OPT 116 Reactive Oxygen Species and Fluorescence
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
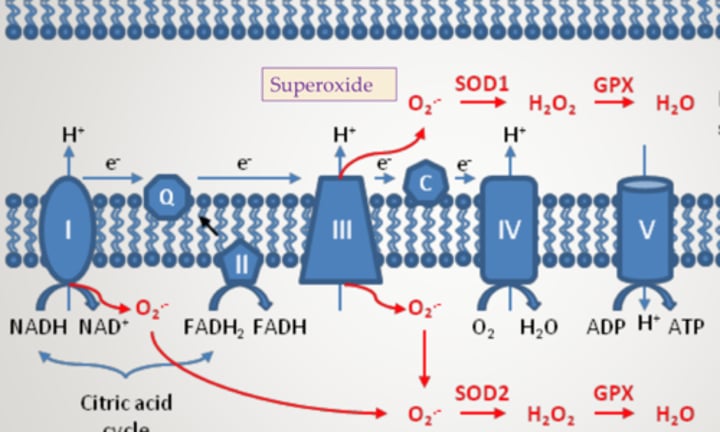
What complexes does superoxide leak from?
I and III
What are the main ocular complications associated with reactive oxygen species?
degenerative retinal damage and cataractogenesis
What is a reactive oxygen species (ROS)?
any reactive oxygen derived molecule capable of independent existence
What classifies an ROS?
-one or more unpaired valence electrons
-highly reactive and short lived
What are the main biologically relevant ROS?
- Superoxide radical
-hydrogen peroxide
-singlet oxygen
-hydroxyl radical

There is a direct relationship between _______ and depth of penetration for eye and skin
wavelength
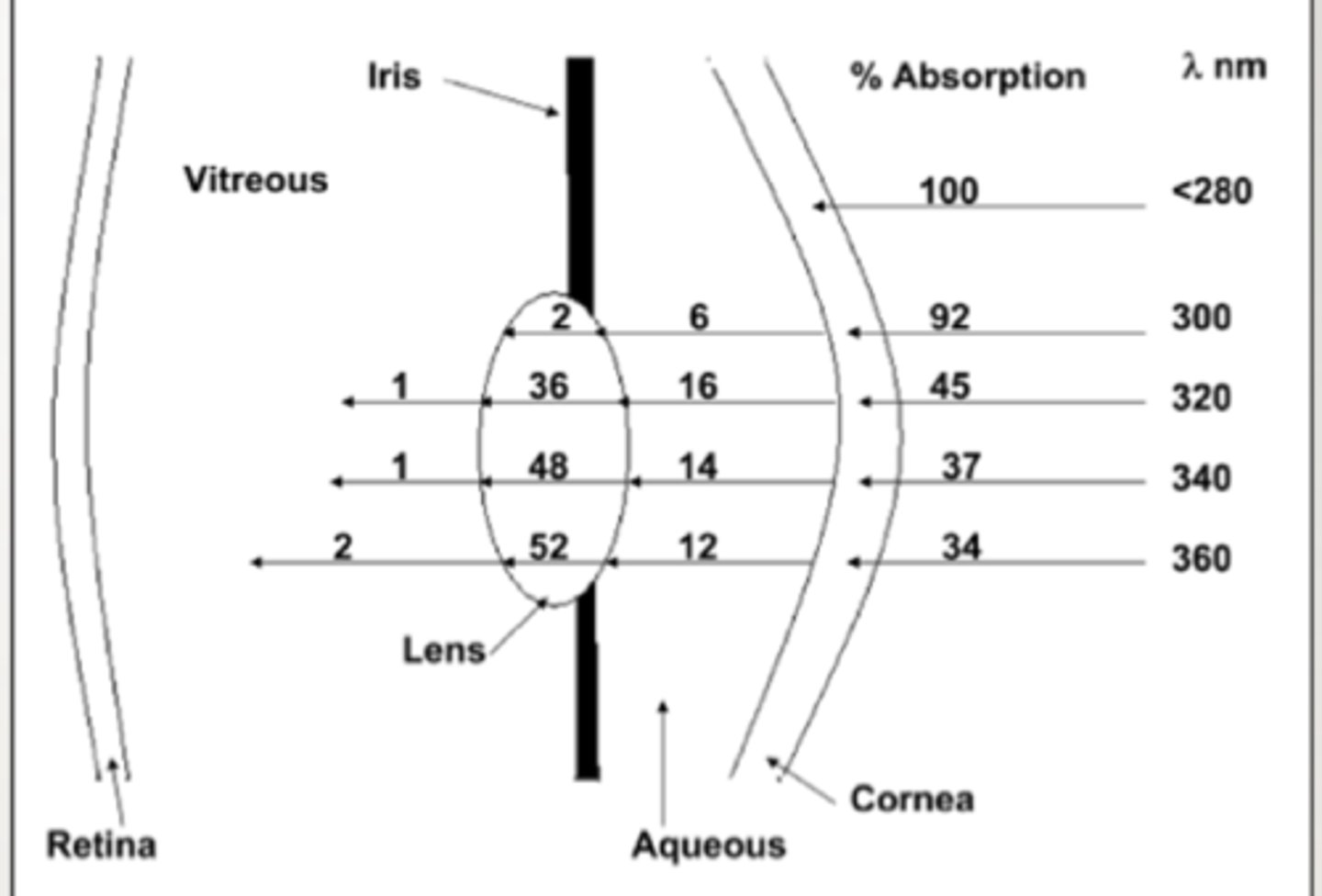
What absorbs UV C?
atmosphere
When does singlet oxygen (1O2) form?
UVA photooxidation; degradation of fatty acids
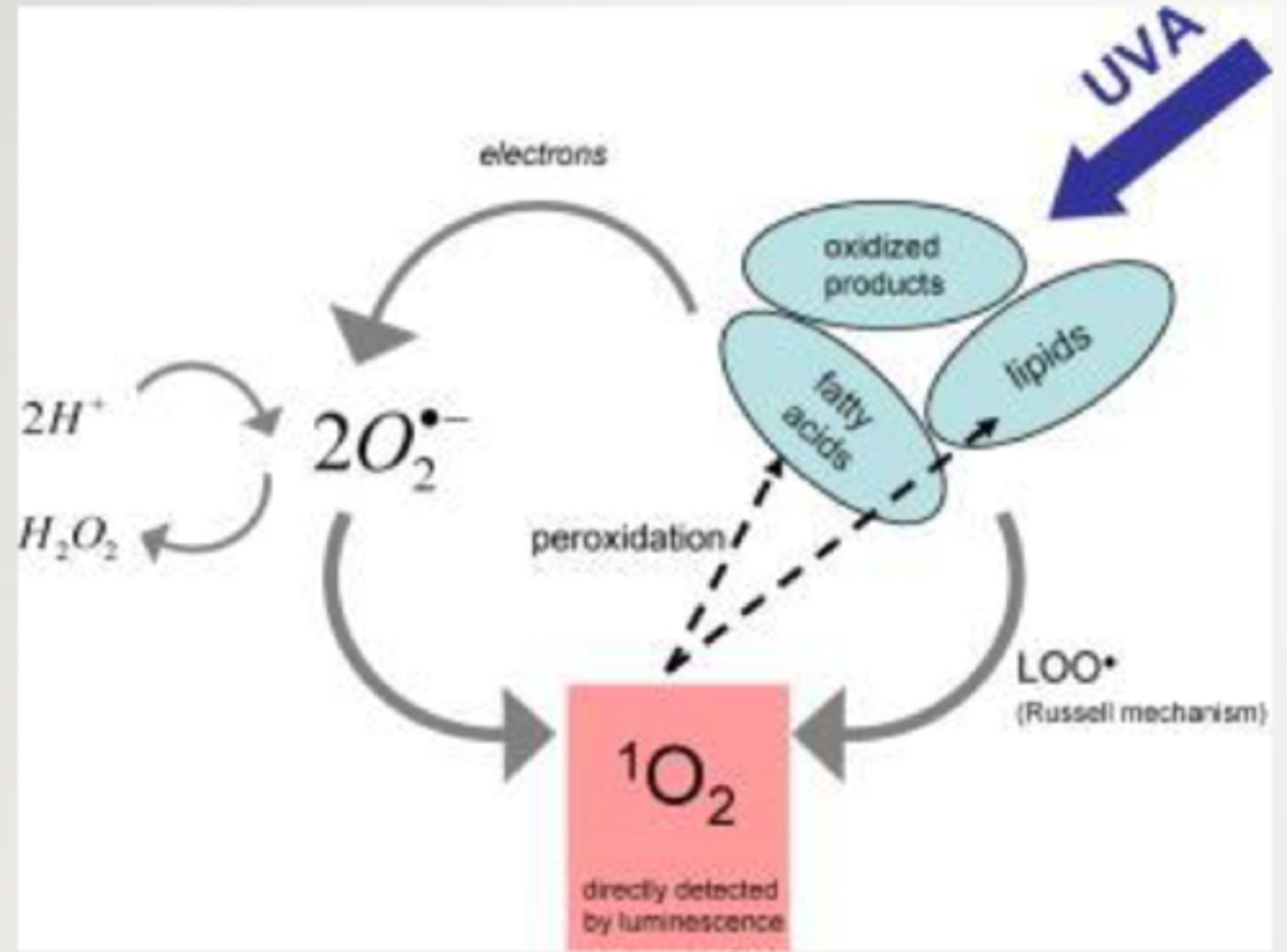
How long does singlet oxygen exist at room temperature?
over one hour
How does singlet oxygen contribute to Keratoconus therapy?
corneal crosslinking with riboflavin (B2)
How does singlet oxygen contribute to photodynamic therapy for wet AMD?
Verteporfin (Visudyne)
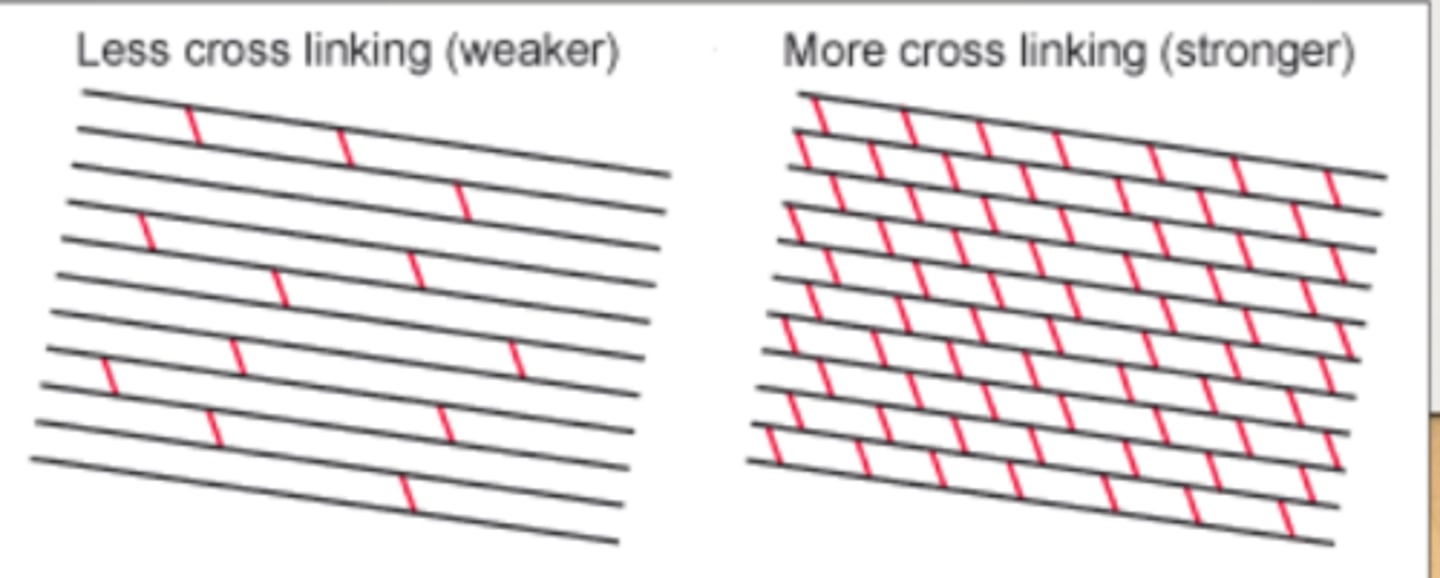
What occurs during corneal cross linking?
UVA + Riboflavin (B2)
-UVA produces reactive oxygen species
-Riboflavin enhances the production of ROS as it absorbs UVA
-ROS (1O2) cause covalent bonds to form between corneal collagen fibers
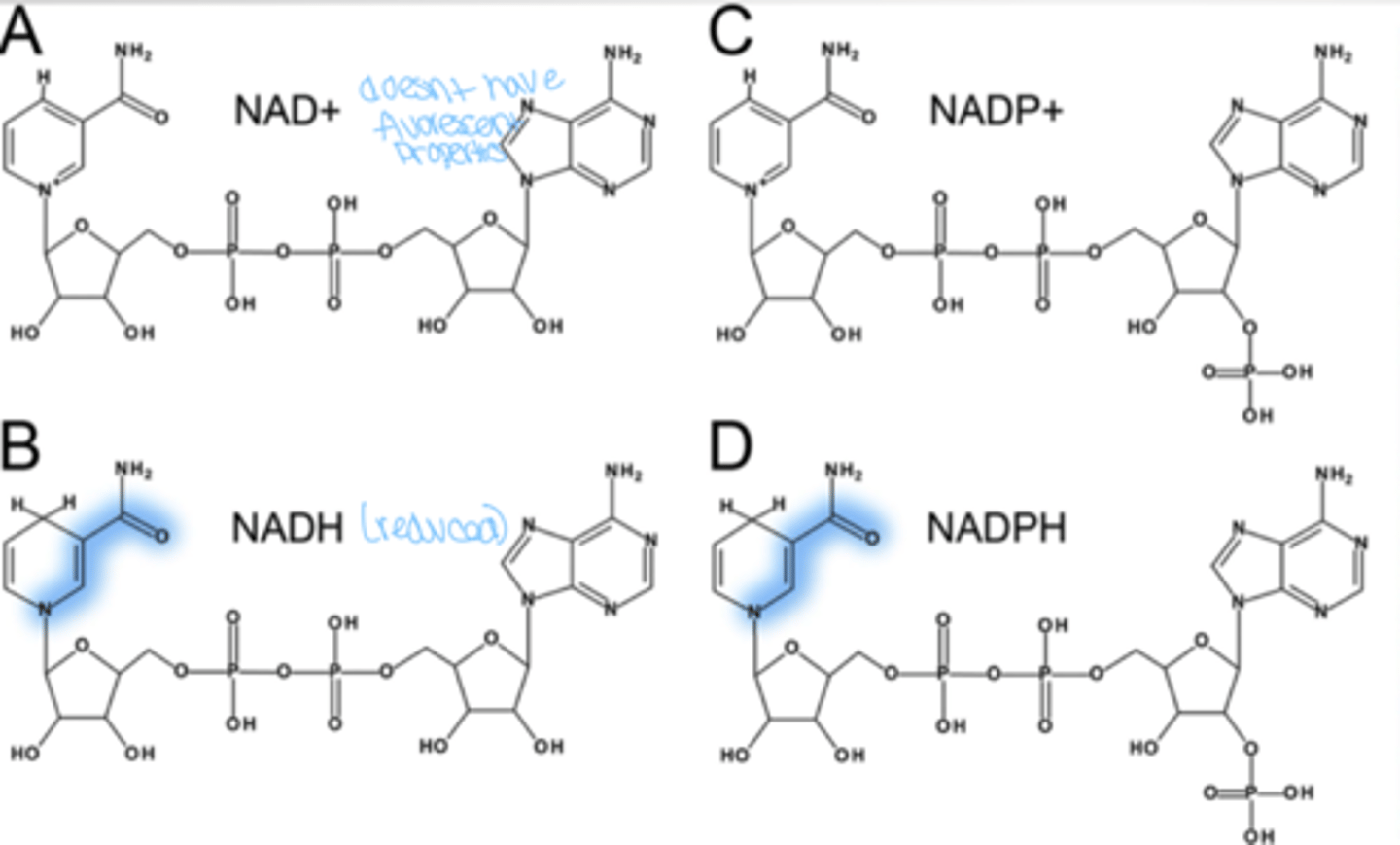
What molecules exhibit fluorescence ?
reduced NAD+ (NADH) and NADPH
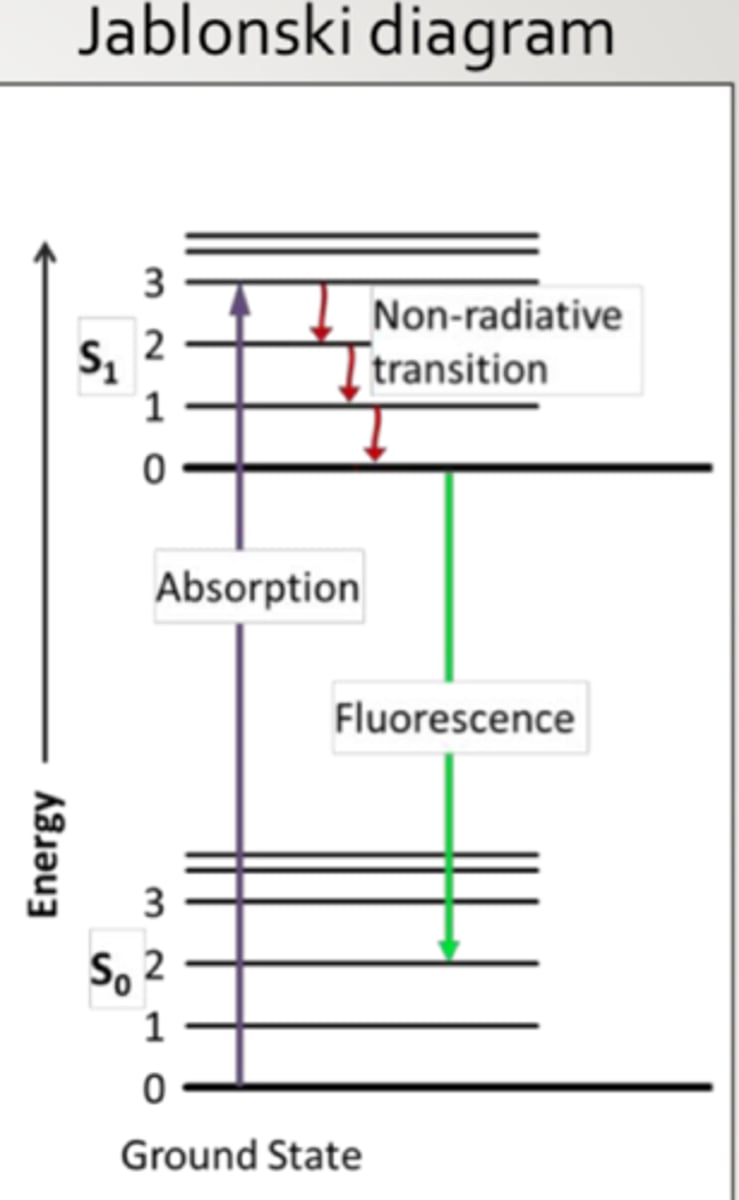
Stokes shift
energy absorbed at shorter wavelength (higher energy), emission at longer wavelength (lower energy)
What are environmental factors effecting fluorescence?
-intensity and duration of exposure
-temperature
Extrinsic fluorescence
unique wavelengths of excitation and emission
Autofluorescence
application of fluorescent substance is not required to achieve fluorescence
What are the main natural substances known to show autofluorescence?
-Lipofuscin (proteins, lipids, and carbs)
-Collagen
-Elastin (collagen+ protein)
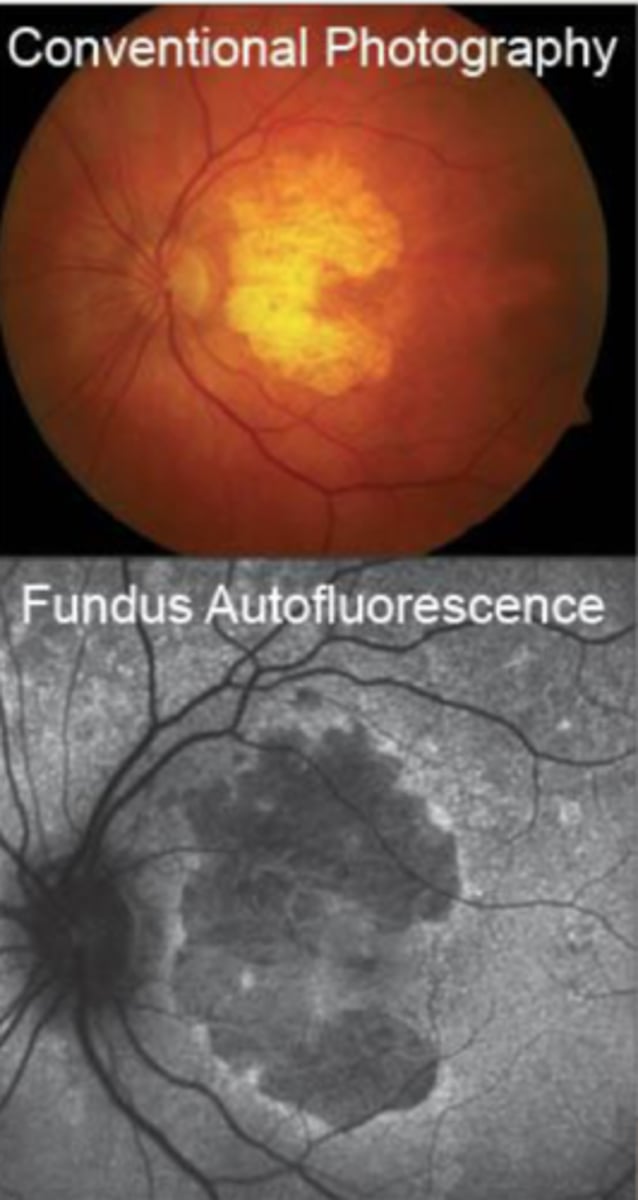
Why is autofluorescence important in terms of fundus?
Lipofuscin in the RPE causes fluorescence a shining appearance to a fundus photo. We want to use autofluorescence to increase contrast to see distinct borders
Why is autofluorescence of the conjunctiva important?
found to be a possible biomarker for cumulative and preclinical UV exposure