ANTHRO 360 EXAM 2
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Homework and Lecture Notes. Chapter 6,7,8,9,11
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What technique(s) might help you reconstruct bones?
Look for segments with matching shaped edges and look at the color of the pieces.
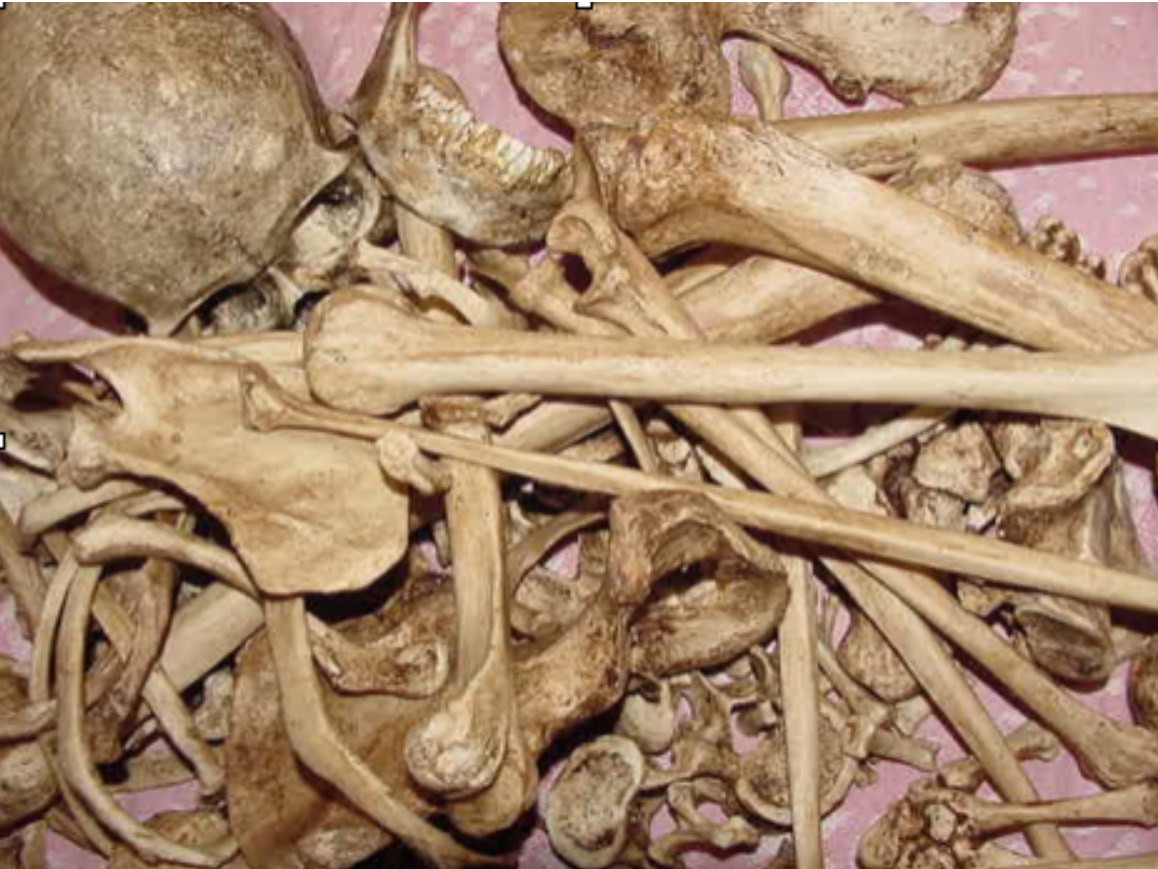
What techniques might you use to separate commingled bones?
Look for consistency in size
Look for duplication of bones
Check the robusticity of the bones
Pay attention to the fused and unfused epiphyses
How many individuals are present in this image?
2
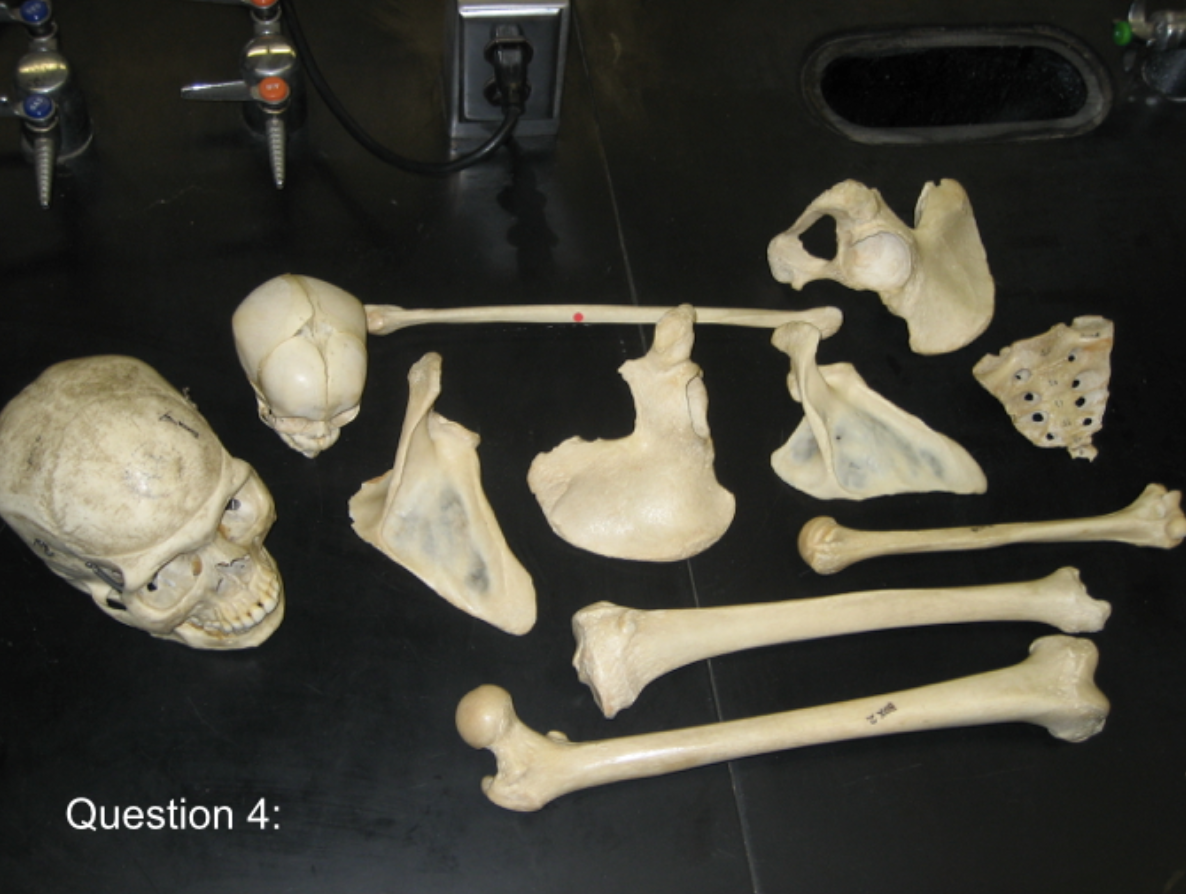

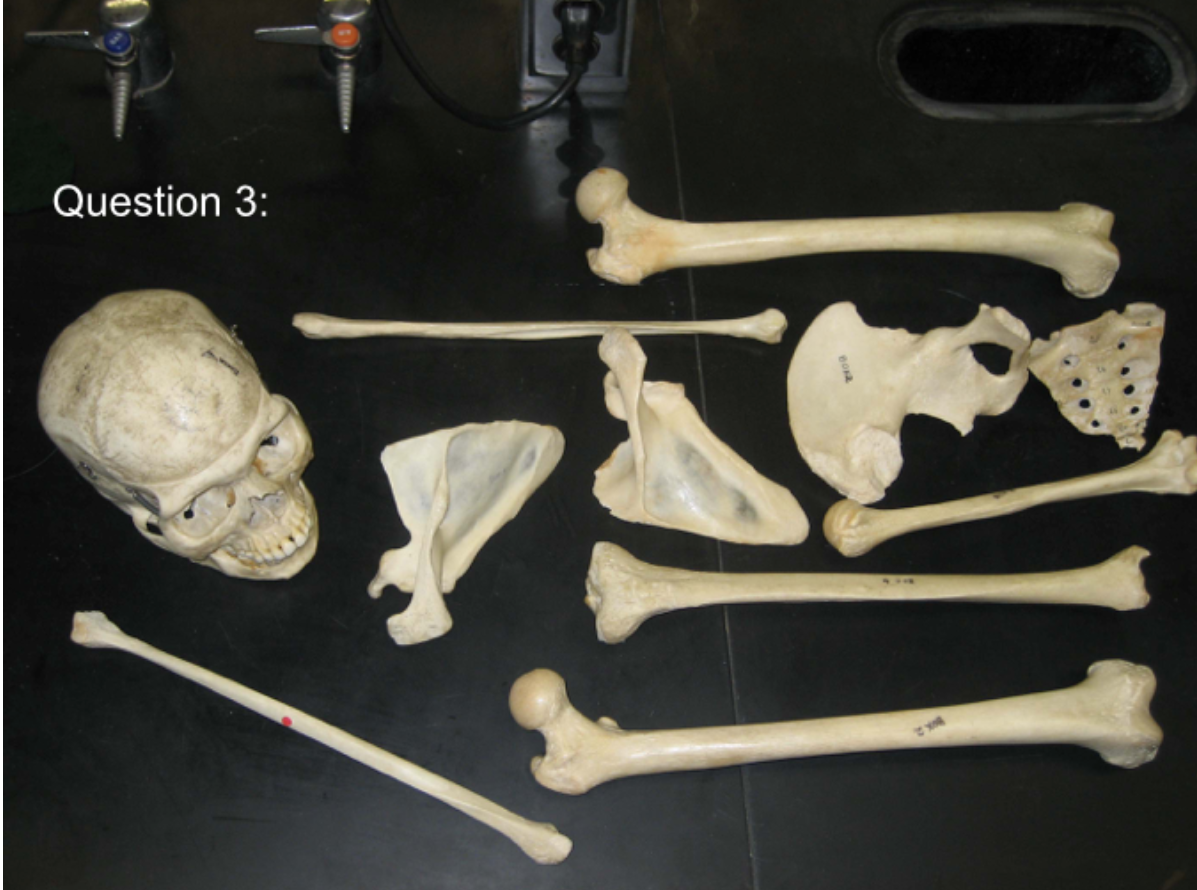
What is the minimum number of individuals for this image?
3
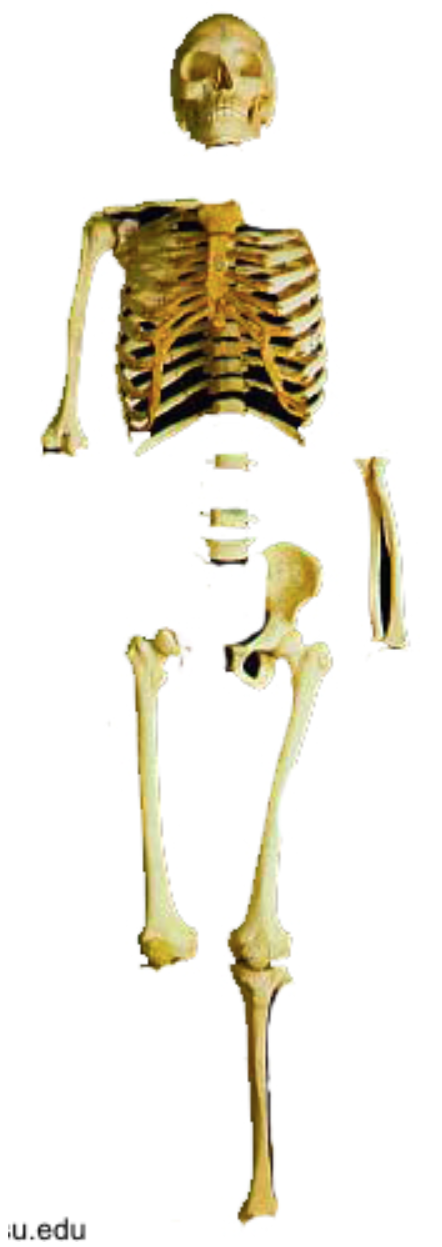
What bones are missing from this individual?
Cervical vertebrae, left clavicle, left humerus, right ulna, right radius, 2 lumbar vertebrae, right os coxa, sacrum, right tibia, right fibula, left fibula, both feet, and both hands
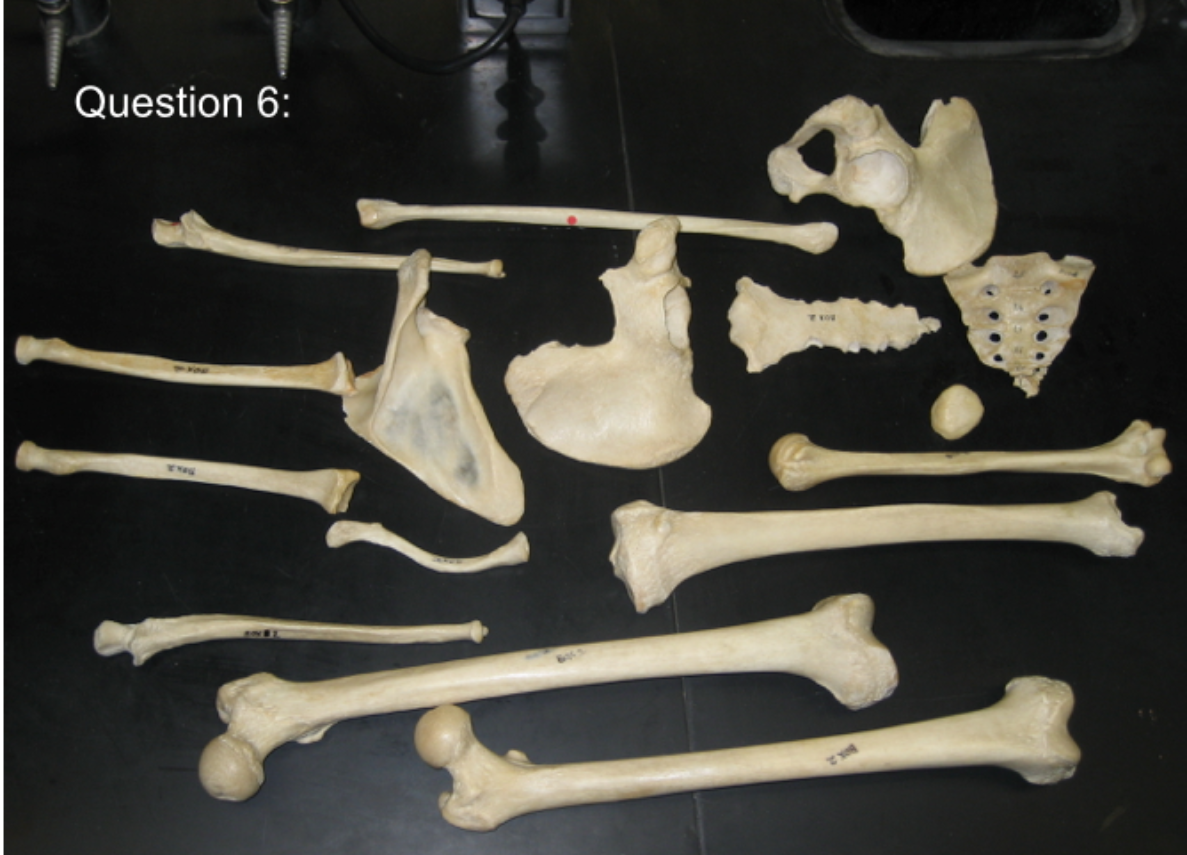

Inventory the remains from this image.
Right humerus, right ulna, left ulna, right radius, left radius, left clavicle, right scapula, sternum, right os coxa, left os coxa, sacrum, right femur, left femur, left tibia, right fibula, right patella
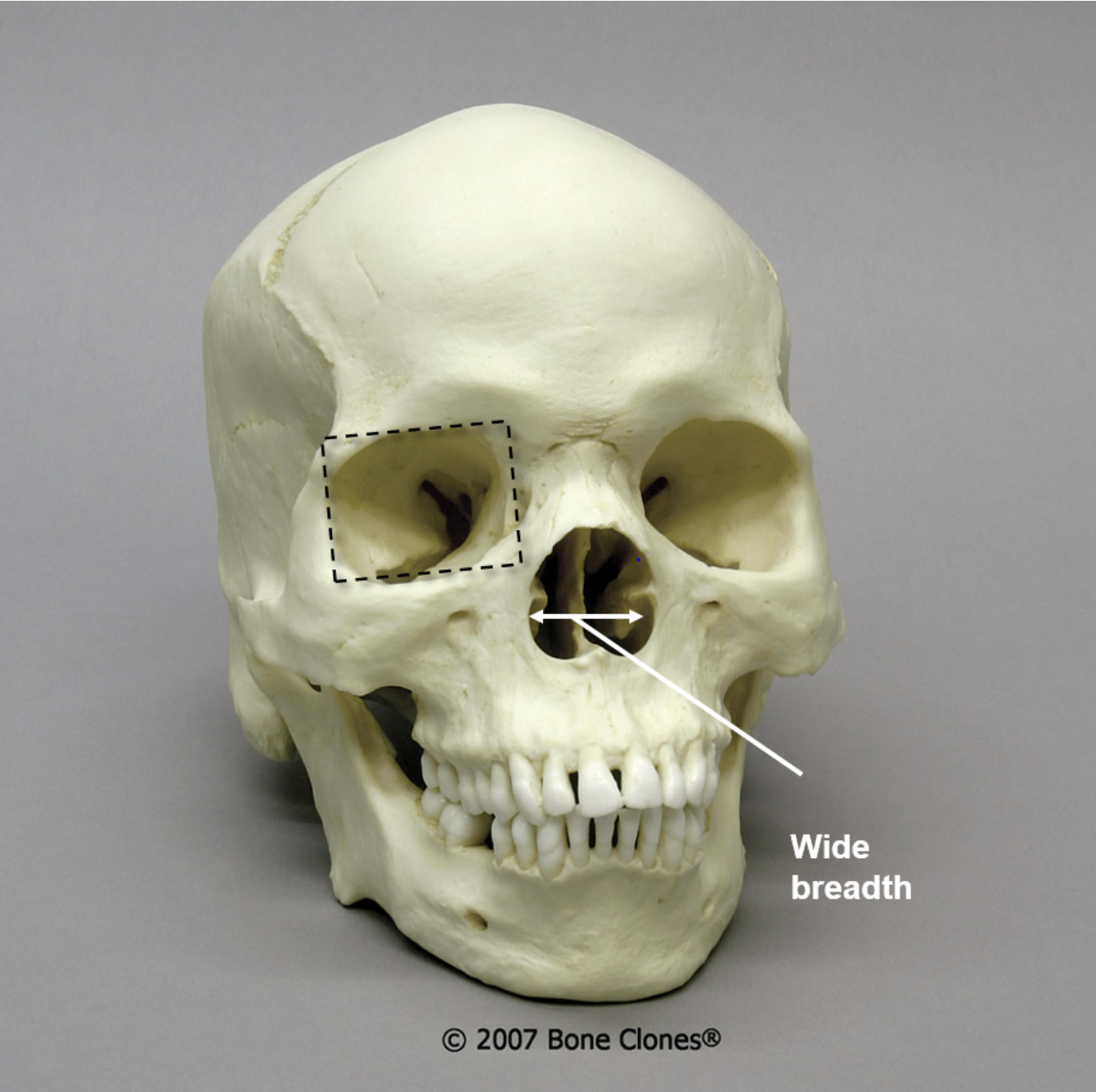
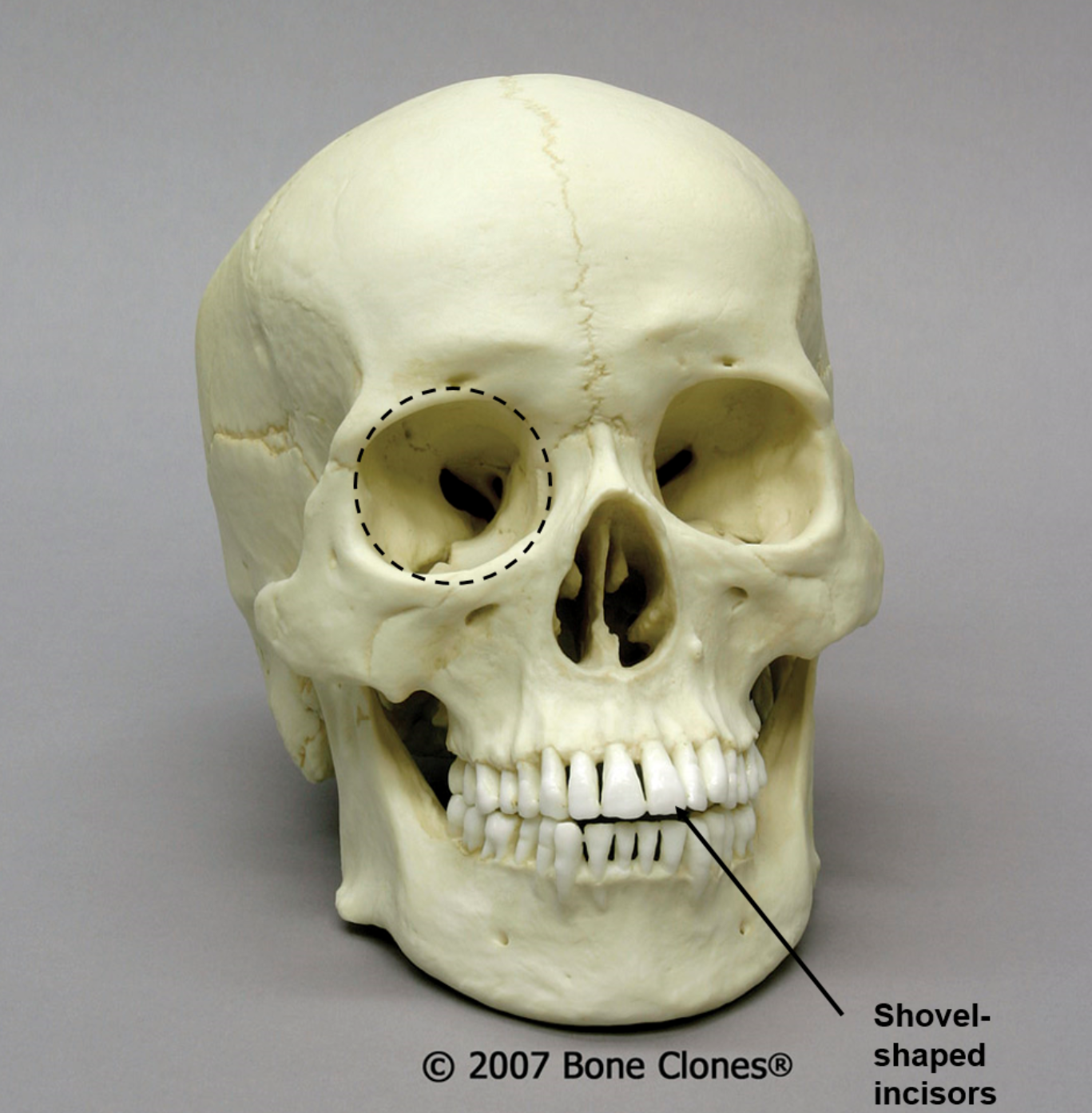
What is the ancestry of this skull?
African
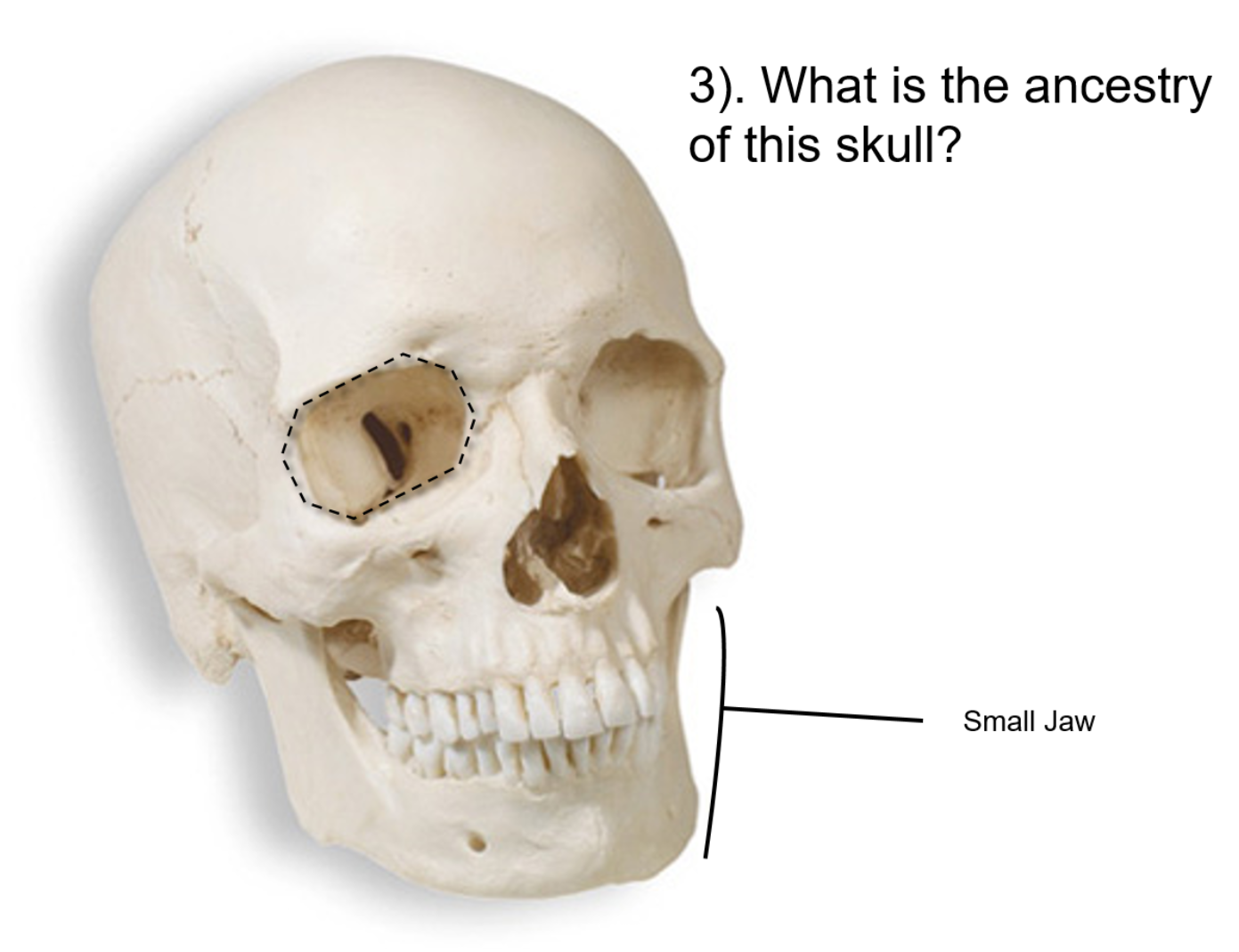
What is the ancestry of this skull?
Asian
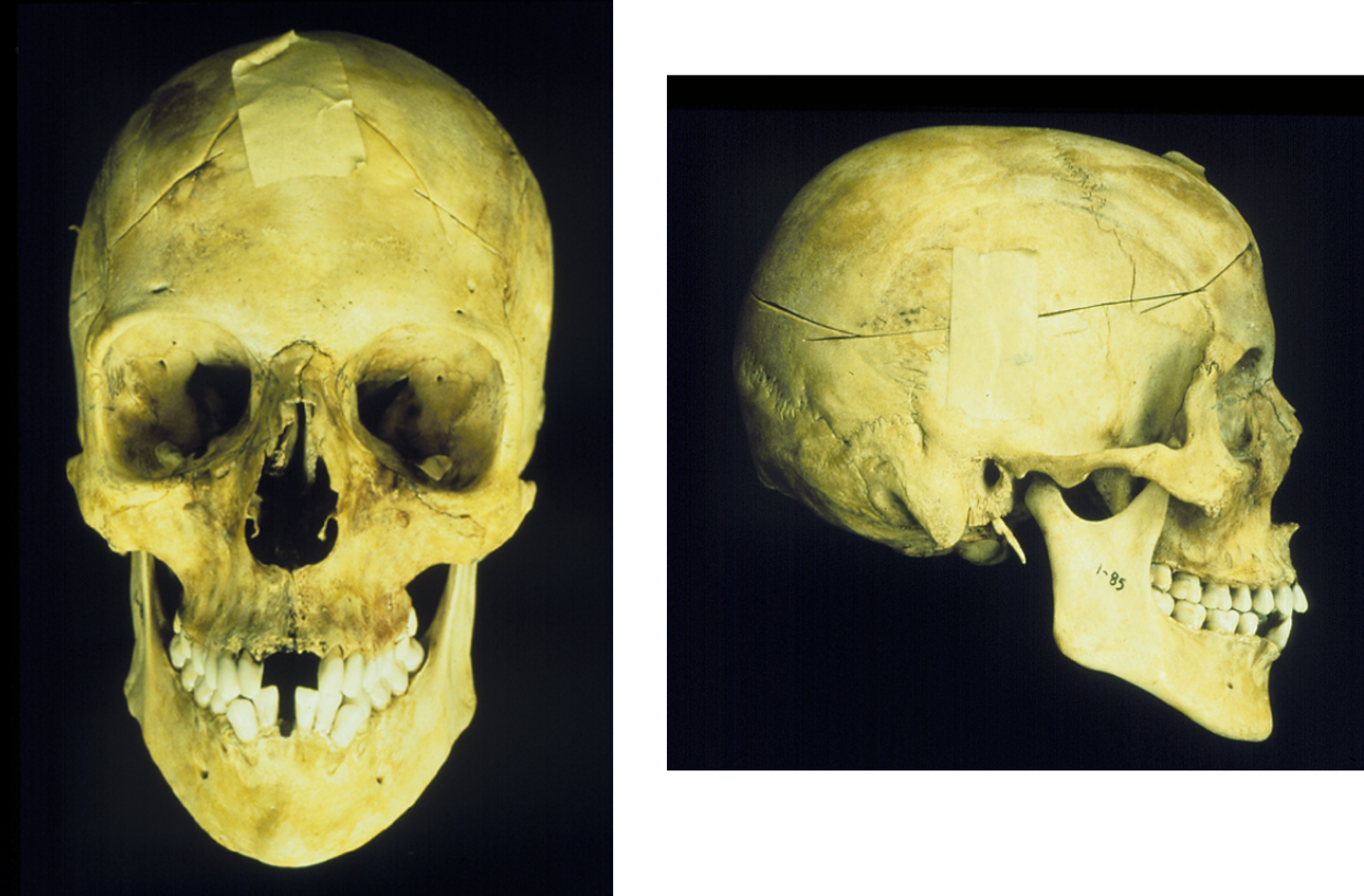
What is the ancestry of this skull?
European

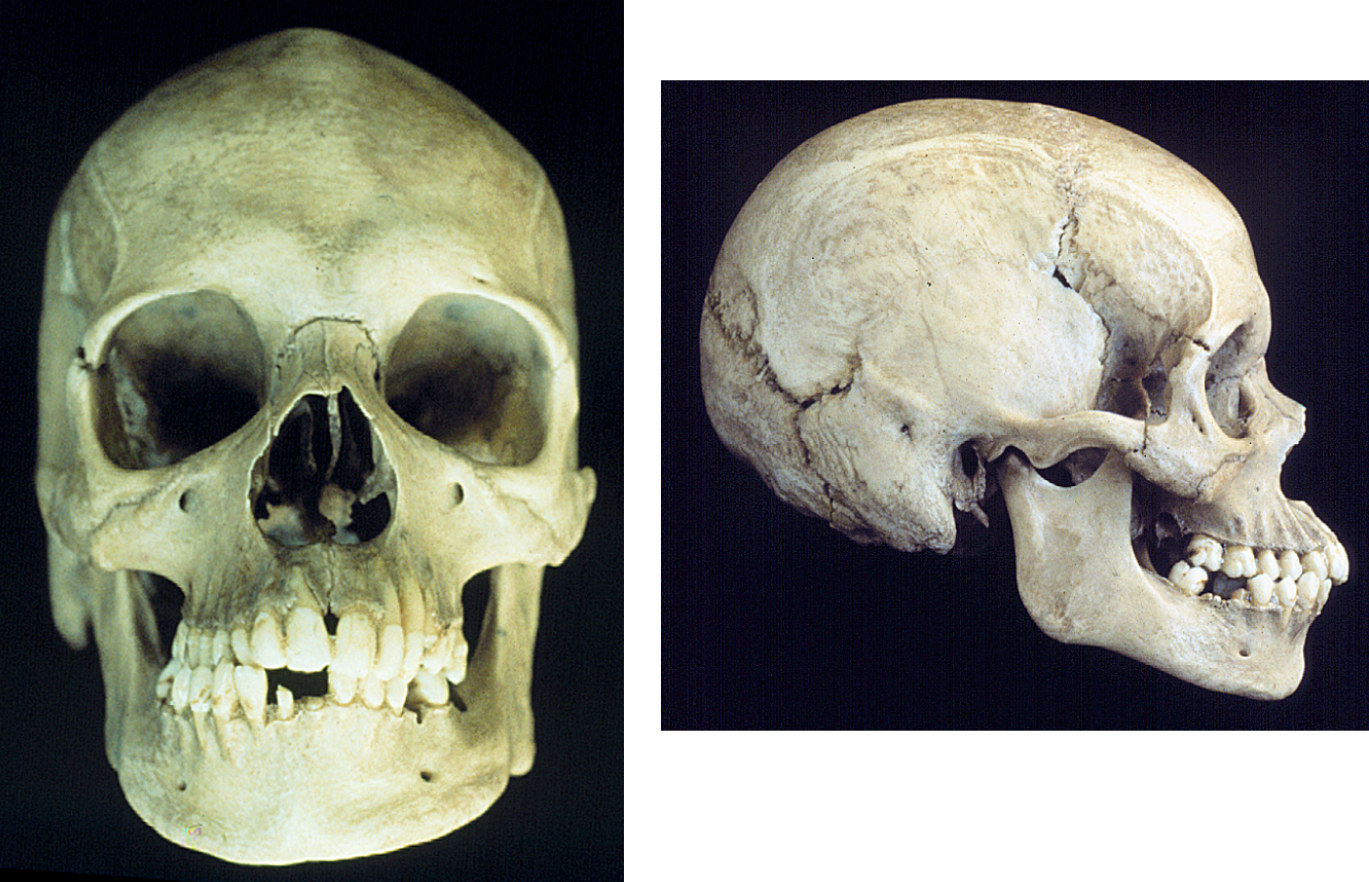
What is the ancestry of this skull?
Asian
What is the ancestry of this skull?
European
What is the ancestry of this skull?
African
What is the ancestry of this skull?
African
Is this skull of White ancestry?
False
Is this individual male or female?
Male
Is this individual male or female?
Female
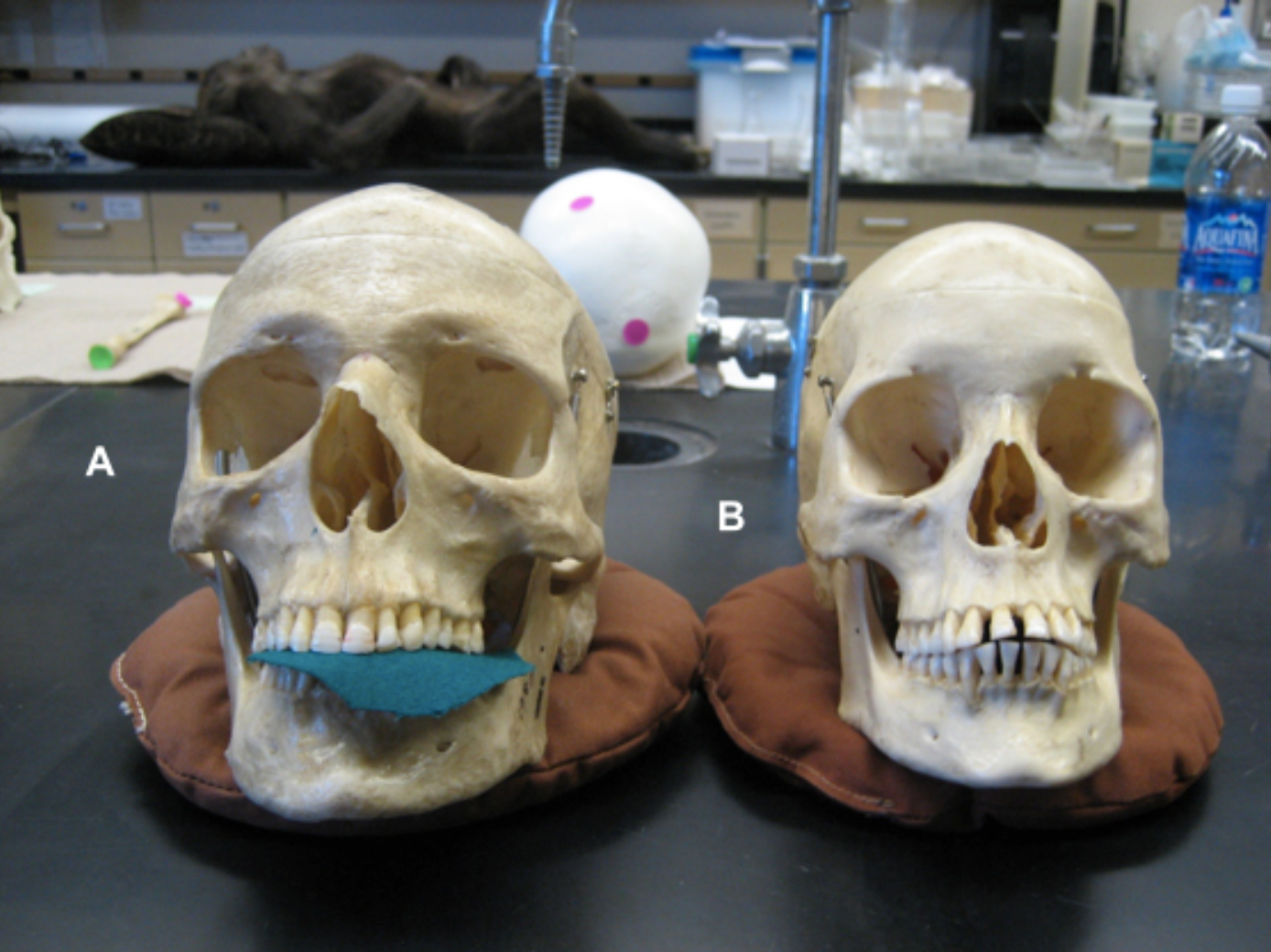
Based on the characteristics discussed in your texts, which of these two individuals is female? Answer: A (the skull on the left) or B (the skull on the right).
B
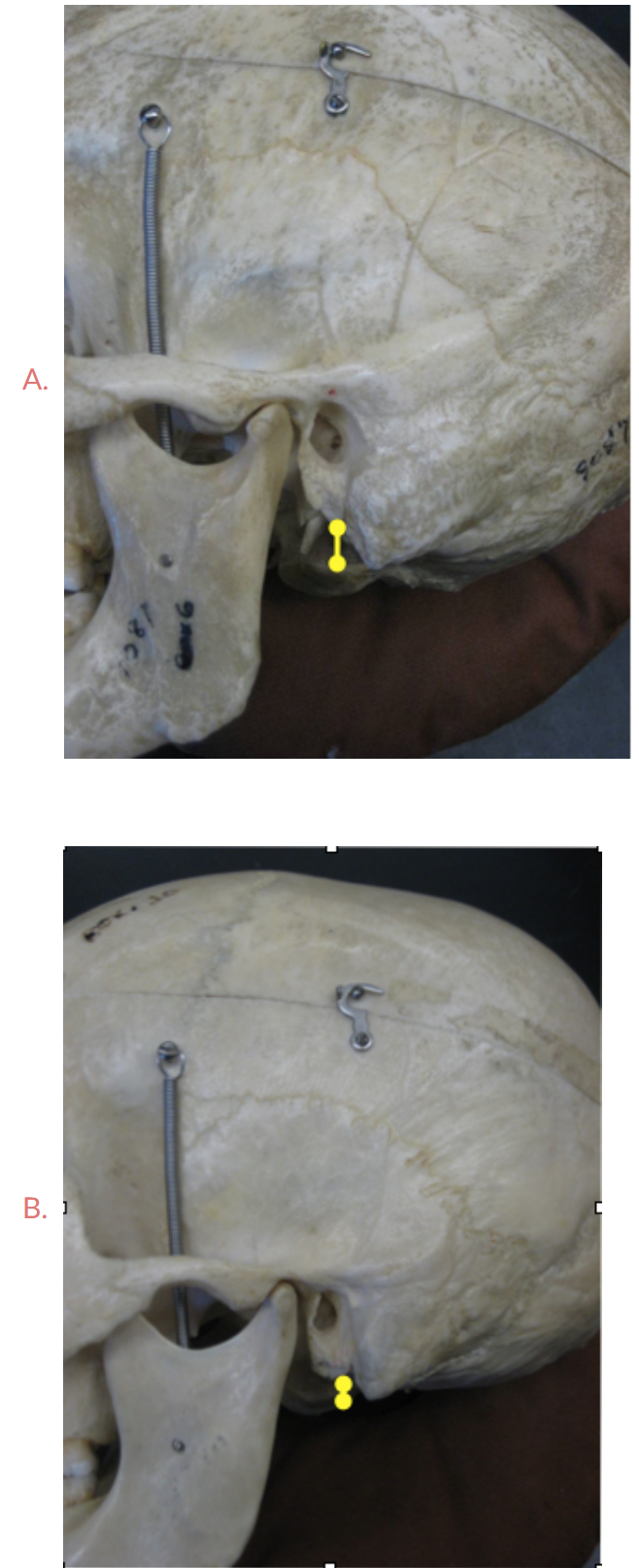
Look at the mastoid processes, which of these skulls is male? Answer: A or B
A
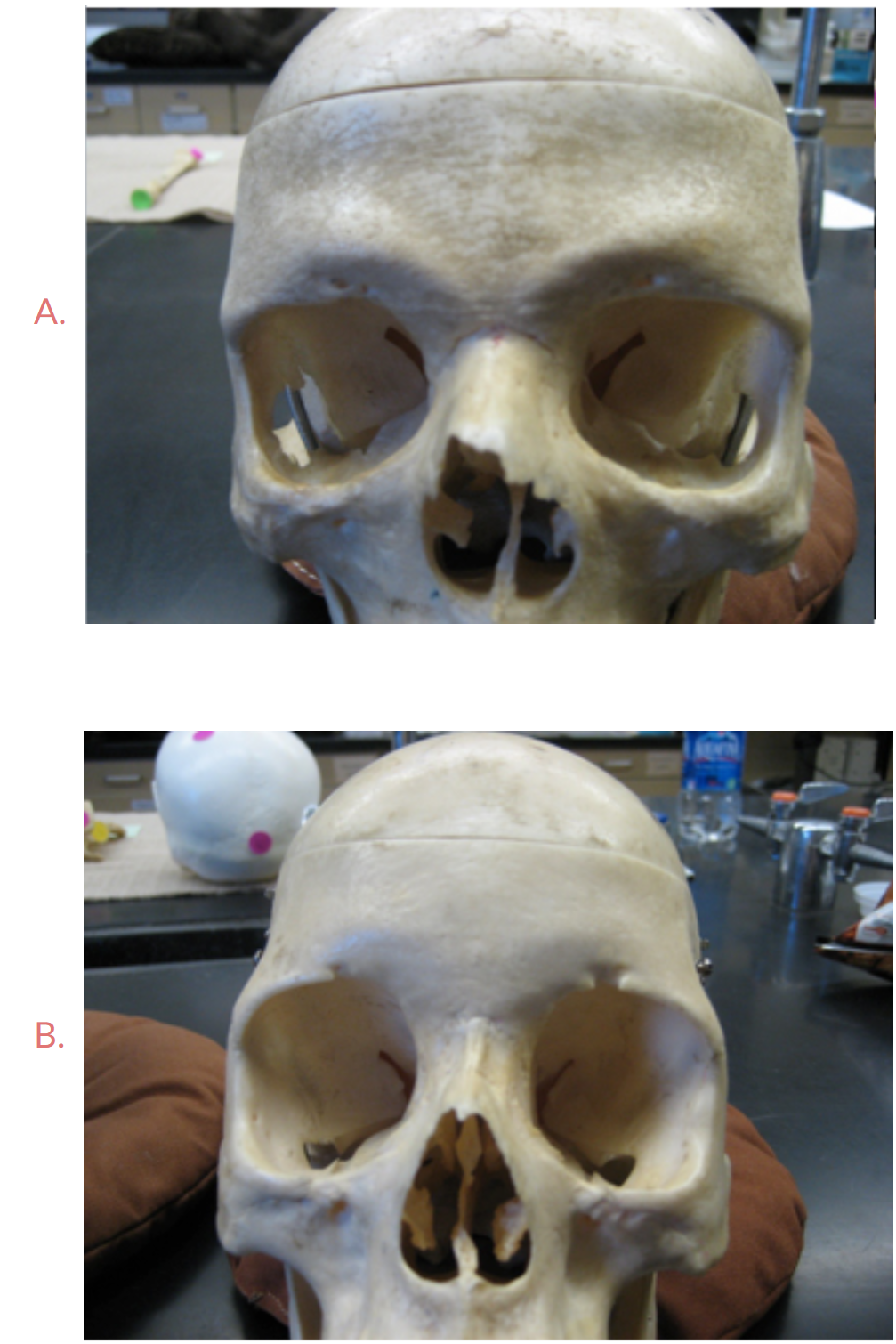
Look at the brow ridges of these two skulls, which one is male? Answer A or B
A
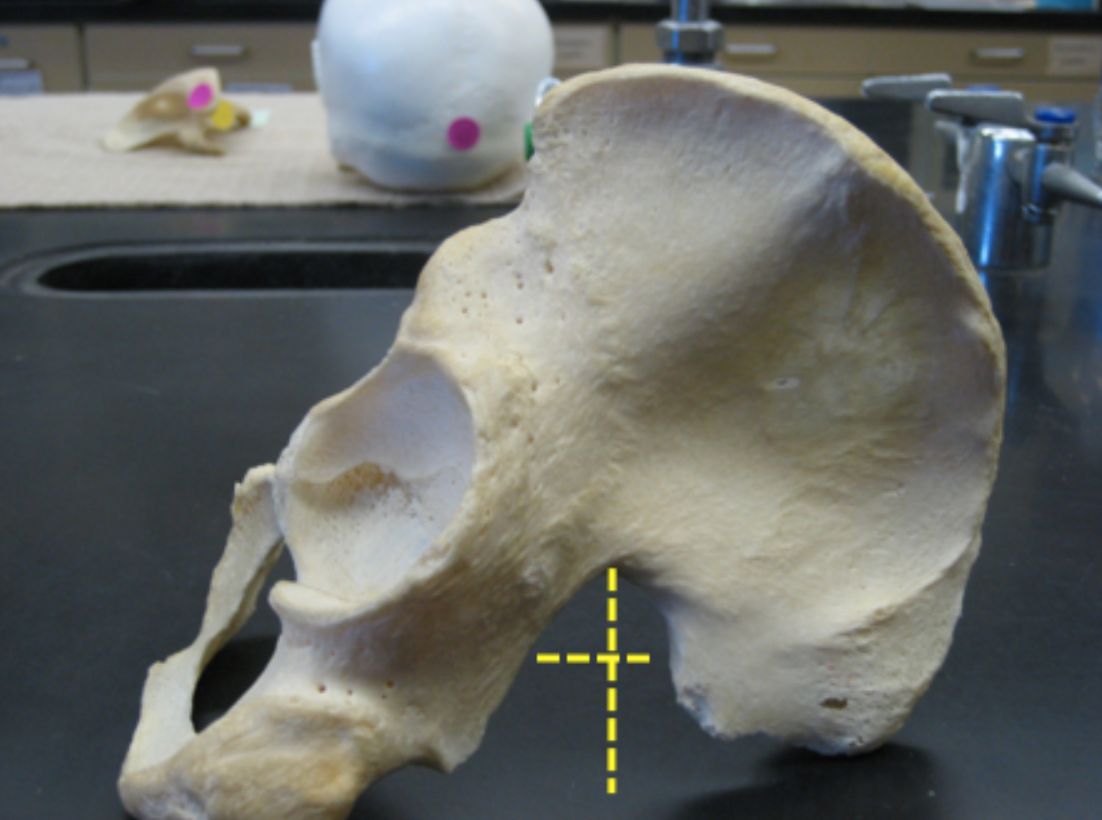
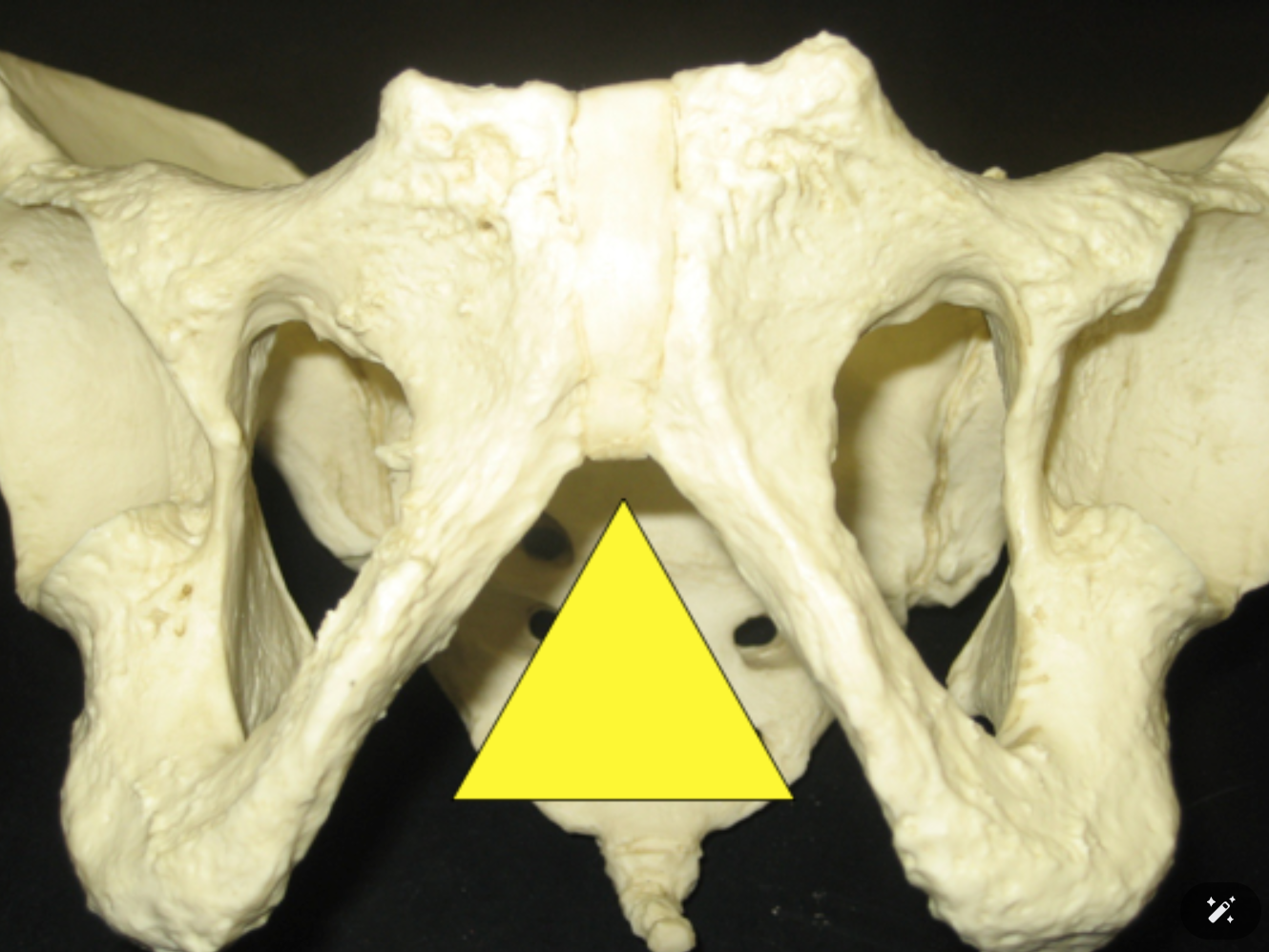
Look at the greater sciatic notch, is this os coxa male? Answer Yes for male, No for female.
True
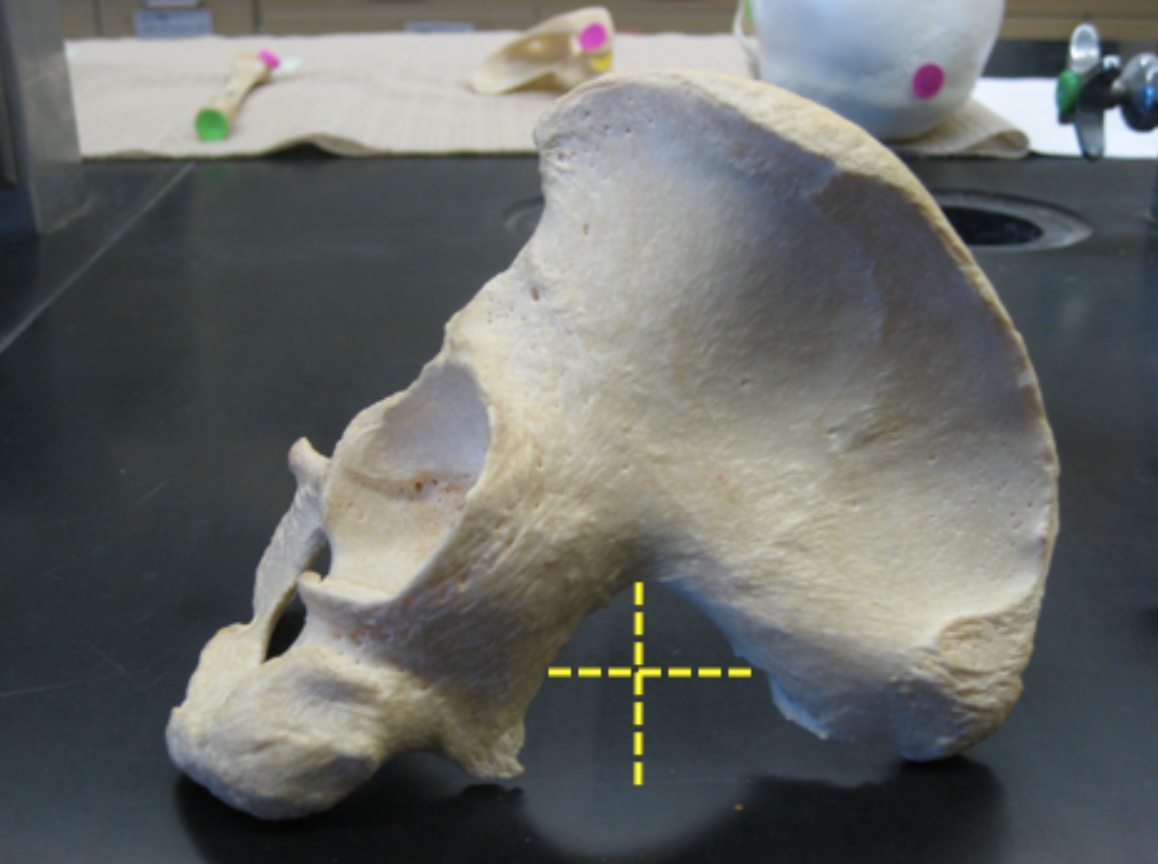
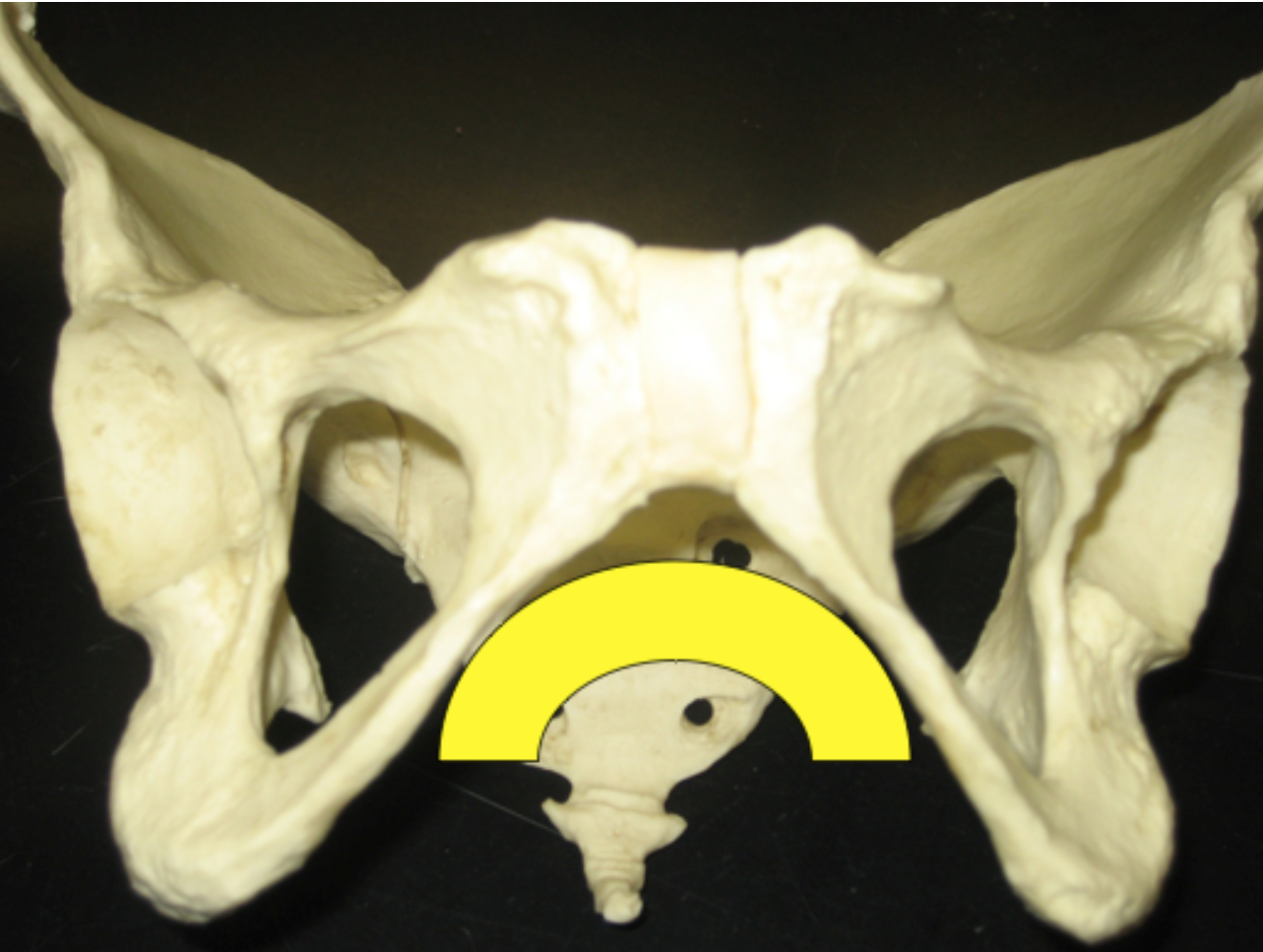
Look at the greater sciatic notch, is this os coxa male?
False
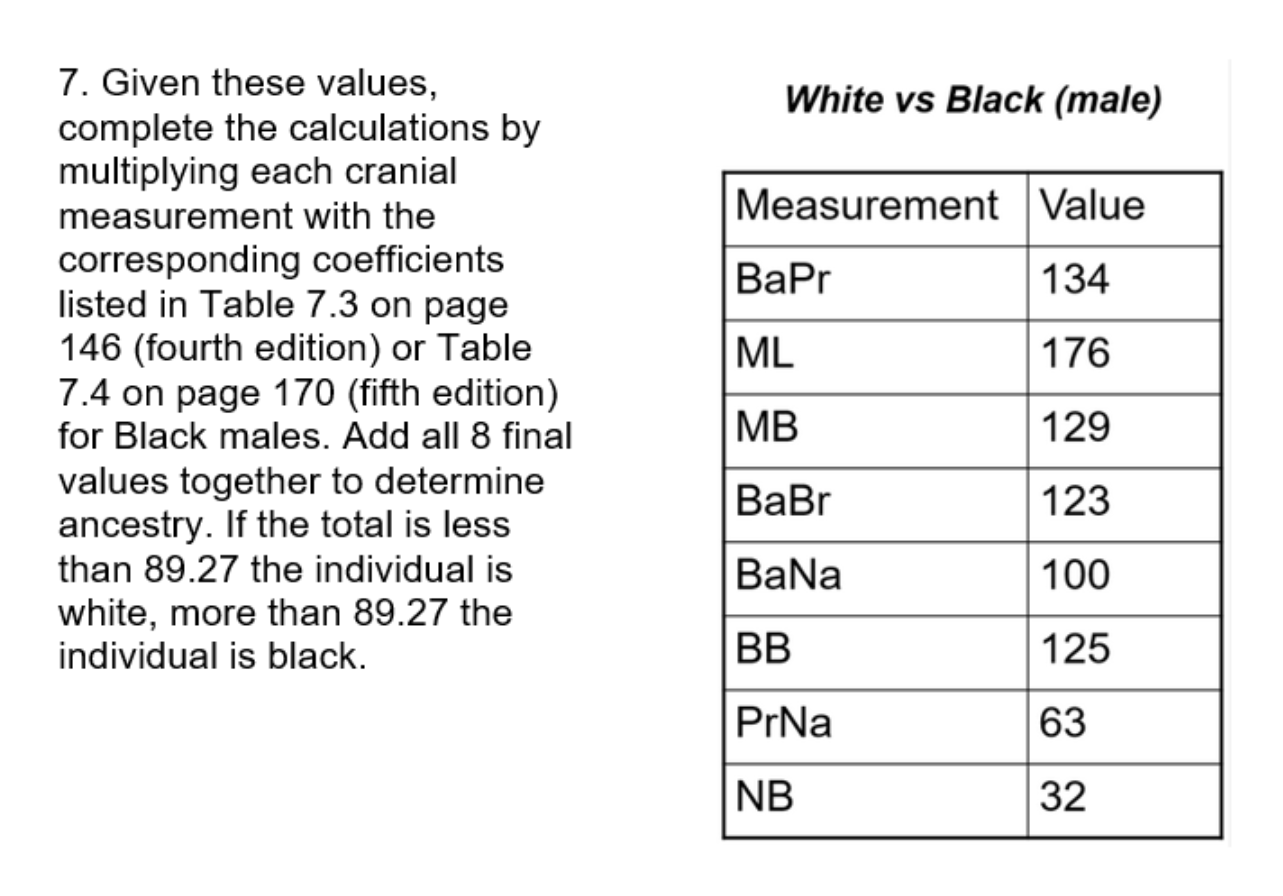
Determine the sex of this African (black) individual based on the measurements below and the discussion of metric methods on page 158 (fourth edition) or 184 (metric methods, fifth edition). Remember, values under 83% are male, while indexes over 88% are female.
Pubic length = 71.57 mm
Ischium length = 68.30 mm
Remember: Pubic length divided by Ishium length times 100 = answer
Female
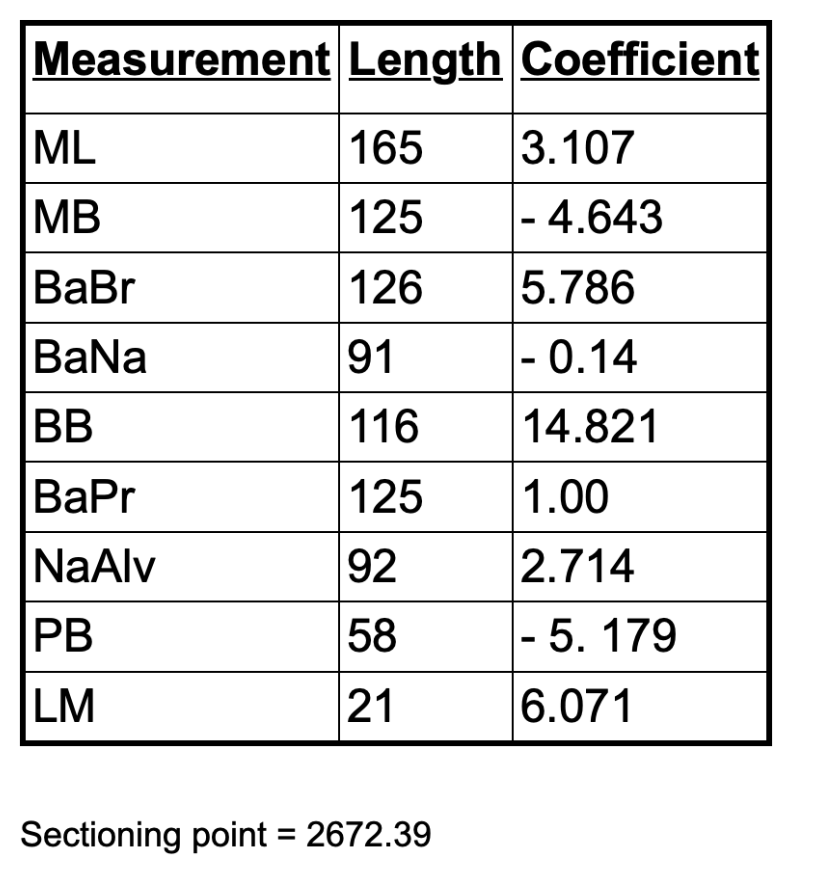
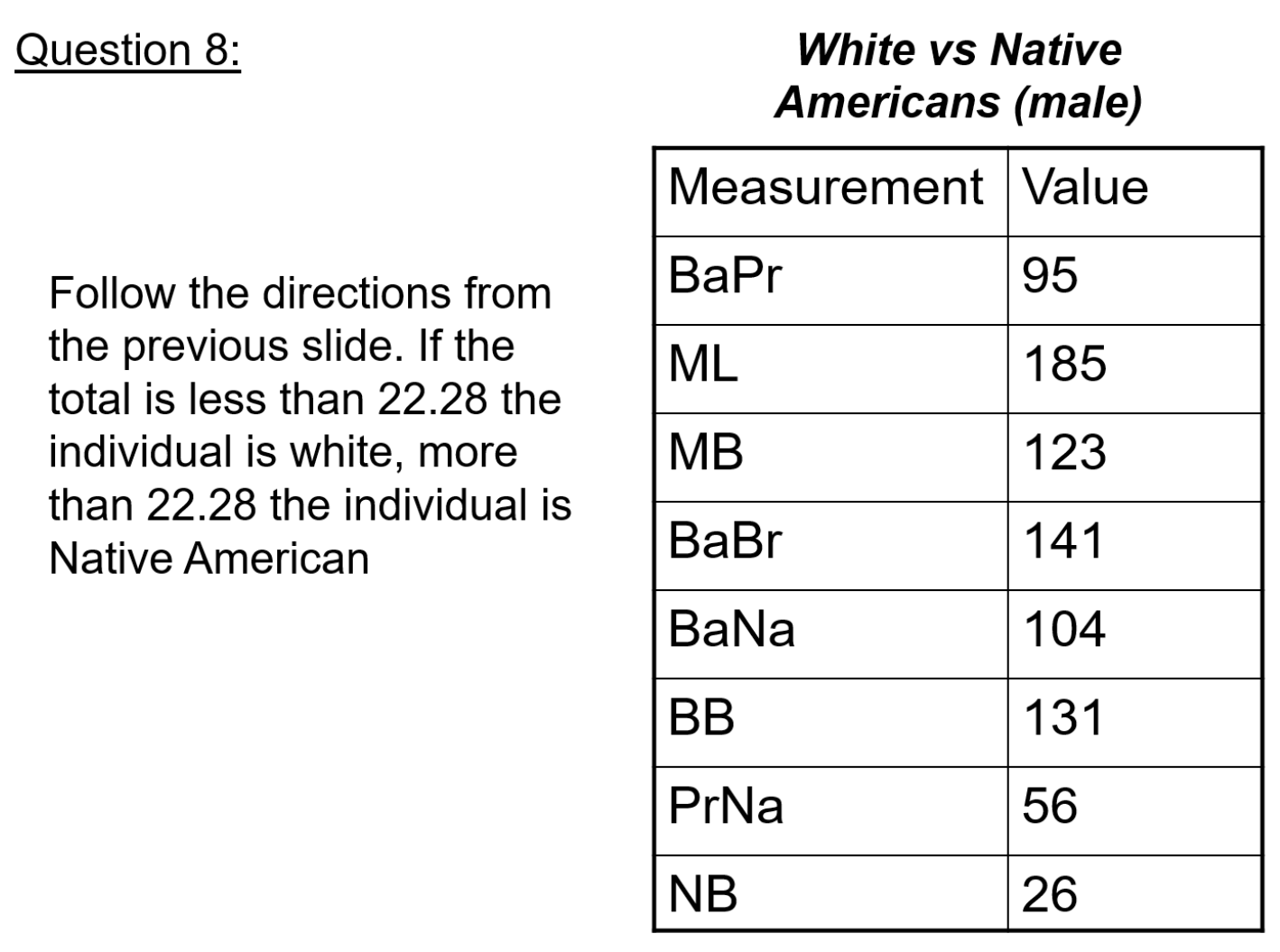
Based on the sum of these cranial measurements, is this individual male or female?
Female
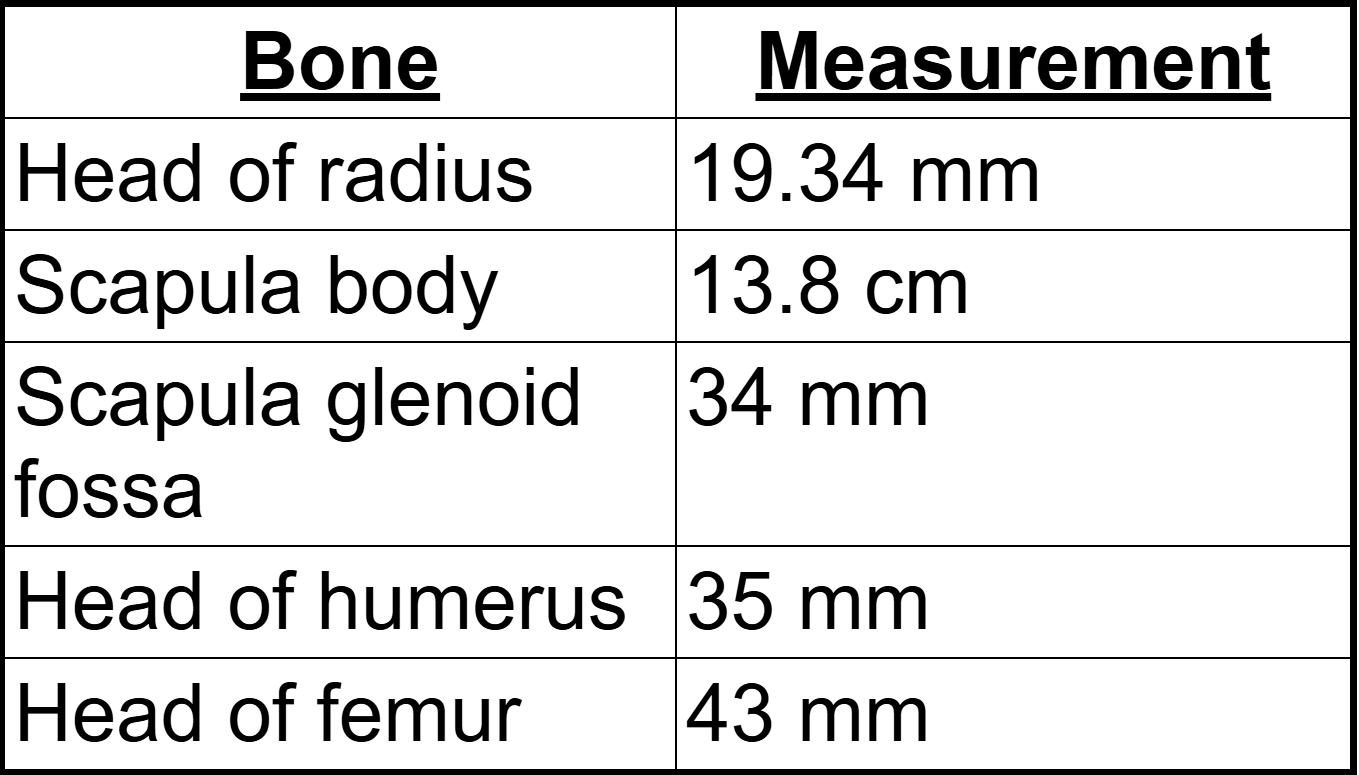
Based on the provided postcranial measurements, is this individual male or female? Answer M for male and F for female, the letter must be capitalized in order to receive credit for your answer.
*note: this is not taking into consideration the length of the femur, fibula, tibia, humerus or ulna.
Female
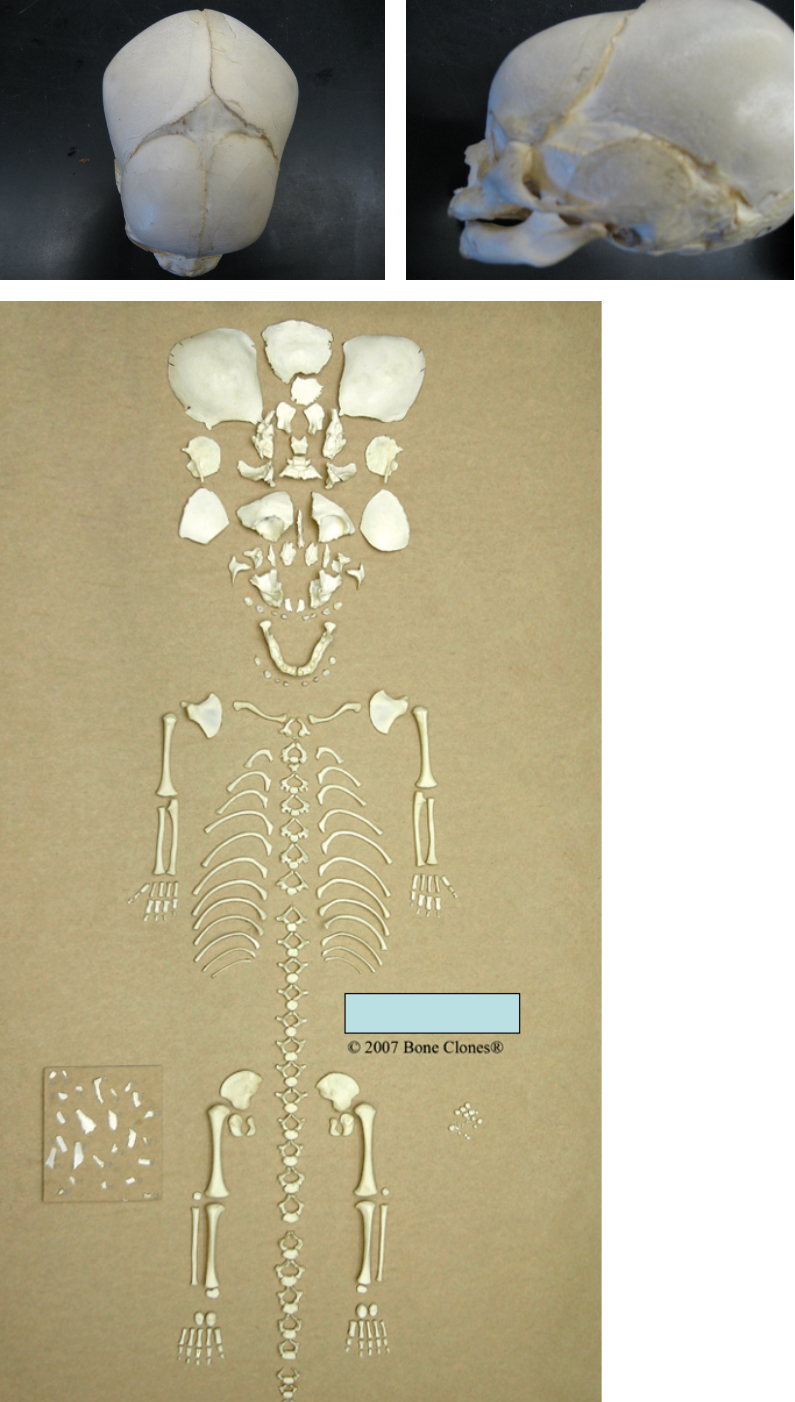
![<p><span>Use your textbook [pages 177-178 (fourth edition) or pages 204-205 (union of primary ossification centers, fifth edition(using the bold line)), or 203-205 (sixth edition)] to determine the approximate age of this subadult based on the measurements given</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6a3eeee4-318c-4494-b495-8e106ea5fcb7.png)
Use your textbook [pages 177-178 (fourth edition) or pages 204-205 (union of primary ossification centers, fifth edition(using the bold line)), or 203-205 (sixth edition)] to determine the approximate age of this subadult based on the measurements given
6
How old was this individual at death?
Full term/soon after birth
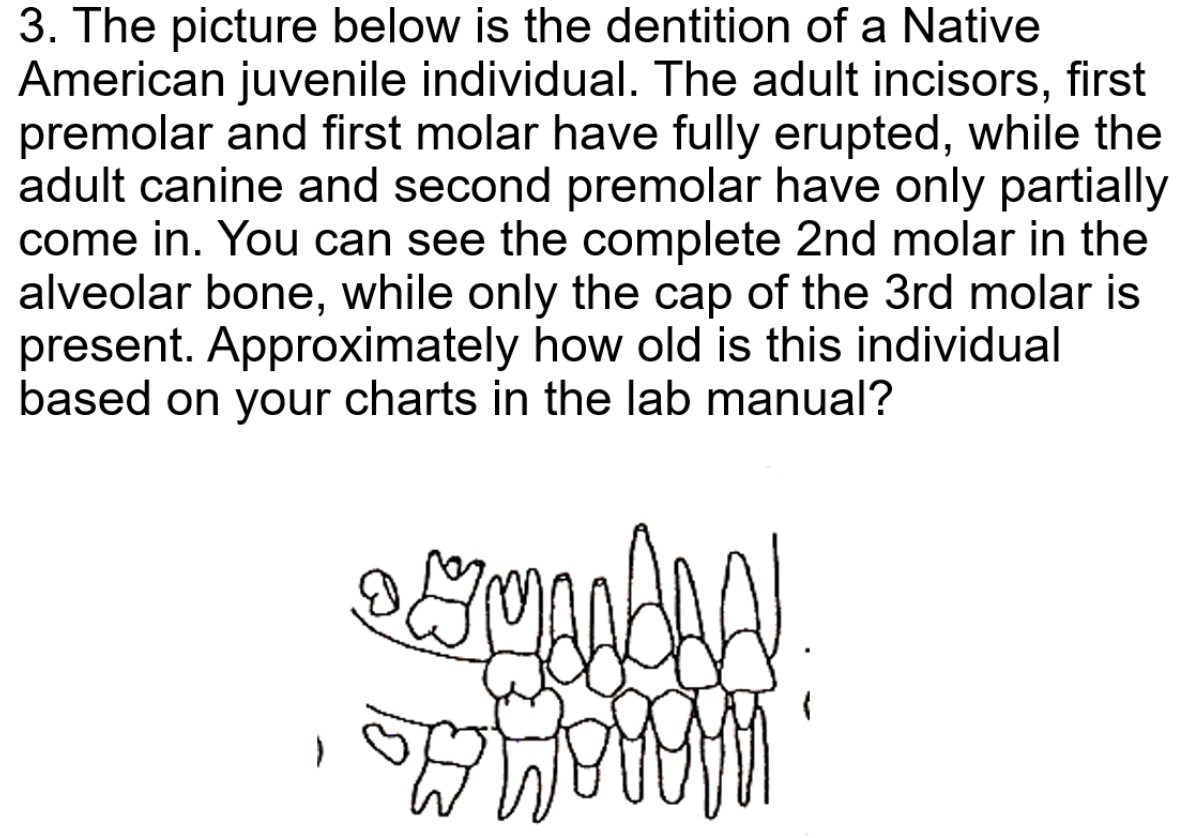
Approximately how old was this Native American individual at death?
11
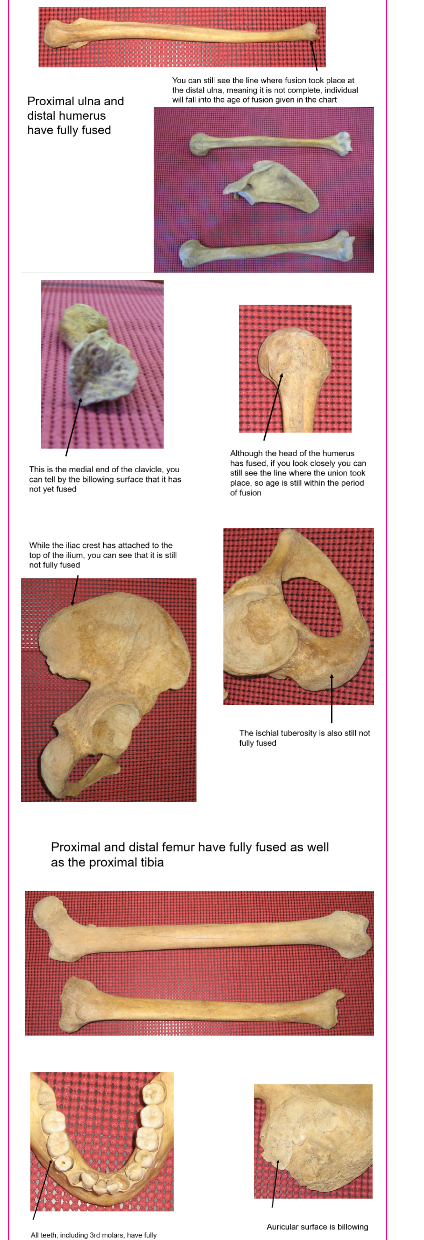
Based on your analysis of the epiphyses for this individual, which of the following answers might have been his age at death?
20
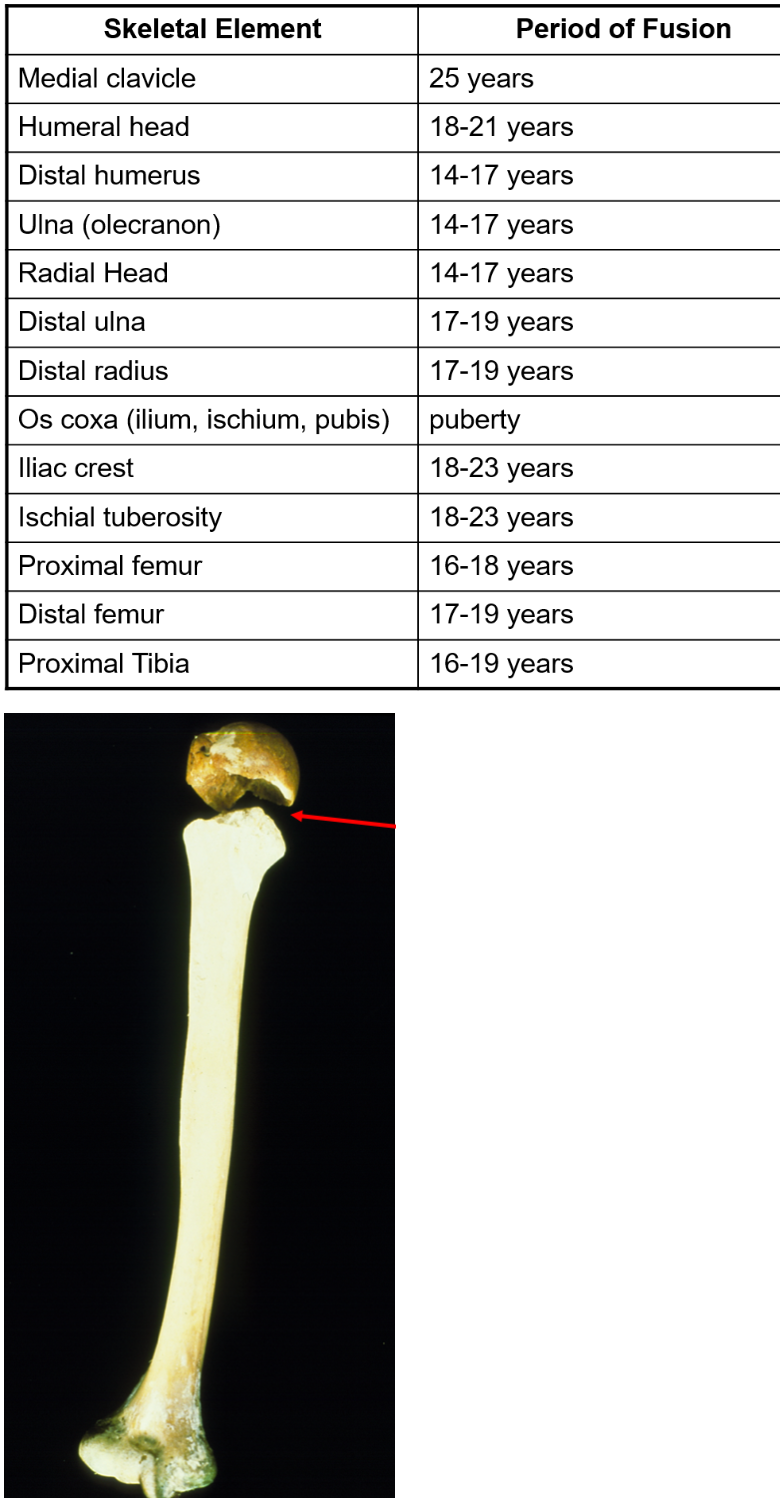
This individual was likely younger than 18-21 years old, true or false.
True
After approximately what age have the majority of epiphyses fused in the skeleton?
25
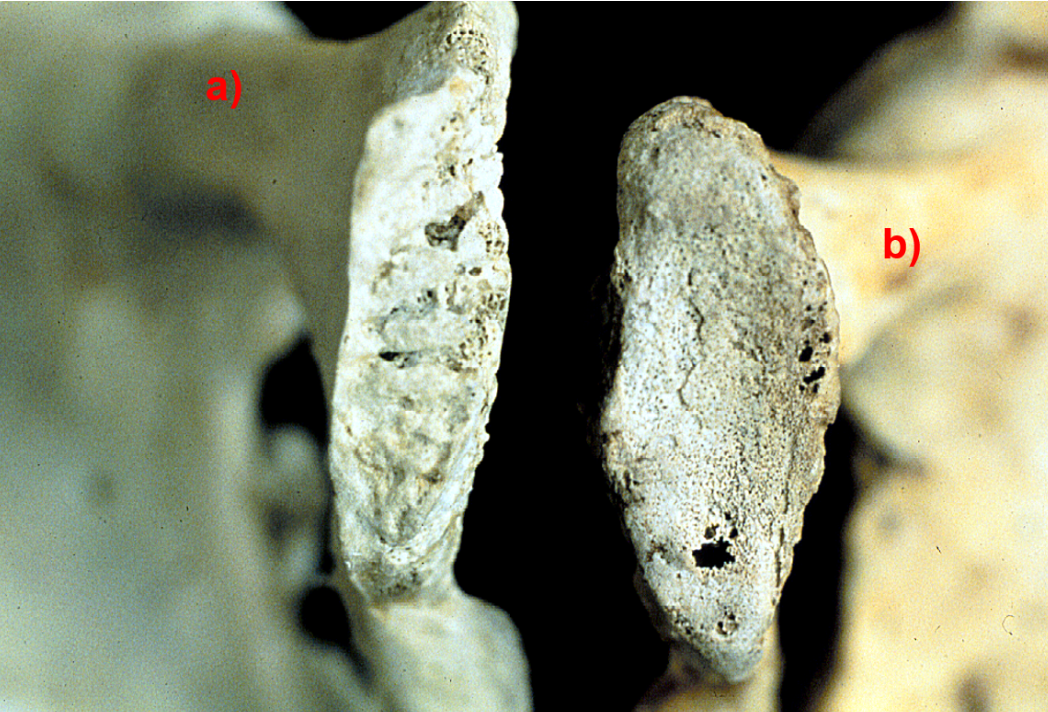
Look at these two pubic symphyses, which one is from a younger individual? Answer A or B, the letter must be capitalized in order to receive credit for your answer
A
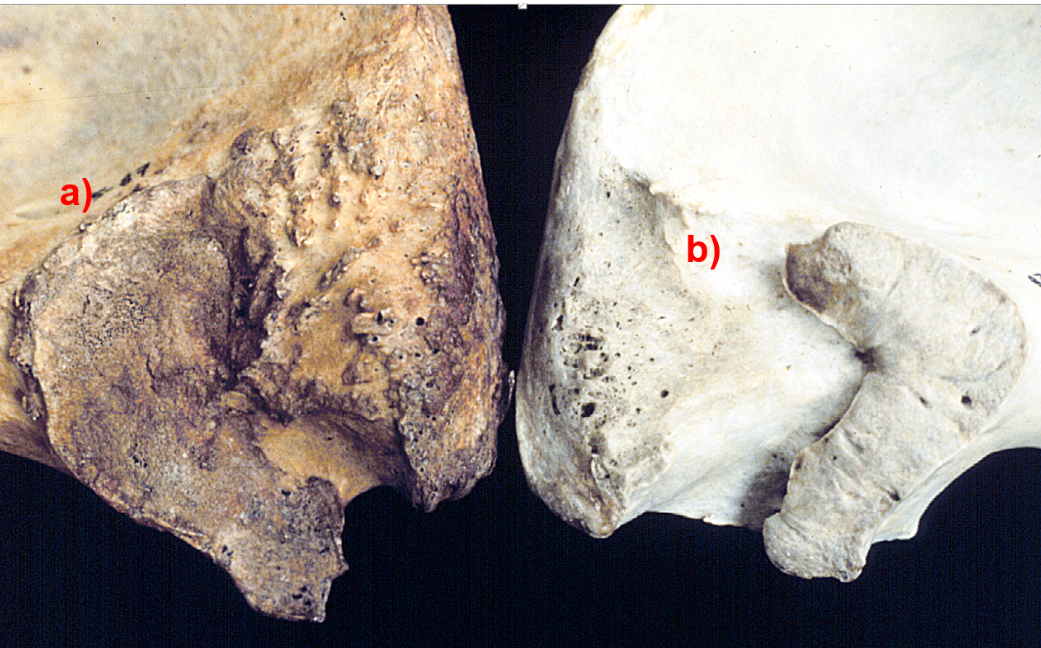
Look at these two auricular surfaces, which one is from an older individual? Answer A or B, the letter must be capitalized in order to receive credit for your answer
A
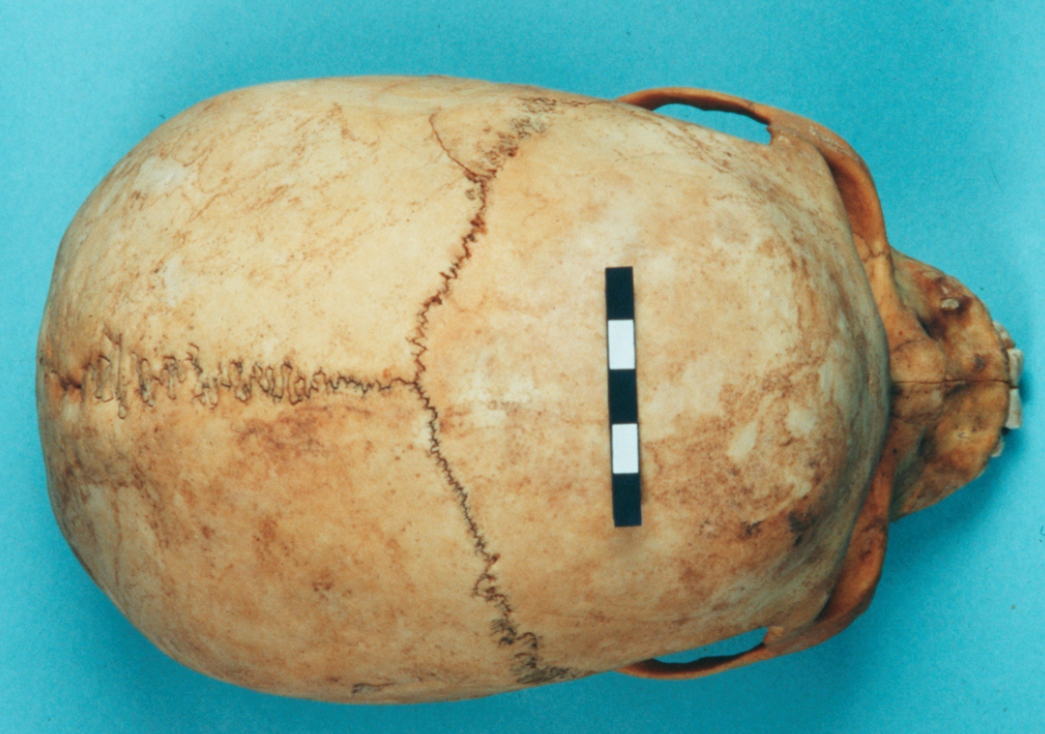
What is the score for the coronal and sagittal sutures of this skull?
0
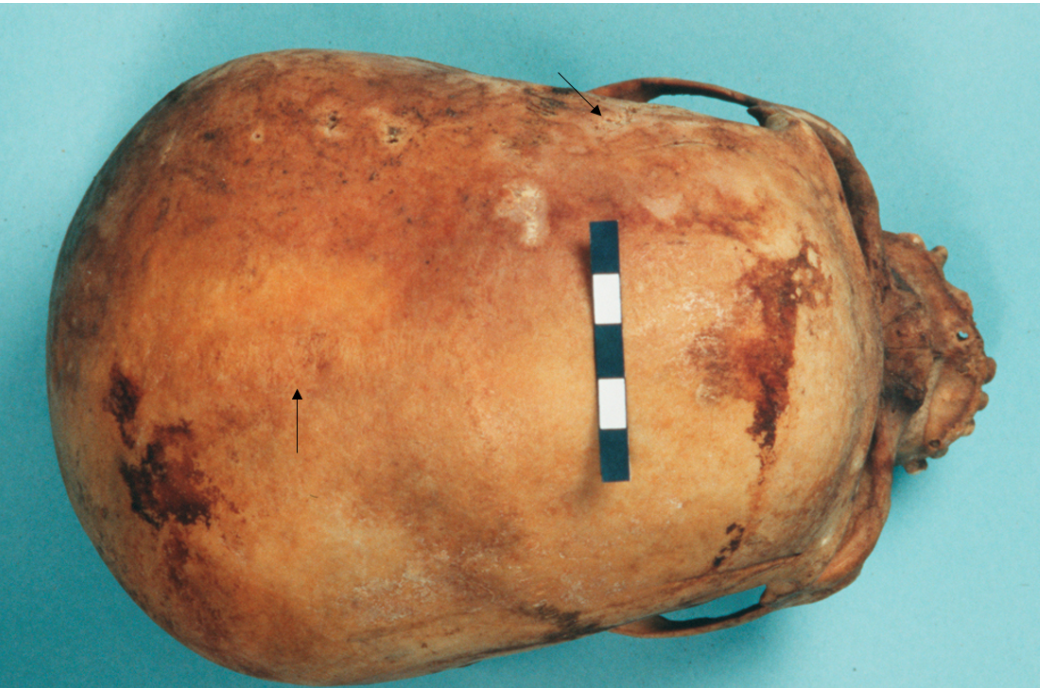
What is the score for the coronal and sagittal sutures of this skull?
2
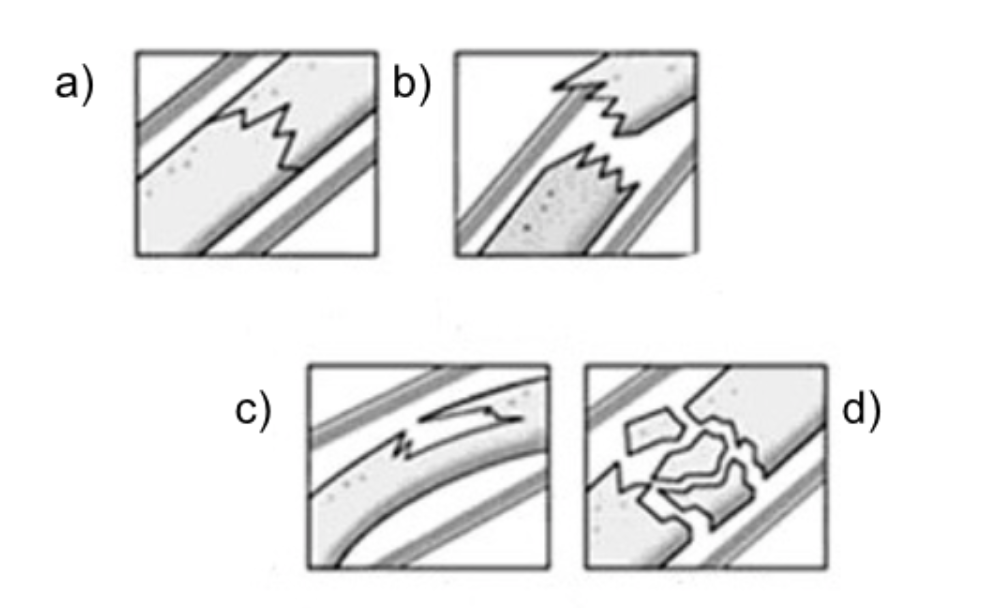
Label each image in order with its associated fracture type
a)simple fracture b)complete fracture c)greenstick fracture d)comminuted fracture
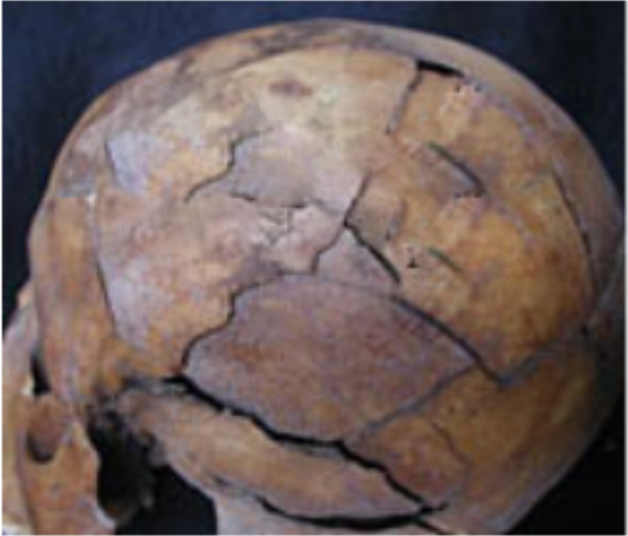

What two types of fractures are exhibited in this skull?
Radiating and concentric (hoop) fractures
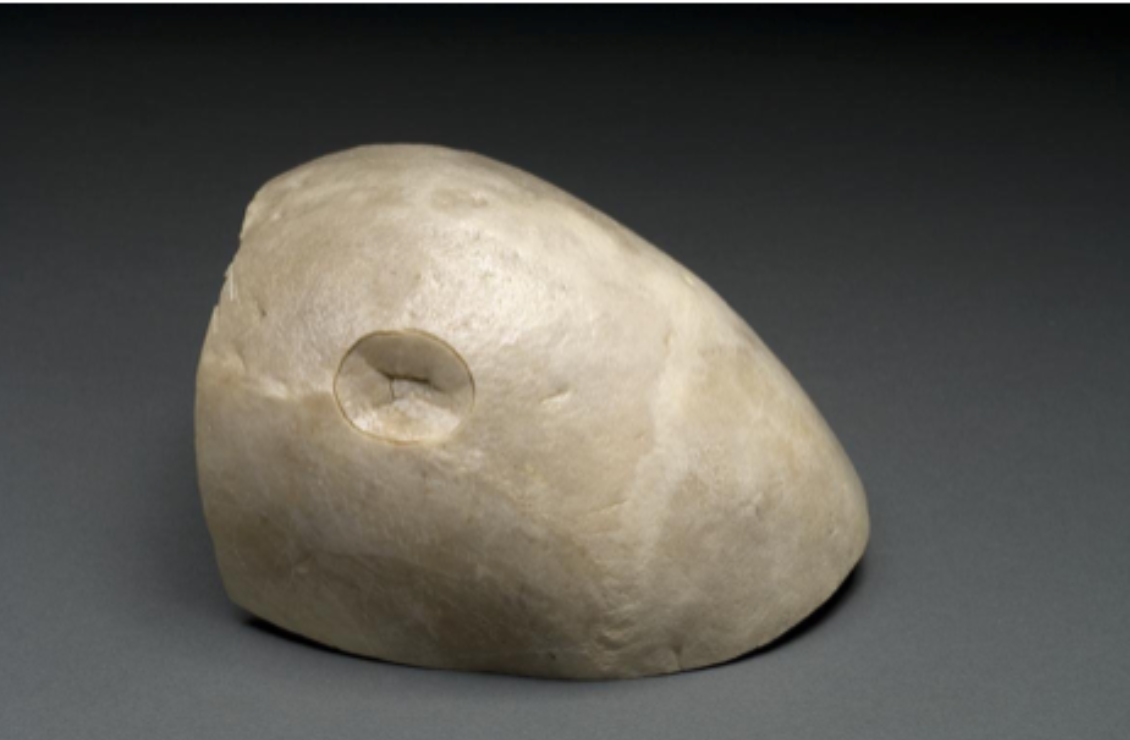

Identify the direction of force, speed of force, focus of force, and type of trauma for this injury.
Compression, dynamic, narrow, blunt
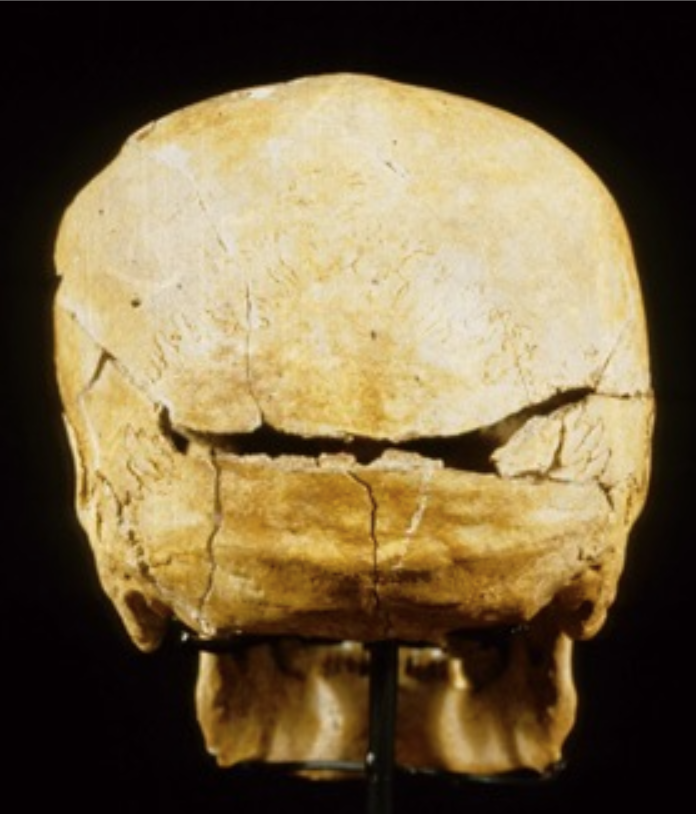
What type of trauma caused this injury and what type of fracture is exhibited?
Sharp and radiating
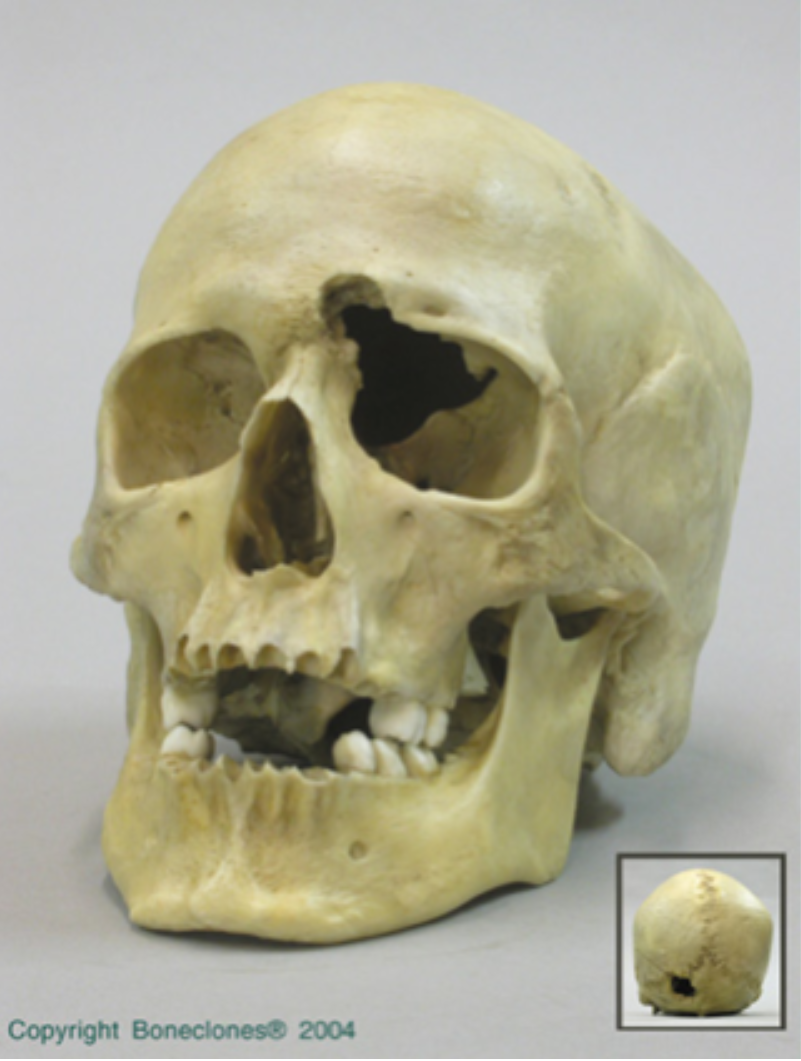
What type of trauma caused this injury?
Projectile
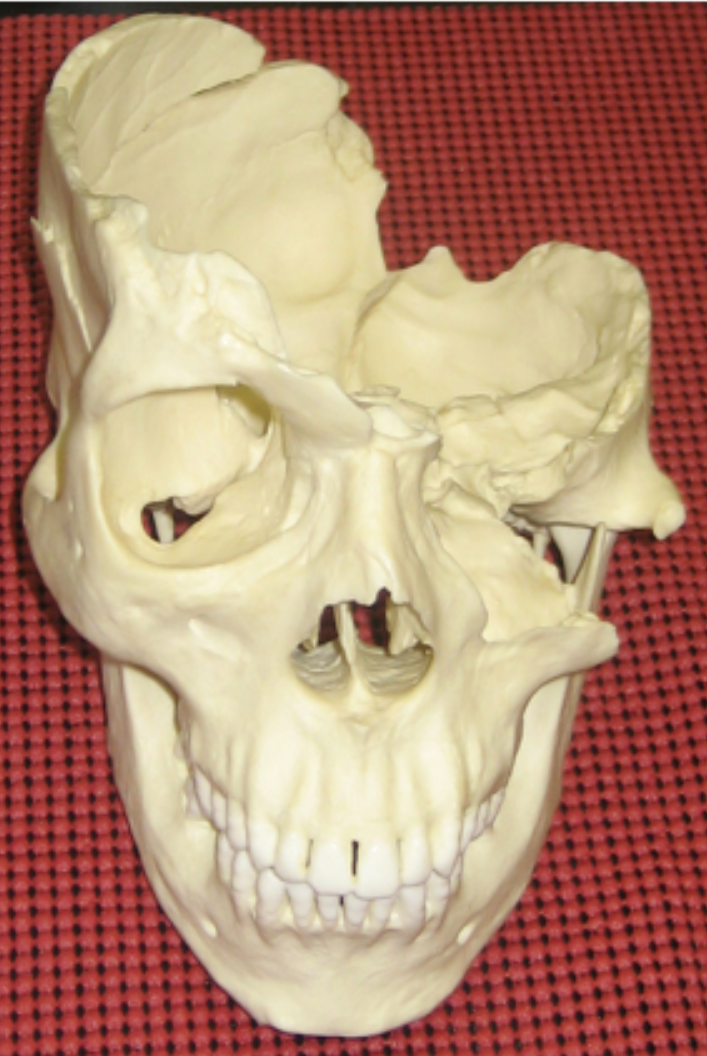
What type of trauma caused this injury?
Sharp
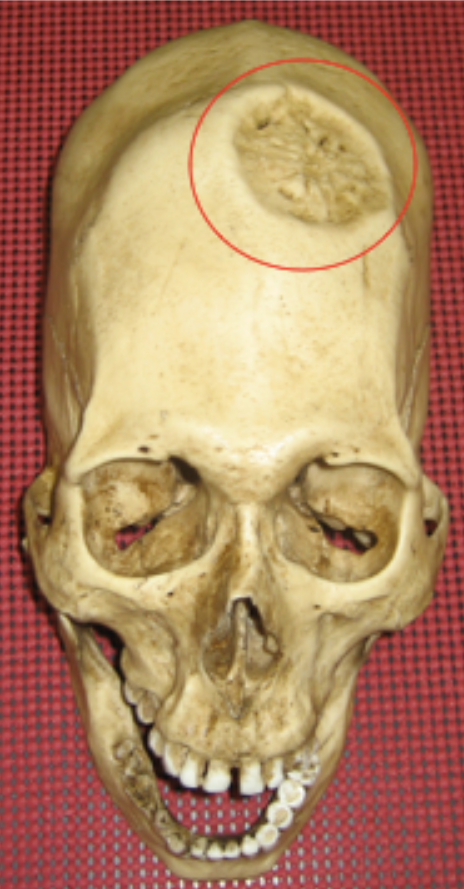
Is this injury antemortem, perimortem, or postmortem?
Antemortem
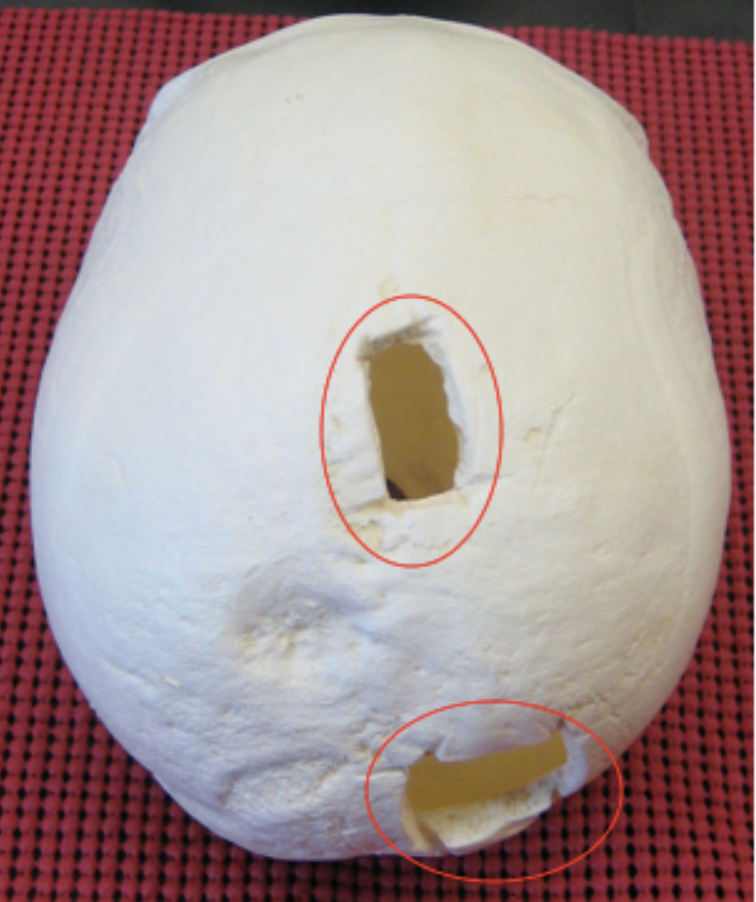
Is this injury antemortem, perimortem, or postmortem?
Perimortem
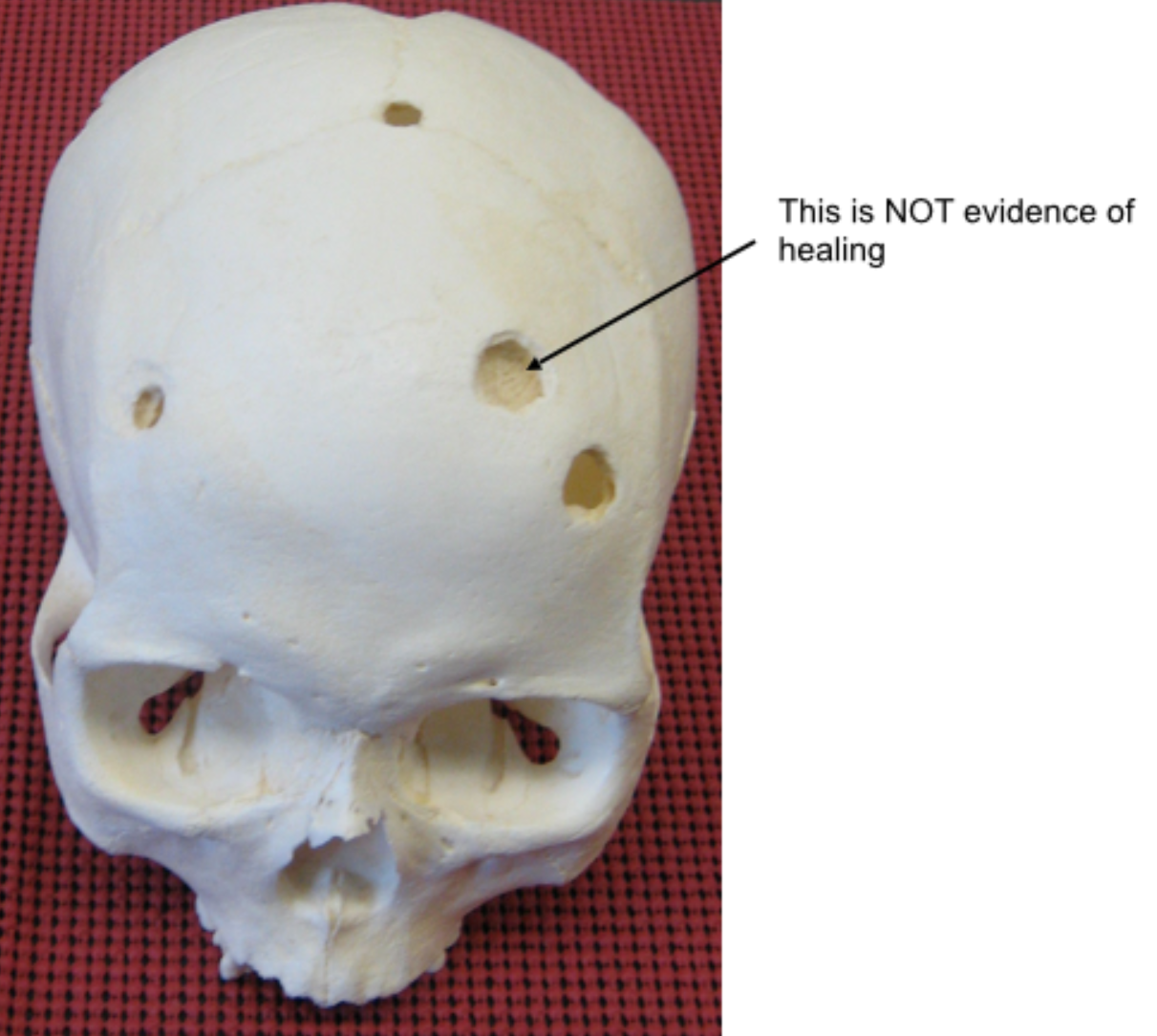
Are these injuries antemortem, perimortem, or postmortem?
Perimortem
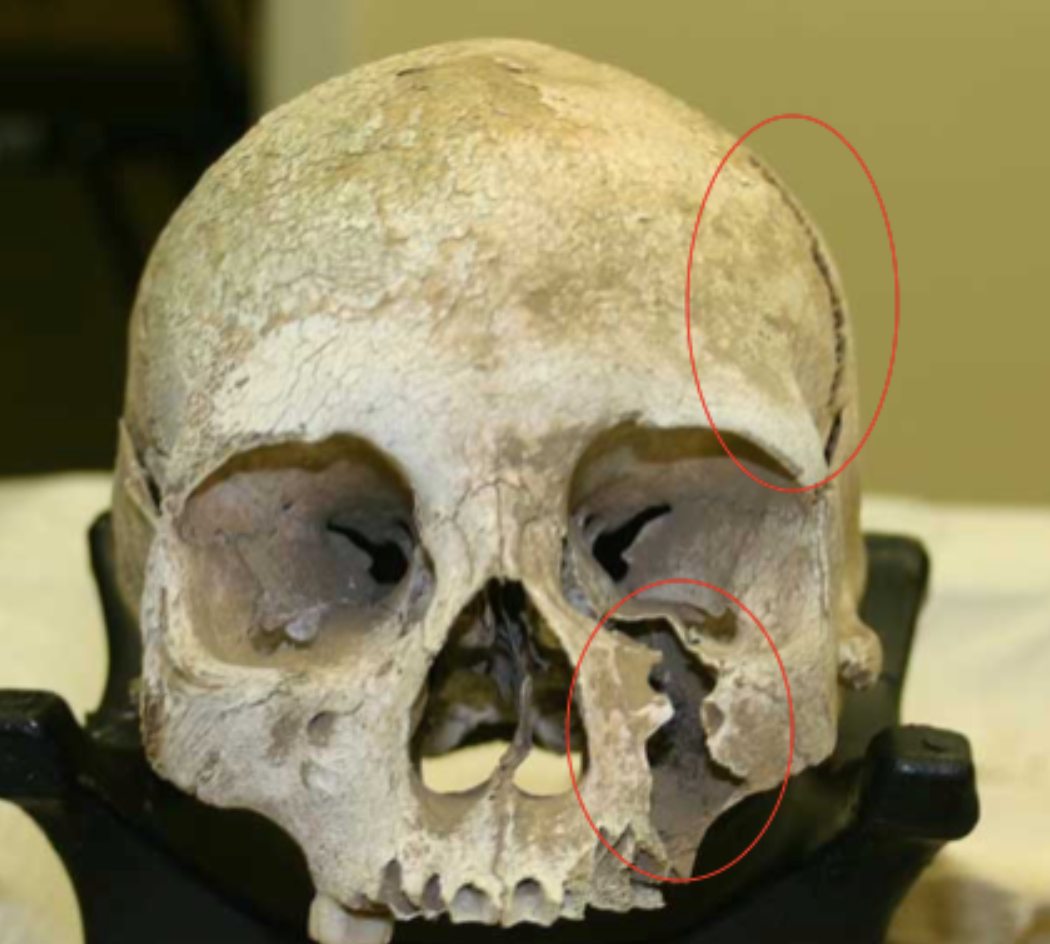
Are these injuries antemortem, perimortem, or postmortem?
Postmortem
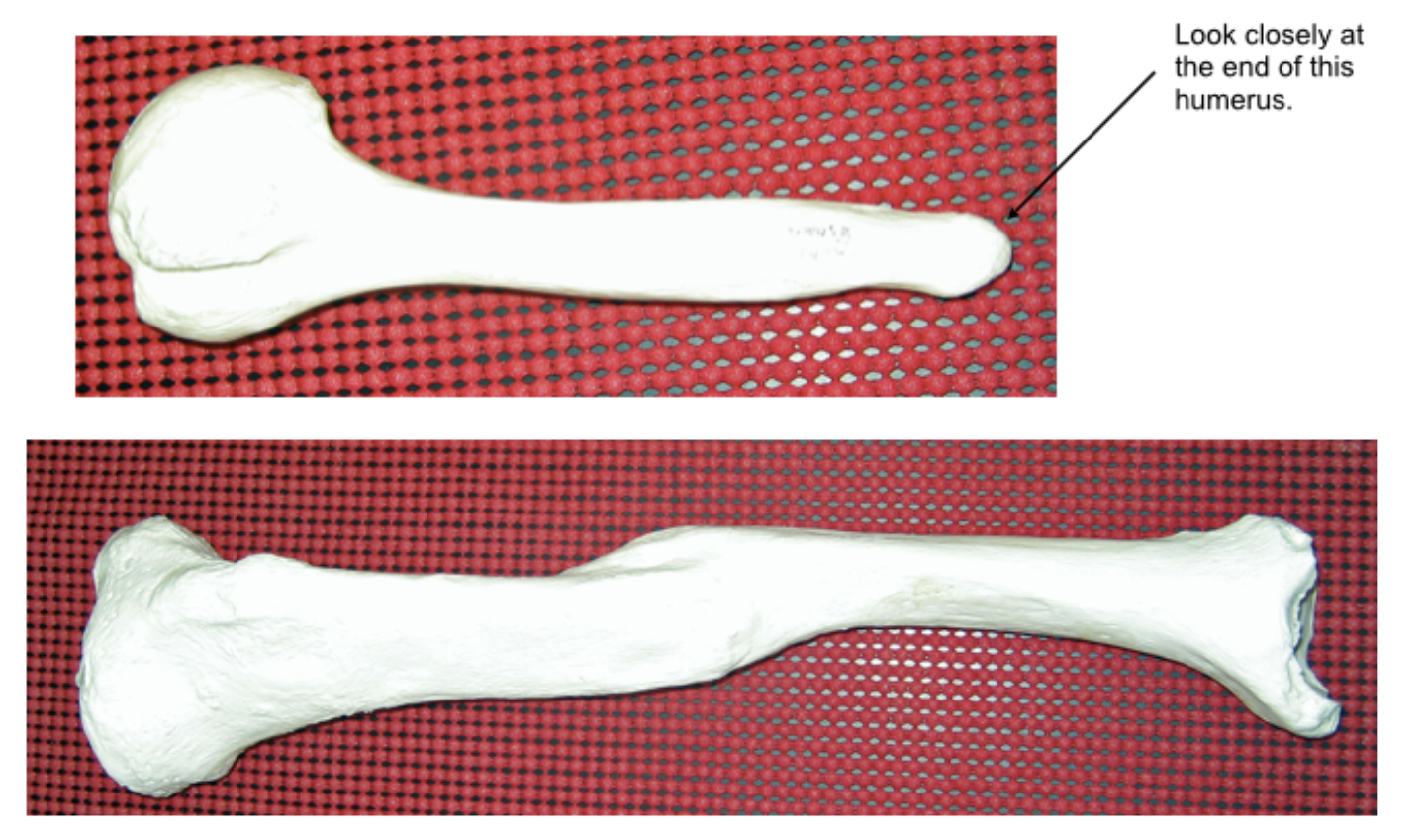
Did these two injuries occur antemortem, perimortem, or postmortem?
Antemortem
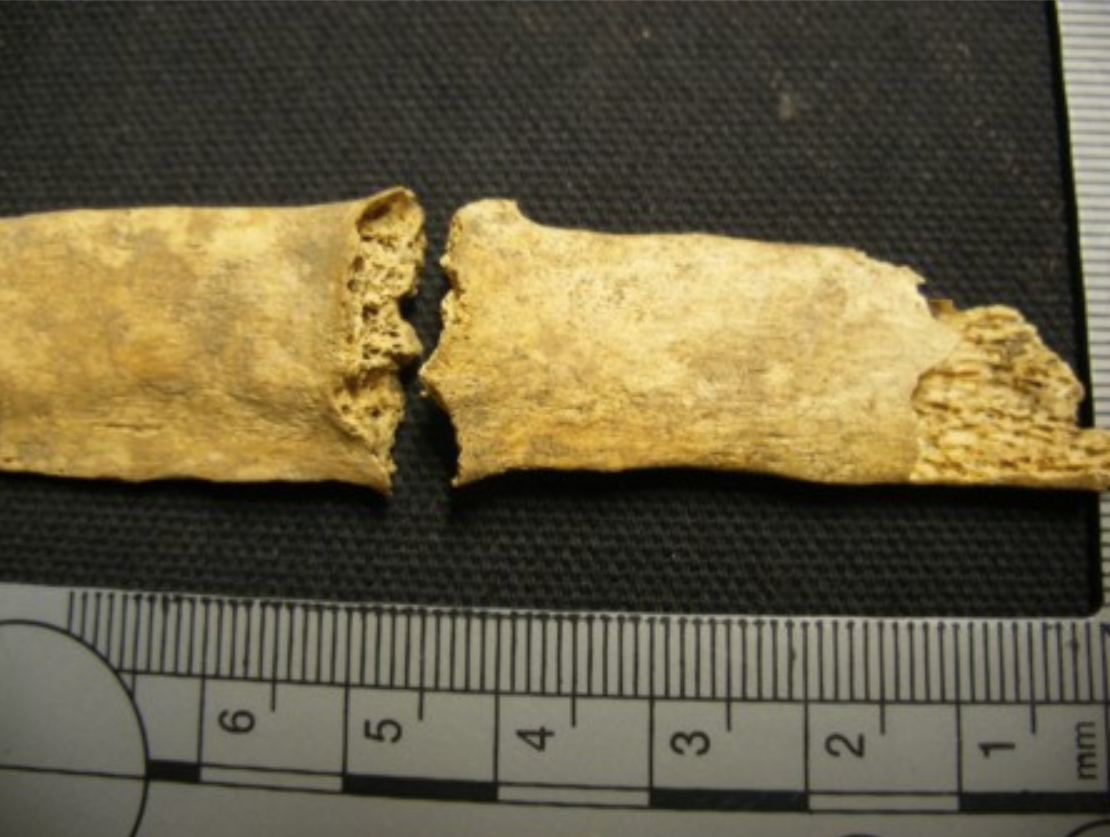

What type of fracture is this and did it occur antemortem or perimortem?
Complete and perimortem