Ischemic Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease) - Module 1
1/233
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
234 Terms
Narrowing of obstruction of the coronary artery(ies) sufficient to prevent adequate blood and oxygen supply to the myocardium (may progress to myocardium damage)
Define Ischemic heart disease
Ischemic heard disease
What does IHD stand for
Inadequate blood and oxygen supply to the myocardium (no permanent damage)
Define ischemia
Inadequate blood and oxygen supply to the point of myocardium damage
Define infarction
Atherosclerotic and non-atherosclerotic
What are the two types of ischemic heart disease causes
Atherosclerosis
What is the most common causes of IHD
False, less common
T/F: non-atherosclerotic causes of IHD is very common
Embolus into coronary artery, trauma, coronary artery dissection/aortic dissection
What are some non-atherosclerotic causes of IHD
Aortic dissection flap can cover coronary artery entrance and stop blood from flowing into coronary artery
Explain how an aortic dissection can lead to IHD
Fatty streak on intima
How does atherosclerotic plaque begging
Starts as fatty steak and progresses into a superficial erosion of endocardial layer. Thrombus forms and occludes artery
Describe how atherosclerotic plaque progresses
Distal to an arterial branching
Where does atherosclerotic plaque usually occur
Age, smoking, DM, dyslipidemia, HTN
What are the major risk factors for IHD
Abdominal obesity, family Hx, obesity, physical inactivity
What are some other predisposing risk factors of IHD
Decreased blood supply to myocardium or increased demand of blood
What are the possible causes of ischemia
True
T/F: ischemia is reversible
Death or necrosis of tissue
What is infarction
Prolonged ischemia, total occlusion of blood flow to the tissue
What causes infarction
If wall is being supplied by multiple arteries, may just cause ischemia
In what instance would a total occlusion of blood in a coronary artery not cause infarction
False, irreversible
T/F: infarction is reversible
CAD and increased metabolic demand
What are the 2 most common causes of myocardial ischemia
Coronary artery disease
What does CAD stand for
Plaque in vessel which impedes blood flow
What is CAD
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or aortic stenosis
What are some causes of increased metabolic demand
Causes more muscle which increases the demand
Explain how hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can cause myocardial ischemia
Heard is working harder against the high afterload so demands for blood
Explain how aortic stenosis can cause myocardial ischemia
Downstream
Does everything downstream or upstream from the obstruction die in infarction
Collateral circulation from another vessel
When would everything downstream from and obstruction NOT die
1 hour
When does cell death start to occur with infarction
4 house
When is cell death complete in infarction
Myocardial infarction
What does MI stand for
Heart attack
What is the more common name for myocardial infarction
Angina pectoris (chest pain) and SOB
What are the 2 main symptoms of ischemia/MI
Syncope, fatigue, can be asymptomatic, sweating, nausea/vomiting, anxiety
What are some other symptoms of ischemia/MI
Women tend to have more vague/slight symptoms. This may include stomach feeling a little off or left shoulder pain
Explain how the symptoms of MI may differ in women
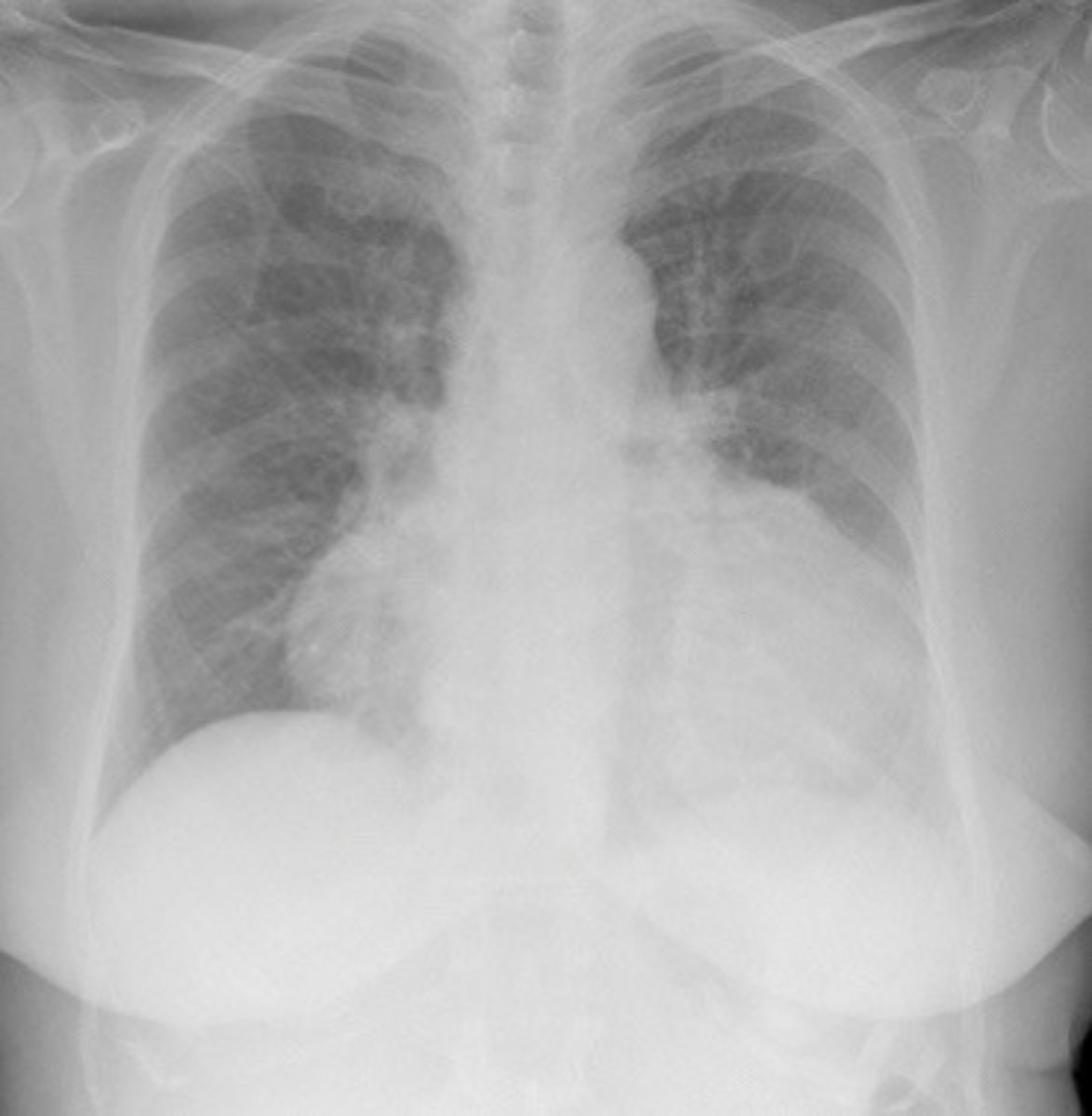
Pulmonary edema and Cardiomegaly
What findings on a CXR may indicate IHD
Heart starts to dilate b/c working so hard
Explain why patients may have Cardiomegaly or pulmonary edema with IHD
Cardiomegaly on CXR
What does this image show
S4, possible S3, MR murmur
What findings on auscultation may indicate IHD
Systolic murmur at apex
What murmur indicates MR
60%
What % of patients have MR after an acute MI
Reduced O2 delivery
What causes angina
Heaviness, burning or aching pain in the chest +/- left arm
What may be some indications of angina
Coronary spasm
What may also cause angina pectoris
Quick/acute thickening or contract of coronary artery that causes decrease blood flow (kinda like a acute stenosis)
What is a coronary spasm
Predictable, regular chest pain
What is stable angina
Stable plaque (slow forming, smooth)
What causes stable angina
Rest or nitroglycerine
What is the treatment of stable angina
Ease pain
What is the purpose of treating stable angina with nitroglycerine
More intense/painful chest pain, not predictable
What is unstable angina
Immediate intervention (emergency)
What is the treatment for unstable angina
Unstable angina
Is stable or unstable angina more concerning
MI causes loss of blood to the heart muscle which interrupts the electrical signals, causing arrhythmias (VT/VF). This then progressing into asystole
Describe how MI can progress into cardiac arrest
VT and VF
What arrhythmias does MI cause
CPR and defibrillator (AED/manual defibrillation)
What is the treatment with someone with MI, VT/VF, asystole
10%
Survival rate drops by ______% every minute with no pulse
Thrombolytic and PCI or emergency bypass
How is the patient treated once the pulse is back after an MI
Non-STEMI
What does NSTEMI stand for
ST elevation
What does STE stand for
Zone of ischemia with small zone of cell death
What causes NSTEMI
Subendocardial MI only (usually)
What type of MI causes NSTEMI
Depressed
What does the ST segment look like with NSTEMI
Transmural
What is another term for STEMI
Through the whole thickness of the myocardium (endo to epi)
What part of the heart wall is affect with a STEMI
Elevated
What does the ST segment look like with STEMI
STEMI (NSTEMI is still bad tho)
Is NSTEMI or STEMI more serious
P wave
What is 1
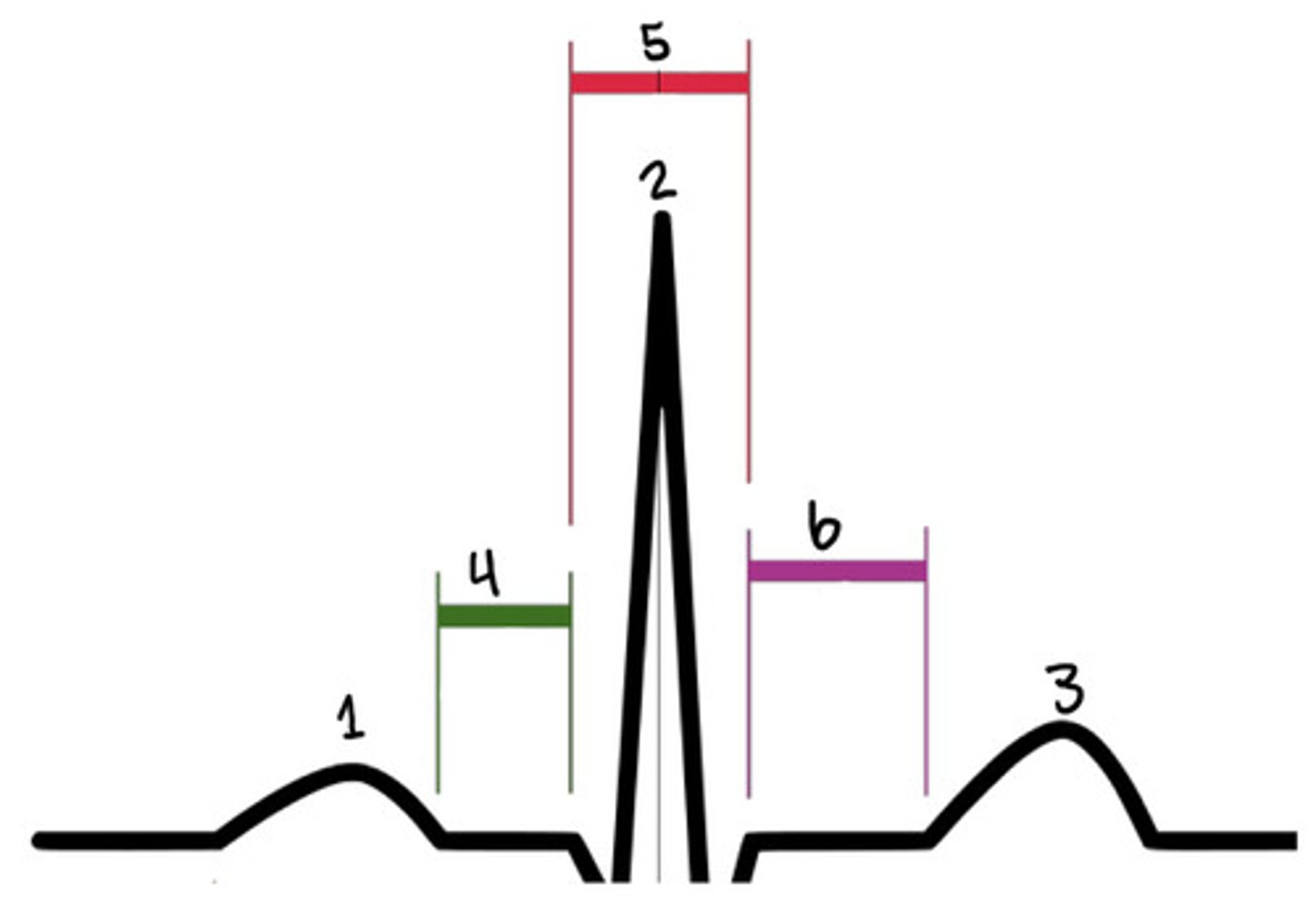
R
What is 2
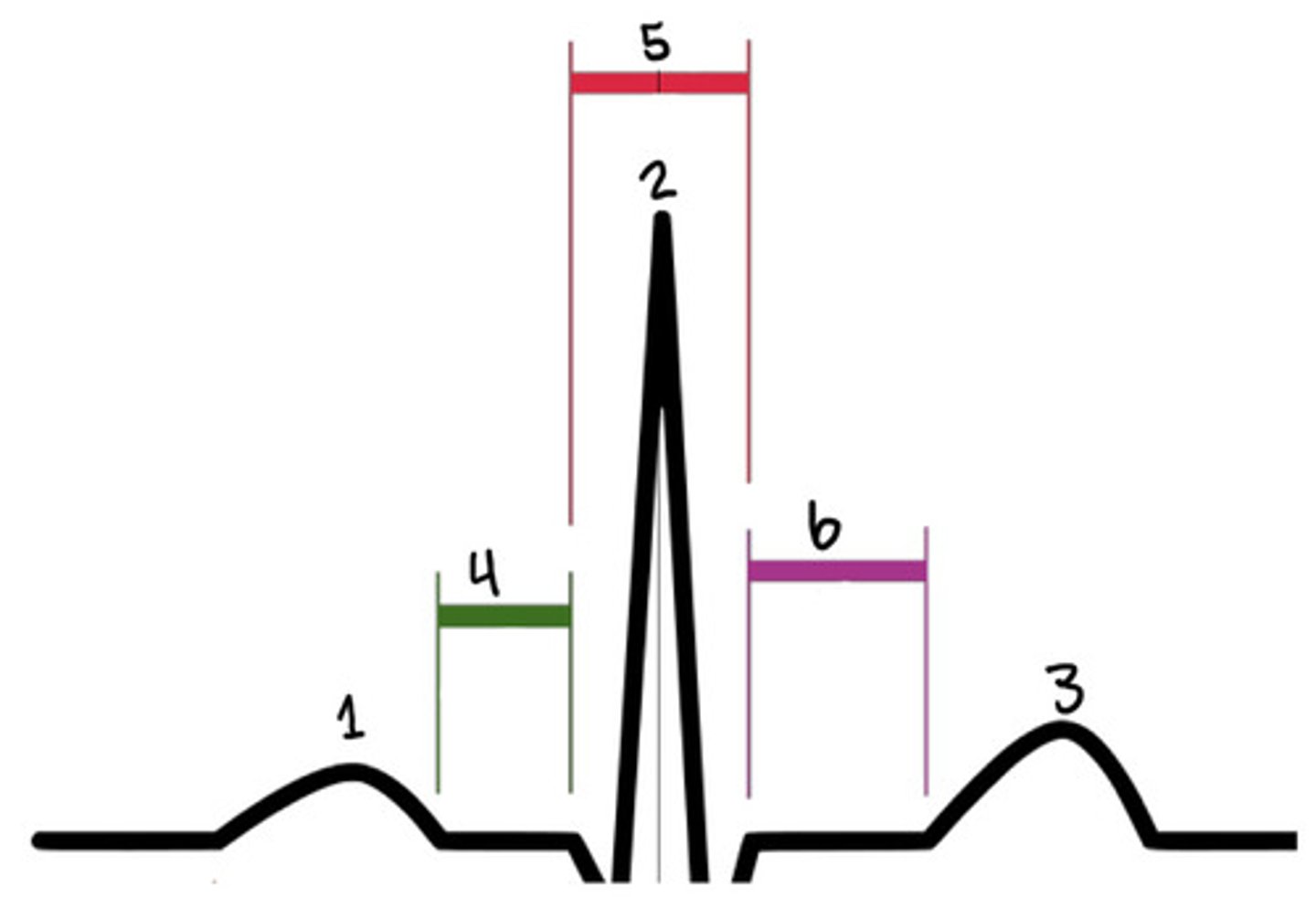
T wave
What is 3
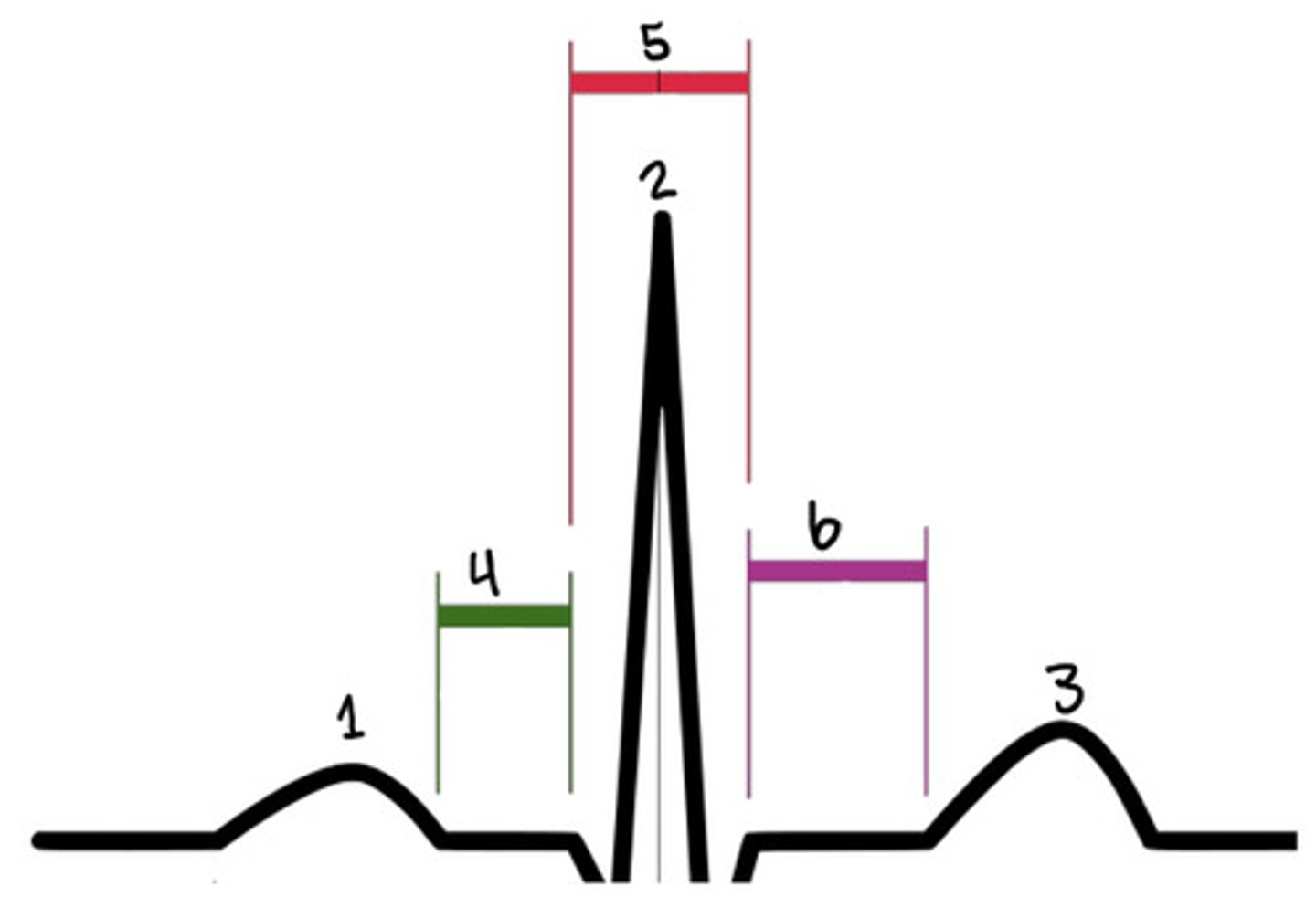
PR segment
What is 4
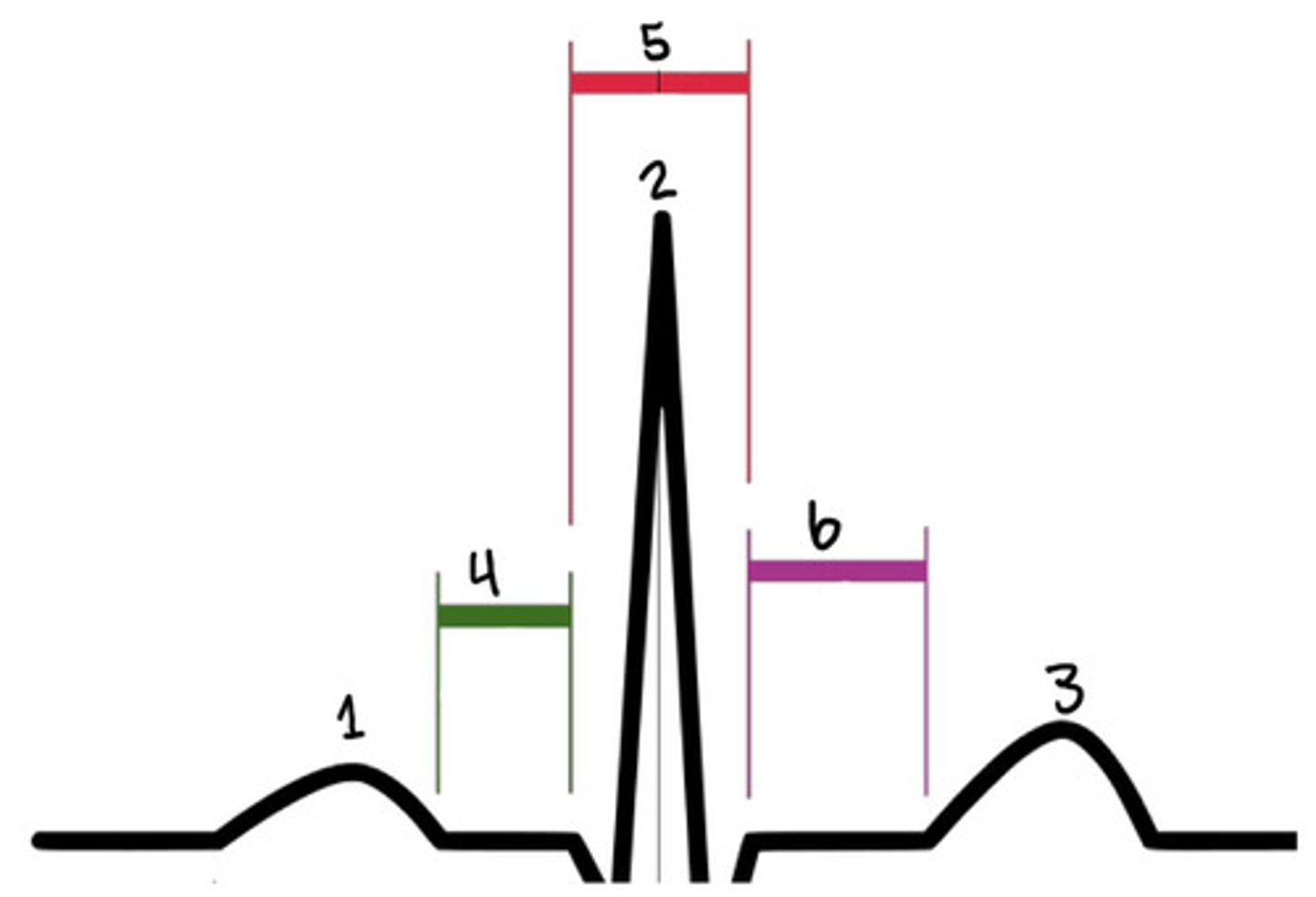
QRS complex
What is 5
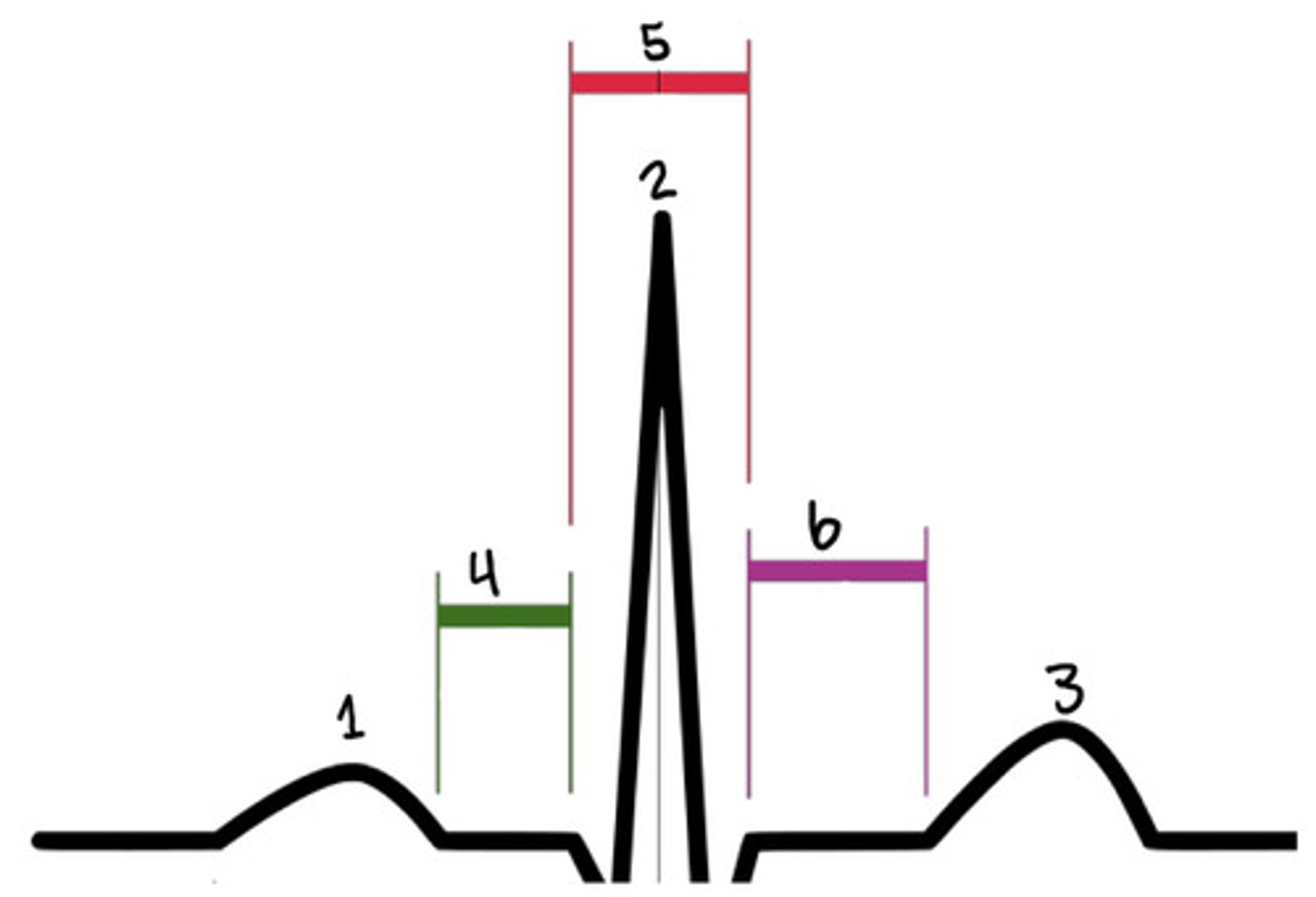
ST segment
What is 6
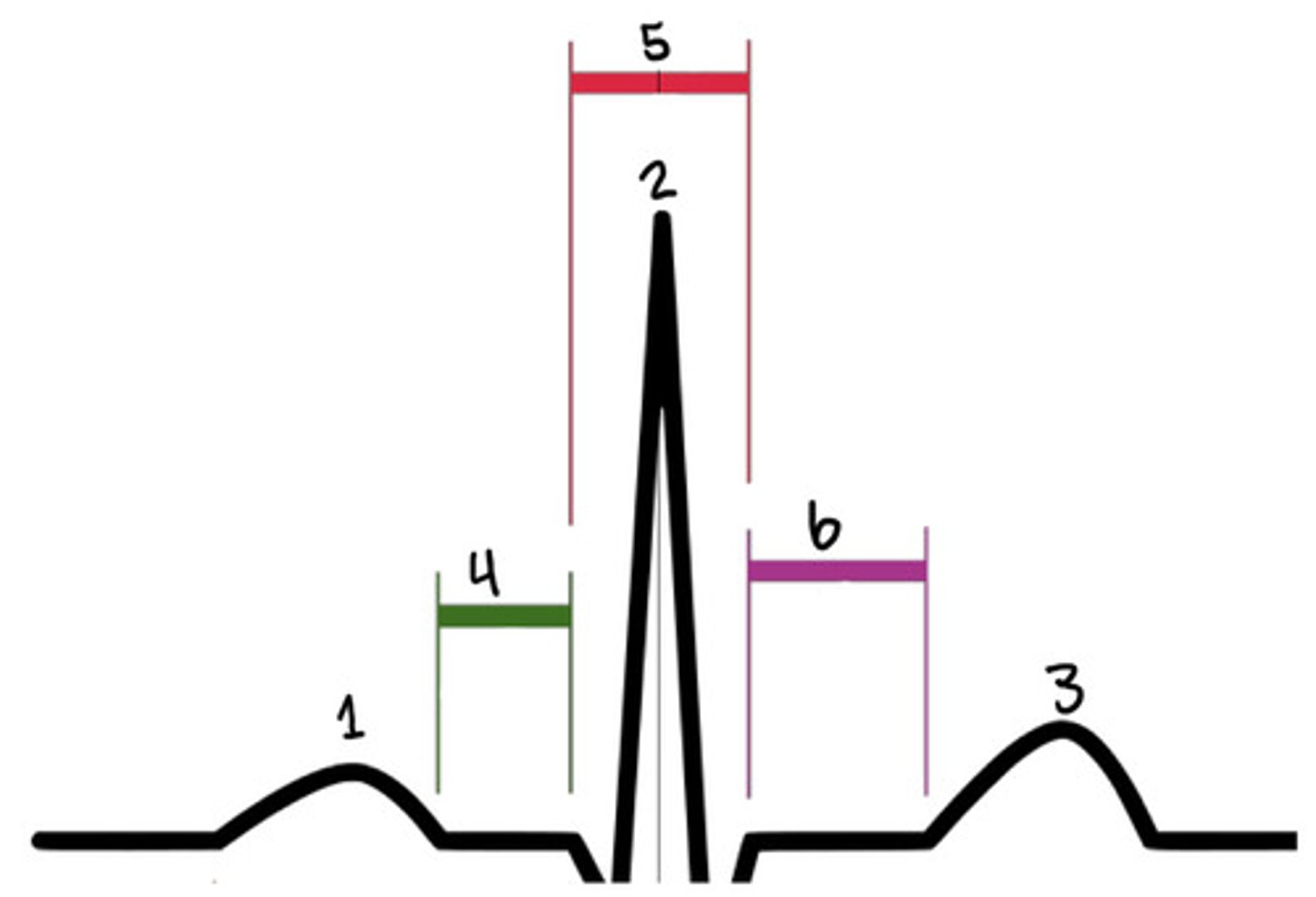
QRS
What represent electric systole
ST segment
What represents mechanical systole
ST segment is same level as TP segment
Describe the normal ECG
Isoelectric
What is another term for a normal ECG
ST segment is lower than TP segment
Describe the appearance of ST depression
Ischemia
What does ST depression indicate
ST segment above TP segment
Describe the appearance of ST elevation
Infarction
What does ST elevation indicate
Normal ECG
What does this image represent
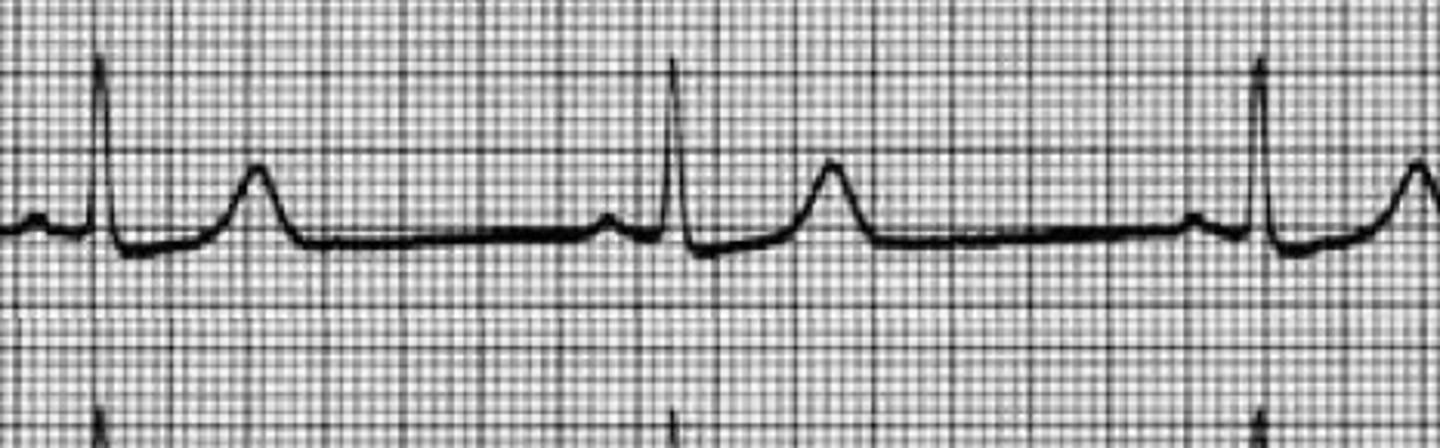
NSTEMI (ST depression)
What does this image represent
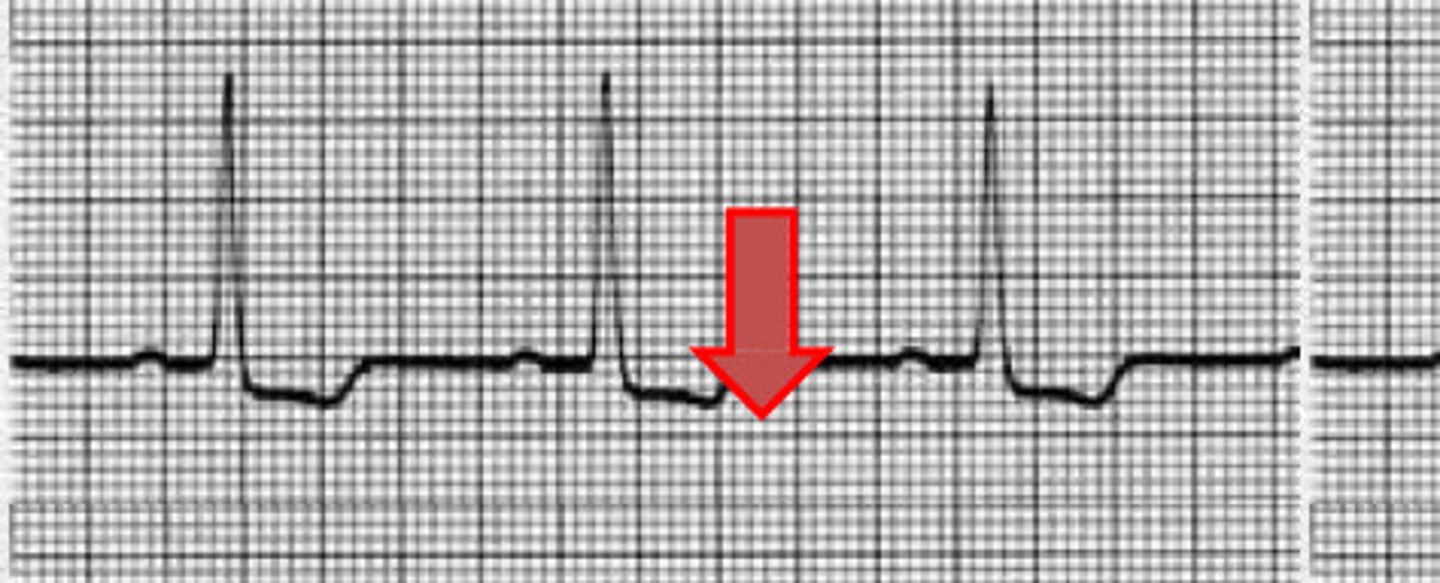
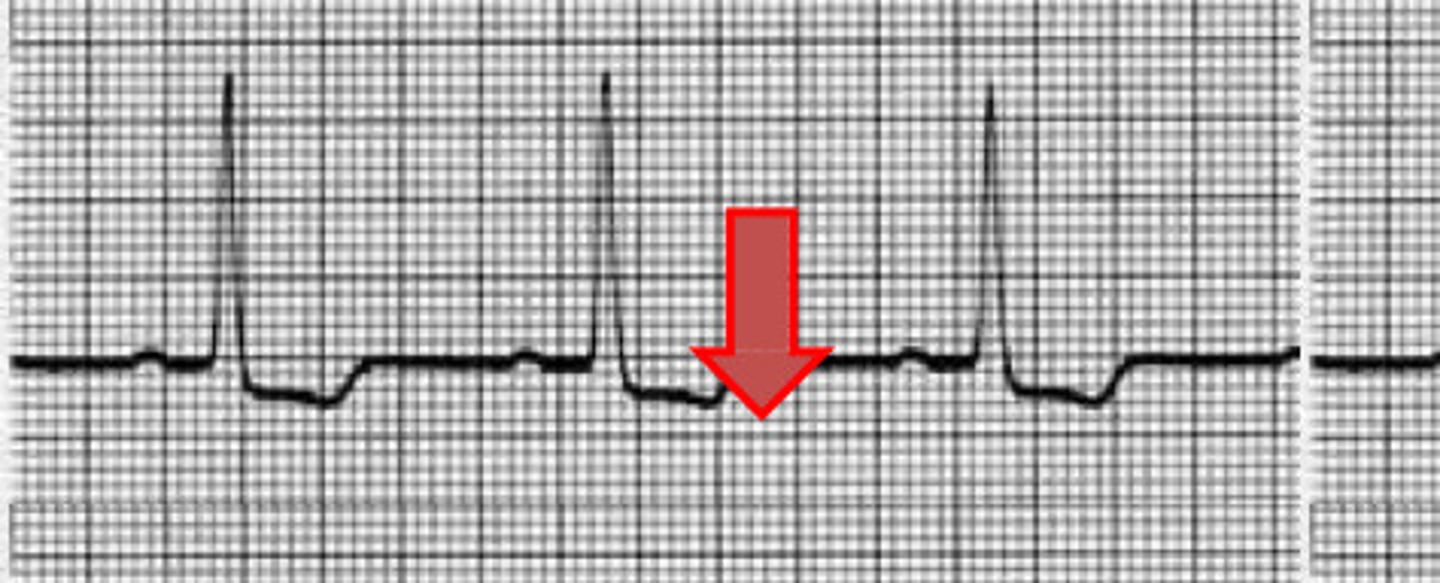
STEMI (ST elevation)
What does this image represent
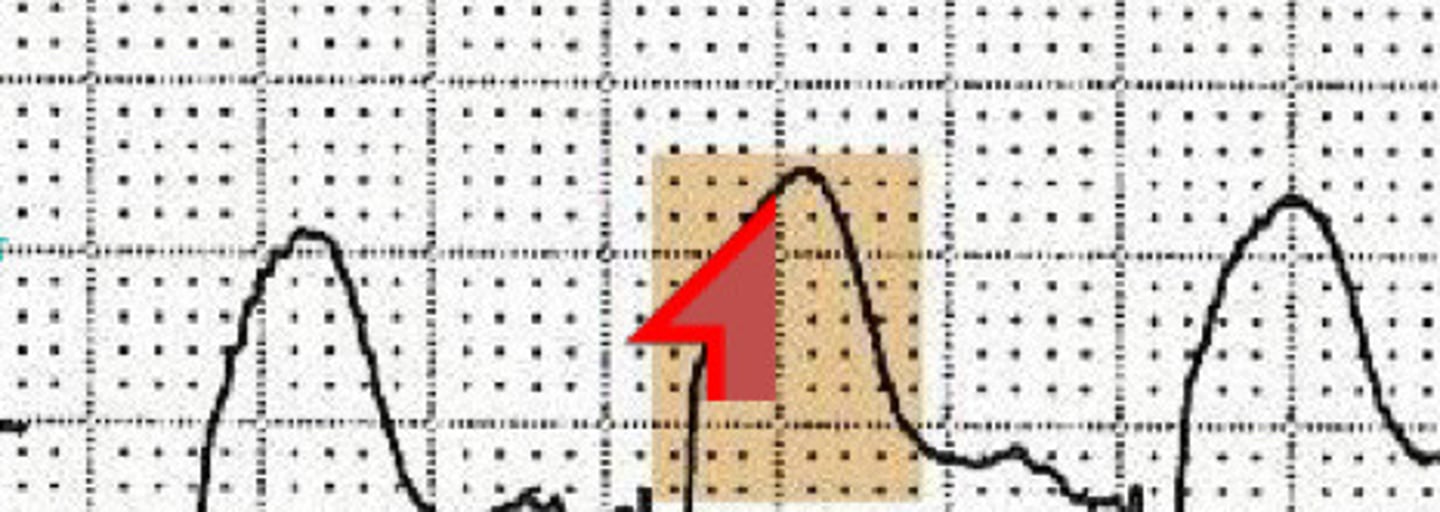
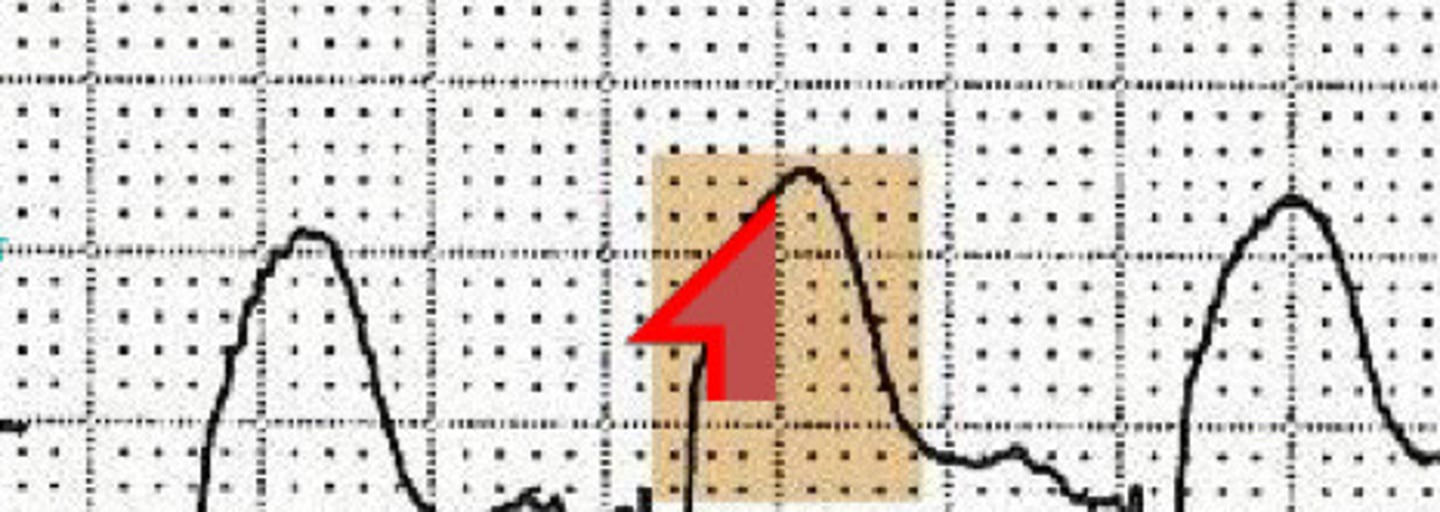
Ischemia
What condition does this ECG indicate
Infarction
What condition does this ECG indicate
Heart blocks (AV block, LBBB), Qwaves peaked T waves, revered T waves, any arrhythmia originating in ventricle
What are some other ECG changes that may indicate MI
Atria and vertices aren't communication
What is an AV block
New LBBB may indicate a MI starting
Describe the relationship between and LBBB and MI
Wide QRS
Describe the appearance of an LBBB
False not always a MI may just be an LBBB
T/F: an LBBB always indicates a MI
LBBB (may indicate MI)
What arrhythmia does this image represent
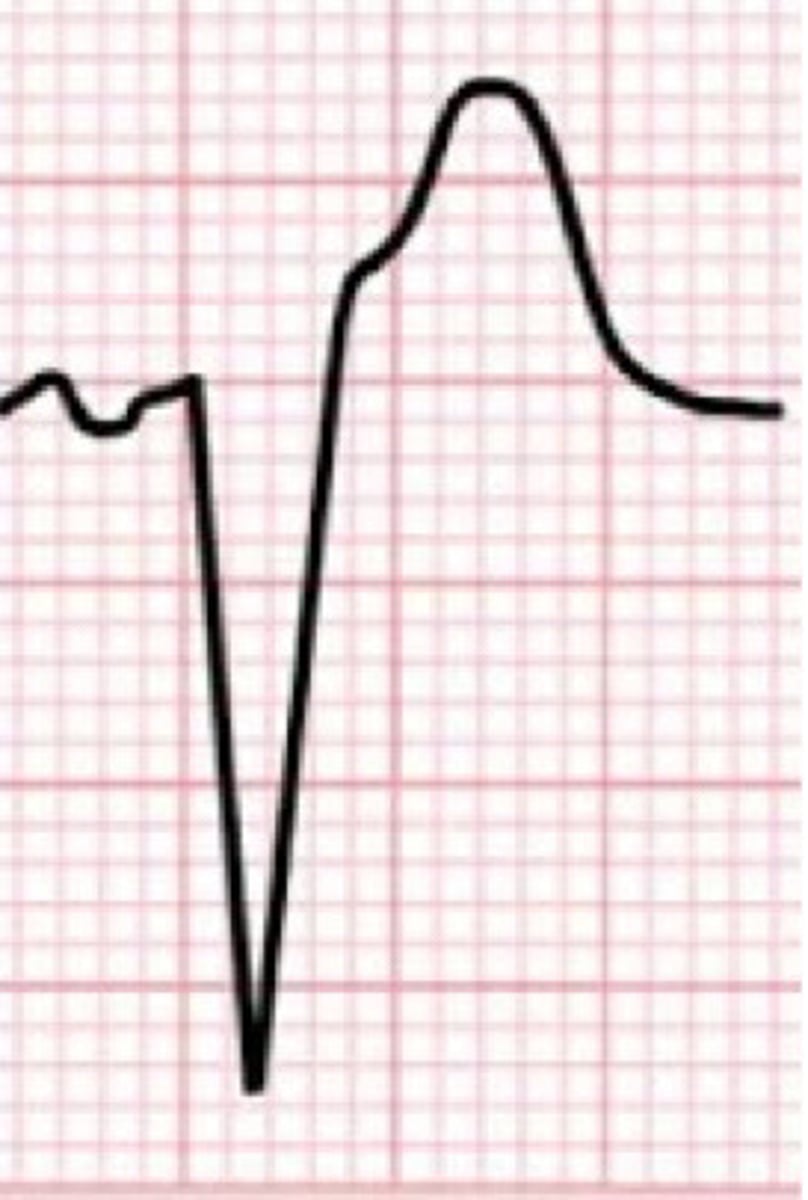
Old MI (from necrotic tissue)
What does Q waves indicate
Acute MI
What does peaked T waves indicate
Chronic ischemia
What does reversed T waves indicate
Lifestyle modifications
What is the treatment for IHD
Quite smoking, diet (avoid salt, fat, alcohol), exercise, stress management, weight loss, BP reduction (treat HTN)
What are some examples of lifestyle modifications for IHD
Nitroglycerine
What is the medication for pain relief
Palvix and warfarin/coumadin
What are some medications for anitcoagulation
IHD causes stagnant flow so try to prevent clots
Why may a patient with IHD be treated with anticoagulation
Decrease HR and afterload
What do beta blockers do