1,000 live births.
Doubling time
The time required for a population to double in size, calculated as 70 divided by the growth rate (Rule of 70).
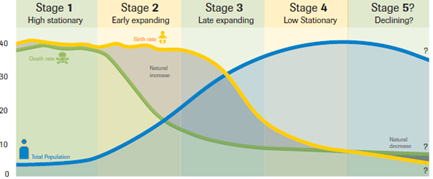
Demographic transition model
A model showing population change over time as a country develops economically, moving through four (sometimes five) stages.
Soil horizons (O, A, B, C)
Layers of soil: O (organic matter), A (topsoil), B (subsoil), C (parent material).
Watershed
An area of land that drains all precipitation to a common water outlet like a river or lake.
Coriolis Effect
The deflection of moving air and water due to Earth's rotation, affecting global wind patterns.
Normal Flow
Warm water flows from SA to Australia and gets subdued so the nutrient-full and cold upwelling happens in SA’s coast. Wet in Australia and dry in South America
Green Revolution
A period of increased agricultural production using high-yield crops, fertilizers, and pesticides.
Irrigation types (drip, flood, furrow, spray)
Methods to water crops—drip is most efficient; flood and furrow are less efficient and cause runoff.
Overfishing
Harvesting fish faster than they can reproduce, leading to population declines and ecosystem disruption.
Impervious surfaces
Surfaces like roads and rooftops that do not absorb water, increasing runoff and flood risk.
Sustainable agriculture
Farming methods like crop rotation and contour plowing that maintain soil health and long-term productivity
Fracking (hydraulic fracturing)
A method of extracting oil and natural gas by injecting high-pressure fluids into rock formations; increases fuel supply but can contaminate groundwater and trigger earthquakes.
Solar (passive / active)
Passive systems use building design to capture heat naturally (greenhouse effect); active systems use technologies like solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity.
Photovoltaic cells
Devices that convert sunlight directly into electricity using semiconductors, commonly used in solar panels.
Geothermal energy
Uses heat from within Earth to generate electricity or heat buildings; renewable and consistent but location-limited.
Cogeneration
The simultaneous production of electricity and useful heat from the same energy source, increasing overall energy efficiency.
Air pollutants (CO, NOx, SO2, PM, O3, lead)
Common harmful substances in the air including carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), particulate matter (PM), ground-level ozone (O3), and lead (Pb).
VOCs
Organic chemical that have a high vapor pressure at ordinary room temperature. (Acetone, Benzene, Ethylene Glycol, Formaldehyde, etc.)
Lead
metal that comes from old paint, gas, and mining. It affects nervous system and kidney damage. Bioaccumulates in food chains
Asbestos
A mineral once used in insulation; when inhaled, it can cause lung diseases including mesothelioma.
Oxygen sag curve
A graph showing how dissolved oxygen decreases downstream from a pollution source due to increased biological oxygen demand.
Sanitary landfill
A controlled landfill that uses liners and leachate collection to reduce environmental contamination.
Greenhouse effect / Greenhouse gases (GHGs)
The natural process where gases like CO₂, CH₄, N₂O, and O3 trap heat in Earth’s atmosphere; intensified by human emissions.
Global warming / Climate change
Long-term rise in Earth's temperature and changes in weather patterns due to increased greenhouse gases.
Carbon footprint
The total greenhouse gas emissions caused directly and indirectly by an individual, organization, or product.
Ozone depletion
Thinning of the ozone layer caused by CFCs and other chemicals, allowing more UV radiation to reach Earth.
CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons)
Man-made chemicals once used in refrigeration and aerosols that destroy ozone in the stratosphere.
Loss of biodiversity
The decline in the variety of life due to human impacts like habitat destruction, climate change, pollution, and invasive species
Invasive species
Non-native organisms that outcompete local species and disrupt ecosystems (lack predators)
Endangered species
Species at high risk of extinction in the near future due to declining populations or habitat loss.
Habitat fragmentation
The breaking up of large habitats into smaller, isolated patches, reducing the ability of species to survive and reproduce.
Kyoto Protocol / Paris Agreement
International agreements to limit greenhouse gas emissions and aim to combat climate change.
Clean Air Act
US law to control air pollution
Clean Water Act
US law regulating pollutant discharges in water
CITES
Protected endangered species by regulating international trade
CERCLA
Fund to clean up hazardous waste
Montreal Protocol
Phased out ozone-depleting substances
Endangered Species Act
Protected endangered species and their habitats from harm
SDWA
Set standards for safe drinking water
Delaney Clause
Prohibited carcinogenic food additives
RCRA
Managed hazardous/non-hazardous waste to protect human health/environment
El Nino
weakened trade winds, warm surface water shifts east toward SA so upwelling decreases.
SA: flooding, warmer
Australia: hotter, drier because of less warm waters that can evaporate and rain
US: wetter winters
La Nina
Same as normal but stronger trade winds toward Australia
Movement of the warm water current is closer to the Australian shoreline.
Enhanced upwelling in SA
SA: cooler, drier
Australia: warmer, wetter
US: south is hotter/drier, north is colder/wetter
Interspecific
competition between different species
Intraspecific
competition between the same species
Resource partitioning
Species competing for similar scarce resources evolve specialized traits that allow them to share the same resources
Coevolution
Changes in the gene pool of one species leads to changes in the gene pool of another to help control population growths of predator/prey species
Parasitism
a relationship where one organism benefits at the expense of another.
Mutualism
a symbiotic relationship where both species benefit from the interaction.
Commensalism
a relationship where one organism benefits while the other is neither helped nor harmed.
Layers of Freshwater Ecosystems
Littoral: lots of sun
Limnetic: depth that sunlight reaches and photosynthesis
Profundal: dak, low oxygen
Benthic: decomposition
Provisioning Benefits
are the products obtained from ecosystems, including food, fresh water, and raw materials.
Regulating Benefits
are the benefits that ecosystems provide by controlling natural processes, including climate regulation, water purification, and pest control
Supporting Benefits
are the services that maintain ecosystem functions, such as soil formation, nutrient cycling, and habitat provision for species.
Lichens
make acid that breaks down rock in primary succession
Composition of gases
78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen, stratosphere has ozone layer
Insolation
Solar radiation per unit area. Cancer on top, Capricorn on bottom
Rain shadow Effect
Moist ocean breezes pass across the ocean and hit the windward side of the mountain and rains to make vegetation. Hot and dry wind is still moving and as it rushes down leeward side, it makes arid and desert-like area
Mining
Overburden: removing the top layer of soil, rock, and other debris to access the underlying mineral resources
Spoils: unwanted rock produced when material is removed from the earth’s surface by mining
Ore: concentrated accumulation of minerals from which economically valuable materials can be extracted
Tailings: rock and other waste removed as impurities when waste mineral material is separated from the metal in an ore
Surface Mining
o Open-pit mining: removing overburden to access ore deposits close to surface (cheaper)
o Strip mining: land is cleared of vegetation/rocks and then dug out in strips (expensive)
o Mountaintop removal: coal is extracted from a mountain by removing overburden and clearcutting forests
Integrated Pest Management
Biological: introduction of natural pest predators
o Farm cat/dog, praying mantis, ladybugs
Physical: barriers that protect crops
o Traps, tilling, screens, week blocker, fences
Chemical: poison that kills pests
o Glyphosate, atrazine, DDT
o Hurt non-target species
Hydrogen Fuel Cell
Combines hydrogen fuel and oxygen from the atmosphere to create electricity, Water vapor is the only emission from the fuel cell, expensive
Acid Rain
Burning fossil fuels emit nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide. They react with water vapor, oxygen, and others to make nitric acid which falls as acid rain
Carbon Oxide
carbon that is bonded to oxygen. Colorless and odorless.
Sources- Naturally exhaled during cellular respiration, given off during the burning of fossil fuels and the burning of biomass, impairs the action of photosynthesis in plants,etc.
Damage- Greenhouse gas that influences climate change.
Sulfur Dioxide
compounds that are made up of sulfur and oxygen.
Sources- Combustion of fossil fuels and some industrial processes, volcanoes and hot springs.
Damage- Can irritate lungs and tissue, can weaken buildings and harm plants when it becomes acid rain, produces a haze, etc.
Nitrogen Oxide
Compounds that are made up of Nitrogen and Oxygen
Sources- The burning of fossil fuels
Damage- Can create ground level ozone which can harm the lungs and other parts of the body, can harm plants, soil, buildings and water when it becomes acid rain.