parasitology lab exam 2
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
what structure carries the hooks in taeniids
proboscis-like structure called rostellum
how many sets of reproductive organs per proglottids in taeniids
1
describe gravid proglottids in taeniids
they have a tree like uterus
how many larval hooks do enclosed oncospheres contain in taenii
6
what distinguishes taeniid eggs from other tapeworm eggs
thick wall and radial striations to give a sunburst appearance.
what are intermediate hosts for taeniid
mammal, usually prey mammals for definitive host
where are adult taeniid’s found
In the predator host’s small intestine
what do taeniid eggs do
they get ingested by the intermediate host. They hatch and penetrate the gut and grow into the intermediate host tissue.
list body parts of adult taeniid
scolex, neck region, and mature proglottids
list taeniid female reproductive systems found in the mature proglottids
ovary, yolk glands, vagina, uterus
list taeniid male reproductive systems found in the mature proglottids
testes and cirrus pouch
T/F cyclophyllidean cestodes eggs usually stay in the uterus until the entire proglottid is shed in the feces
True
which worm genus is smaller, echinococcus or teaniid
echinococcus is smaller
protoscolex is a stage/structure of what
a portion of a unilocular hydatid cyst located inside the broad capsule. found in echinococcus and taenia spp.
what occurs within each chamber the of germinal membrane of E. multilocular cysts?
larval scolices (protoscolices)
how does multilocular hydatid cyst affect host tissue?
Grows very invasively
do cysticercoid larvae develop in intermediate or definitive host and what kind of organism is it?
in intermediate and arthropods
what kind of larvae have inverted scolexes
taenia
what type has fluid filled cysts?
taenia species
is cysticercoid cyst fluid filled or solid tissue
solid tissue cyst
most common tapeworm of cats and dogs
Dipylidium
What is the intermediate host of D. caninum?
flea or uncommonly lice
How do dogs and cats become infected with D. caninum?
by ingesting fleas that contain the larva
list some differences between proglottids of taenia and dipylidium
the taenia has larger more pronounced sexual organs and Dipylidium has 2 vaginas or the exits or whateva
which genus doesn’t have much of any hooks or suckers on the scolex
Diphyllobothrium
what is unique about the Diphyllobothrium proglottid?
genital pore median instead of lateral
what genus of tapeworms does not have hooks on the eggs and may have an operculum
Pseudophyllidean tapeworm eggs
describe Pseudophyllidean maturation
Egg → Coracidium → Procercoid → Plerocercoid → adult
what are general characteristics of Trematoda and what are they aka
Flukes. Adults possess suckers for attachment and all species are parasitic
what is the important subclass of trematodes
Digenea- seen in people and land animals
describe trematoda life cycle/characteristics
endoparasites(internal), asexual reproduction in snail host with sexual reproduction in the vertebrate host.
T/F - Digenea have a low specificity for their snail host
False, they do have high specificity for the snail host.
What organism has a digestive system composed of pharynx leading into a branched cecum or ceca(plural)
Digenea trematodes
describe trematode eggs
operculated (have cap), brown or yellow
what are the 6 stages of trematode life cycle
egg, miracidium, asexual reproduction in the snail, cercaria, metacecaria, adult.
Where do trematode eggs need to be and how can they be found in a sample.
They need to be somewhere near a snail for survival and they can be tested for using sedimentation technique in fecal samples.
what is unique about the miracidium stage
This stage emerges from the egg, they have cilia, and they swim and penetrate the snail intermediate host.
Describe the first step of asexual reproduction in the snail host.
miracidium loses its cilia and becomes a reproductive body called a sporocyst
sporocyst?
produces larval stages within itself, a stage of trematodes particularly stichosomes
what do the sporocyst larval stages turn into? And what do they do?
Redia, escape the sporocyst and invade the snail gonads/digestive gland.
What is formed by the redia
Cercariae
stage of trematode that has a short free living existence before penetrating the second intermediate host. Some species encyst on vegetation and other have tails for swimming.
Cercaria
what is a metacercaria?
A stage of trematodes that is encysted. It can be encysted in a secondary intermediate host which is highly variable or just on vegetation. It is ingested by the definitive host.
is fasciola a large or small trematode
very large
what is ceca?
intestine, simple forked blind pouches
what is the oral and potential ventral suckers for
digestive system, intake food, and attachment organs
Muscular pharynx and tubular esophagus belong to what system in what genus
digestive system in trematoda
are trematodes hermaphrodites
yes, except stichosomes
list the female organs of a trematode
ovary, vitelline aka yolk glands, uterus, and genital pore
list the male organs of trematodes
paired testis and cirrus and cirrus pouch (acts as a penis)
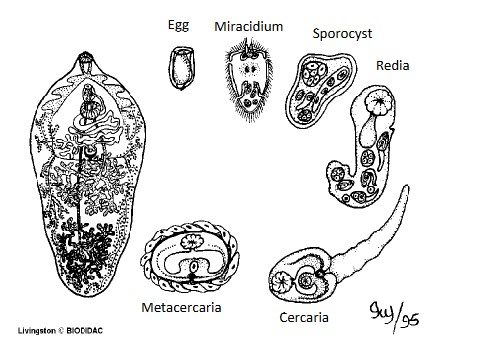
what genus does this depict
trematode
what does digenetic mean
requires two or most hosts to complete the life cycle
what family of trematodes is very important for human medicine.
Schistosomes
what is unique about schistosomes?
The have separate sexes
what are the 3 main species of Schistosomes that impact humans
S. mansoni, s.haematobium, and s. japonicum
where do S. mansoni and S. japonicum live in humans?
These two species live in mesenteric veins
where does S. haematobium live?
veins in the bladder
in what species does the male wrap his body around the female in a state of permanent copulation? and what is the name of the grove that the female fits into?
S. mansoni and gynecophoric canal
what is the primary source of pathology for schistosomes
eggs as they pass through tissue to reach the gut/bladder.
what can happen if mesenteric schistosome eggs are moved into the liver?
they can cause inflammation and granuloma formation
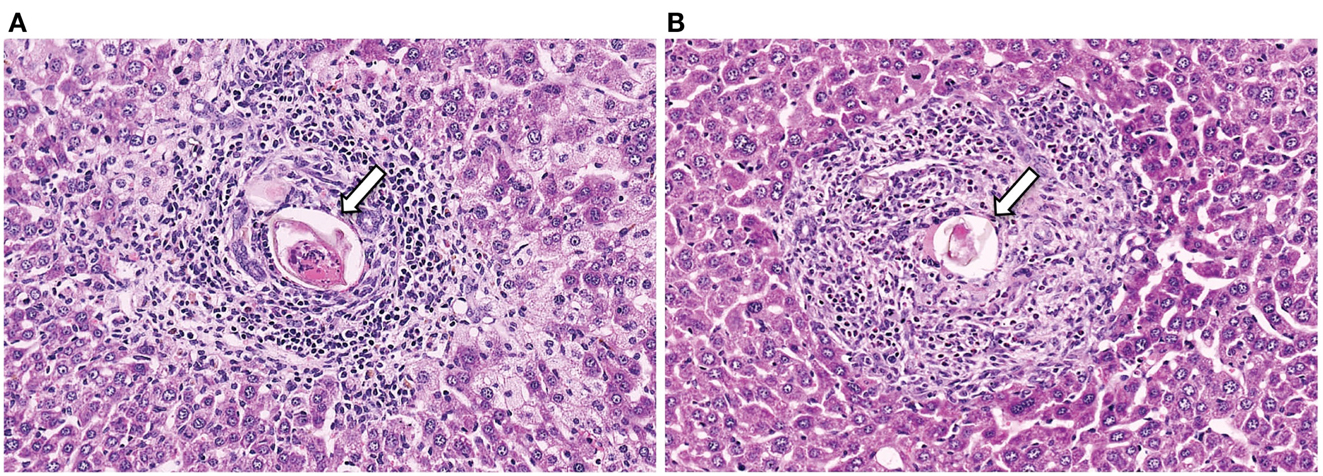
how are trematode eggs tested for?
fecal examination but sedimentation test instead of fecal flotation
How many suckers does Fasciola have?
2
What is the function of the vitelline glands?
provide essential nutrients for egg formation including the hard shell and embryo nutrients
How big is a Fasciola egg?
~140 microns long by ~75 microns wide
How do you tell the difference between a male and female schistosome?
Males are short and stouter with a distinct ventral groove. Females are darker and smoother, longer and slender.
What is the gynecophoric canal?
where the female worm resides in schistosome reproduction
What structures present in the adult are also present in the cercaria?
basically everything except the tail and penetration glands
What stages of the fluke life cycle are found in the snail?
miracidium, sporocysts, rediae, and cercariae
How does H&E staining work
hematoxylin stains nucleic acids dark blue or black and eosin stains the cytoplasm pink-magenta
Trichrome stain
used to identify protozoan parasites in fecal smears. the cytoplasm stains blue/green and the nuclei stain red/magenta
Iron-hematoxylin stain
used for nuclei morphology, used on fecal smears and tissue sections. Cytoplasm stains yellow gold and the hematoxylin stains the nucleus dark blue/ black
Giemsa stain
usually used on blood smears but also the other two. cytoplasm stains bluish and nuclei stain red/magenta
pseudopodia
the way amoebas move, clear areas.
what is the difference between vesicular and compact nuclei
how tight the chromatin are, vesicular is more lose and considered to contain a lot of fluid.
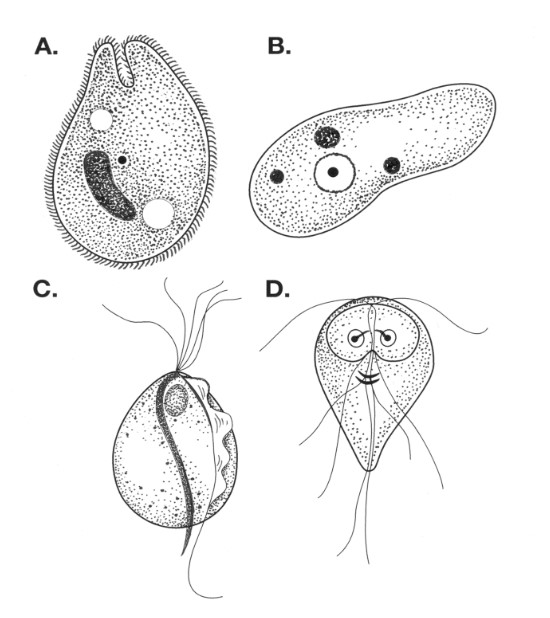
what stage is this
trophozoite stage
what stage is this
cyst stage (fecal)
what phylum is toxoplasma
apicomplexa
what are the unique organelles in apicomplexa
rhoptries, micronemes, and dense granules. also the apicoplast
rhoptries function
responsible for forming the parasitophorous vacuole that houses the parasite inside the cell.
Micronemes function
Release adhesin proteins that begin initial attachment to the host cell and allow the gliding motility so the parasite can explore the surface of the host cell.
what do the dense granules do
modify the vacuole housing the parasite to increase survival and replication chance of success.
dense granules are found where
cytoplasm
how often does taxoplasma divide once it invades a host cell
every 6-8 hours
What is the divalent cation that plays a critical messenger role during Toxoplasma egress?
calcium ion Ca2+
Is Toxoplasma enclosed in a vacuole inside the host cell or is free in cytoplasm?
inside a special vacuole
Why is the intracellular life cycle of Toxoplasma is called as the lytic cycle?
the rapid replication of the tachyzoite stage causes the cell to burst or lyse
what parasite causes malaria
Plasmodium
what are merozoites
invasive asexual stage of plasmodium produced in the liver that rapidly infect RBCs
most important blood protozoan pathogen in domestic animals and one of the most important in humans.
Babesia
How is Babesia transmitted
tick (ixodes scapularis) transmitted parasite, specifically the sporozoite stage.
where are babesia merozoites formed?
vertabrate red blood cells, usually seen at 2 in a cell sometimes 4
what is the most useful diagnostic procedure for babesia
geimsa staining blood smears
what species of Babesia affect cattle?
B. bovis and B. bigemina
what species of babesia affect dogs
B. canis and B. gibsoni
what species of babesia targets humans
B. microti
what is the causative agent of Chagas Disease
what disease does Trypanosoma cruzi cause
how is Trypanosoma cruzi transfered
through the feces of triatomine bugs
is T. cruzi intra or extra cellular
extracellular
what can chronic infections of T. cruzi lead to?
heart failure
what are the 4 stages of Trypanosoma
Trypomastigote, Epimastigote, Promastigote, Amastigote